Setting up your App domain for SharePoint 2013
from:http://sharepointchick.com/archive/2012/07/29/setting-up-your-app-domain-for-sharepoint-2013.aspx
The most important change in SharePoint 2013 for developers is the introduction of SharePoint apps. An app for SharePoint is a small and isolated application that provides a specific bit of functionality. SharePoint apps can and have to be added to or removed from a site by the site owner. Apps have their own, isolated URLs, which are separate from the URLs of the sites where the app is being deployed to and where the app is being used. In order to provide isolation apps run in their own domain, instead of in the same domain name as your farm. Using a different domain name for apps helps prevent cross-site scripting between apps and SharePoint sites.
Each installation of an app has its own unique URL within the app domain. The app’s URL is based on a template “http://[app prefix][app hash].[app domain]/[relative site url]/[app name]. When you add an app to a site, a subweb of that site is created to host the app content. This subweb is not visible on the Site Contents page though.
Because apps run in their own app domain you will have to configure Domain Name Services (DNS) in your environment in order to be able to host apps. There is a page on TechNet that describes how to setup you DNS, but because it took me a while to get it all working I decided to write a step by step guide, which is what you’re reading now.
You can choose whether you want your app domain to be a subdomain of the domain that hosts the SharePoint environment (option B), or whether you want to create a completely new domain for your apps (option A). Creating a new domain specifically to host your apps in is a bit more secure, but it also requires a little bit more configuration. I will describe both approaches in this article. If you don’t have control over your DNS you will have to ask an administrator to perform these steps for you.
Option A: Create a new domain to host your apps in
- Go to “Start”
- Click on “Administrative Tools”
- Select “DNS”
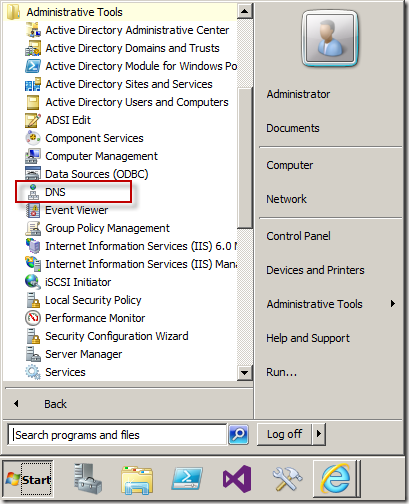
- Right click “Forward Lookup Zones” and select “New Zone…”
- Click “Next”
- Keep the default and click “Next” again
- In most cases, especially if your development server is in it’s own domain you can use the default on the next tab again and can just click “Next”
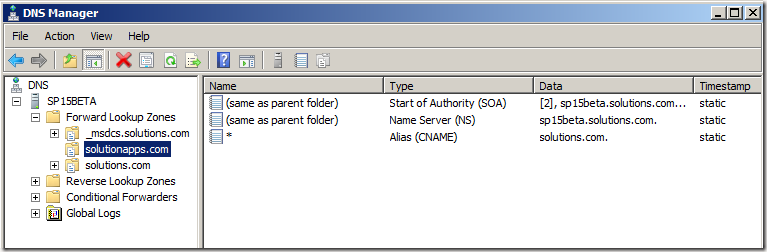
- You now have to specify a zone name. It’s up to you what you choose here. My domain name is “solutions.com” and for my app domain I will use “solutionapps.com”
- Click “Next”
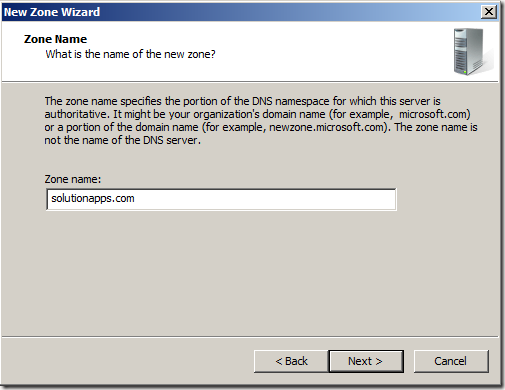
- Click “Next”
- Click “Finish”
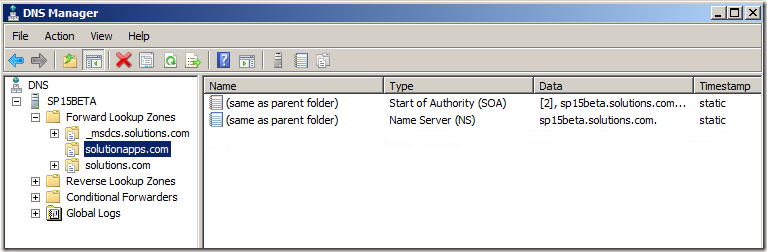
- Right click on your new zone and select “New Alias (CNAME)…”
- Fill in a * for “Alias name (uses parent domain if left blank)”
- Click “Browse”
- Double click on your server name
- Double click “Forward Lookup Zones”
- Double click the domain of your SharePoint environment. In my case this is “solutions.com”.
- Select “(Same as parent folder)” and click “OK”
- Click “OK”.
* Note that selecting the FQDN of the domain in here will only work in single server scenarios. If you are using more than one server you should be pointing to the DNS record of the web server in here. This is either the DNS A record for the web server, or the DNS record of the primary cluster address for NLB environments.
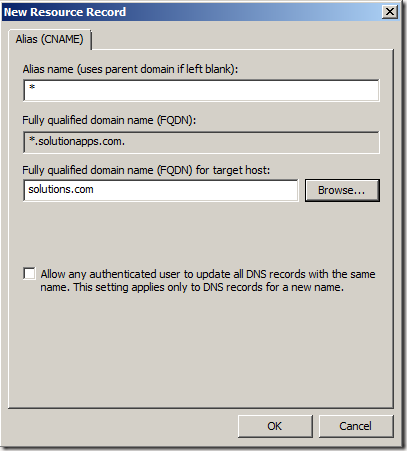
- You are now done setting up your DNS and it should look like this:
Option B: Create a subdomain to host your apps in
- Go to “Start”
- Click on “Administrative Tools”
- Select “DNS”
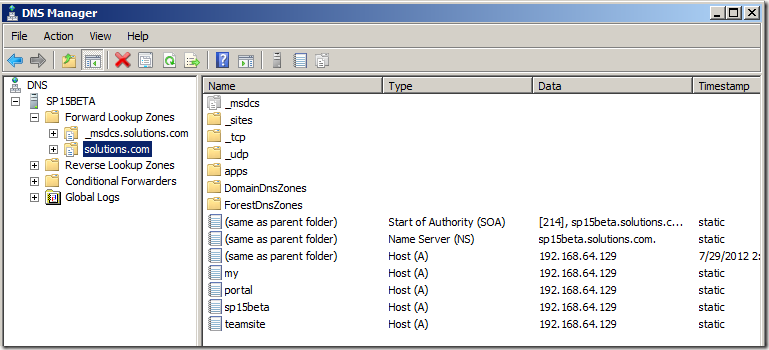
- Right click on the name of your domain and select “New Alias (CNAME)…”
- Fill in “*.app” for “Alias name (uses parent domain if left blank)”
- Click “Browse”
- Double click on your server name
- Double click “Forward Lookup Zones”
- Double click the domain of your SharePoint environment. In my case this is “solutions.com”
- Select “(Same as parent folder)” and click “OK”
- Click “OK”
* Note that selecting the FQDN of the domain in here will only work in single server scenarios. If you are using more than one server you should be pointing to the DNS record of the web server in here. This is either the DNS A record for the web server, or the DNS record of the primary cluster address for NLB environments.

- You are now done setting up your DNS and it should look like this:

Configuring SharePoint
I’m assuming you already created an App Management and a Subscription Settings Service Application and that you already started the App Management and Subscription Settings services on your servers. If not this MSDN article will tell you how to. Note that you have to use PowerShell to create the Subscription Settings Service Application. There is no user interface for it.
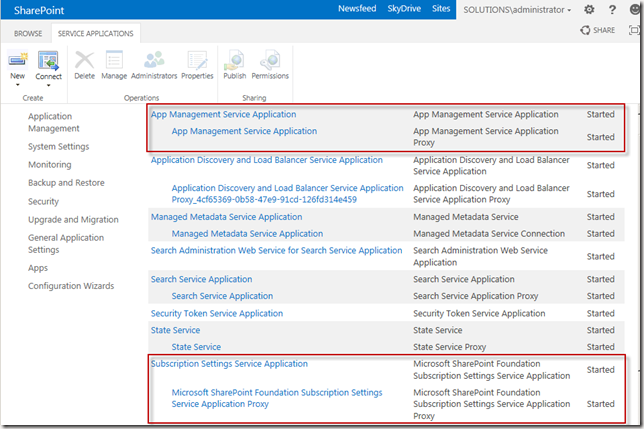
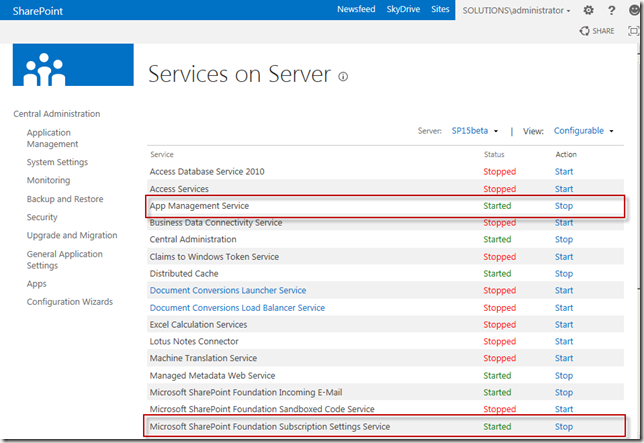
- Go to Central Administration
- Click on “Apps” in the left side navigation
- Click “Configure App URLs”
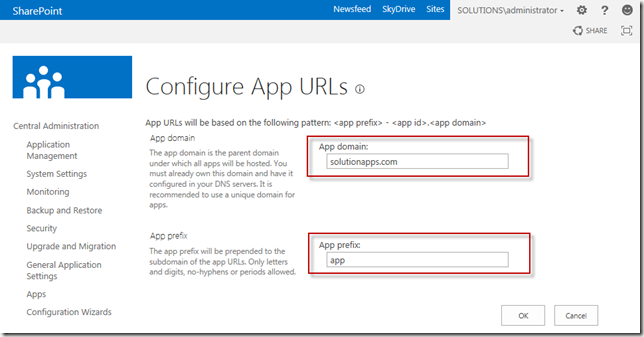
- Fill in the URL of the app domain that you configured. If you choose to use Option A the url will be something like “solutionapps.com”, if you choose to use Option B it will look like app.solutions.com.
- Fill in an app prefix. This can be anything you like, although it is best to keep this short. I used “app” myself.
Two example urls for two different apps on the same site are:
http://app-fef8493a3feb20.solutionapps.com/sites/apptest/[App1AppName]/Pages/Home.aspx
http://app-fef8493a3feb1d.solutionapps.com/sites/apptest/[App2AppName]/Pages/Default.aspx
As you can see both apps have their own app hash, but both are in the same domain.
Beware of host headers
You are now ready to deploy your apps. Because of all this extra domain stuff though there are a few things you should know about your web applications and site collections.
If you are using a host header for your web application apps won’t just work for that web application. Because of how the redirect for the app domain works IIS will try to resolve the app url by using the default IIS web site, which of course doesn’t work. If you want to use host headers for your web applications you have to create an extra web application that is listening on port 80 (or 443 if you are using https) and that doesn’t have a host header.
This means that you have to create a web application like you normally would. You have to make sure that you select port 80 (or 443 if you are using https) and you should not fill in a host header. Note that you have to stop the Default Web Site in IIS in order to be able to do this. The web application will use the server name as its url. The web application can be empty except for a root site collection.
Another option is to use web applications without host headers and to create Host Header Site Collections. Be aware that Host Header Site Collections cannot be created via the user interface, they can only be created by using PowerShell.
Setting up your App domain for SharePoint 2013的更多相关文章
- BEGINNING SHAREPOINT® 2013 DEVELOPMENT 第2章节--SharePoint 2013 App 模型概览 SharePoint 2013 App 模型
BEGINNING SHAREPOINT® 2013 DEVELOPMENT 第2章节--SharePoint 2013 App 模型概览 SharePoint 2013 App 模型 你能够通过两个 ...
- [Forward]Visual Guide: Setting up My Sites in SharePoint 2013
from http://blog.sharedove.com/adisjugo/index.php/2012/07/25/visual-guide-setting-up-my-sites-in-sh ...
- SharePoint 2013 APP 开发示例 系列
SharePoint 2013 APP 安全: SharePoint 2013 APP 开发示例 (一)List 读写 SharePoint 2013 APP 开发示例 (二)获取用户信息 Share ...
- BEGINNING SHAREPOINT® 2013 DEVELOPMENT 第1章节--SharePoint 2013 介绍 处理开发者需求
BEGINNING SHAREPOINT® 2013 DEVELOPMENT 第1章节--SharePoint 2013 介绍 处理开发者需求 SharePoint本质上是一个平台.你 ...
- SharePoint 2013 - App Domain Configuration
1. 首先,在DNS服务器上创建app domain,建议使用一个新domain,而不是当前domain的 sub domain,参考此文章的 Option A: Create a new domai ...
- SharePoint 2013 搭建app本地开发环境
使用SharePoint App,如果要通过应用程序目录分发 SharePoint 相关应用程序,如具有完全控制权限的 SharePoint 相关应用程序(无法部署到 Office 365 网站),则 ...
- "此站点已经禁用应用程序"在sharepoint 2013中通过v2013部署app提示该错误
该错误的原文是:the apps are disabled in this site 可以在yahoo或者bing上搜索这个错误,可以找到解决办法: msdn上也有该错误解决办法,但是如果搜索中文,目 ...
- Install SharePoint 2013 on Windows Server 2012 without a domain
Any setup of Team Foundation Server is not complete until you have at least tried t work with ShareP ...
- SharePoint 2013 APP 开发示例 (四)JQuery访问REST
这个示例里,我们将用JQuery AJAX去发送一个 REST请求,并查看返回结果.为了让我们更好地理解REST 接口,我们将添加一个输入框让用户可以指定REST的URL, 这将让我们尝试着用构造的U ...
随机推荐
- PyAMF and django ForeignKey
In order to support this, PyAMF needs to provide a synonym mapping between fields. Until then, you c ...
- 使用Python画ROC曲线以及AUC值
from:http://kubicode.me/2016/09/19/Machine%20Learning/AUC-Calculation-by-Python/ AUC介绍 AUC(Area Unde ...
- 使用ECMAscript5中的forEach函数遍历数组
1 var a = [1,2,3]; 2 a.forEach(function(value,index,arr){ 3 arr[index] = value + index; 4 }) 5 conso ...
- java中产生对象的两种方式
/* * 普通new对象的过程! */ Person pp = new Person(); System.out.println(pp); /* * 利用代用参数的构造器产生对象实例! * 首先获得相 ...
- PowerMock 简介--转载
原文地址:https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-powermock/ EasyMock 以及 Mockito 都因为可以极大地简化单元测试的书 ...
- 初学Flask(1)
今天在学习Flask,边看官方文档一边动手运行例子,以注释的形式写了一些笔记,分享给大家. Flask官方文档,快速入门: ex1: #coding:utf-8 ################### ...
- Html5+css3+angularjs+jquery+webAPi 开发手机web(一)
前言 随着浏览器的发展 HTML5+CSS3 的使用也越来越广泛,一直想学这个,想学那个折腾下来几乎没学到什么东西.工作经验告诉我,要掌握一门技术,就需要在项目中去磨练, 所以我就准备开发一个手机端的 ...
- 更加优雅地搭建SSH框架(使用java配置)
时代在不断进步,大量基于xml的配置所带来的弊端也显而易见,在XML配置和直接注解式配置之外还有一种有趣的选择方式-JavaConfig,它是在Spring 3.0开始从一个独立的项目并入到Sprin ...
- IOS开发UI基础UITableView的属性
UITableView UITableView内置了两种样式:UITableViewStylePlain,UITableViewStyleGrouped <UITableViewDataSour ...
- [SQL] Oracle基础语法
1.安装: oracle11g server 这里的口令为sys和system的密码.(10版本以前默认用户会有系统默认密码.) Oracle 11g 默认用户名和密码 oracle11g clien ...
