算法:数字推盘游戏--重排九宫(8-puzzle)
一、数字推盘游戏
数字推盘游戏(n-puzzle)是一种最早的滑块类游戏,常见的类型有十五数字推盘游戏和八数字推盘游戏等。也有以图画代替数字的推盘游戏。可能Noyes Palmer Chapman在1874年发明十五数字推盘,但Sam Loyd则在1891年也宣称为其发明。
八数字推盘(又名重排九宫)则同样是Noyes Palmer Chapman在1870年代发明,并且马丁·加德纳在科学科普杂志上寻求更快的解答。也有人宣称重排九宫是传统中国游戏,来自洛书,并且为华容道的祖先。
二、分支界定法
给定一个具有 8 个图块的 3×3 板(每个图块都有一个 1 到 8 的数字)和一个空白空间(用 0 代表)。目的是将数字放置在图块上,以使用空白的空间匹配最终配置。我们可以将四个相邻的(左,右,上方和下方)图块滑动到空白区域。
通常可以使用 DFS、BFS 搜索算法来进行暴力破解。本文利用分支界定法,来“智能”的排名函数(近似于成本函数)来加快对成本节点的搜索,这里每一个节点都存有当前移动后整个方块的分布,从而避免在找不到最终答案的子树继续搜索。
分支界定法基本上涉及三种类型的节点:
- 存活节点,是已生成但尚未生成其子节点的节点;
- 当前正在扩展的节点,探索它的子节点;
- 死亡节点,死节点是生成的节点,将不再扩展或探索。死节点的所有子节点均已扩展。
成本函数:C(x) = g(x) + h(x)。
g(x) 是当前节点到根节点的成本(即路径长度)。h(x) 是当前除开空白块外与答案节点错位(放错位置)的成本,假设在往上下左右任一方向移动图块的成本为 1。
给定初始状态和目的状态:
 下图显示了上述算法从给定的8-Puzzle初始配置达到最终配置所遵循的路径。注意,仅具有最小成本函数值的节点被扩展。
下图显示了上述算法从给定的8-Puzzle初始配置达到最终配置所遵循的路径。注意,仅具有最小成本函数值的节点被扩展。
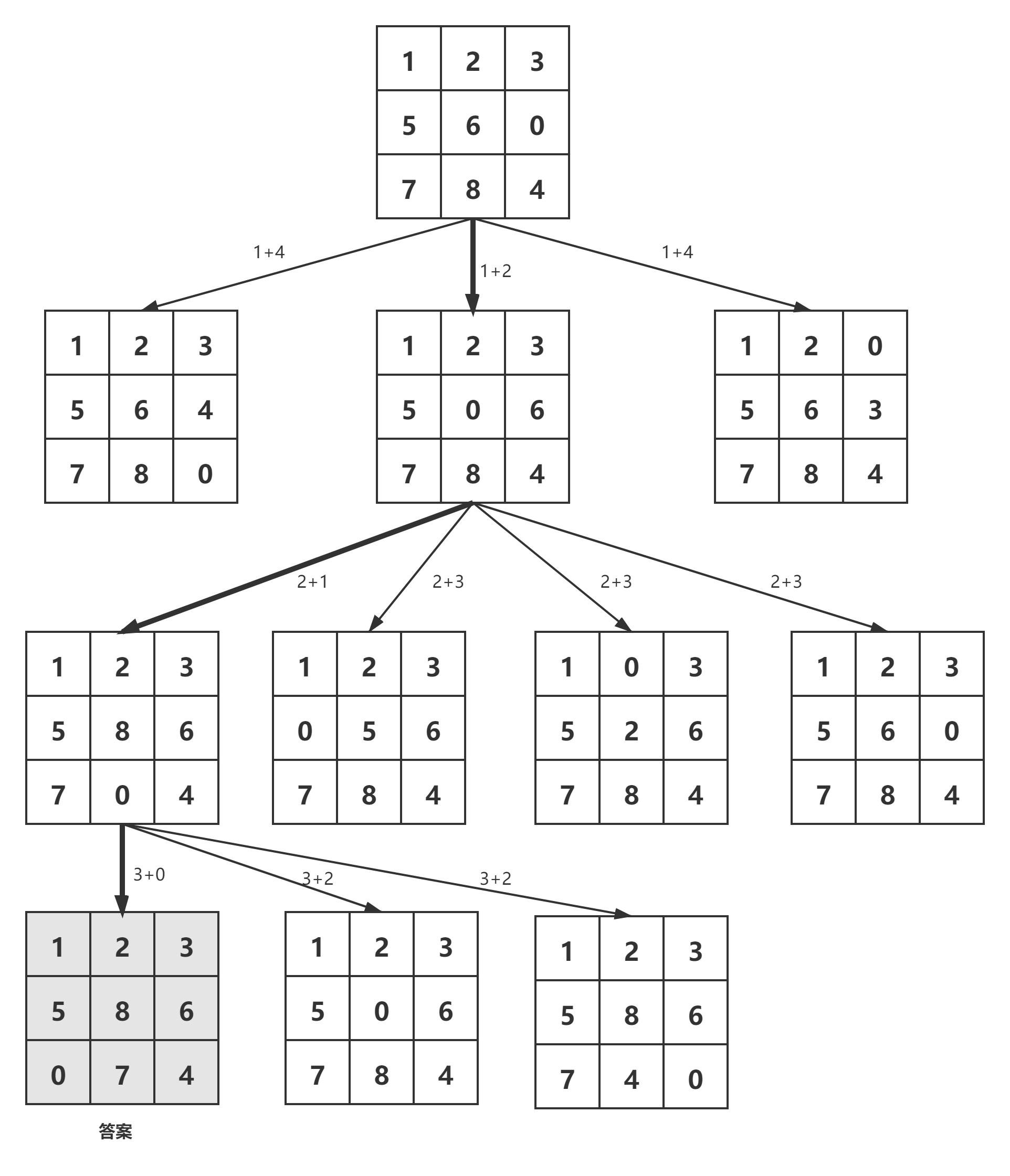
(注意:以上是本算法的流程图)
三、分支界定法的实现
节点的构造:
1 /**
2 * 节点
3 */
4 private class Node {
5 private Node parent;
6 private int[][] mat;
7 private int x, y;
8 private int cost;
9 private int level;
10 private Node() {
11 mat = new int[N][N];
12 }
13 }
插入一个新节点:
1 /**
2 * 分配一个新节点
3 *
4 * @param mat
5 * @param x
6 * @param y
7 * @param newX
8 * @param newY
9 * @param level
10 * @param parent
11 * @return
12 */
13 private Node newNode(int[][] mat, int x, int y, int newX, int newY, int level, Node parent) {
14 Node node = new Node();
15 node.parent = parent;
16
17 copyMatrix(mat, node.mat);
18
19 swap(node.mat, x, y, newX, newY);
20
21 node.cost = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
22 node.level = level;
23
24 node.x = newX;
25 node.y = newY;
26
27 return node;
28 }
计算错位成本:
1 /**
2 * 计算错位方块的数量, 即不在目标位置的非空白块的数量
3 *
4 * @param initial
5 * @param finals
6 * @return
7 */
8 private int calculateCost(int[][] initial, int[][] finals) {
9 int count = 0;
10 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
11 for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
12 if (initial[i][j] != 0 && initial[i][j] != finals[i][j]) {
13 count++;
14 }
15 return count;
16 }
利用优先队列(PriorityQueue)来实现分支界定法:
1 /**
2 * 分支界定法解决问题
3 *
4 * @param initial
5 * @param x
6 * @param y
7 * @param finals
8 */
9 private void solve(int[][] initial, int x, int y, int[][] finals) {
10 // 创建优先级队列以存储搜索树的活动节点
11 PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comp());
12
13 // 创建一个根节点并计算其成本
14 Node root = newNode(initial, x, y, x, y, 0, null);
15 root.cost = calculateCost(initial, finals);
16
17 // 将根添加到活动节点列表中;
18 pq.add(root);
19
20 // 查找成本最低的活动节点,
21 // 将其子级添加到活动节点列表中,并最后将其从列表中删除。
22 while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
23 // 查找估计成本最低的活动节点, 找到的节点将从活动节点列表中删除
24 Node min = pq.poll();
25
26 // 如果min是一个答案节点
27 if (min.cost == 0) {
28 printPath(min);
29 return;
30 }
31
32 // 为每个min节点的孩子
33 // 一个节点最多4个孩子
34 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
35 if (isSafe(min.x + row[i], min.y + col[i])) {
36 // 创建一个子节点并计算它的成本
37 Node child = newNode(min.mat, min.x, min.y,
38 min.x + row[i], min.y + col[i],
39 min.level, min);
40 child.cost = calculateCost(child.mat, finals);
41
42 // 将min的孩子添加到活动节点列表
43 pq.add(child);
44 }
45 }
46 }
47 }
分支定界是一种算法设计范例,通常用于解决组合优化问题。 这些问题通常在时间复杂度上呈指数关系(2^N),在最坏的情况下可能需要探索所有可能的排列(扩展完堆中所有可能的节点)。 分支界定相对较快地解决了这些问题。但是在最坏的情况下,我们需要完全计算整个树。充其量,我们只需要完全计算一条穿过树的路径,然后修剪其余路径即可。
本文源代码:
1 package algorithm;
2
3 import java.util.Comparator;
4 import java.util.PriorityQueue;
5
6 /**
7 * 重排九宫,或者称之为八码数问题,或是说数字推盘问题4,使用分支界定法实现
8 */
9 public class EightPuzzle {
10 // 方阵边长
11 private static final int N = 3;
12
13 // 坐标的行列索引向下、左、上、右
14 private static final int[] row = {1, 0, -1, 0};
15 private static final int[] col = {0, -1, 0, 1};
16
17 /**
18 * 节点
19 */
20 private class Node {
21 private Node parent;
22 private int[][] mat;
23 private int x, y;
24 private int cost;
25 private int level;
26 private Node() {
27 mat = new int[N][N];
28 }
29 }
30
31 /**
32 * 用于堆排序的比较对象
33 */
34 class Comp implements Comparator<Node> {
35 @Override
36 public int compare(Node o1, Node o2) {
37 return (o1.cost + o1.level) - (o2.cost + o2.level);
38 }
39 }
40
41 /**
42 * 打印矩阵
43 *
44 * @param mat
45 */
46 private void printMatrix(int[][] mat) {
47 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
48 for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
49 System.out.print(mat[i][j] + " ");
50 System.out.println();
51 }
52 }
53
54 /**
55 * 交换二维矩阵中的值
56 *
57 * @param mat
58 * @param x
59 * @param y
60 * @param newX
61 * @param newY
62 */
63 private void swap(int[][] mat, int x, int y, int newX, int newY) {
64 int tmp = mat[x][y];
65 mat[x][y] = mat[newX][newY];
66 mat[newX][newY] = tmp;
67 }
68
69 /**
70 * 矩阵复制
71 *
72 * @param arr1
73 * @param arr2
74 */
75 private static void copyMatrix(int[][] arr1, int[][] arr2) {
76 for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++)
77 System.arraycopy(arr1[i], 0, arr2[i], 0, arr1[0].length);
78
79 }
80
81 /**
82 * 分配一个新节点
83 *
84 * @param mat
85 * @param x
86 * @param y
87 * @param newX
88 * @param newY
89 * @param level
90 * @param parent
91 * @return
92 */
93 private Node newNode(int[][] mat, int x, int y, int newX, int newY, int level, Node parent) {
94 Node node = new Node();
95 node.parent = parent;
96
97 copyMatrix(mat, node.mat);
98
99 swap(node.mat, x, y, newX, newY);
100
101 node.cost = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
102 node.level = level;
103
104 node.x = newX;
105 node.y = newY;
106
107 return node;
108 }
109
110 /**
111 * 计算错位方块的数量, 即不在目标位置的非空白块的数量
112 *
113 * @param initial
114 * @param finals
115 * @return
116 */
117 private int calculateCost(int[][] initial, int[][] finals) {
118 int count = 0;
119 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
120 for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
121 if (initial[i][j] != 0 && initial[i][j] != finals[i][j]) {
122 count++;
123 }
124 return count;
125 }
126
127 /**
128 * 检查(x,y)是否为有效矩阵坐标
129 *
130 * @param x
131 * @param y
132 * @return
133 */
134 private boolean isSafe(int x, int y) {
135 return (x >= 0 && x < N && y >= 0 && y < N);
136 }
137
138 /**
139 * 打印路径
140 *
141 * @param root
142 */
143 private void printPath(Node root) {
144 if (root == null)
145 return;
146 printPath(root.parent);
147 printMatrix(root.mat);
148 System.out.println();
149 }
150
151 /**
152 * 分支界定法解决问题
153 *
154 * @param initial
155 * @param x
156 * @param y
157 * @param finals
158 */
159 private void solve(int[][] initial, int x, int y, int[][] finals) {
160 // 创建优先级队列以存储搜索树的活动节点
161 PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comp());
162
163 // 创建一个根节点并计算其成本
164 Node root = newNode(initial, x, y, x, y, 0, null);
165 root.cost = calculateCost(initial, finals);
166
167 // 将根添加到活动节点列表中;
168 pq.add(root);
169
170 // 查找成本最低的活动节点,
171 // 将其子级添加到活动节点列表中,并最后将其从列表中删除。
172 while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
173 // 查找估计成本最低的活动节点, 找到的节点将从活动节点列表中删除
174 Node min = pq.poll();
175
176 // 如果min是一个答案节点
177 if (min.cost == 0) {
178 printPath(min);
179 return;
180 }
181
182 // 为每个min节点的孩子
183 // 一个节点最多4个孩子
184 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
185 if (isSafe(min.x + row[i], min.y + col[i])) {
186 // 创建一个子节点并计算它的成本
187 Node child = newNode(min.mat, min.x, min.y,
188 min.x + row[i], min.y + col[i],
189 min.level, min);
190 child.cost = calculateCost(child.mat, finals);
191
192 // 将min的孩子添加到活动节点列表
193 pq.add(child);
194 }
195 }
196 }
197 }
198
199 public static void main(String[] args) {
200 int[][] initial =
201 {
202 {1, 2, 3},
203 {5, 6, 0},
204 {7, 8, 4}
205 };
206
207 int[][] finals =
208 {
209 {1, 2, 3},
210 {5, 8, 6},
211 {0, 7, 4}
212 };
213
214 // 0的位置(空白块)
215 int x = 1, y = 2;
216
217 EightPuzzle eightPuzzle = new EightPuzzle();
218 eightPuzzle.solve(initial, x, y, finals);
219
220 }
221 }
算法:数字推盘游戏--重排九宫(8-puzzle)的更多相关文章
- Java基础知识强化之IO流笔记70:Properties练习之 如何让猜数字小游戏只能玩5次的案例
1. 使用Properties完成猜数字小游戏只能玩5次的案例: 2. 代码实现: (1)猜数字游戏GuessNumber: package cn.itcast_08; import java.uti ...
- 洛谷P1118 数字三角形游戏
洛谷1118 数字三角形游戏 题目描述 有这么一个游戏: 写出一个1-N的排列a[i],然后每次将相邻两个数相加,构成新的序列,再对新序列进行这样的操作,显然每次构成的序列都比上一次的序列长度少1,直 ...
- java猜数字小游戏
/* * * 猜数字小游戏 * * 先由系统生成一个2-100之间的随机数字, * * 然后捕获用户从控制台中输入的数字是否与系统生成的随机数字相同, * * 如果相同则统计用户所猜的次数,并给出相应 ...
- 简单的C语言猜数字小游戏
猜数字小游戏可谓是C语言最为基础的一个知识点了,我们可以在此基础上进行延伸,实现随机数的猜测,然后是加入再来一局的模式,等等.这里是抛砖引玉,希望你能做出你的经典之作. #include <st ...
- python 游戏(数字推理游戏Bagels)
1.游戏思路和流程图 实现功能:玩家猜测三位不一样的数字,猜错了有提示,提示分别为(位置错误数字正确),(位置和数字正确),(数字和位置都不正确) 游戏流程图 2. 使用模块和游戏提示 import ...
- jquery开发的数字相加游戏(你能玩几分)
jquery开发的数字相加游戏,我在一轮中玩了632分(如下图),你能玩几分,哈哈... 我要试一试 下面贡献下这款“数字相加游戏”的开发过程. html部分: <div class=" ...
- 一款纯css3实现的数字统计游戏
今天给大家分享一款纯css3实现的数字统计游戏.这款游戏的规则的是将所有的数字相加等于72.这款游戏的数字按钮做得很美观,需要的时候可以借用下.一起看下效果图: 在线预览 源码下载 实现的代码. ...
- 洛谷P1132 数字生成游戏
P1132 数字生成游戏 题目描述 小明完成了这样一个数字生成游戏,对于一个不包含0的数字s来说,有以下3种生成新的数的规则: 将s的任意两位对换生成新的数字,例如143可以生成314,413,134 ...
- 【转】Java数字抽奖游戏核心代码
1. [代码][Java]代码 package com.luiszhang.test; import java.util.Arrays; /** * NumberLotteryGame * 一个 ...
随机推荐
- (2)java Spring Cloud+Spring boot+mybatis企业快速开发架构之SpringCloud-Spring Cloud是什么?Spring Cloud版本介绍
Spring Cloud 是一系列框架的有序集合.它利用 Spring Boot 的开发便利性,巧妙地简化了分布式系统基础设施的开发,如服务注册.服务发现.配置中心.消息总线.负载均衡.断路器.数 ...
- Spring Boot 2.x 之 Logging
[源起] 最近在看Apollo的源码,发现其all-in-one项目的脚本demo.sh在执行的时候,竟然没有向控制台输出Spring Boot的日志. 我们修改后构建的Fat Jar,在启动时却打印 ...
- 解决IE浏览器 点击子元素重复调用执行 mouseover 与mouseout兼容性问题
将函数配对换为下面2个就可以解决兼容性问题. mouseenter() mouseleave(0
- Roslyn(CSharpScript).Net脚本编译引擎使用过程内存增涨与稳定的方式
目 录 1. 引用程序集... 1 2. 内存增涨的情况... 2 3. 内存稳定的情况... 4 1. 引用程序集 Roslyn 是微软公司开源的 .N ...
- Docker系列(21)- DockerFile介绍
DockerFile介绍 dockerfile是用来构建docker镜像的文件!命令参数脚本! 构建步骤 编写一个dockerfile文件 docker build构建成为一个镜像 docker ru ...
- Writing in the Science 01
INTRODUCTION What makes good writing? Good writing communicates an idea clearly and effectively. Goo ...
- django对layui中csrf_token处理方式及其它一些处理
第一:由于layui官方是没有csrf_token处理机制,所以,在使用layui中post请求,请不要按layui官方提供的两种方法进行设置 官方设置如下: table.render({ elem: ...
- centos修改ssh默认端口号的方法
修改/etc/ssh/sshd_config配置文件(注意:这里是sshd_config,而不是ssh_config) vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config 在sshd_config文件中添 ...
- Redis分布式锁,看完不懂你打我
简易的redis分布式锁 加锁: set key my_random_value NX PX 30000 这个命令比setnx好,因为可以同时设置过期时间.不设置过期时间,应用挂了,解不了锁,就一直锁 ...
- 【深度学习】线性回归(Linear Regression)——原理、均方损失、小批量随机梯度下降
1. 线性回归 回归(regression)问题指一类为一个或多个自变量与因变量之间关系建模的方法,通常用来表示输入和输出之间的关系. 机器学习领域中多数问题都与预测相关,当我们想预测一个数值时,就会 ...
