"《算法导论》之‘线性表’":基于静态分配的数组的顺序表
首先,我们来搞明白几个概念吧(参考自网站数据结构及百度百科)。
线性表
线性表是最基本、最简单、也是最常用的一种数据结构。线性表中数据元素之间的关系是一对一的关系,即除了第一个和最后一个数据元素之外,其它数据元素都是首尾相接的。线性表的逻辑结构简单,便于实现和操作。在实现线性表数据元素的存储方面,一般可用顺序存储结构和链式存储结构两种方法。
顺序表
用顺序存储方法存储的线性表简称为顺序表(Sequential List)。顺序表的存储方法是把线性表的结点按逻辑次序依次存放在一组地址连续的存储单元里。
链表
链接方式存储的线性表简称为链表(Linked List)。
顺序表和链表的比较如下:
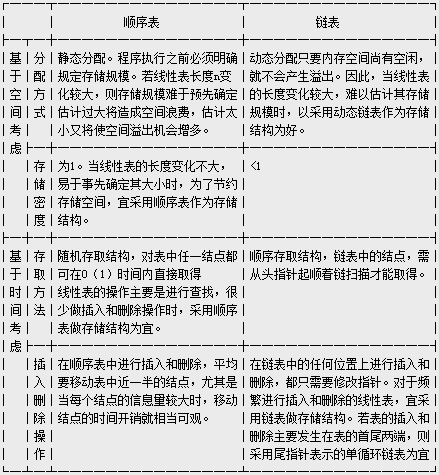
注:存储密度(Storage Density)是指结点数据本身所占的存储量和整个结点结构所占的存储量之比,即“存储密度=(结点数据本身所占的存储量)/(结点结构所占的存储总量)”。
下文将具体讲述如何实现基于静态分配的数组的顺序表:
具体算法可以参考网页顺序表上实现的基本运算及Larry Nyhoff的《数据结构与算法分析》。我的做法基本跟他们是一样的,只是我又额外多了一部分:Boost单元测试。对于如何进行Boost单元测试可以参考本人之前写过的一篇文章如何在VS2013中进行Boost单元测试。
我设计的顺序表类如下:
// seqlist.h
1 #ifndef SEQLIST
#define SEQLIST #include <iostream>
#include <cassert>
#include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int CAPACITY = ;
typedef int ElementType; class SeqList
{
public:
SeqList();
virtual ~SeqList();
bool empty() const;
void clear();
bool insert(const int pos, const ElementType val);
bool erase(const int pos);
void display() const;
bool setSeqList(const ElementType *tmpList, const int len);
int getLenOfList() const;
ElementType getItem(const int pos);
ElementType * getSeqList(); // 保留,不推荐使用,因为在使用过程中无法进行越界检查 private:
int lenOfList; // 线性链表长度
ElementType seqList[CAPACITY]; }; #endif
// seqlist.cpp
#include "seqlist.h" SeqList::SeqList()
{
// initialization
lenOfList = ;
fill(seqList, seqList + CAPACITY - , );
// memset(SeqList, 1, CAPACITY*sizeof(int));
} SeqList::~SeqList()
{ } bool SeqList::empty() const
{
return lenOfList == ;
} void SeqList::clear()
{
lenOfList = ;
fill(seqList, seqList + CAPACITY - , );
} bool SeqList::insert(const int pos, const ElementType val)
{
bool success = false;
// assert(lenOfList != CAPACITY); // 这里的assert分成两行写,是为了方便定位错误发生的地方
// assert(0 <= pos <= lenOfList);
if (lenOfList == CAPACITY)
{
cerr << "No space for insertion!" << endl;
}
else if (pos < || pos > lenOfList)
{
cerr << "The position " << pos <<
" you want to insert is less than zero or exceeds the length of the list!" << endl;
throw out_of_range("throw out_of_range"); // 抛出一个越界异常
}
else
{
int tmpCount = lenOfList - pos;
for (int i = ; i < tmpCount; i++)
{
seqList[lenOfList - i] = seqList[lenOfList - i - ];
}
seqList[pos] = val;
lenOfList++;
success = true;
}
return success;
} bool SeqList::erase(const int pos)
{
bool success = false;
// assert(lenOfList != 0);
// assert(0 <= pos <= lenOfList);
if (lenOfList == )
{
cerr << "There is no elements in the list!" << endl;
}
else if (pos < || pos > lenOfList)
{
cerr << "The position " << pos <<
" you want to erase is less than zero or exceeds the length of the list!" << endl;
throw out_of_range("throw out_of_range"); // 抛出一个越界异常
}
else
{
int tmp = lenOfList - pos;
for (int i = ; i < tmp - ; i++)
{
seqList[pos + i] = seqList[pos + i + ];
}
seqList[lenOfList - ] = ;
lenOfList--;
success = true;
}
return success;
} void SeqList::display() const
{
cout << "***Start Displaying***" << endl;
if (lenOfList == )
{
cerr << "There is no element in the the list!" << endl;
}
else
{
for (int i = ; i < lenOfList; i++)
{
cout << i << " : " << seqList[i] << endl;
}
cout << "***End Displaying***" << endl;
}
} bool SeqList::setSeqList(const ElementType *tmpList, const int len)
{
// assert(len <= CAPACITY);
bool success = false;
if (len <= CAPACITY)
{
for (int i = ; i < len; i++)
{
seqList[i] = *(tmpList++);
}
lenOfList = len;
success = true;
}
else
{
cerr << "The length of the array you set exceeds the CAPACITY." << endl;
throw out_of_range("throw out_of_range"); // 抛出一个越界异常
}
return success;
} int SeqList::getLenOfList() const
{
return lenOfList;
} ElementType SeqList::getItem(const int pos)
{
// assert(0 <= pos <= lenOfList);
if (pos < || pos > lenOfList)
{
cerr << "The item at " << pos << " you want to get does not exist!" << endl;
throw out_of_range("throw out_of_range"); // 抛出一个越界异常
}
else
{
return seqList[pos];
}
} ElementType * SeqList::getSeqList()
{
return seqList;
}
seqlist.cpp
单元测试所用到的代码如下:
// BoostUnitTest.cpp
#define BOOST_TEST_MODULE ArrayList_Test_Module #include "stdafx.h"
#include "D:\VSProject\Algorithm\List\SeqList\SeqList\SeqList\seqlist.h" struct ArrayList_Fixture
{
ArrayList_Fixture()
{
BOOST_TEST_MESSAGE("Setup fixture");
testArrayList = new SeqList();
}
~ArrayList_Fixture()
{
BOOST_TEST_MESSAGE("Teardown fixture");
delete testArrayList;
} SeqList * testArrayList;
}; // BOOST_AUTO_TEST_SUITE(ArrayList_Test_Suite)
BOOST_FIXTURE_TEST_SUITE(ArrayList_Test_Suite, ArrayList_Fixture) BOOST_AUTO_TEST_CASE(ArrayList_Abnormal_Test)
{
// Set values to the array list
int testArray[] = { , , , , }; // 5 个元素
int testLenOfList = sizeof(testArray) / sizeof(int);
testArrayList->setSeqList(testArray, testLenOfList);
// BOOST_REQUIRE_THROW(testArrayList->setArrayList(testArray, testLenOfList), out_of_range); // Method getItem-----------------------------------------------
// If the position of the item you want to get is less than zero
BOOST_REQUIRE_THROW(testArrayList->getItem(-), out_of_range);
// If the position of the item you want to get is larger than the length of the list
BOOST_REQUIRE_THROW(testArrayList->getItem(), out_of_range); // Method insert-------------------------------------------------
// If the inserting position is less than zero
BOOST_REQUIRE_THROW(testArrayList->insert(-, ), out_of_range);
BOOST_REQUIRE(testArrayList->getLenOfList() == testLenOfList); // If the inserting position is larger than the length of the list
BOOST_REQUIRE_THROW(testArrayList->insert(, ), out_of_range);
BOOST_REQUIRE(testArrayList->getLenOfList() == testLenOfList); // Method erase-------------------------------------------------
// If the erasing position is less than zero
BOOST_REQUIRE_THROW(testArrayList->erase(-), out_of_range);
BOOST_REQUIRE(testArrayList->getLenOfList() == testLenOfList); // If the erasing position is larger than the length of the list
BOOST_REQUIRE_THROW(testArrayList->erase(), out_of_range);
BOOST_REQUIRE(testArrayList->getLenOfList() == testLenOfList); } BOOST_AUTO_TEST_CASE(ArrayList_Normal_Test)
{
bool expected;
bool actual;
// Method empty-------------------------------------------------
expected = true;
actual = testArrayList->empty();
BOOST_REQUIRE(expected == actual); // Set values to the array list
int testArray[] = { , , , , }; // 5 个元素
int testLenOfList = sizeof(testArray) / sizeof(int);
testArrayList->setSeqList(testArray, testLenOfList);
// BOOST_REQUIRE_THROW(testArrayList->setArrayList(testArray, testLenOfList), out_of_range); // Method getItem-----------------------------------------------
BOOST_REQUIRE(testArrayList->getItem() == testArray[]); // Method empty-------------------------------------------------
expected = false;
actual = testArrayList->empty();
BOOST_REQUIRE(expected == actual); // Method insert-------------------------------------------------
expected = true;
actual = testArrayList->insert(, );
BOOST_REQUIRE(expected == actual);
BOOST_REQUIRE(testArrayList->getLenOfList() == testLenOfList + );
BOOST_REQUIRE(testArrayList->getItem() == ); // Method erase-------------------------------------------------
expected = true;
actual = testArrayList->erase();
BOOST_REQUIRE(expected, actual);
BOOST_REQUIRE(testArrayList->getLenOfList() == testLenOfList);
BOOST_REQUIRE(testArrayList->getItem() == testArray[]); } BOOST_AUTO_TEST_SUITE_END();
BoostUnitTest.cpp
我在单元测试中偏向于使用REQUIRE型的判断,这样方便我检测出问题出现在哪。另外,我在单元测试中偏向于按“正常测试”和“不正常测试”两类进行测试。
本篇博文的代码均托管到Taocode : http://code.taobao.org/p/datastructureandalgorithm/src/.
"《算法导论》之‘线性表’":基于静态分配的数组的顺序表的更多相关文章
- "《算法导论》之‘线性表’":基于动态分配的数组的顺序表
我们利用静态分配的数组来实现的顺序表的局限还是挺大的,主要在于它的容量是预先定好的,用户不能根据自己的需要来改变.如果为了后续用户能够自己调整顺序表的大小,动态地分配数组空间还是很有必要的.基于动态分 ...
- hrbustoj 1545:基础数据结构——顺序表(2)(数据结构,顺序表的实现及基本操作,入门题)
基础数据结构——顺序表(2) Time Limit: 1000 MS Memory Limit: 10240 K Total Submit: 355(143 users) Total Accep ...
- C++利用动态数组实现顺序表(不限数据类型)
通过类模板实现顺序表时,若进行比较和遍历操作,模板元素可以通过STL中的equal_to仿函数实现,或者通过回调函数实现.若进行复制操作,可以采用STL的算法函数,也可以通过操作地址实现.关于回调函数 ...
- 使用JAVA数组实现顺序表
1,引入了JAVA泛型类,因此定义了一个Object[] 类型的数组,从而可以保存各种不同类型的对象. 2,默认构造方法创建了一个默认大小为16的Object数组:带参数的构造方法创建一个指定长度的O ...
- C语言利用动态数组实现顺序表(不限数据类型)
实现任意数据类型的顺序表的初始化,插入,删除(按值删除:按位置删除),销毁功能.. 顺序表结构体 实现顺序表结构体的三个要素:(1)数组首地址:(2)数组的大小:(3)当前数组元素的个数. //顺序表 ...
- 线性表源码分享(c++),包含顺序表、单链表、循环链表、双向链表
---恢复内容开始--- 我是一个c++和数据结构的初学者,本文主要是把清华大学出版社的数据结构(用面向对象方法与c++语言描述)(第2版)这本书中第二章线性表的源码抄下来,在学习的过程中有助于加深印 ...
- 【Coding算法导论】第4章:最大子数组问题
Coding算法导论 本系列文章主要针对算法导论一书上的算法,将书中的伪代码用C++实现 代码未经过大量数据测试,如有问题,希望能在回复中指出! (一)问题描述 给定一个数组,求数组中连续的子数组的和 ...
- python基础下的数据结构与算法之顺序表
一.什么是顺序表: 线性表的两种基本的实现模型: 1.将表中元素顺序地存放在一大块连续的存储区里,这样实现的表称为顺序表(或连续表).在这种实现中,元素间的顺序关系由它们的存储顺序自然表示. 2.将表 ...
- 数据结构4:顺序表(线性表的顺序存储结构)及C语言实现
逻辑结构上呈线性分布的数据元素在实际的物理存储结构中也同样相互之间紧挨着,这种存储结构称为线性表的顺序存储结构. 也就是说,逻辑上具有线性关系的数据按照前后的次序全部存储在一整块连续的内存空间中,之间 ...
随机推荐
- EBS技术开发之VPD策略
VPD (虚拟专用数据库的简称),主要作用是根据运行环境的上下文,隐式的添加条 件. 好处是在数据库层解决细粒度的角色权限访问,避免在中间层写大量代码:坏处 是数据屏蔽的逻辑太隐蔽了,对于分析查找问题 ...
- Hazelcast集群原理分析
简介 hazelcast其中一个很重要的应用就是可以将多个应用服务器组成一个分布式环境的应用,形成一个cluster.这个cluster可以选举出一个master来对外工作.而cluster中的各台服 ...
- Android逆向工程
在Root前提下,我们可以使用Hooker方式绑定so库,通过逆向方式篡改数值,从而达到所谓破解目的.然而,目前无论是软件加固方式,或是数据处理能力后台化,还是客户端数据真实性验证,都有了一定积累和发 ...
- java项目管理工具maven使用初级
一.前言 早就知道maven 在java 项目的管理方面名声显赫,于是就想着学习掌握之,于是查阅了大量文档.发现这些文档的作者都是java 的大腕,大多都是站在掌握了一定maven 基础 ...
- JBOSS EAP 6 系列四 EJB实现——调用(贯穿始终的模块)
本文主要介绍在JBOSS EAP 6.2(或者JBOSS AS7)中模块是如何贯穿EJB实现的始终.延续上一博文<认识模块的使用>的话题继续聊JBOSS做为模块申明式容器的这一特性在EJB ...
- hbase高性能读取数据
有时需要从hbase中一次读取大量的数据,同时对实时性有较高的要求.可以从两方面进行考虑:1.hbase提供的get方法提供了批量获取数据方法,通过组装一个list<Get> gets即可 ...
- CUDA5.5 的环境变量设置
为了方便,我写了这个文件用于设置cuda5.5的环境变量. 其中有些环境变量可能用不到,大家根据需要修改就是了. export CUDA_HOME=/usr/local/cuda-5.5 export ...
- 任务定义器——SocketProcessor
将socket扔进线程池前需要定义好任务,要进行哪些逻辑处理由SocketProcessor定义,根据线程池的约定,作为任务必须扩展Runnable.用如下伪代码表示 protected class ...
- 微信公众号Unauthorized API function
在进行微信公众号第三方开发的时候经常遇到这个问题,有两个原因: 1. 你的公众号没有这个api的功能(比如你是个人订阅号等). 2. 你的公众号有这个功能,但是你公众号没有进行认证. 具体可以查看微信 ...
- python类:属性
http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/50708616 Python 中的 property 属性 Python中有个很赞的概念,叫做prope ...
