[算法竞赛入门经典] 象棋 ACM/ICPC Fuzhou 2011, UVa1589 较详细注释
Description:
Xiangqi is one of the most popular two-player board games in China. The game represents a battle between two armies with the goal of capturing the enemy’s “general” piece. In this problem, you are given a situation of later stage in the game. Besides, the red side has already “delivered a check”. Your work is to check whether the situation is “checkmate”.
Now we introduce some basic rules of Xiangqi. Xiangqi is played on a 10×9 board and the pieces are placed on the intersections (points). The top left point is (1,1) and the bottom right point is (10,9). There are two groups of pieces marked by black or red Chinese characters, belonging to the two players separately. During the game, each player in turn moves one piece from the point it occupies to another point. No two pieces can occupy the same point at the same time. A piece can be moved onto a point occupied by an enemy piece, in which case the enemy piece is "captured" and removed from the board. When the general is in danger of being captured by the enemy player on the enemy player’s next move, the enemy player is said to have "delivered a check". If the general's player can make no move to prevent the general's capture by next enemy move, the situation is called “checkmate”.
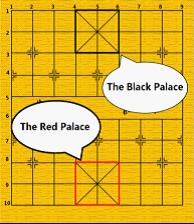
We only use 4 kinds of pieces introducing as follows: General: the generals can move and capture one point either vertically or horizontally and cannot leave the “palace” unless the situation called “flying general” (see the figure above). “Flying general” means that one general can “fly” across the board to capture the enemy general if they stand on the same line without intervening pieces.
General: the generals can move and capture one point either vertically or horizontally and cannot leave the “palace” unless the situation called “flying general” (see the figure above). “Flying general” means that one general can “fly” across the board to capture the enemy general if they stand on the same line without intervening pieces. Chariot: the chariots can move and capture vertically and horizontally by any distance, but may not jump over intervening pieces
Chariot: the chariots can move and capture vertically and horizontally by any distance, but may not jump over intervening pieces Cannon: the cannons move like the chariots, horizontally and vertically, but capture by jumping exactly one piece (whether it is friendly or enemy) over to its target.
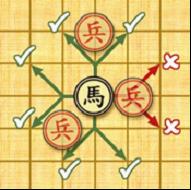
Cannon: the cannons move like the chariots, horizontally and vertically, but capture by jumping exactly one piece (whether it is friendly or enemy) over to its target. Horse: the horses have 8 kinds of jumps to move and capture shown in the left figure. However, if there is any pieces lying on a point away from the horse horizontally or vertically it cannot move or capture in that direction (see the figure below), which is called “hobbling the horse’s leg”.
Horse: the horses have 8 kinds of jumps to move and capture shown in the left figure. However, if there is any pieces lying on a point away from the horse horizontally or vertically it cannot move or capture in that direction (see the figure below), which is called “hobbling the horse’s leg”.
Now you are given a situation only containing a black general, a red general and several red chariots, cannons and horses, and the red side has delivered a check. Now it turns to black side’s move. Your job is to determine that whether this situation is “checkmate”.
Input
There is a blank line between two test cases. The input ends by 0 0 0.
Output
Sample Input
Sample Output
NO
Hint
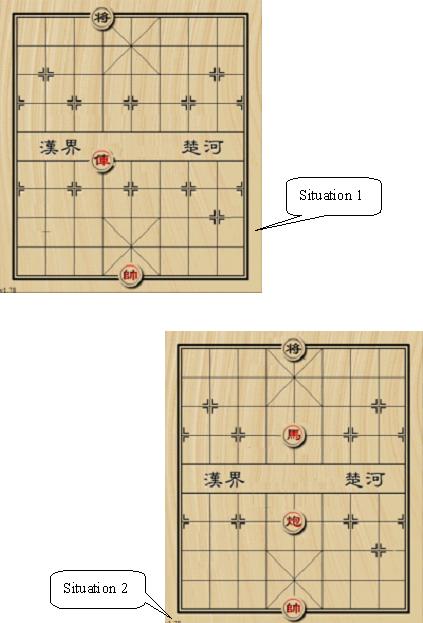
In the first situation, the black general is checked by chariot and “flying general”.
In the second situation, the black general can move to (1, 4) or (1, 6) to stop check.
See the figure above.
/* G是主将,R是车,H是马,C是炮,考虑蹩马腿,将帅不能照面 , 题目暗示下一步走棋的是黑方
* validMoveH 函数中的参数direct的值代表的马移动的方位,如下图
*
* (1)* (2)*
*
* (3)* (4)*
*
* (5)* (6)*
*
* (7)* (8)*
*/ #include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
enum TRAVERSE_TYPE{ X,Y }; // 区间遍历枚举类型
enum MOVE_TYPE{ UP,DOWN,LEFT,RIGHT }; // 移动方向枚举类型
struct Pos{
Pos(int nX,int nY):x(nX),y(nY) { }
Pos() = default;
int x;
int y;
};
vector<Pos> R,H,C; // 储存棋盘上红⽅存在的⼦
int map[][]; // 模拟棋盘
char mmap[][]; // 存储红方除主将外落⼦的类型
Pos general_b,general_r; // ⿊⽅、红⽅主将位置
int others(int begin,int end,int index,TRAVERSE_TYPE type); // 返回某个区间段上落⼦的个数
vector<MOVE_TYPE> validMoveG(); // 返回⼀个⿊将可以⾛的⽅向的stack
bool gensfight(Pos t); // 两主将照⾯的情况
bool RfightG(); // 红⽅⻋⾯对⿊⽅将情况
bool HfightG(); // 红⽅⻢⾯对⿊⽅将情况
bool CfightG(); // 红⽅炮⾯对⿊⽅将情况
bool RUN(int x,int y); // 将所有情况跑⼀遍
bool validMoveH(int x,int y,int direct); // 判断⻢⾛的情况是否合法
void erasing(int x,int y); // ⿊主将⾛过的地⽅如果有落⼦会被抹掉 int main()
{
int n;
while(cin >> n >> general_b.x >> general_b.y
&& n && general_b.x && general_b.y){ // 主循环
R.clear(); H.clear(); C.clear();
memset(map,,sizeof(map));memset(mmap,,sizeof(mmap));
map[general_b.x][general_b.y] = ; // 先将黑主将录入棋盘
while(n--)
{
char type; int posX; int posY;
cin >> type >> posX >> posY;
map[posX][posY] = ; // 在每次询问中,不管输入什么类型落子,先录入棋盘
if(type == 'G'){ // 类型为红方主将
general_r.x = posX;
general_r.y = posY;
}else if(type == 'R'){ // 类型为红方车
R.emplace_back(Pos(posX,posY));
mmap[posX][posY] = 'R'; // mmap数组的作用可在之后的erasing函数中清楚
}else if(type == 'H'){ // 类型为红方马
H.emplace_back(Pos(posX,posY));
mmap[posX][posY] = 'H';
}else{ // 类型为红方炮
C.emplace_back(Pos(posX,posY));
mmap[posX][posY] = 'C';
}
}
if(gensfight({general_b.x,general_b.y})){ // 分支1:直接出现主将对⾯情况
cout <<"NO" << endl; continue;
}
/* 分支2 (不出现主将直接面对)*/
auto op = validMoveG(); // 获得⿊⽅主将可⾛⽅向的vector数组
bool yes; // yes若为true表示红方已将死黑方
for(auto &e : op){ // 只要⿊⽅主将有⼀种⾛法不会被将死就输出NO
yes = false;
// general_b 与 general_r 分别代表黑方主将与红方主将,见17行声明
if(e == MOVE_TYPE::UP && RUN(general_b.x-,general_b.y)) yes = true;
else if(e == MOVE_TYPE::DOWN && RUN(general_b.x+,general_b.y)) yes = true;
else if(e == MOVE_TYPE::LEFT && RUN(general_b.x,general_b.y-)) yes = true;
else if(e == MOVE_TYPE::RIGHT && RUN(general_b.x,general_b.y+)) yes = true;
if(!yes) break; // 对于黑主将每一种走法,只要此走法不会被将死,那么黑方目前未被将死
}
yes ? printf("YES\n") : printf("NO\n");
}
return ;
} bool gensfight(Pos t){
if(t.y != general_r.y) return false; // 如果两主将不在⼀条直线上直接否定
return others(general_r.x,t.x,t.y,TRAVERSE_TYPE::X) == ;
}
bool RfightG(Pos t){for(auto &e : R){ // 将所有⻋遍历,看看它们上下左右是否直接与⿊⽅主将照⾯
bool equalsX = ( e.x == t.x ), equalsY = ( e.y == t.y ); //直接照⾯的前提是它们⾄少在同⼀条直线上
if(!(equalsX || equalsY)) continue; // 如果此⻋不满⾜条件考虑下⼀个⻋
if(equalsX){
if(others(e.y,t.y,e.x,TRAVERSE_TYPE::Y) == ) return true;
}else{
if(others(e.x,t.x,e.y,TRAVERSE_TYPE::X) == ) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
bool HfightG(Pos t){ // 将所有⻢遍历,看看它们是否直接踩到⿊⽅主将
for(auto &e : H){ // 只要有⼀匹⻢移动合法且直接踩到⿊主将则返回true
// validMoveH检查马的移动是否合法(包括蹩马脚、棋盘越界)
if(e.y- == t.y && e.x- == t.x && validMoveH(e.x,e.y,)) return true;
if(e.y+ == t.y && e.x- == t.x && validMoveH(e.x,e.y,)) return true;
if(e.y- == t.y && e.x- == t.x && validMoveH(e.x,e.y,)) return true;
if(e.y+ == t.y && e.x- == t.x && validMoveH(e.x,e.y,)) return true;
if(e.y- == t.y && e.x+ == t.x && validMoveH(e.x,e.y,)) return true;
if(e.y+ == t.y && e.x+ == t.x && validMoveH(e.x,e.y,)) return true;
if(e.y- == t.y && e.x+ == t.x && validMoveH(e.x,e.y,)) return true;
if(e.y+ == t.y && e.x+ == t.x && validMoveH(e.x,e.y,)) return true;
}
return false; // 程序控制流到达这里当且仅当所有存在的马均不能杀死黑主将
}
bool CfightG(Pos t){ // 将所有炮遍历,看看它们是否直接轰到⿊⽅主将
for(auto &e : H){
bool equalsX = ( e.x == t.x ), equalsY = ( e.y == t.y ); // 炮打到⿊将的前提是它们⾄少在同⼀条直线上
if(!(equalsX || equalsY)) continue; // 如果此炮不满⾜条件考虑下⼀个炮
if(equalsX){
int count = others(e.y,t.y,e.x,TRAVERSE_TYPE::Y);
if(count != ) continue; // 考虑炮杀死黑主将的前提是它们之间仅有一个落子
else return true; // 只要有一个炮能做到即返回true
}else{
int count = others(e.x,t.x,e.y,TRAVERSE_TYPE::X);
if(count == || count > ) continue;else return true;
}
}
return false;
}
int others(int begin,int end,int index,TRAVERSE_TYPE type){
// 该函数计算同一直线上两落子之间落子的个数,index是指在遍历中固定不动的下标
if(begin > end) swap(begin,end);
int cnt = ;
if(type == TRAVERSE_TYPE::X){
for(int i = begin + ;i < end;i ++) if(map[i][index]) cnt++;
}else{ // (type == TRAVERSE_TYPE::Y)
for(int i = begin + ;i < end;i ++) if(map[index][i]) cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
vector<MOVE_TYPE> validMoveG(){
// 该函数将黑主将可走的方向放进一个临时vector并返回
vector<MOVE_TYPE> temp;
if(general_b.y != ) temp.push_back(MOVE_TYPE::LEFT);
if(general_b.y != ) temp.push_back(MOVE_TYPE::RIGHT);
if(general_b.x != ) temp.push_back(MOVE_TYPE::UP);
if(general_b.x != ) temp.push_back(MOVE_TYPE::DOWN);
return temp;
}
inline
bool RUN(int x,int y){
// 该函数负责检查黑主将在每一种走法下是否会被一种存在类型的红方落子杀死
erasing(x,y); // 由于黑主将的下一个落点完全可能有一个红方棋子挡住,那么它可以直接吃掉也就是删除此落子
Pos t(x,y);
return RfightG(t) || HfightG(t) || CfightG(t) || gensfight(t);
}
bool validMoveH(int x,int y,int direct){
if(direct==){ // 这些map都代表会蹩马脚的位置,必须保证此位置没有落子
if(!(y- >= && x- >= && !map[x-][y])) return false;
}else if(direct==){
if(!(y+ <= && x- >= && !map[x-][y])) return false;
}else if(direct==){
if(!(y- >= && x- >= && !map[x][y-])) return false;
}else if(direct==){
if(!(y+ <= && x- >= && !map[x][y+])) return false;
}else if(direct==){
if(!(y- >= && x+ <= && !map[x][y-])) return false;
}else if(direct==){
if(!(y+ <= && x+ <= && !map[x][y+])) return false;
}else if(direct==){
if(!(y- >= && x+ <= && !map[x+][y])) return false;
}else if(direct==){
if(!(y+ <= && x+ <= && !map[x+][y])) return false;
}
return true;
}
void erasing(int x,int y){
// 检查棋盘上(x,y)处落子的类型,如果存在即将它从它的集合中删除
if(mmap[x][y]=='R'){
for(vector<Pos>::const_iterator it = R.begin();it != R.end();it
++)if(it->x==x && it->y==y) R.erase(it);
}else if(mmap[x][y]=='H'){
for(vector<Pos>::const_iterator it = H.begin();it != H.end();it
++)
if(it->x==x && it->y==y) H.erase(it);
}else if(mmap[x][y]=='C'){
for(vector<Pos>::const_iterator it = C.begin();it != C.end();it
++)
if(it->x==x && it->y==y) C.erase(it);
}
}
点击"+"查看代码
[算法竞赛入门经典] 象棋 ACM/ICPC Fuzhou 2011, UVa1589 较详细注释的更多相关文章
- (Step1-500题)UVaOJ+算法竞赛入门经典+挑战编程+USACO
http://www.cnblogs.com/sxiszero/p/3618737.html 下面给出的题目共计560道,去掉重复的也有近500题,作为ACMer Training Step1,用1年 ...
- [刷题]算法竞赛入门经典 3-12/UVa11809
书上具体所有题目:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1hssH0KO 题目:算法竞赛入门经典 3-4/UVa11809:Floating-Point Numbers 代码: //UVa11 ...
- [刷题]算法竞赛入门经典 3-10/UVa1587 3-11/UVa1588
书上具体所有题目:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1hssH0KO 题目:算法竞赛入门经典 3-10/UVa1587:Box 代码: //UVa1587 - Box #include&l ...
- [刷题]算法竞赛入门经典 3-7/UVa1368 3-8/UVa202 3-9/UVa10340
书上具体所有题目:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1hssH0KO 都是<算法竞赛入门经典(第二版)>的题目,标题上没写(第二版) 题目:算法竞赛入门经典 3-7/UVa13 ...
- [刷题]算法竞赛入门经典 3-4/UVa455 3-5/UVa227 3-6/UVa232
书上具体所有题目:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1hssH0KO 题目:算法竞赛入门经典 3-4/UVa455:Periodic Strings 代码: //UVa455 #inclu ...
- [刷题]算法竞赛入门经典 3-1/UVa1585 3-2/UVa1586 3-3/UVa1225
书上具体所有题目:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1hssH0KO(我也是在网上找到的pdf,但不记得是从哪里搜刮到的了,就重新上传了一遍) PS:第一次写博客分享我的代码,不知道我对c ...
- 算法竞赛入门经典训练指南——UVA 11300 preading the Wealth
A Communist regime is trying to redistribute wealth in a village. They have have decided to sit ever ...
- 算法竞赛入门经典+挑战编程+USACO
下面给出的题目共计560道,去掉重复的也有近500题,作为ACMer Training Step1,用1年到1年半年时间完成.打牢基础,厚积薄发. 一.UVaOJ http://uva.onlinej ...
- 算法竞赛入门经典 LA 4329(树状数组)
题意: 一排有着不同能力值的人比赛,规定裁判的序号只能在两人之间,而且技能值也只能在两人之间 问题: <算法竞赛入门经典-训练指南>的分析: 上代码: #include<iostre ...
随机推荐
- winserver-记录共享文件夹操作日志
abstract 1.在共享文件夹上开启审计. 2.在日志中查看操作记录. 开启审计 共享文件夹属性 选择审计 添加审计用户 选择用户及审计事件 日志查看 运行eventvwr 在windowslog ...
- 我的第一个python web开发框架(40)——后台日志与异常处理
后台权限和底层框架的改造终于完成了,小白也终于可以放下紧悬着的心,可以轻松一下了.这不他为了感谢老菜,又找老菜聊了起来. 小白:多谢老大的帮忙,系统终于改造完成了,可以好好放松一下了. 老菜:呵呵,对 ...
- Socket与WebScoket
socket 英文socket的意思是插座,网络中的Socket是一个抽象的接口,可以理解为网络中连接的两端.通常被叫做套接字接口,其意义在对传输层进行封装屏蔽了传输层的复杂性.它并不是一个协议,是为 ...
- GUI编程实战
1.拆分窗格:JSplistPane package swing; /** * swing 实战 */ import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; public ...
- VS2019 实用设置
本文记录了 VS2019 预览版使用过程中的一些设置,这些设置也同样适用于 VS2017,我们可以根据个人的实际情况进行修改. 滚动条(Scroll Bar) 将滚动条设置为 map mode 后,则 ...
- 佳文赏析:How to uninstall Linux
来源:https://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/linux-uninstall.html This article was suggested to me by a re ...
- rabbitmq 出现 com.rabbitmq.client.ShutdownSignalException: , ..................
-classpath "C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_144\jre\lib\charsets.jar;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1. ...
- Excel提取字符串示例
1.提取两个字符中间的字
- python3使用ctypes在windows中访问C和C++动态链接库函数示例
python3使用ctypes在windows中访问C和C++动态链接库函数示例 这是我们的第一个示例,我们尽量简单,不传参,不返回,不访问其他的动态链接库 一 测试环境介绍和准备 测试环境: 操作系 ...
- P1339 [USACO09OCT]热浪Heat Wave
我太lj了,所以趁着夜色刷了道最短路的水题....然后,,我炸了. 题目描述: The good folks in Texas are having a heatwave this summer. T ...
