Flink Batch Hash Aggregate
数据类型要求
BatchPhysicalHashAggRule match 条件会判断 isAggBufferFixedLength(agg)
为什么要求 aggCall 的类型是 Fixed Length 的才可以使用 HashAggregate ?
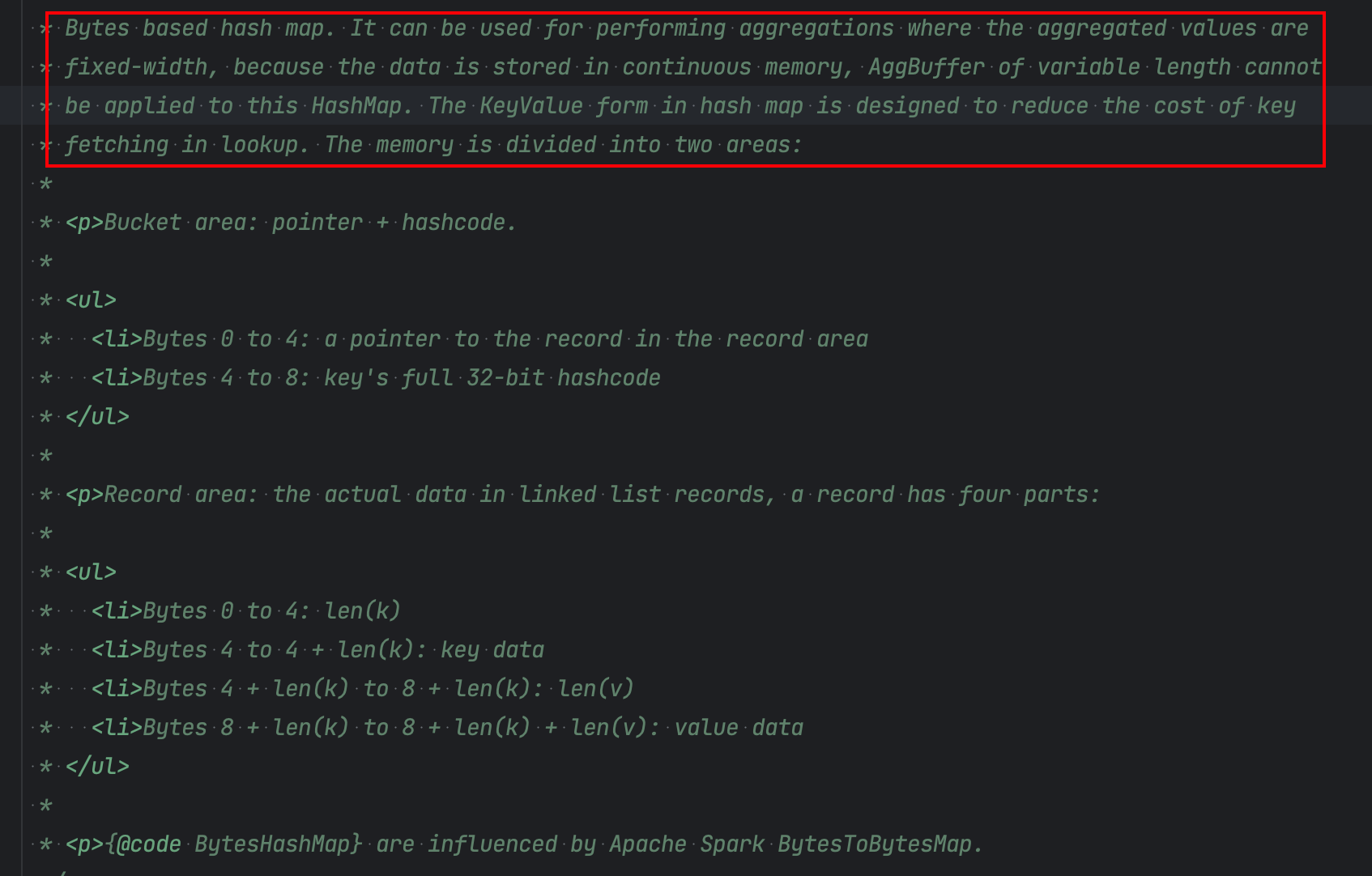
因为在 HashAggregate 中, 依赖于 BytesHashMap 数据结构来存储 keyValue 数据. 而 ByteHashMap 不支持变长的 value
ByteHashMap 结构
实现参考自 Spark BytesToBytesMap , 以二进制结构存储实现的 hashMap. 其目的就是绕过 JVM 的 GC, 直接将数据序列化之后存储到基于堆外的 MemorySegment 上.
数据分为两个部分 Bucket Area 和 Record Area. 分别存储 key 和对应的 record.
public BinaryRowData append(LookupInfo<K, BinaryRowData> lookupInfo, BinaryRowData value)
throws IOException {
try {
if (numElements >= growthThreshold) {
growAndRehash();
// update info's bucketSegmentIndex and bucketOffset
lookup(lookupInfo.key);
}
BinaryRowData toAppend = hashSetMode ? reusedValue : value;
int pointerToAppended = recordArea.appendRecord(lookupInfo, toAppend);
bucketSegments
.get(lookupInfo.bucketSegmentIndex)
.putInt(lookupInfo.bucketOffset, pointerToAppended);
bucketSegments
.get(lookupInfo.bucketSegmentIndex)
.putInt(lookupInfo.bucketOffset + ELEMENT_POINT_LENGTH, lookupInfo.keyHashCode);
numElements++;
recordArea.setReadPosition(pointerToAppended);
((RecordArea) recordArea).skipKey();
return recordArea.readValue(reusedValue);
} catch (EOFException e) {
numSpillFiles++;
spillInBytes += recordArea.getSegmentsSize();
throw e;
}
public int appendRecord(LookupInfo<K, BinaryRowData> lookupInfo, BinaryRowData value)
throws IOException {
final long oldLastPosition = outView.getCurrentOffset();
// serialize the key into the BytesHashMap record area
int skip = keySerializer.serializeToPages(lookupInfo.getKey(), outView);
long offset = oldLastPosition + skip;
// serialize the value into the BytesHashMap record area
valueSerializer.serializeToPages(value, outView);
if (offset > Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
LOG.warn(
"We can't handle key area with more than Integer.MAX_VALUE bytes,"
+ " because the pointer is a integer.");
throw new EOFException();
}
return (int) offset;
}
BytesHashMap 本身没有实现更新的功能, 但是 lookup 得到的结果 LookupInfo 中包含了 kv pair, value 作为 BinaryRow 是可以直接更新的.
public static final class LookupInfo<K, V> {
boolean found;
K key;
V value;
/**
* The hashcode of the look up key passed to {@link BytesMap#lookup(K)}, Caching this
* hashcode here allows us to avoid re-hashing the key when inserting a value for that key.
* The same purpose with bucketSegmentIndex, bucketOffset.
*/
int keyHashCode;
int bucketSegmentIndex;
int bucketOffset;
}
例如 Hash Aggregate 的过程代码如下
val processCode =
s"""
| // input field access for group key projection and aggregate buffer update
|${ctx.reuseInputUnboxingCode(inputTerm)}
| // project key from input
|$keyProjectionCode
| // look up output buffer using current group key
|$lookupInfo = ($lookupInfoTypeTerm) $aggregateMapTerm.lookup($currentKeyTerm);
|$currentAggBufferTerm = ($binaryRowTypeTerm) $lookupInfo.getValue();
|
|if (!$lookupInfo.isFound()) {
| $lazyInitAggBufferCode
| // append empty agg buffer into aggregate map for current group key
| try {
| $currentAggBufferTerm =
| $aggregateMapTerm.append($lookupInfo, ${initedAggBuffer.resultTerm});
| } catch (java.io.EOFException exp) {
| $dealWithAggHashMapOOM
| }
|}
| // aggregate buffer fields access
|${ctx.reuseInputUnboxingCode(currentAggBufferTerm)}
| // do aggregate and update agg buffer
|${aggregate.code}
|""".stripMargin.trim
当 lookup info 找到时, 就执行 aggregate.code, 以 sum 生成的 codegen 为例, 从 lookup info 中获取 Agg buffer, 计算完就直接回写 BinaryRow 了
// look up output buffer using current group key
lookupInfo$10 = (org.apache.flink.table.runtime.util.collections.binary.BytesMap.LookupInfo) aggregateMap$9.lookup(currentKey$4);
currentAggBuffer$14 = (org.apache.flink.table.data.binary.BinaryRowData) lookupInfo$10.getValue();
// 累加
isNull$19 = isNull$18 || isNull$17;
result$20 = -1L;
if (!isNull$19) {
result$20 = (long) (field$18 + field$17);
}
// 更新
if (isNull$22) {
currentAggBuffer$14.setNullAt(0);
} else {
currentAggBuffer$14.setLong(0, result$22);
}
如果 BinaryRow 中的部分字段为变长, 是没法直接原地更新的, 这就为什么 Hash Aggregate 要求 agg buffer 为定长.
解决这个问题的, 最简单的思路就是, BytesHashMap 是为了去除 JVM 管理, 那为了简化对于非定长的, 还是 Fallback 到 JVM 的对象, Spark ObjectHashAggregate 就是这种思路.
但是这种情况下的问题是堆内存你不知道什么时候触发 spill. 基于非堆时, 已使用大小都是已知的, 而堆上就不确定了, 比较容易触发 oom 或者 GC 问题, Spark 中 flush 就按照保守估计的 key 超过一定数量就 spill.
但总的来说, 性能应该优于 SortAggregate 的
Spark:
Spark SQL 查询引擎– HashAggregateExec & ObjectHashAggregateExec
[SPARK-17949][SQL] A JVM object based aggregate operator
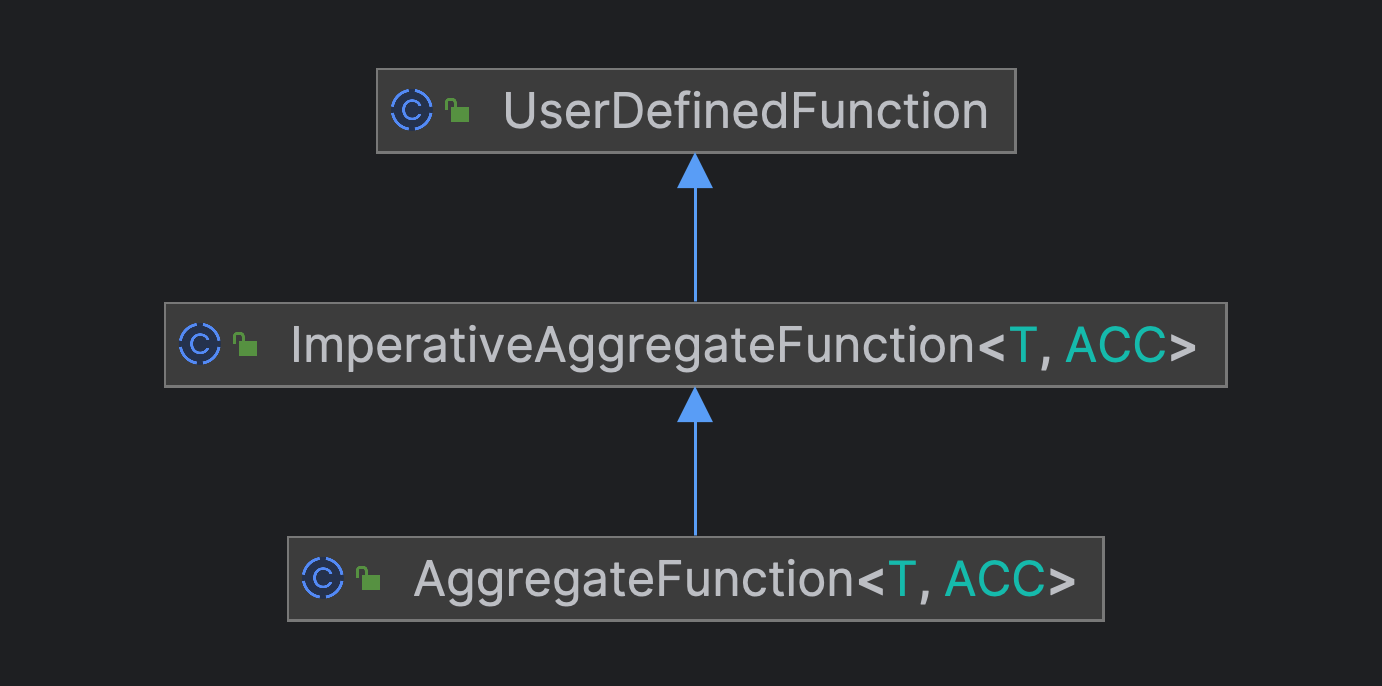
DeclarativeAggregateFunction & ImperativeAggregateFunction
另一个限制是 HashAggregate 中强要求了 Agg 函数需要时 DeclarativeAggregateFunction 类型的. 聚合函数的实现有两类
- DeclarativeAggregateFunction 声明式, 基于 Expression Api 描述
- ImperativeAggregateFunction 命令式, 一般面向用户 api (UDAF 继承)
public Expression[] accumulateExpressions() {
return new Expression[] {
/* sum = */ ifThenElse(
isNull(operand(0)),
sum,
ifThenElse(
isNull(operand(0)),
sum,
ifThenElse(isNull(sum), operand(0), adjustedPlus(sum, operand(0)))))
};
}
public void accumulate(Row accumulator, String s) {
final String max = (String) accumulator.getField(0);
if (max == null || s.compareTo(max) > 0) {
accumulator.setField(0, s);
}
}
从直观来看, ImperativeAggregateFunction 的 accumulate 方法没有返回值, 所以 ACC 一定是个复杂类型, 否则累计值无法更新. 因此 ImperativeAggregateFunction 的 agg 类型一定不是 Fixed type.
而 DeclarativeAggregateFunction 的 accumulate 函数是一个表达式, 表达式是有返回值的. 比如 ifThenElse 最终返回的就是其中一个值. 因此可以直接为 Long 类型.
这一点上我觉得 ImperativeAggregateFunction 应该也是可以改造成这种形式的, 这样对于用户的 UDAF 来说是更友好的, 可以避免额外的包装, 硬生生变成一个非 Fixed Length 的类型.
所以在 HashAggregate Codegen 目前只支持 DeclarativeAggregateFunction 声明的聚合函数. Codegen 中代码依赖. 由于上面 ImperativeAggregateFunction 的类型一定推导不出 Fixed type, 所以 ImperativeAggregateFunction 不会走到HashAggregate
Spark
从 Spark 来看 Agg 函数的接口会更清楚一些, spark 中有五类接口(也许更多)
- 用户API
- UserDefinedAggregateFunction 会封装成 -> ImperativeAggregate. 但每次传输给用户时, 都会进行序列化和反序列化
- Aggregator :
org.apache.spark.sql.functions#udaf-> 创建出ScalaAggregator继承自TypedImperativeAggregate用户可以定义任意类型的 Agg Buf. - 两个类型的比较
- 内部API
- DeclarativeAggregate: for aggregation functions that are specified using Catalyst expressions. 生命式
- ImperativeAggregate: for aggregation functions that are specified in terms of initialize(), update(), and merge() functions that operate on Row-based aggregation buffers. 命令式 InternalRow 作为内部类型
- TypedImperativeAggregate 任意类型作为 ACC 命令式
从这个定义来看, 并没有说 ImperativeAggregate 适用于 Variable Length 的类型.
abstract class ImperativeAggregate extends AggregateFunction with CodegenFallback {
/**
* Initializes the mutable aggregation buffer located in `mutableAggBuffer`.
*
* Use `fieldNumber + mutableAggBufferOffset` to access fields of `mutableAggBuffer`.
*/
def initialize(mutableAggBuffer: InternalRow): Unit
/**
* Updates its aggregation buffer, located in `mutableAggBuffer`, based on the given `inputRow`.
*
* Use `fieldNumber + mutableAggBufferOffset` to access fields of `mutableAggBuffer`.
*
* Note that, the input row may be produced by unsafe projection and it may not be safe to cache
* some fields of the input row, as the values can be changed unexpectedly.
*/
def update(mutableAggBuffer: InternalRow, inputRow: InternalRow): Unit
/**
* Combines new intermediate results from the `inputAggBuffer` with the existing intermediate
* results in the `mutableAggBuffer.`
*
* Use `fieldNumber + mutableAggBufferOffset` to access fields of `mutableAggBuffer`.
* Use `fieldNumber + inputAggBufferOffset` to access fields of `inputAggBuffer`.
*
* Note that, the input row may be produced by unsafe projection and it may not be safe to cache
* some fields of the input row, as the values can be changed unexpectedly.
*/
def merge(mutableAggBuffer: InternalRow, inputAggBuffer: InternalRow): Unit
}
}
TypedImperativeAggregate, 他的接口定义就是泛型, 因此可以定义任意类型作为 ACC type. 这类接口就是上面所支持的 ObjectHashAggregate 的类型
/**
* Updates the aggregation buffer object with an input row and returns a new buffer object. For
* performance, the function may do in-place update and return it instead of constructing new
* buffer object.
*
* This is typically called when doing Partial or Complete mode aggregation.
*
* @param buffer The aggregation buffer object.
* @param input an input row
*/
def update(buffer: T, input: InternalRow): T
/**
* Merges an input aggregation object into aggregation buffer object and returns a new buffer
* object. For performance, the function may do in-place merge and return it instead of
* constructing new buffer object.
*
* This is typically called when doing PartialMerge or Final mode aggregation.
*
* @param buffer the aggregation buffer object used to store the aggregation result.
* @param input an input aggregation object. Input aggregation object can be produced by
* de-serializing the partial aggregate's output from Mapper side.
*/
def merge(buffer: T, input: T): T
HashAggregate 算子
ProcessCode
val processCode =
s"""
| // input field access for group key projection and aggregate buffer update
|${ctx.reuseInputUnboxingCode(inputTerm)}
| // project key from input
|$keyProjectionCode
| // look up output buffer using current group key
|$lookupInfo = ($lookupInfoTypeTerm) $aggregateMapTerm.lookup($currentKeyTerm);
|$currentAggBufferTerm = ($binaryRowTypeTerm) $lookupInfo.getValue();
|
|if (!$lookupInfo.isFound()) {
| $lazyInitAggBufferCode
| // append empty agg buffer into aggregate map for current group key
| try {
| $currentAggBufferTerm =
| $aggregateMapTerm.append($lookupInfo, ${initedAggBuffer.resultTerm});
| } catch (java.io.EOFException exp) {
| $dealWithAggHashMapOOM
| }
|}
| // aggregate buffer fields access
|${ctx.reuseInputUnboxingCode(currentAggBufferTerm)}
| // do aggregate and update agg buffer
|${aggregate.code}
|""".stripMargin.trim
Append 写入数据时, 当内存不足时(申请 segment 申请不到), 会触发 EOFException. 在 processCode 的逻辑中就会执行 dealWithAggHashOOM 的逻辑. 这里会分两种
- Local: 对于 local 阶段如果出现 OOM 那么就将当前
BytesHashMap中保存的数据下发即outputResultFromMap. 下发完成后清空 Map 再尝试插入一次retryAppends"""
|$logMapOutput
| // hash map out of memory, output directly
|$outputResultFromMap
| // retry append
|$retryAppend
""".stripMargin
- Global: 当出现内存不足时, 触发 sort and spill, 将内存数据先排序, 再写入本地
val dealWithAggHashMapOOM =
s"""
|$logMapSpilling
| // hash map out of memory, spill to external sorter
|if ($sorterTerm == null) {
| $createSorter
|}
| // sort and spill
|$sorterTerm.sortAndSpill(
| $aggregateMapTerm.getRecordAreaMemorySegments(),
| $aggregateMapTerm.getNumElements(),
| new $memPoolTypeTerm($aggregateMapTerm.getBucketAreaMemorySegments()));
| // retry append
|$retryAppend
""".stripMargin
EndInput
val endInputCode = if (isFinal) {
val memPoolTypeTerm = classOf[BytesHashMapSpillMemorySegmentPool].getName
s"""
|if ($sorterTerm == null) {
| // no spilling, output by iterating aggregate map.
| $outputResultFromMap
|} else {
| // spill last part of input' aggregation output buffer
| $sorterTerm.sortAndSpill(
| $aggregateMapTerm.getRecordAreaMemorySegments(),
| $aggregateMapTerm.getNumElements(),
| new $memPoolTypeTerm($aggregateMapTerm.getBucketAreaMemorySegments()));
| // only release floating memory in advance.
| $aggregateMapTerm.free(true);
| // fall back to sort based aggregation
| $fallbackToSortAggCode
|}
""".stripMargin
} else {
s"$outputResultFromMap"
}
- Local 阶段: 将 Map 中剩余的数据遍历下发
outputResultFromMap - Global 阶段:
- 没有发生过 Spill, 将 Map 中剩余的数据遍历下发
outputResultFromMap - 发生过 Spill. 先将最后一批内存的数据
sortAndSpill写入本地, 再执行 fallbackToSortAgg 的逻辑, 即执行 SortAgg
- 没有发生过 Spill, 将 Map 中剩余的数据遍历下发
Flink Batch Hash Aggregate的更多相关文章
- Flink Batch SQL 1.10 实践
Flink作为流批统一的计算框架,在1.10中完成了大量batch相关的增强与改进.1.10可以说是第一个成熟的生产可用的Flink Batch SQL版本,它一扫之前Dataset的羸弱,从功能和性 ...
- Apache Flink - Batch(DataSet API)
Flink DataSet API编程指南: Flink中的DataSet程序是实现数据集转换的常规程序(例如,过滤,映射,连接,分组).数据集最初是从某些来源创建的(例如,通过读取文件或从本地集合创 ...
- flink batch wordcount
1.POJO方式 public class WordCountPojo { public static class Word{ private String word; private int fre ...
- SQL Server-聚焦查询计划Stream Aggregate VS Hash Match Aggregate(二十)
前言 之前系列中在查询计划中一直出现Stream Aggregate,当时也只是做了基本了解,对于查询计划中出现的操作,我们都需要去详细研究下,只有这样才能对查询计划执行的每一步操作都了如指掌,所以才 ...
- 终于等到你!阿里正式向 Apache Flink 贡献 Blink 源码
摘要: 如同我们去年12月在 Flink Forward China 峰会所约,阿里巴巴内部 Flink 版本 Blink 将于 2019 年 1 月底正式开源.今天,我们终于等到了这一刻. 阿里妹导 ...
- Flink学习笔记:Flink API 通用基本概念
本文为<Flink大数据项目实战>学习笔记,想通过视频系统学习Flink这个最火爆的大数据计算框架的同学,推荐学习课程: Flink大数据项目实战:http://t.cn/EJtKhaz ...
- flink学习笔记-快速生成Flink项目
说明:本文为<Flink大数据项目实战>学习笔记,想通过视频系统学习Flink这个最火爆的大数据计算框架的同学,推荐学习课程: Flink大数据项目实战:http://t.cn/EJtKh ...
- Flink架构,源码及debug
序 工作中用Flink做批量和流式处理有段时间了,感觉只看Flink文档是对Flink ProgramRuntime的细节描述不是很多, 程序员还是看代码最简单和有效.所以想写点东西,记录一下,如果能 ...
- [源码解析] GroupReduce,GroupCombine 和 Flink SQL group by
[源码解析] GroupReduce,GroupCombine和Flink SQL group by 目录 [源码解析] GroupReduce,GroupCombine和Flink SQL grou ...
- Blink: How Alibaba Uses Apache Flink
This is a guest post from Xiaowei Jiang, Senior Director of Alibaba’s search infrastructure team. Th ...
随机推荐
- #floyd,斜率#洛谷 1354 房间最短路问题
题目 在一个长宽均为10,入口出口分别为(0,5),(10,5)的房间里有几堵墙, 每堵墙上有两个缺口,求入口到出口的最短路径. 分析 暴力建图,判断两个点是否有墙堵住, 可以求斜率然后判断所交点不能 ...
- 这一次,让我们一起来搞懂MySQL
欢迎加入我的专栏,和我一起开始 MySQL 学习之旅. 从日常的开发和优化中,一步步地从一个数据库小白成为 MySQL 调优的开发人员.回想起来,从我第一次带创建索引至今,已经有十个年头了.在这个过程 ...
- 上海站报名启动! 2023年开源产业生态大会OpenHarmony生态分论坛
作为年内开源领域不容错过的科技盛宴,2023年开源产业生态大会将于12月19日在上海盛大开幕.本次活动由上海市经济和信息化委员会.上海市科学技术协会和"科创中国"开源创新联合体 ...
- HMS Core助力开发者打造高品质游戏,共创智玩新生态
2021年8月1日,华为HMS Core.Sparkle游戏应用创新沙龙在上海举行.会上,华为HMS Core团队与游戏行业开发者围绕3D图形渲染.网络加速.精准运营等多个话题,探讨了游戏应用开发技术 ...
- 应用可靠性与性能不给力?HarmonyOS HiViewDFX了解一下
原文链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Y44jUEB3ttlijbMDPrBcNg,点击链接查看更多技术内容: 作为基础软件服务子系统的HarmonyOS HiViewD ...
- Bill的挑战
看数据范围就知道应该要状压,也不难看出应该压缩位数的状态.所以设f[i][j]为前i位,相互匹配的字符串的状态. 那么,就会有 f[i+1][j&a[i][ch]]=(f[i+1][j& ...
- 【4】Spring框架的起源
在我们的<Java Spring框架入门教程>中对 Spring 框架进行了十分详尽的介绍和剖析,但在学习 Spring Boot 之前,在这里回顾一下 Spring 是怎么出现的. Sp ...
- 结构化数据上的 TopN 运算
1. 最大值 / 最小值 最大值 / 最小值可以理解为 TopN 查询中,N 等于 1 时的情况,因为很常用所以单独拿出来讲一下.取最大值 / 最小值是很常见的需求,例如一班数学最高分是多少, ...
- RabbitMQ总体介绍
历史-从开始到现在 RabbitMQ是一个Erlang开发的AMQP(Advanced Message Queuing Protocol )的开源实现.AMQP 的出现其实也是应了广大人民群众的需求, ...
- HarmonyOS NEXT应用开发案例——列表编辑实现
介绍 本示例介绍用过使用ListItem组件属性swipeAction实现列表左滑编辑效果的功能. 该场景多用于待办事项管理.文件管理.备忘录的记录管理等. 效果图预览 使用说明: 点击添加按钮,选择 ...