最大流EK算法/DINIC算法学习
之前一直觉得很难,没学过网络流,毕竟是基础知识现在重新来看。
定义一下网络流问题,就是在一幅有向图中,每条边有两个属性,一个是cap表示容量,一个是flow
表示流过的流量。我们要求解的问题就是从S点到T点最多可以跑多少流量。用比较学术的话说,就是 一个有向图 G=(V,E);有两个特别的点:源点s、汇点t;图中每条边(u,v)∈E,有一个非负值的容量C(u,v),流量F(u,v)。
定义一下"残流网络":即当前边还可以流过的流量,也就是cap-flow。
其中,在最大流的问题中,我们要满足三个条件:
1:容量限制:f(u,v)<c(u,v),即每条边流过的流量不能超过容量上限。
2:斜对称性:(f(u,v)=-f(v,u))在后面的运用中,我们叫做一旦有物品从u运到v,那么则肯定有一个可退流从v运到u(这里不懂得稍后解释正确性)。
3:流量平衡:简单来说就是除了源点和汇点,没有其他点可以保存货物。显然f(s,u)==f(v,t)。也就是说非ST节点不累计流量,流进的等于流出的流量。
最大流问题,就是使得f(s,u)=f(v,t)达到最大。
现在讨论如何解决这个问题,有一个很容易想到的贪心思路是:我们暴力的从S点到T点找可行路,一旦找到一条路,总流量就加上这条路径上的MIN{cap-flow} ,因为最小的限制最大的。
比如下图: <c,f>表示当前弧的容量及流过的流量。
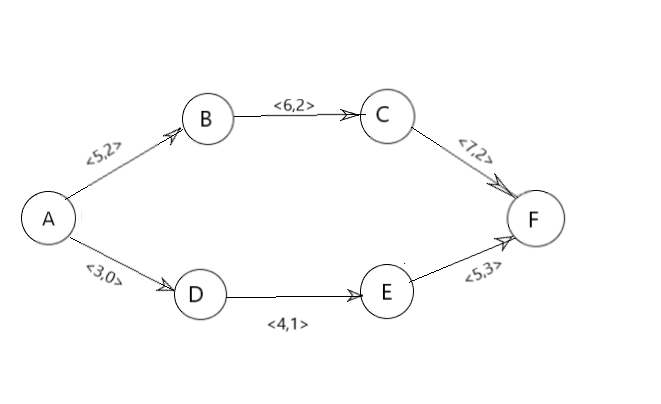
如果我们要求A->F的最大流的话,先找到第一条可行路(A->B->C->F),这条路上的最大允许通过的流量是5-2=3,执行之后,A->B这条路上就满流了,也就是不能从A->B在通过流量了。第二次找的时候显然只能找到(A->D->E->F)这条路,最大通过流量是5-3=2 ,第三次就找不到路了。答案就是2+3=5;
这样看来这种方法貌似可行,可惜的是有一点没考虑到,如果我们第一次找到的路影响到后面的流的行走导致最优解发生变化怎么办。程序没有反悔的机会,比如下图:
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1532
Drainage Ditches
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 20435 Accepted Submission(s): 9804
time it rains on Farmer John's fields, a pond forms over Bessie's
favorite clover patch. This means that the clover is covered by water
for awhile and takes quite a long time to regrow. Thus, Farmer John has
built a set of drainage ditches so that Bessie's clover patch is never
covered in water. Instead, the water is drained to a nearby stream.
Being an ace engineer, Farmer John has also installed regulators at the
beginning of each ditch, so he can control at what rate water flows into
that ditch.
Farmer John knows not only how many gallons of water
each ditch can transport per minute but also the exact layout of the
ditches, which feed out of the pond and into each other and stream in a
potentially complex network.
Given all this information, determine
the maximum rate at which water can be transported out of the pond and
into the stream. For any given ditch, water flows in only one direction,
but there might be a way that water can flow in a circle.
input includes several cases. For each case, the first line contains
two space-separated integers, N (0 <= N <= 200) and M (2 <= M
<= 200). N is the number of ditches that Farmer John has dug. M is
the number of intersections points for those ditches. Intersection 1 is
the pond. Intersection point M is the stream. Each of the following N
lines contains three integers, Si, Ei, and Ci. Si and Ei (1 <= Si, Ei
<= M) designate the intersections between which this ditch flows.
Water will flow through this ditch from Si to Ei. Ci (0 <= Ci <=
10,000,000) is the maximum rate at which water will flow through the
ditch.
1 2 40
1 4 20
2 4 20
2 3 30
3 4 10
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
int cap[][];
int a[],p[];
int n,m;
int bfs(int s,int t)
{
queue<int>q;
memset(p,-,sizeof(p));
q.push(s);
a[s]=inf;
p[s]=;
while(!q.empty()){
int u=q.front();q.pop();
if(u==t)break;
for(int i=;i<=n;++i)
{
if(i!=s&&cap[u][i]>&&p[i]==-){
p[i]=u;
a[i]=min(cap[u][i],a[u]);
q.push(i);
}
}
}
if(p[t]==-)return -;
return a[t];
}
int maxflow(int s,int t)
{
int ret=,delta=;
while((delta=bfs(s,t))!=-){
int k=t;
while(k!=s){
int las=p[k];
cap[las][k]-=delta;
cap[k][las]+=delta;
k=p[k];
}
ret+=delta;
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
int i,j,k;
int u,v,w;
while(cin>>m>>n){
memset(cap,,sizeof(cap));
memset(a,,sizeof(a));
for(i=;i<=m;++i){
cin>>u>>v>>w;
if(u==v)continue;
cap[u][v]+=w;
}
cout<<maxflow(,n)<<endl;
}
return ;
}
贴上一发DINIC算法的,数据不大所以看不出来二者的时间差异。
DINIC算法先跑bfs对点进行分层,然后逐层跑阻塞流来增广。
当前边优化,用一个cur[u]记录u点当前遍历到那一条边了,下一次再访问到u的时候直接从上一次记录的
边开始遍历,减少很多遍历的时间。因为已经访问过的边肯定已经满了(最大化)所以不必要再访问了。
多路增广,当前弧优化,炸点。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
const int maxn=;
struct Edge
{
int v,cap,flow,next;
}e[maxn<<];
int first[maxn],d[maxn],cur[maxn],tot,N,M;
bool vis[maxn];
void add(int u,int v,int cap,int flow){
e[tot]=Edge{v,cap,flow,first[u]};
first[u]=tot++;
}
bool bfs(){
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
memset(d,,sizeof(d));
queue<int>q;
q.push();
d[]=;
vis[]=;
while(!q.empty()){
int u=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i=first[u];~i;i=e[i].next){
if(!vis[e[i].v]&&e[i].cap>e[i].flow){
vis[e[i].v]=;
d[e[i].v]=d[u]+;
q.push(e[i].v);
}
}
}
return vis[N]; }
int dfs(int u,int a){
if(u==N||a==) return a;
int flow=,f;
for(int &i=cur[u];~i;i=e[i].next){
if(d[e[i].v]==d[u]+ && (f=dfs(e[i].v,min(a,e[i].cap-e[i].flow)))>){
e[i].flow+=f;
e[i^].flow-=f;
flow+=f;
a-=f;
if(!a) break;
}
}
return flow;
}
void solve(){
int ans=;
while(bfs()){
for(int i=;i<=N;++i) cur[i]=first[i];
ans+=dfs(,inf);
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
int main(){
while(scanf("%d%d",&M,&N)!=EOF){
tot=;
memset(first,-,sizeof(first));
int u,v,w;
while(M--){
scanf("%d%d%d",&u,&v,&w);
add(u,v,w,);
add(v,u,,);
}
solve();
}
return ;
}
/*
5 4
1 2 40
1 4 20
2 4 20
2 3 30
3 4 10
*/
最大流EK算法/DINIC算法学习的更多相关文章
- 最大流EK和Dinic算法
最大流EK和Dinic算法 EK算法 最朴素的求最大流的算法. 做法:不停的寻找增广路,直到找不到为止 代码如下: @Frosero #include <cstdio> #include ...
- POJ1273:Drainage Ditches(最大流入门 EK,dinic算法)
http://poj.org/problem?id=1273 Description Every time it rains on Farmer John's fields, a pond forms ...
- 网络最大流算法—Dinic算法及优化
前置知识 网络最大流入门 前言 Dinic在信息学奥赛中是一种最常用的求网络最大流的算法. 它凭借着思路直观,代码难度小,性能优越等优势,深受广大oier青睐 思想 $Dinic$算法属于增广路算法. ...
- Dinic算法学习
转自 此文虽为转载,但博主的网络流就是从这开始的,认为写的不错 网络流基本概念 什么是网络流 在一个有向图上选择一个源点,一个汇点,每一条边上都有一个流量上限(以下称为容量),即经过这条边的流量不能超 ...
- 网络流入门—用于最大流的Dinic算法
"网络流博大精深"-sideman语 一个基本的网络流问题 最早知道网络流的内容便是最大流问题,最大流问题很好理解: 解释一定要通俗! 如右图所示,有一个管道系统,节点{1,2,3 ...
- 网络流(最大流-Dinic算法)
摘自https://www.cnblogs.com/SYCstudio/p/7260613.html 网络流定义 在图论中,网络流(Network flow)是指在一个每条边都有容量(Capacity ...
- Dinic算法(研究总结,网络流)
Dinic算法(研究总结,网络流) 网络流是信息学竞赛中的常见类型,笔者刚学习了最大流Dinic算法,简单记录一下 网络流基本概念 什么是网络流 在一个有向图上选择一个源点,一个汇点,每一条边上都有一 ...
- 网络流入门--最大流算法Dicnic 算法
感谢WHD的大力支持 最早知道网络流的内容便是最大流问题,最大流问题很好理解: 解释一定要通俗! 如右图所示,有一个管道系统,节点{1,2,3,4},有向管道{A,B,C,D,E},即有向图一张. ...
- dinic 算法 基本思想及其模板
“网络流博大精深”—sideman语 一个基本的网络流问题 感谢WHD的大力支持 最早知道网络流的内容便是最大流问题,最大流问题很好理解: 解释一定要通俗! 如右图所示,有一个管道系统,节点{1,2, ...
随机推荐
- Super Jumping! Jumping! Jumping!---hdu1087(动态规划)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1087 题意就是给你n个数,找出某个序列的最大和,这个序列满足依次增大的规则: 哎,这个题之前做过,但是 ...
- php smarty模板引擎
<?php /* 一.什么是smarty? smarty是一个使用PHP写出来的模板PHP模板引擎,它提供了逻辑与外在内容的分离,简单的讲, 目的就是要使用PHP程序员同美工分离,使用的程序员改 ...
- beego——参数配置
beego目前支持INI.XML.JSON.YAML格式的配置文件解析,但是默认采用了INI格式解析,用户可以通过简单的配置就可以获得很大的灵活性. 一.默认配置解析 beego 默认会解析当前应用下 ...
- jupyter常用快捷键
Jupyter Notebook 有两种键盘输入模式.即命令模式和编辑模式,这与 vim有些类似. 在编辑模式下,可以往单元中键入代码或文本,此时单元格被绿色的框线包围,且命令模式下的快捷键不生效. ...
- Python(迭代、三元表达式、列表生成、生成器、迭代器)
迭代 什么是迭代 1 重复 2 下次重复一定是基于上一次的结果而来 如果给定一个list或tuple,我们可以通过for循环来遍历这个list或tuple,这种遍历我们称为迭代(Iteration). ...
- Java并发(1):synchronized
虽然多线程编程极大地提高了效率,但是也会带来一定的隐患.比如说两个线程同时往一个数据库表中插入不重复的数据,就可能会导致数据库中插入了相同的数据.今天我们就来一起讨论下线程安全问题,以及Java中提供 ...
- ceph存储安装配置
1.修改yum源: 1.安装yum源:sudo yum install -y yum-utils sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo https://dl.fedor ...
- PAT 天梯赛 L1-021. 重要的话说三遍 【水】
题目链接 https://www.patest.cn/contests/gplt/L1-021 AC代码 #include <iostream> #include <cstdio&g ...
- java注解1
http://computerdragon.blog.51cto.com/6235984/1210969 http://blog.csdn.net/it_man/article/details/440 ...
- libvirt-qemu-虚拟机设备热插拔
cpu热插拔 # virsh setvcpus $domain_name --count 4 --live (--config可写入配置文件永久保存) #前提条件和后续激活参考<libvirt- ...
