Flink - NetworkEnvironment
NetworkEnvironment 是一个TaskManager对应一个,而不是一个task对应一个
其中最关键的是networkBufferPool,
operator产生的中间结果,ResultPartition,或是input数据,InputGate
都是需要memory来暂存的,这就需要networkBufferPool来管理这部分内存
/**
* Network I/O components of each {@link TaskManager} instance. The network environment contains
* the data structures that keep track of all intermediate results and all data exchanges.
*
* When initialized, the NetworkEnvironment will allocate the network buffer pool.
* All other components (netty, intermediate result managers, ...) are only created once the
* environment is "associated" with a TaskManager and JobManager. This happens as soon as the
* TaskManager actor gets created and registers itself at the JobManager.
*/
public class NetworkEnvironment { private final NetworkEnvironmentConfiguration configuration; private final NetworkBufferPool networkBufferPool; private ConnectionManager connectionManager; private ResultPartitionManager partitionManager; private ResultPartitionConsumableNotifier partitionConsumableNotifier; /**
* ExecutionEnvironment which is used to execute remote calls with the
* {@link JobManagerResultPartitionConsumableNotifier}
*/
private final ExecutionContext executionContext; /**
* Initializes all network I/O components.
*/
public NetworkEnvironment(
ExecutionContext executionContext,
FiniteDuration jobManagerTimeout,
NetworkEnvironmentConfiguration config) throws IOException { // create the network buffers - this is the operation most likely to fail upon
// mis-configuration, so we do this first
try {
networkBufferPool = new NetworkBufferPool(config.numNetworkBuffers(),
config.networkBufferSize(), config.memoryType());
}
catch (Throwable t) {
throw new IOException("Cannot allocate network buffer pool: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
}
}
NetworkBufferPool
先看看networkBufferPool,
首先,它管理了一堆的BufferPool,而不是buffer,因为一个task manager只有一个networkBufferPool,所以对于每个task,需要分配一个buffer pool
再者,它的内存管理和memory manager一样的模式,从heap或off-heap申请相应数量的segments放入availableMemorySegments中
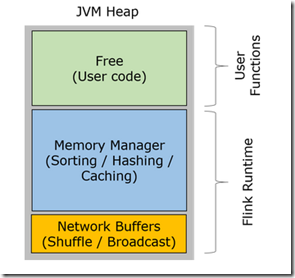
可以看到底下黄色部分,就是分配给networkBufferPool的heap
/**
* The NetworkBufferPool is a fixed size pool of {@link MemorySegment} instances
* for the network stack.
*
* The NetworkBufferPool creates {@link LocalBufferPool}s from which the individual tasks draw
* the buffers for the network data transfer. When new local buffer pools are created, the
* NetworkBufferPool dynamically redistributes the buffers between the pools.
*/
public class NetworkBufferPool implements BufferPoolFactory { private final int totalNumberOfMemorySegments; //该Pool所管理的所有MemorySegment的数量 private final int memorySegmentSize; //memorySegment的大小,size private final Queue<MemorySegment> availableMemorySegments; //可用的MemorySegment队列 private final Set<LocalBufferPool> managedBufferPools = new HashSet<LocalBufferPool>(); //管理一组LocalBufferPool,每个task需要分配一个 public final Set<LocalBufferPool> allBufferPools = new HashSet<LocalBufferPool>(); private int numTotalRequiredBuffers; /**
* Allocates all {@link MemorySegment} instances managed by this pool.
*/
public NetworkBufferPool(int numberOfSegmentsToAllocate, int segmentSize, MemoryType memoryType) { this.totalNumberOfMemorySegments = numberOfSegmentsToAllocate;
this.memorySegmentSize = segmentSize; final long sizeInLong = (long) segmentSize; try {
this.availableMemorySegments = new ArrayBlockingQueue<MemorySegment>(numberOfSegmentsToAllocate); //availableMemorySegments按totalNumberOfMemorySegments分配
}
catch (OutOfMemoryError err) { } try {
if (memoryType == MemoryType.HEAP) { //可以选择是从heap或off-heap分配
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfSegmentsToAllocate; i++) {
byte[] memory = new byte[segmentSize];
availableMemorySegments.add(MemorySegmentFactory.wrapPooledHeapMemory(memory, null));
}
}
else if (memoryType == MemoryType.OFF_HEAP) {
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfSegmentsToAllocate; i++) {
ByteBuffer memory = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(segmentSize);
availableMemorySegments.add(MemorySegmentFactory.wrapPooledOffHeapMemory(memory, null));
}
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown memory type " + memoryType);
}
}
} public MemorySegment requestMemorySegment() {
return availableMemorySegments.poll(); //request就是从availableMemorySegments里面取一个
} // This is not safe with regard to destroy calls, but it does not hurt, because destroy happens
// only once at clean up time (task manager shutdown).
public void recycle(MemorySegment segment) {
availableMemorySegments.add(segment); //而回收就是放回availableMemorySegments
} @Override
public BufferPool createBufferPool(int numRequiredBuffers, boolean isFixedSize) throws IOException {
// It is necessary to use a separate lock from the one used for buffer
// requests to ensure deadlock freedom for failure cases.
synchronized (factoryLock) { // Ensure that the number of required buffers can be satisfied.
// With dynamic memory management this should become obsolete.
if (numTotalRequiredBuffers + numRequiredBuffers > totalNumberOfMemorySegments) { //确定已经required的加上这次require的没有超过总量
throw new IOException(String.format("Insufficient number of network buffers: " +
"required %d, but only %d available. The total number of network " +
"buffers is currently set to %d. You can increase this " +
"number by setting the configuration key '%s'.",
numRequiredBuffers,
totalNumberOfMemorySegments - numTotalRequiredBuffers,
totalNumberOfMemorySegments,
ConfigConstants.TASK_MANAGER_NETWORK_NUM_BUFFERS_KEY));
} this.numTotalRequiredBuffers += numRequiredBuffers; //增加numTotalRequiredBuffers // We are good to go, create a new buffer pool and redistribute
// non-fixed size buffers.
LocalBufferPool localBufferPool = new LocalBufferPool(this, numRequiredBuffers); //创建LocalBufferPool,这时并不会把segement给他,request是lazy的 // The fixed size pools get their share of buffers and don't change
// it during their lifetime.
if (!isFixedSize) { //如果不是Fixed,可以动态把多的segment分配出去
managedBufferPools.add(localBufferPool);
} allBufferPools.add(localBufferPool); //管理localBufferPool redistributeBuffers(); return localBufferPool;
}
} // Must be called from synchronized block
//目的就是把多余的segement也分配出去,利用起来
private void redistributeBuffers() throws IOException {
int numManagedBufferPools = managedBufferPools.size(); if (numManagedBufferPools == 0) {
return; // necessary to avoid div by zero when no managed pools
} // All buffers, which are not among the required ones
int numAvailableMemorySegment = totalNumberOfMemorySegments - numTotalRequiredBuffers; //多的Segments // Available excess (not required) buffers per pool
int numExcessBuffersPerPool = numAvailableMemorySegment / numManagedBufferPools; //多的平均到每个bufferpool // Distribute leftover buffers in round robin fashion
int numLeftoverBuffers = numAvailableMemorySegment % numManagedBufferPools; //余数 int bufferPoolIndex = 0; for (LocalBufferPool bufferPool : managedBufferPools) {
int leftoverBuffers = bufferPoolIndex++ < numLeftoverBuffers ? 1 : 0; //余数可能是1或0 bufferPool.setNumBuffers(bufferPool.getNumberOfRequiredMemorySegments() + numExcessBuffersPerPool + leftoverBuffers); //在getNumberOfRequiredMemorySegments的基础上加上多余的
}
}
可看到,当一个task需要申请buffer pool时,要先createBufferPool
即,在从availableMemorySegments中取出相应数量的segement,封装成LocalBufferPool,返回
这里有个managedBufferPools,表示bufferpool的size是可以动态变化的,
redistributeBuffers会平均将现有可用的segments分配到所有当前的managedBufferPools上去
LocalBufferPool
class LocalBufferPool implements BufferPool {
private final NetworkBufferPool networkBufferPool; //总的bufferPool
// The minimum number of required segments for this pool
private final int numberOfRequiredMemorySegments; //要求申请的MemorySegments的个数,最小个数
// The current size of this pool
private int currentPoolSize; //实际的MemorySegments的个数,如果不是fixed,可能会多
// The currently available memory segments. These are segments, which have been requested from
// the network buffer pool and are currently not handed out as Buffer instances.
private final Queue<MemorySegment> availableMemorySegments = new ArrayDeque<MemorySegment>(); //缓存MemorySegment的队列
// Buffer availability listeners, which need to be notified when a Buffer becomes available.
// Listeners can only be registered at a time/state where no Buffer instance was available.
private final Queue<EventListener<Buffer>> registeredListeners = new ArrayDeque<EventListener<Buffer>>();
// Number of all memory segments, which have been requested from the network buffer pool and are
// somehow referenced through this pool (e.g. wrapped in Buffer instances or as available segments).
private int numberOfRequestedMemorySegments; //已经分配的MemorySegments的个数
private boolean isDestroyed;
private BufferPoolOwner owner; //owner复杂去释放networkBufferPool的buffer
LocalBufferPool(NetworkBufferPool networkBufferPool, int numberOfRequiredMemorySegments) {
this.networkBufferPool = networkBufferPool;
this.numberOfRequiredMemorySegments = numberOfRequiredMemorySegments; //初始化的时候,numberOfRequiredMemorySegments,currentPoolSize相等
this.currentPoolSize = numberOfRequiredMemorySegments;
}
@Override
public int getMemorySegmentSize() {
return networkBufferPool.getMemorySegmentSize(); //MemorySegment本身的size
}
@Override
public int getNumBuffers() {
synchronized (availableMemorySegments) {
return currentPoolSize; //当前local pool的size
}
}
private Buffer requestBuffer(boolean isBlocking) throws InterruptedException, IOException {
synchronized (availableMemorySegments) {
returnExcessMemorySegments(); //把多申请的MemorySegment还回去,如果动态的情况下,是可能的
boolean askToRecycle = owner != null;
while (availableMemorySegments.isEmpty()) { //如果availableMemorySegments中没有现成的
if (numberOfRequestedMemorySegments < currentPoolSize) { //只有在numberOfRequestedMemorySegments小于currentPoolSize,才能继续申请
final MemorySegment segment = networkBufferPool.requestMemorySegment(); //从networkBufferPool中申请一块
if (segment != null) {
numberOfRequestedMemorySegments++;
availableMemorySegments.add(segment);
continue; //如果申请到继续
}
}
if (askToRecycle) { //如果申请不到,说明networkBufferPool也没有buffer了
owner.releaseMemory(1); //试图让owner去让networkBufferPool释放一块
}
if (isBlocking) {
availableMemorySegments.wait(2000);
}
else {
return null;
}
}
return new Buffer(availableMemorySegments.poll(), this);
}
}
@Override
public void recycle(MemorySegment segment) {
synchronized (availableMemorySegments) {
if (isDestroyed || numberOfRequestedMemorySegments > currentPoolSize) {
returnMemorySegment(segment); //直接还回networkBufferPool
}
else {
EventListener<Buffer> listener = registeredListeners.poll();
if (listener == null) { //如果没有listen,直接把segment放回availableMemorySegments
availableMemorySegments.add(segment);
availableMemorySegments.notify(); //触发通知availableMemorySegments有新的segment
}
else {
try {
listener.onEvent(new Buffer(segment, this)); //如果有listener,触发onEvent让listener去处理这个segment
}
catch (Throwable ignored) {
availableMemorySegments.add(segment);
availableMemorySegments.notify();
}
}
}
}
}
@Override
public void setNumBuffers(int numBuffers) throws IOException {
synchronized (availableMemorySegments) {
checkArgument(numBuffers >= numberOfRequiredMemorySegments, "Buffer pool needs at least " + numberOfRequiredMemorySegments + " buffers, but tried to set to " + numBuffers + ".");
currentPoolSize = numBuffers;
returnExcessMemorySegments();
// If there is a registered owner and we have still requested more buffers than our
// size, trigger a recycle via the owner.
if (owner != null && numberOfRequestedMemorySegments > currentPoolSize) {
owner.releaseMemory(numberOfRequestedMemorySegments - numBuffers);
}
}
}
}
associateWithTaskManagerAndJobManager
NetworkEnvironment首先需要做的是associate,然后才能用
NetworkEnvironment 中有很多组件,是需要在绑定TaskManagerAndJobManager时,才需要去初始化的
/**
* This associates the network environment with a TaskManager and JobManager.
* This will actually start the network components.
*
* @param jobManagerGateway Gateway to the JobManager.
* @param taskManagerGateway Gateway to the TaskManager.
*
* @throws IOException Thrown if the network subsystem (Netty) cannot be properly started.
*/
public void associateWithTaskManagerAndJobManager(
ActorGateway jobManagerGateway,
ActorGateway taskManagerGateway) throws IOException
{
synchronized (lock) { if (this.partitionConsumableNotifier == null &&
this.partitionManager == null &&
this.taskEventDispatcher == null &&
this.connectionManager == null)
{
// good, not currently associated. start the individual components LOG.debug("Starting result partition manager and network connection manager");
this.partitionManager = new ResultPartitionManager();
this.taskEventDispatcher = new TaskEventDispatcher();
this.partitionConsumableNotifier = new JobManagerResultPartitionConsumableNotifier(
executionContext,
jobManagerGateway,
taskManagerGateway,
jobManagerTimeout); this.partitionStateChecker = new JobManagerPartitionStateChecker(
jobManagerGateway, taskManagerGateway); // ----- Network connections -----
final Option<NettyConfig> nettyConfig = configuration.nettyConfig();
connectionManager = nettyConfig.isDefined() ? new NettyConnectionManager(nettyConfig.get())
: new LocalConnectionManager(); try {
LOG.debug("Starting network connection manager");
connectionManager.start(partitionManager, taskEventDispatcher, networkBufferPool);
}
catch (Throwable t) {
throw new IOException("Failed to instantiate network connection manager: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
}
else {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Network Environment is already associated with a JobManager/TaskManager");
}
}
}
主要是初始化一系列组件,TaskEventDispatcher,ConnectionManager, ResultPartitionManager
JobManagerResultPartitionConsumableNotifier, JobManagerPartitionStateChecker
对于ConnectionManager,这里如果定义了netty,会创建NettyConnectionManager
这里面,主要是初始化Netty client和Netty server
否则是创建LocalConnectionManager
而对于ResultPartitionManager, 主要就是用于track所有的result partitions,
核心结构为, Table<ExecutionAttemptID, IntermediateResultPartitionID, ResultPartition> registeredPartitions = HashBasedTable.create();
这个会记录所有的ResultPartition
/**
* The result partition manager keeps track of all currently produced/consumed partitions of a
* task manager.
*/
public class ResultPartitionManager implements ResultPartitionProvider { private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ResultPartitionManager.class); public final Table<ExecutionAttemptID, IntermediateResultPartitionID, ResultPartition>
registeredPartitions = HashBasedTable.create(); private boolean isShutdown; public void registerResultPartition(ResultPartition partition) throws IOException {
synchronized (registeredPartitions) {
checkState(!isShutdown, "Result partition manager already shut down."); ResultPartitionID partitionId = partition.getPartitionId(); ResultPartition previous = registeredPartitions.put(partitionId.getProducerId(), partitionId.getPartitionId(), partition);
}
}
}
JobManagerResultPartitionConsumableNotifier,比较关键,通知JobMananger,ResultPartition已经ready,可以开始consume
private static class JobManagerResultPartitionConsumableNotifier implements ResultPartitionConsumableNotifier {
/**
* {@link ExecutionContext} which is used for the failure handler of {@link ScheduleOrUpdateConsumers}
* messages.
*/
private final ExecutionContext executionContext;
private final ActorGateway jobManager;
private final ActorGateway taskManager;
private final FiniteDuration jobManagerMessageTimeout;
@Override
public void notifyPartitionConsumable(JobID jobId, final ResultPartitionID partitionId) {
final ScheduleOrUpdateConsumers msg = new ScheduleOrUpdateConsumers(jobId, partitionId); //通知jobmanager,去deployconsumer
Future<Object> futureResponse = jobManager.ask(msg, jobManagerMessageTimeout); //等JobManager的回复
futureResponse.onFailure(new OnFailure() { //失败,即无法deploy consumer
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable failure) {
LOG.error("Could not schedule or update consumers at the JobManager.", failure);
// Fail task at the TaskManager
FailTask failMsg = new FailTask(
partitionId.getProducerId(),
new RuntimeException("Could not notify JobManager to schedule or update consumers",
failure));
taskManager.tell(failMsg);
}
}, executionContext);
}
}
RegisterTask
在NetworkEnvironment中比较重要的操作,是注册task,需要为task的resultpartition和inputgate分配bufferpool
public void registerTask(Task task) throws IOException {
final ResultPartition[] producedPartitions = task.getProducedPartitions();
final ResultPartitionWriter[] writers = task.getAllWriters();
ResultPartitionConsumableNotifier jobManagerNotifier;
synchronized (lock) {
for (int i = 0; i < producedPartitions.length; i++) {
final ResultPartition partition = producedPartitions[i];
final ResultPartitionWriter writer = writers[i];
// Buffer pool for the partition
BufferPool bufferPool = null;
try {
bufferPool = networkBufferPool.createBufferPool(partition.getNumberOfSubpartitions(), false); //创建LocalPool,注意Reqired的segment数目是Subpartitions的数目,即一个subP一个segment
partition.registerBufferPool(bufferPool); //把localPool注册到ResultPartition
partitionManager.registerResultPartition(partition); //注册到partitionManager
}
// Register writer with task event dispatcher
taskEventDispatcher.registerWriterForIncomingTaskEvents(writer.getPartitionId(), writer);
}
// Setup the buffer pool for each buffer reader
final SingleInputGate[] inputGates = task.getAllInputGates();
for (SingleInputGate gate : inputGates) {
BufferPool bufferPool = null;
try {
bufferPool = networkBufferPool.createBufferPool(gate.getNumberOfInputChannels(), false);
gate.setBufferPool(bufferPool);
}
// Copy the reference to prevent races with concurrent shut downs
jobManagerNotifier = partitionConsumableNotifier;
}
for (ResultPartition partition : producedPartitions) {
// Eagerly notify consumers if required.
if (partition.getEagerlyDeployConsumers()) { //如果是eager的方式,通知jobmanager,可以deploy consumer了
jobManagerNotifier.notifyPartitionConsumable(
partition.getJobId(), partition.getPartitionId());
}
}
}
Flink - NetworkEnvironment的更多相关文章
- 追源索骥:透过源码看懂Flink核心框架的执行流程
li,ol.inline>li{display:inline-block;padding-right:5px;padding-left:5px}dl{margin-bottom:20px}dt, ...
- Flink中的数据传输与背压
一图道尽心酸: 大的原理,上游的task产生数据后,会写在本地的缓存中,然后通知JM自己的数据已经好了,JM通知下游的Task去拉取数据,下游的Task然后去上游的Task拉取数据,形成链条. 但是在 ...
- Flink整体执行流程
以Flink源码中自带的WordCount为例,执行的入口从用户程序的execute()函数入手,execute()的源码如下: public JobExecutionResult execute(S ...
- [源码分析] 从源码入手看 Flink Watermark 之传播过程
[源码分析] 从源码入手看 Flink Watermark 之传播过程 0x00 摘要 本文将通过源码分析,带领大家熟悉Flink Watermark 之传播过程,顺便也可以对Flink整体逻辑有一个 ...
- 1、flink介绍,反压原理
一.flink介绍 Apache Flink是一个分布式大数据处理引擎,可对有界数据流和无界数据流进行有状态计算. 可部署在各种集群环境,对各种大小的数据规模进行快速计算. 1.1.有界数据流和无界 ...
- 透过源码看懂Flink核心框架的执行流程
前言 Flink是大数据处理领域最近很火的一个开源的分布式.高性能的流式处理框架,其对数据的处理可以达到毫秒级别.本文以一个来自官网的WordCount例子为引,全面阐述flink的核心架构及执行流程 ...
- apache flink 入门
配置环境 包括 JAVA_HOME jobmanager.rpc.address jobmanager.heap.mb 和 taskmanager.heap.mb taskmanager.number ...
- Flink 1.1 – ResourceManager
Flink resource manager的作用如图, FlinkResourceManager /** * * <h1>Worker allocation steps</h1 ...
- Apache Flink初接触
Apache Flink闻名已久,一直没有亲自尝试一把,这两天看了文档,发现在real-time streaming方面,Flink提供了更多高阶的实用函数. 用Apache Flink实现WordC ...
随机推荐
- 安装切换openjdk
安装各种版本openjdk sudo apt-get install openjdk-6-jdk sudo apt-get install openjdk-7-jdk sudo apt-get ins ...
- ViewState与Session [转]
昨天偶然看到网上有人讨论究竟是该用viewstate还是session来保存信息. 忽然觉得有必要去深入的研究一下这两个东东了,我们先来看深入分析一下viewstate, 为了分析的相对完整性,先从简 ...
- Find All Duplicates in an Array
Given an array of integers, 1 ≤ a[i] ≤ n (n = size of array), some elements appear twice and others ...
- Socket通信(一)
代码及PDF下载链接:http://download.csdn.net/detail/u010312811/9683034 例程1:实现服务器与客户端的连接与简单数据收发 参考链接:http://bl ...
- 【原创】js实现一个可随意拖拽排序的菜单导航栏
1.想做这个效果的原因主要是用在UC上看新闻发现他们的导航菜单很有趣.无聊的时候在哪划着玩了很久.所以就干脆自己写一个.原效果如下 2.整体效果如下,在已推荐和未添加里面每个小方块可以触摸移动位置互换 ...
- ios推送-B/S架构-socket
B/S架构项目,某一用户登录后执行了某些动作需要向在手机登录的对应的用户推送消息 通过socket实现 1.socket服务器:使用C#的window服务(该服务监听两个端口:比如平台8889,手机8 ...
- (转)ShardedJedisPool的使用
package com.test; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import redis.clients.jedis.Jedi ...
- MFC中CListCtrl控件的使用方法
定义一个派生类CViewList 派生于CListCtrl 在要包含该控件的类(CView)中定义一个CViewList类型的变量 CViewList m_wndListView; 在CView响应的 ...
- 自定义Toast和RatingBar的简单用例
Toast是一个包含用户点击消息.Toast类会帮助你创建和显示这些.Android中的Toast是一种简易的消息提示框. 当视图显示给用户,在应用程序中显示为浮动 向右划动五角星增加 单击按钮显示自 ...
- SubSonic指南中文版
翻译:王鹏程张原 王伟策划:毛凌志2009年1月北京工业大学软件学院PS:有问题反馈至http://lexus.cnblogs.comGetting Started with SubSonicBy S ...
