Shredding Company (hdu 1539 dfs)
Shredding Company
Time Limit: 5000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 445 Accepted Submission(s): 124
unusual basic characteristics.
The shredder takes as input a target number and a sheet of paper with a number written on it.
It shreds (or cuts) the sheet into pieces each of which has one or more digits on it.
The sum of the numbers written on each piece is the closest possible number to the target number, without going over it.
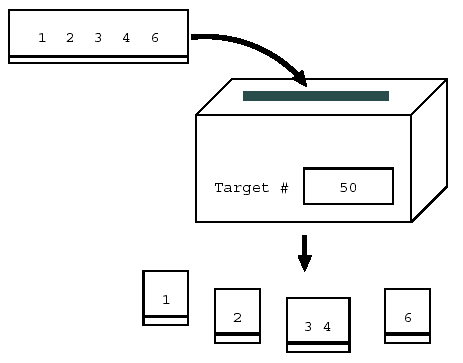
For example, suppose that the target number is 50, and the sheet of paper has the number 12346. The shredder would cut the sheet into four pieces, where one piece has 1, another has 2, the third has 34, and the fourth has 6. This is because their sum 43 (=
1 + 2 + 34 + 6) is closest to the target number 50 of all possible combinations without going over 50. For example, a combination where the pieces are 1, 23, 4, and 6 is not valid, because the sum of this combination 34 (= 1 + 23 + 4 + 6) is less than the
above combination's 43. The combination of 12, 34, and 6 is not valid either, because 52 (= 12 + 34 + 6) is greater than the target number of 50.
There are also three special rules:
If the target number is the same as the number on the sheet of paper, then the paper is not cut. For example, if the target number is 100 and the number on the sheet of paper is also 100, then the paper is not cut.
If it not possible to make any combination whose sum is less than or equal to the target number, then error is printed on a display. For example, if the target number is 1 and the number on the sheet of paper is 123, it is not possible to make any valid combination,
as the combination with the smallest possible sum is 1, 2, 3. The sum for this combination is 6, which is greater than the target number, and thus error is printed.
If there is more than one possible combination where the sum is closest to the target number without going over it, then rejected is printed on a display. For example, if the target number is 15, and the number on the sheet of paper is 111, then there are two
possible combinations with the highest possible sum of 12: (a) 1 and 11 and (b) 11 and 1; thus rejected is printed.
In order to develop such a shredder, you have decided to first make a simple program that would simulate the above characteristics and rules. Given two numbers, where the first is the target number and the second is the number on the sheet of paper to be shredded,
you need to figure out how the shedder should "cut up" the second number.
t1 num1
t2 num2
. . .
tn numn
0 0
Each test case consists of the following two positive integers, which are separated by one space: (1) the first integer (ti above) is the target number; (2) the second integer (numi above) is the number that is on the paper to be shredded.
Neither integers may have a 0 as the first digit, e.g., 123 is allowed but 0123 is not. You may assume that bother integers are at most 6 digits in length. A line consisting of two zeros signals the end of the input.
sum part1 part2 . . .
rejected
error
In the first type, partj and sum have the following meaning:
Each partj is a number on one piece of shredded paper. The order of partj corresponds to the order of the original digits on the sheet of paper.
sum is the sum of the numbers after being shredded, i.e., sum = part1 + part2 + . . .
Each number should be separated by one space.
The message error is printed if it is not possible to make any combination, and rejected if there is more than one possible combination.
No extra characters including spaces are allowed at the beginning of each line, nor at the end of each line.
50 12346
376 144139
927438 927438
18 3312
9 3142
25 1299
111 33333
103 862150
6 1104
0 0
43 1 2 34 6
283 144 139
927438 927438
18 3 3 12
error
21 1 2 9 9
rejected
103 86 2 15 0
rejected
pid=1849" target="_blank" style="color:rgb(26,92,200); text-decoration:none">1849
1848pid=1847" target="_blank" style="color:rgb(26,92,200); text-decoration:none">1847
pid=1404" target="_blank" style="color:rgb(26,92,200); text-decoration:none">1404
pid=1517" target="_blank" style="color:rgb(26,92,200); text-decoration:none">1517
题意:给一串数把他拆成若干份,使他们的和小于等于给定的goal,而且尽可能接近goal。
思路:dfs暴力枚举,注意可能不止6位。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <queue>
#pragma comment (linker,"/STACK:102400000,102400000")
#define pi acos(-1.0)
#define eps 1e-6
#define lson rt<<1,l,mid
#define rson rt<<1|1,mid+1,r
#define FRE(i,a,b) for(i = a; i <= b; i++)
#define FREE(i,a,b) for(i = a; i >= b; i--)
#define FRL(i,a,b) for(i = a; i < b; i++)
#define FRLL(i,a,b) for(i = a; i > b; i--)
#define mem(t, v) memset ((t) , v, sizeof(t))
#define sf(n) scanf("%d", &n)
#define sff(a,b) scanf("%d %d", &a, &b)
#define sfff(a,b,c) scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c)
#define pf printf
#define DBG pf("Hi\n")
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std; #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define mod 1000000009
const int maxn = 1005;
const int MAXN = 2005;
const int MAXM = 200010;
const int N = 1005; char str[maxn];
int a[maxn],b[maxn];
int goal,len;
int Max;
vector<int>ans,vec;
vector<vector<int> >out; void dfs(int pos,int sum)
{
if (sum+b[len]-b[pos-1]>goal) return ; //当前的sum加上剩下全部单个数之和比goal还大那肯定不行
if (pos==len+1&&sum<=goal)
{
if (Max<=sum)
{
ans.push_back(sum);
if (out.size()!=0)
out.pop_back();
out.push_back(vec);
Max=sum;
}
return ;
}
for (int i=pos;i<=len;i++) //枚举终点
{
int s=0;
for (int j=pos;j<=i;j++)
{
s=s*10+a[j];
}
vec.push_back(s);
dfs(i+1,sum+s);
vec.pop_back();
}
return ;
} int main()
{
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("C:/Users/lyf/Desktop/IN.txt","r",stdin);
#endif
int i,j;
while (scanf("%d %s",&goal,str+1))
{
if (goal==0&&str[1]=='0') break;
int x=0;
memset(b,0,sizeof(b));
len=strlen(str+1);
for (i=1;i<=len;i++)
{
a[i]=str[i]-'0';
x=x*10+str[i]-'0';
b[i]=b[i-1]+a[i];
}
if (x==goal){
printf("%d %d\n",goal,goal);
continue;
}
if (b[len]>goal){
printf("error\n");
continue;
}
Max=0;
out.clear();
ans.clear();
vec.clear();
dfs(1,0);
int sz=ans.size();
if (ans[sz-1]==ans[sz-2]) printf("rejected\n");
else
{
printf("%d",ans[sz-1]);
for (i=0;i<out[0].size();i++)
printf(" %d",out[0][i]);
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
Shredding Company (hdu 1539 dfs)的更多相关文章
- POJ 1416 Shredding Company 回溯搜索 DFS
Shredding Company Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 6173 Accepted: 3361 ...
- POJ1416——Shredding Company(DFS)
Shredding Company DescriptionYou have just been put in charge of developing a new shredder for the S ...
- Shredding Company(dfs)
Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 3519 Accepted: 2009 Description You h ...
- POJ 1416 Shredding Company【dfs入门】
题目传送门:http://poj.org/problem?id=1416 Shredding Company Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Tot ...
- poj1416 Shredding Company
Shredding Company Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 5379 Accepted: 3023 ...
- 搜索+剪枝 POJ 1416 Shredding Company
POJ 1416 Shredding Company Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 5231 Accep ...
- Shredding Company
Shredding Company Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 4653 Accepted: 2675 Des ...
- POJ 1416:Shredding Company
Shredding Company Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 4713 Accepted: 2714 ...
- HDU 5143 DFS
分别给出1,2,3,4 a, b, c,d个 问能否组成数个长度不小于3的等差数列. 首先数量存在大于3的可以直接拿掉,那么可以先判是否都是0或大于3的 然后直接DFS就行了,但是还是要注意先判合 ...
随机推荐
- vscode常用的快捷键
对于编程人员来说,记住一些常用的快捷键能够提高工作效率:我认为,对于编程人员来说,掌握一些常用的快捷键是非常有必要的! Ctrl + Shift + N 打开新的编辑器窗口 Ctrl + Shift ...
- NS2学习笔记(四)
这几天学习NS2,虽然国内很多人使用,但系统的教材资料不多,只能一边看中文教材,一边看英文手册,知识点也是零零散散.过段时间等能将所有知识点串上,再总结总结.现只讲一些零碎的点记录一下. 添加新的协议 ...
- Sqoop 产生背景(一)
Sqoop 的产生主要源于: 1.目前很多使用hadoop技术的企业,有大量的数据存储在传统关系型数据库中. 2.早期由于工具的缺乏,hadoop与传统数据库之间的数据传输非常困难. 1)传统数据库中 ...
- 单例模式在多线程环境下的lazy模式为什么要加两个if(instance==null)
刚才在看阿寻的博客”C#设计模式学习笔记-单例模式“时,发现了评论里有几个人在问单例模式在多线程环境下为什么lazy模式要加两个if进行判断,评论中的一个哥们剑过不留痕,给他们写了一个demo来告诉他 ...
- [hihocoder][Offer收割]编程练习赛58
最大的K-偏差排列 每次取可选范围里的最大的数字,如果最左侧的数字还没有使用就直接使用最左侧的数字 #pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102 ...
- SQL基本操作——创建索引
CREATE INDEX 语句用于在表中创建索引.在不读取整个表的情况下,索引使数据库应用程序可以更快地查找数据. 索引:您可以在表中创建索引,以便更加快速高效地查询数据.用户无法看到索引,它们只能被 ...
- Objective-C在ARC下结合GCD的单例模式和宏模版
单例模式在iOS开发过程中经常用到,苹果提供过objective c单例的比较官方的写法: static MyGizmoClass *sharedGizmoManager = nil; + (MyGi ...
- nuxt https
我用的模板是nxut-express,版本是:1.4.2.服务器:阿里云.一.申请免费证书:网站能通过https访问,首先得申请https证书,付费的阿里云上有售卖的,一年几千块.免费的可以通过cer ...
- 黑苹果开启retina,大分辨率的方法
首先,管理分辨率RDM的软件这里下载: http://pan.baidu.com/s/1bpjL07P 在终端输入: curl -o ~/enable-HiDPI.sh https://raw.git ...
- [LUOGU]4932 浏览器
\(\_\_stdcall\)大佬出的题\(Orz\) 我们惊奇地发现,加入\(\_\_popcount(x)\)和\(\_\_popcount(y)\)的奇偶数性相同,那么\(\_\_popcoun ...
