Tree - Rooted Trees
Rooted Trees
A graph G = (V, E) is a data structure where V is a finite set of vertices and E is a binary relation on Vrepresented by a set of edges. Fig. 1 illustrates an example of a graph (or graphs).
Fig. 1
A free tree is a connnected, acyclic, undirected graph. A rooted tree is a free tree in which one of the vertices is distinguished from the others. A vertex of a rooted tree is called "node."
Your task is to write a program which reports the following information for each node u of a given rooted tree T:
- node ID of u
- parent of u
- depth of u
- node type (root, internal node or leaf)
- a list of chidlren of u
If the last edge on the path from the root r of a tree T to a node x is (p, x), then p is the parent of x, and xis a child of p. The root is the only node in T with no parent.
A node with no children is an external node or leaf. A nonleaf node is an internal node
The number of children of a node x in a rooted tree T is called the degree of x.
The length of the path from the root r to a node x is the depth of x in T.
Here, the given tree consists of n nodes and evey node has a unique ID from 0 to n-1.
Fig. 2 shows an example of rooted trees where ID of each node is indicated by a number in a circle (node). The example corresponds to the first sample input.
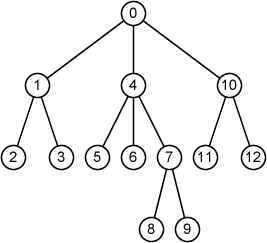
Fig. 2
Input
The first line of the input includes an integer n, the number of nodes of the tree.
In the next n lines, the information of each node u is given in the following format:
id k c1 c2 ... ck
where id is the node ID of u, k is the degree of u, c1 ... ck are node IDs of 1st, ... kth child of u. If the node does not have a child, the k is 0.
Output
Print the information of each node in the following format ordered by IDs:
node id: parent = p , depth = d, type, [c1...ck]
p is ID of its parent. If the node does not have a parent, print -1.
d is depth of the node.
type is a type of nodes represented by a string (root, internal node or leaf). If the root can be considered as a leaf or an internal node, print root.
c1...ck is the list of children as a ordered tree.
Please follow the format presented in a sample output below.
Constraints
- 1 ≤ n ≤ 100000
Sample Input 1
13
0 3 1 4 10
1 2 2 3
2 0
3 0
4 3 5 6 7
5 0
6 0
7 2 8 9
8 0
9 0
10 2 11 12
11 0
12 0
Sample Output 1
node 0: parent = -1, depth = 0, root, [1, 4, 10]
node 1: parent = 0, depth = 1, internal node, [2, 3]
node 2: parent = 1, depth = 2, leaf, []
node 3: parent = 1, depth = 2, leaf, []
node 4: parent = 0, depth = 1, internal node, [5, 6, 7]
node 5: parent = 4, depth = 2, leaf, []
node 6: parent = 4, depth = 2, leaf, []
node 7: parent = 4, depth = 2, internal node, [8, 9]
node 8: parent = 7, depth = 3, leaf, []
node 9: parent = 7, depth = 3, leaf, []
node 10: parent = 0, depth = 1, internal node, [11, 12]
node 11: parent = 10, depth = 2, leaf, []
node 12: parent = 10, depth = 2, leaf, []
Sample Input 2
4
1 3 3 2 0
0 0
3 0
2 0
Sample Output 2
node 0: parent = 1, depth = 1, leaf, []
node 1: parent = -1, depth = 0, root, [3, 2, 0]
node 2: parent = 1, depth = 1, leaf, []
node 3: parent = 1, depth = 1, leaf, []
Note
You can use a left-child, right-sibling representation to implement a tree which has the following data:
- the parent of u
- the leftmost child of u
- the immediate right sibling of u
Reference
Introduction to Algorithms, Thomas H. Cormen, Charles E. Leiserson, Ronald L. Rivest, and Clifford Stein. The MIT Press.
有根树的存储, 根据数据看出不是二叉树, 故用孩子兄弟表示法存储(左孩子, 右兄弟)
利用递归求树的深度时, 若是左孩子则深度加一, 右孩子(兄弟节点)还是当前深度
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 100005
#define NIL -1 struct Node {
int parent;
int left;
int right;
}; Node T[MAX];
int n, D[MAX]; void print(int u)
{
int i, c;
cout << "node " << u << ": ";
cout << "parent = " << T[u].parent << ", ";
cout << "depth = " << D[u] << ", "; if(T[u].parent == NIL)
{
cout << "root, ";
}
else if(T[u].left == NIL)
{
cout << "leaf, ";
}
else
{
cout << "internal node, ";
} cout << "["; for(i = 0, c = T[u].left; c != NIL; ++ i, c = T[c].right)
{
if(i) cout << ", ";
cout << c;
} cout << "]" << endl;
} // 递归求深度
void rec(int u, int p)
{
D[u] = p;
if(T[u].right != NIL)
{
rec(T[u].right, p);
}
if(T[u].left != NIL)
{
rec(T[u].left, p + 1);
}
} int main()
{
int i, j, d, v, c, l, r;
cin >> n;
for(i = 0; i < n; ++ i)
{
T[i].parent = T[i].left = T[i].right = NIL;
} for(i = 0; i < n; ++ i)
{
cin >> v >> d;
for(j = 0; j < d; ++ j)
{
cin >> c;
if(j == 0)
{
T[v].left = c; // 父节点的左孩子为c
}
else
{
T[l].right = c; // 当前兄弟节点为c
}
l = c; // 记录前一个兄弟节点
T[c].parent = v;
}
}
for(i = 0; i < n; ++ i)
{
if(T[i].parent == NIL)
{
r = i;
}
} rec(r, 0); for(i = 0; i < n; ++ i)
{
print(i);
} return 0;
} /*
13
0 3 1 4 10
1 2 2 3
2 0
3 0
4 3 5 6 7
5 0
6 0
7 2 8 9
8 0
9 0
10 2 11 12
11 0
12 0
*/
Tree - Rooted Trees的更多相关文章
- HDU p1294 Rooted Trees Problem 解题报告
http://www.cnblogs.com/keam37/p/3639294.html keam所有 转载请注明出处 Problem Description Give you two definit ...
- 【Aizu - ALDS1_7_A】Rooted Trees(树的表达)
Rooted Trees Descriptions: A graph G = (V, E) is a data structure where V is a finite set of vertice ...
- 有根树的表达 Aizu - ALDS1_7_A: Rooted Trees
有根树的表达 题目:Rooted Trees Aizu - ALDS1_7_A A graph G = (V, E) is a data structure where V is a finite ...
- 10.3 Implementing pointers and objects and 10.4 Representing rooted trees
Algorithms 10.3 Implementing pointers and objects and 10.4 Representing rooted trees Allocating an ...
- HDU1294 Rooted Trees Problem(整数划分 组合数学 DP)
讲解见http://www.cnblogs.com/IMGavin/p/5621370.html, 4 可重组合 dfs枚举子树的节点个数,相乘再累加 1 #include<iostream& ...
- HDU 1294 Rooted Trees Problem
题目大意:求有n个节点的树有几种? 题解:http://www.cnblogs.com/keam37/p/3639294.html #include <iostream> typedef ...
- [LeetCode] Minimum Height Trees 最小高度树
For a undirected graph with tree characteristics, we can choose any node as the root. The result gra ...
- Minimum Height Trees
For a undirected graph with tree characteristics, we can choose any node as the root. The result gra ...
- LeetCode Minimum Height Trees
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-height-trees/ 题目: For a undirected graph with tree cha ...
随机推荐
- 西数常用TREX命令
西数常用TREX命令 trex命令:dut1 简便找盘idp或info did查看硬盘信息chkresfall检测固件smart 查看SMART表clrsmart 清SMART表svmod 0x.. ...
- JavaScript十大古怪之处(出自众妙之门)
1. null是一个对象: alert(typeof null); //objects NULL表示没有值,那么很明显他不能作为任何东西的实例,所以下式应该等于false: alert(null i ...
- 使用itext导出pdf
导出pdf这个功能是在工作中遇到的,写这个功能的时候遇到了不少的问题,比如中文乱码,不显示的问题,这些问题在我不断的测试,研究后都一一解决了. 第一步,先导入所需要的jar包 第一个jar包是用于解决 ...
- Java温故而知新(3)异常处理机制
异常处理是程序设计中一个非常重要的方面,也是程序设计的一大难点,从C开始,你也许已经知道如何用if...else...来控制异常了,也许是自发的,然而这种控制异常痛苦,同一个异常或者错误如果多个地方出 ...
- zookeeper学习实践1-实现分布式锁
引言 ZooKeeper是一个分布式的,开放源码的分布式应用程序协调服务,是Google的Chubby一个开源的实现,是Hadoop和Hbase的重要组件.它是一个为分布式应用提供一致性服务的软件,提 ...
- 怎样关闭占用80端口的pid为4的进程
我也被这个问题给纠结了好几天.重装系统都三次了.终于找到原因了:我用的是sqlserver 2008;解决方法:window-sqlserver 2008-配置工具-sqlserver 配置管理器 找 ...
- javascript图片预加载
图片预加载是非常常见的一个功能,PC和移动端都会用到,尤其是在移动端,只要涉及到较多图片的加载都会用到该技术.下面是移动端用到的,引入了zepto. <!DOCTYPE html> < ...
- vue-cli脚手架项目实例
看完了配置,接下来通过一个实例,更清晰地了解这些文件之间的联系,顺带练习练习vue相关知识. 1.安装 打开命令行控制器,系统自带cmd或者git bash等都可以,按照顺序输入如下指令,耐心等待每一 ...
- 安装配置postgreSQL+pgcli+pgadmin3
记录了postgreSQL数据库的完整的安装配置过程,以及postgreSQL的pgcli命令行智能提醒扩展,pgadmin3图形化管理客户端的配置安装.此postgresql是bigsql版安装详情 ...
- android中的内部存储与外部存储
我们先来考虑这样一个问题: 打开手机设置,选择应用管理,选择任意一个App,然后你会看到两个按钮,一个是清除缓存,另一个是清除数据,那么当我们点击清除缓存的时候清除的是哪里的数据?当我们点击清除数据的 ...
