String类的源码分析
之前面试的时候被问到有没有看过String类的源码,楼主当时就慌了,回来赶紧补一课。
1.构造器(构造方法)
String类提供了很多不同的构造器,分别对应了不同的字符串初始化方法,此处从源码中摘录如下:
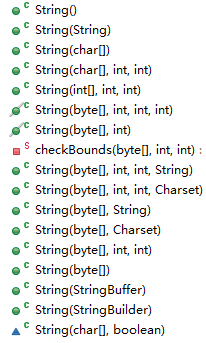
其中蓝色的实心三角表示no modifier(没有修饰符,friendly),表示只能被同一个包中的所有类访问,而不同包中的类不能访问。
这里举了一些示例,来说明这些构造器的用法:
String string = new String();
System.out.println(string.isEmpty());

String string = new String("hello world");
System.out.println(string);

char[] arr = {'A','B', 'C', '1', '2', '3'};
String arrString = new String(arr);
System.out.println(arrString);

char[] arr = {'A','B', 'C', '1', '2', '3'};
String arrString = new String(arr, 1, 4);
System.out.println(arrString);

int[] codepoints = {101, 97, 98, 99};
String string = new String(codepoints, 0, 3);
System.out.println(string);

StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer("hello");
2 buffer.append(" world");
3 String string = new String(buffer);
4 System.out.println(string);

StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("hello");
builder.append(" world");
String string = new String(builder);
System.out.println(string);

这里提到构造器,笔者想补充一个问题:构造器真的没有返回值吗?既然没有返回值,那么为什么不能用void关键字来修饰?
解析:其实这只是Java语法上的一个规定。实际上,类的构造器是有返回值的,当我们用new关键字来调用构造器时,会返回一个该类的实例对象,并将这个实例对象在堆内存中的地址赋给了一个该类类型的引用变量。因此,构造器的返回值类型总是当前类,所以就无须定义返回值类型。但必须注意的是,不能在构造器里显式地使用return关键字来返回当前类的对象,因为构造器的返回值是隐式的。
2.成员方法
- charAt(int index) 返回字符串中下标为index的字符,返回值为char型
String string = new String("hello world");
System.out.println(string.charAt(0));

- codePointAt(int index) 返回下标为index的字符的unicode码
- codePointBefore(int index) 返回下标为index-1的字符的unicode码
- codePointCount(int beginIndex, int endIndex) 返回下标从beginIndex到endIndex的字符数
String string = "hello world";
System.out.print(string.charAt(4)+" ");
System.out.println(string.codePointAt(4));
System.out.print(string.charAt(4)+" ");
System.out.println(string.codePointBefore(5));
System.out.println(string.codePointCount(0, 6));

- equals(Object obj) 比较两个字符串是否相同,返回值为true或者false,此外还有equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString),即忽略大小写的比较
注意:1.字符串之间的比较时,比较的是字符串的内容而不是地址,并且只能用于比较String类型,因为StringBuffer和StringBuilder都没有equals()方法;
2.非字符串之间的比较时,比较的是引用的地址而不是内容,可以用于StringBuffer和StringBuilder类型。
String string = "hello";
System.out.println(string.equals("hello")); //true String s1 = "hello";
System.out.println(string.equals(s1)); //true String s2 = new String("hello");
String s3 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(s2.equals(s3)); //true /* 注意:StringBuffer和StringBuilder都没有equals()方法
所以调用equals()方法时,比较的是引用变量的地址,所以结果均为false*/
StringBuffer s4 = new StringBuffer("hello");
StringBuilder s5 = new StringBuilder("hello");
StringBuffer s6 = new StringBuffer("hello");
StringBuilder s7 = new StringBuilder("hello");
System.out.println(s1.equals(s4)); //false
System.out.println(s2.equals(s5)); //false
System.out.println(s4.equals(s5)); //false
System.out.println(s4.equals(s6)); //false
System.out.println(s5.equals(s7)); //fals
String string = "hello";
System.out.println(string.equalsIgnoreCase("Hello")); //true
- toCharArray() 字符串转换为数组,返回值为一个char类型的数组
注意:字符数组转换为字符串可以用构造器String(char[]) 实现
String string = "hello world";
char[] charArr = string.toCharArray();
for(char ch: charArr){
System.out.print(ch+" ");
}

- 此外,String类还有很多成员方法,这里简单列举一些常用的:
startsWith(String prefix) endsWith(String suffix) indexOf(int ch) indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) lastIndexOf(int ch) lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) indexOf(String str) indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) substring(int beginIndex) substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) replace(char oldChar, char newChar) matches(String regex) contains(CharSequence s) replaceAll(String regex, String replacement) split(String regex) toLowerCase() toUpperCase() trim()
String类的源码分析的更多相关文章
- JDK中String类的源码分析(二)
1.startsWith(String prefix, int toffset)方法 包括startsWith(*),endsWith(*)方法,都是调用上述一个方法 public boolean s ...
- JDK中String类的源码分析(一)
1.String类是final的,不允许被继承 /** The value is used for character storage. */ private final char value[]; ...
- Spring-MongoDB 关键类的源码分析
本文分析的是 spring-data-mongodb-1.9.2.RELEASE.jar 和 mongodb-driver-core-3.2.2.jar. 一.UML Class Diagram 核心 ...
- Set集合架构和常用实现类的源码分析以及实例应用
说明:Set的实现类都是基于Map来实现的(HashSet是通过HashMap实现的,TreeSet是通过TreeMap实现的). (01) Set 是继承于Collection的接口.它是一个不允许 ...
- String,StringBuffer,StringBuilder源码分析
1.类结构 String Diagrams StringBuffer Diagrams StringBuilder Diagrams 通过以上Diagrams可以看出,String,StringBuf ...
- Mybatis Mapper接口是如何找到实现类的-源码分析
KeyWords: Mybatis 原理,源码,Mybatis Mapper 接口实现类,代理模式,动态代理,Java动态代理,Proxy.newProxyInstance,Mapper 映射,Map ...
- java类uuid源码分析
通用唯一识别码(英语:Universally Unique Identifier,简称UUID)是一种软件建构的标准,亦为自由软件基金会组织在分散式计算环境领域的一部份.UUID的目的,是让分散式系统 ...
- 【Cocos2d-x 3.x】 动作类Action源码分析
游戏设计中,动作是不可缺少的,Cocos2d-x中所有的动作都继承自Action类,而Action类继承自Ref和Clonable类,整个动作类继承体系如图: FiniteTimeAction是所有瞬 ...
- String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder源码分析
利用反编译具体看看"+"的过程 1 public class Test 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) 4 { 5 int ...
随机推荐
- hdu4746 Mophues
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4746 题意:给出n, m, p,求有多少对a, b满足gcd(a, b)的素因子个数<=p,(其 ...
- ASM的备份集在文件系统上恢复测试
背景:最近时常有客户咨询这类问题,其实很简单一个操作,但由于每个人的理解差异,也容易出现各种问题或者误解,本文主要总结下这个过程以及常遇到的问题处理. 环境:Site A(Oracle RAC 11. ...
- Html5笔记之小结
随着Android,IOS手机,平板等各种App的不断扩增,加上对过去传统HTML的的各种不完善,例如视频依靠Flash,对手机和桌面的不兼容等等.HTML5来了,来解决这些问题了. Html5是W3 ...
- Vue相关(过渡动画)
Vue 过渡 && 动画 一.CSS过渡 1.transition标签可以用来封装需要过渡的元素,添加entering/leaving 过渡, 条件是: (1)使用条件渲染语句 v-i ...
- DFS和BFS(无向图)Java实现
package practice; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Stack; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.* ...
- Weave 如何与外网通信?- 每天5分钟玩转 Docker 容器技术(66)
上一节我们学习了 Weave 网络内部如何通信,今天讨论 Weave 如何与外界通信. weave 是一个私有的 VxLAN 网络,默认与外部网络隔离.外部网络如何才能访问到 weave 中的容器呢? ...
- django 5 form1
---------------------Form表单验证(用户请求验证+生成HTML标签) 示例:用户管理 a. 添加用户页面 - 显示HTML标签 - 提交:数据验证 - 成功之后保存 - 错误显 ...
- django源码解析一(请求处理流程)
1.我们都知道WSGI是一个规范,规范了server和application之间通信的一些约束,server端在监听到请求之后,会把请求转给application去处理,他们之间关联起来的桥梁是一个e ...
- 【ACM小白成长撸】--计算单词个数
我判断单词个数的方法,根据空格‘ ’的个数 分情况 当没有单词的时候 判断第一个符号,即a[0] == ‘\0’时,赋值给存储个数的数组 当遇到空格时,只有前面一个字符不是空格字符,后面一个字符不是空 ...
- Project 3:N级魔方阵
魔方阵:由n*n个数字所组成的n阶方阵,具有各对角线,各横列与纵行的数字和都相等的性质,称为魔方阵.而这个相等的和称为魔术数字.若填入的数字是从1到n*n,称此种魔方阵为n阶正规魔方阵. 目标:输入一 ...
