Input系统—ANR原理分析(转)
一. 概述
当input事件处理得慢就会触发ANR,那ANR内部原理是什么,哪些场景会产生ANR呢。 “工欲善其事必先利其器”,为了理解input ANR原理,前面几篇文章疏通了整个input框架的处理流程,都是为了这篇文章而做铺垫。在正式开始分析ANR触发原理以及触发场景之前,先来回顾一下input流程。
1.1 InputReader
点击查看大图:
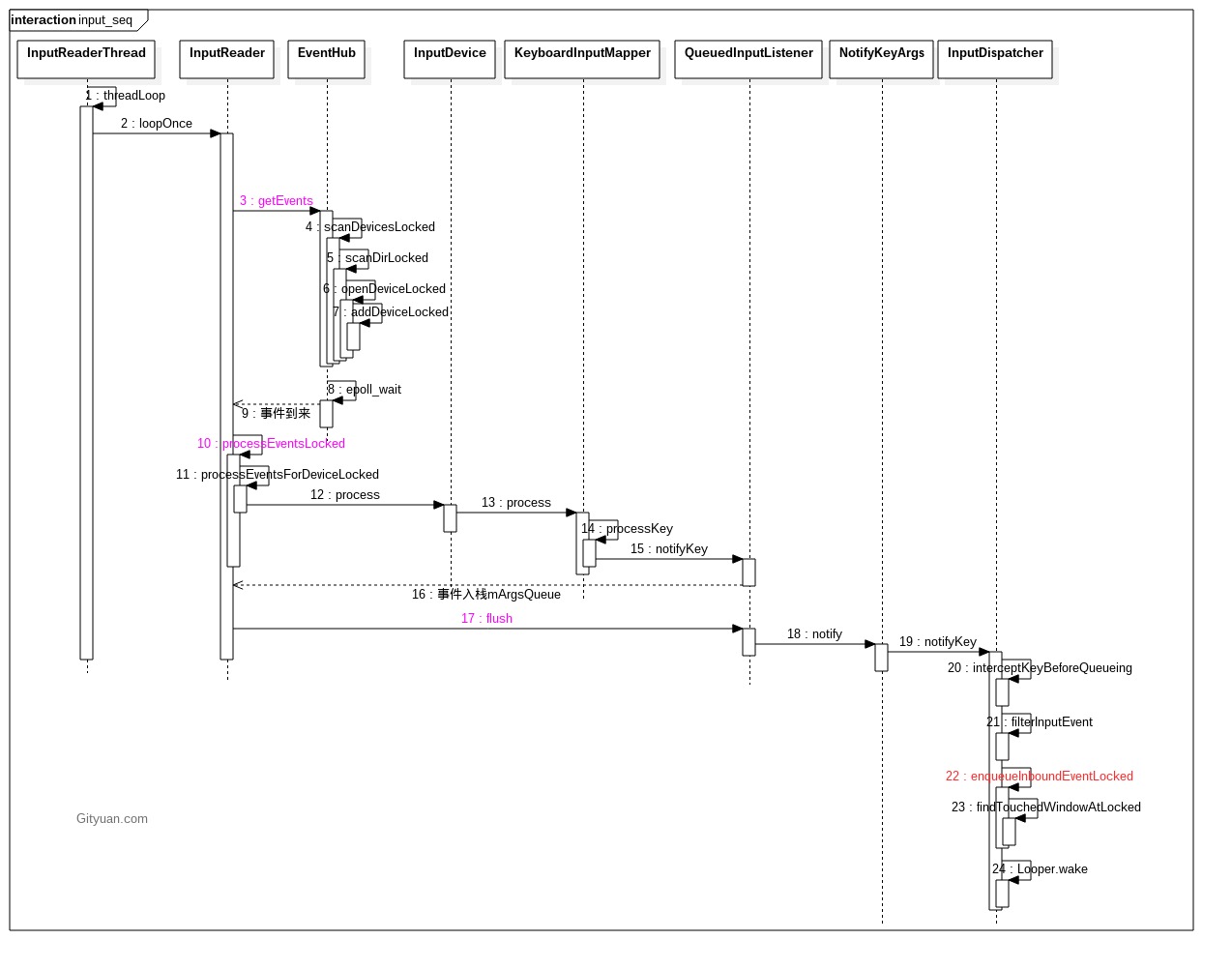
InputReader的主要工作分两部分:
- 调用EventHub的getEvents()读取节点/dev/input的input_event结构体转换成RawEvent结构体,RawEvent根据不同InputMapper来转换成相应的EventEntry,比如按键事件则对应KeyEntry,触摸事件则对应MotionEntry。
- 转换结果:inut_event -> EventEntry;
- 将事件添加到mInboundQueue队列尾部,加入该队列前有以下两个过滤:
- IMS.interceptKeyBeforeQueueing:事件分发前可增加业务逻辑;
- IMS.filterInputEvent:可拦截事件,当返回值为false的事件都直接拦截,没有机会加入mInboundQueue队列,不会再往下分发;否则进入下一步;
- enqueueInboundEventLocked:该事件放入mInboundQueue队列尾部;
- mLooper->wake:并根据情况来唤醒InputDispatcher线程.
- KeyboardInputMapper.processKey()的过程, 记录下按下down事件的时间点.
1.2 InputDispatcher
点击查看大图:
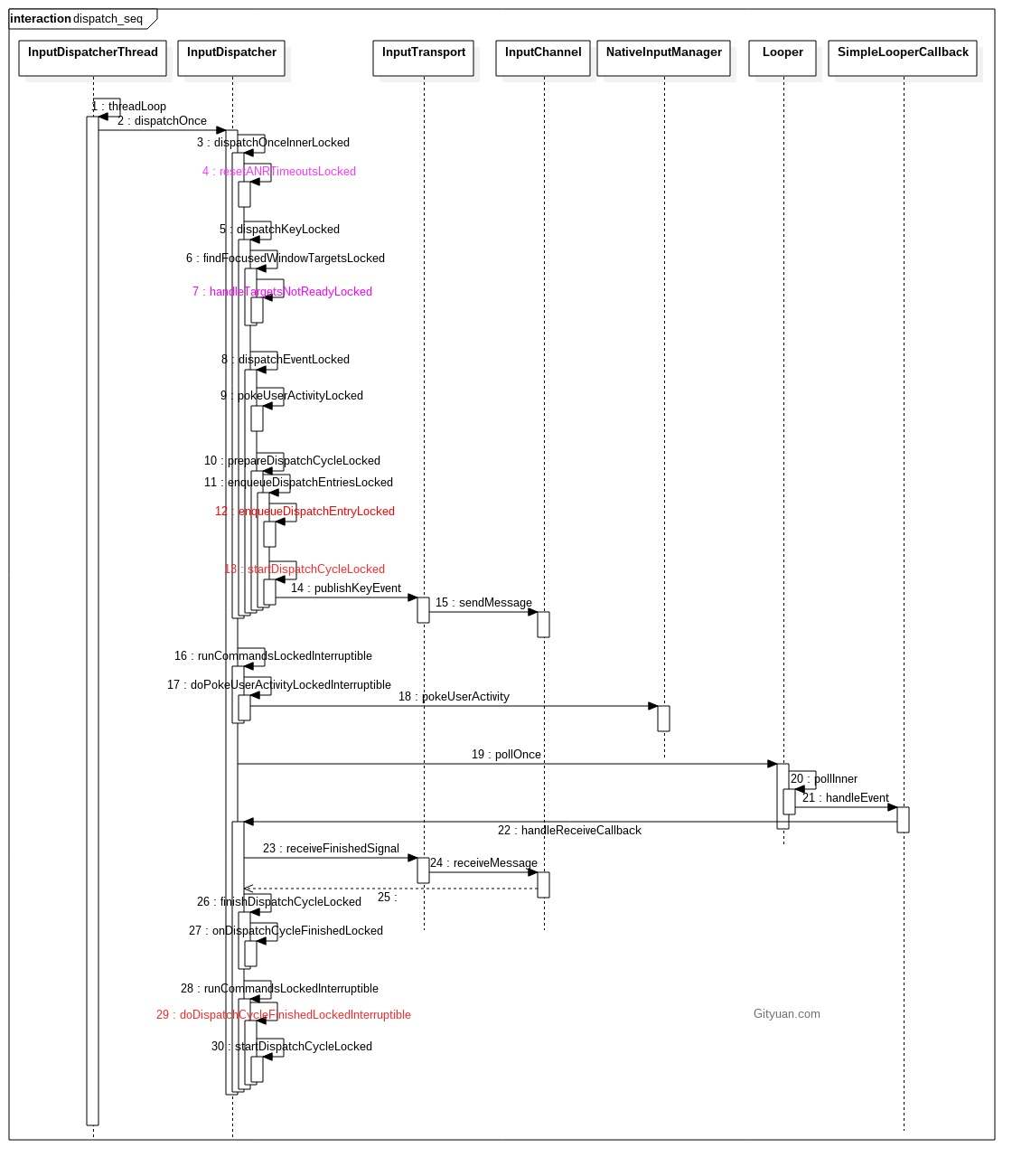
- dispatchOnceInnerLocked(): 从InputDispatcher的
mInboundQueue队列,取出事件EventEntry。另外该方法开始执行的时间点(currentTime)便是后续事件dispatchEntry的分发时间(deliveryTime) - dispatchKeyLocked():满足一定条件时会添加命令doInterceptKeyBeforeDispatchingLockedInterruptible;
- enqueueDispatchEntryLocked():生成事件DispatchEntry并加入connection的
outbound队列 - startDispatchCycleLocked():从outboundQueue中取出事件DispatchEntry, 重新放入connection的
waitQueue队列; - runCommandsLockedInterruptible():通过循环遍历地方式,依次处理mCommandQueue队列中的所有命令。而mCommandQueue队列中的命令是通过postCommandLocked()方式向该队列添加的。ANR回调命令便是在这个时机执行。
- handleTargetsNotReadyLocked(): 该过程会判断是否等待超过5s来决定是否调用onANRLocked().
流程15中sendMessage是将input事件分发到app端,当app处理完该事件后会发送finishInputEvent()事件. 接下来又回到pollOnce()方法.
1.3 UI Thread
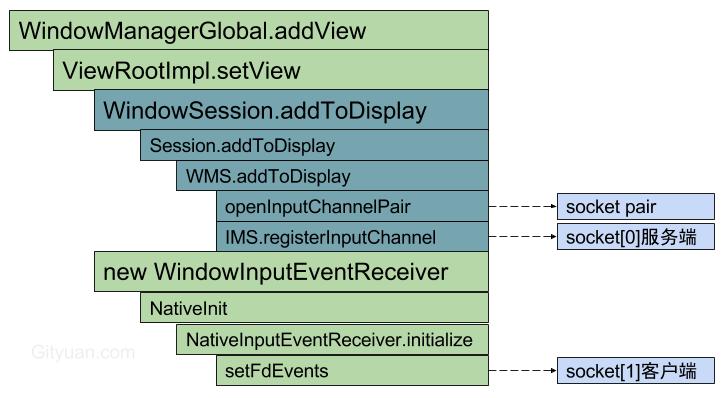
- “InputDispatcher”线程监听socket服务端,收到消息后回调InputDispatcher.handleReceiveCallback();
- UI主线程监听socket客户端,收到消息后回调NativeInputEventReceiver.handleEvent().
对于ANR的触发主要是在InputDispatcher过程,下面再从ANR的角度来说一说ANR触发过程。
二. ANR处理流程
ANR时间区别便是指当前这次的事件dispatch过程中执行findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked()方法到下一次执行resetANRTimeoutsLocked()的时间区间. 以下5个时机会reset. 都位于InputDispatcher.cpp文件:
- resetAndDropEverythingLocked
- releasePendingEventLocked
- setFocusedApplication
- dispatchOnceInnerLocked
- setInputDispatchMode
简单来说, 主要是以下4个场景,会有机会执行resetANRTimeoutsLocked:
- 解冻屏幕, 系统开/关机的时刻点 (thawInputDispatchingLw, setEventDispatchingLw)
- wms聚焦app的改变 (WMS.setFocusedApp, WMS.removeAppToken)
- 设置input filter的过程 (IMS.setInputFilter)
- 再次分发事件的过程(dispatchOnceInnerLocked)
当InputDispatcher线程 findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked()过程调用到handleTargetsNotReadyLocked,且满足超时5s的情况则会调用onANRLocked().
2.1 onANRLocked
[-> InputDispatcher.cpp]
void InputDispatcher::onANRLocked(nsecs_t currentTime, const sp<InputApplicationHandle>& applicationHandle,const sp<InputWindowHandle>& windowHandle,nsecs_t eventTime, nsecs_t waitStartTime, const char* reason) {float dispatchLatency = (currentTime - eventTime) * 0.000001f;float waitDuration = (currentTime - waitStartTime) * 0.000001f;ALOGI("Application is not responding: %s. ""It has been %0.1fms since event, %0.1fms since wait started. Reason: %s",getApplicationWindowLabelLocked(applicationHandle, windowHandle).string(),dispatchLatency, waitDuration, reason);//捕获ANR的现场信息time_t t = time(NULL);struct tm tm;localtime_r(&t, &tm);char timestr[64];strftime(timestr, sizeof(timestr), "%F %T", &tm);mLastANRState.clear();mLastANRState.append(INDENT "ANR:\n");mLastANRState.appendFormat(INDENT2 "Time: %s\n", timestr);mLastANRState.appendFormat(INDENT2 "Window: %s\n",getApplicationWindowLabelLocked(applicationHandle, windowHandle).string());mLastANRState.appendFormat(INDENT2 "DispatchLatency: %0.1fms\n", dispatchLatency);mLastANRState.appendFormat(INDENT2 "WaitDuration: %0.1fms\n", waitDuration);mLastANRState.appendFormat(INDENT2 "Reason: %s\n", reason);dumpDispatchStateLocked(mLastANRState);//将ANR命令加入mCommandQueueCommandEntry* commandEntry = postCommandLocked(& InputDispatcher::doNotifyANRLockedInterruptible);commandEntry->inputApplicationHandle = applicationHandle;commandEntry->inputWindowHandle = windowHandle;commandEntry->reason = reason;}
发生ANR调用onANRLocked()的过程会将doNotifyANRLockedInterruptible加入mCommandQueue。 在下一轮InputDispatcher.dispatchOnce的过程中会先执行runCommandsLockedInterruptible()方法,取出 mCommandQueue队列的所有命令逐一执行。那么ANR所对应的命令doNotifyANRLockedInterruptible,接下来看该方法。
3.2 doNotifyANRLockedInterruptible
[-> InputDispatcher.cpp]
void InputDispatcher::doNotifyANRLockedInterruptible(CommandEntry* commandEntry) {mLock.unlock();//[见小节3.3]nsecs_t newTimeout = mPolicy->notifyANR(commandEntry->inputApplicationHandle, commandEntry->inputWindowHandle,commandEntry->reason);mLock.lock();//newTimeout =5s [见小节3.8]resumeAfterTargetsNotReadyTimeoutLocked(newTimeout,commandEntry->inputWindowHandle != NULL? commandEntry->inputWindowHandle->getInputChannel() : NULL);}
mPolicy是指NativeInputManager
3.3 NativeInputManager.notifyANR
[-> com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp]
nsecs_t NativeInputManager::notifyANR(const sp<InputApplicationHandle>& inputApplicationHandle,const sp<InputWindowHandle>& inputWindowHandle, const String8& reason) {JNIEnv* env = jniEnv();jobject inputApplicationHandleObj =getInputApplicationHandleObjLocalRef(env, inputApplicationHandle);jobject inputWindowHandleObj =getInputWindowHandleObjLocalRef(env, inputWindowHandle);jstring reasonObj = env->NewStringUTF(reason.string());//调用Java方法[见小节3.4]jlong newTimeout = env->CallLongMethod(mServiceObj,gServiceClassInfo.notifyANR, inputApplicationHandleObj, inputWindowHandleObj,reasonObj);if (checkAndClearExceptionFromCallback(env, "notifyANR")) {newTimeout = 0; //抛出异常,则清理并重置timeout}...return newTimeout;}
先看看register_android_server_InputManager过程:
int register_android_server_InputManager(JNIEnv* env) {int res = jniRegisterNativeMethods(env, "com/android/server/input/InputManagerService",gInputManagerMethods, NELEM(gInputManagerMethods));jclass clazz;FIND_CLASS(clazz, "com/android/server/input/InputManagerService");...GET_METHOD_ID(gServiceClassInfo.notifyANR, clazz,"notifyANR","(Lcom/android/server/input/InputApplicationHandle;Lcom/android/server/input/InputWindowHandle;Ljava/lang/String;)J");...}
可知gServiceClassInfo.notifyANR是指IMS.notifyANR
3.4 IMS.notifyANR
[-> InputManagerService.java]
private long notifyANR(InputApplicationHandle inputApplicationHandle,InputWindowHandle inputWindowHandle, String reason) {//[见小节3.5]return mWindowManagerCallbacks.notifyANR(inputApplicationHandle, inputWindowHandle, reason);}
此处mWindowManagerCallbacks是指InputMonitor对象。
3.5 InputMonitor.notifyANR
[-> InputMonitor.java]
public long notifyANR(InputApplicationHandle inputApplicationHandle,InputWindowHandle inputWindowHandle, String reason) {AppWindowToken appWindowToken = null;WindowState windowState = null;boolean aboveSystem = false;synchronized (mService.mWindowMap) {if (inputWindowHandle != null) {windowState = (WindowState) inputWindowHandle.windowState;if (windowState != null) {appWindowToken = windowState.mAppToken;}}if (appWindowToken == null && inputApplicationHandle != null) {appWindowToken = (AppWindowToken)inputApplicationHandle.appWindowToken;}//输出input事件分发超时logif (windowState != null) {Slog.i(WindowManagerService.TAG, "Input event dispatching timed out "+ "sending to " + windowState.mAttrs.getTitle()+ ". Reason: " + reason);int systemAlertLayer = mService.mPolicy.windowTypeToLayerLw(WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_SYSTEM_ALERT);aboveSystem = windowState.mBaseLayer > systemAlertLayer;} else if (appWindowToken != null) {Slog.i(WindowManagerService.TAG, "Input event dispatching timed out "+ "sending to application " + appWindowToken.stringName+ ". Reason: " + reason);} else {Slog.i(WindowManagerService.TAG, "Input event dispatching timed out "+ ". Reason: " + reason);}mService.saveANRStateLocked(appWindowToken, windowState, reason);}if (appWindowToken != null && appWindowToken.appToken != null) {//【见小节3.6.1】boolean abort = appWindowToken.appToken.keyDispatchingTimedOut(reason);if (! abort) {return appWindowToken.inputDispatchingTimeoutNanos; //5s}} else if (windowState != null) {//【见小节3.6.2】long timeout = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().inputDispatchingTimedOut(windowState.mSession.mPid, aboveSystem, reason);if (timeout >= 0) {return timeout * 1000000L; //5s}}return 0;}
发生input相关的ANR时在system log输出ANR信息,并且tag为WindowManager. 主要有3类log:
- Input event dispatching timed out sending to [windowState.mAttrs.getTitle()]
- Input event dispatching timed out sending to application [appWindowToken.stringName)]
- Input event dispatching timed out sending.
3.6 DispatchingTimedOut
3.6.1 Token.keyDispatchingTimedOut
[-> ActivityRecord.java :: Token]
final class ActivityRecord {static class Token extends IApplicationToken.Stub {public boolean keyDispatchingTimedOut(String reason) {ActivityRecord r;ActivityRecord anrActivity;ProcessRecord anrApp;synchronized (mService) {r = tokenToActivityRecordLocked(this);if (r == null) {return false;}anrActivity = r.getWaitingHistoryRecordLocked();anrApp = r != null ? r.app : null;}//[见小节3.7]return mService.inputDispatchingTimedOut(anrApp, anrActivity, r, false, reason);}...}}
3.6.2 AMS.inputDispatchingTimedOut
public long inputDispatchingTimedOut(int pid, final boolean aboveSystem, String reason) {...ProcessRecord proc;long timeout;synchronized (this) {synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) {proc = mPidsSelfLocked.get(pid); //根据pid查看进程record}timeout = getInputDispatchingTimeoutLocked(proc);}//【见小节3.7】if (!inputDispatchingTimedOut(proc, null, null, aboveSystem, reason)) {return -1;}return timeout;}
inputDispatching的超时为KEY_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT,即timeout = 5s。
3.7 AMS.inputDispatchingTimedOut
public boolean inputDispatchingTimedOut(final ProcessRecord proc,final ActivityRecord activity, final ActivityRecord parent,final boolean aboveSystem, String reason) {...final String annotation;if (reason == null) {annotation = "Input dispatching timed out";} else {annotation = "Input dispatching timed out (" + reason + ")";}if (proc != null) {...//通过handler机制,交由“ActivityManager”线程执行ANR处理过程。mHandler.post(new Runnable() {public void run() {appNotResponding(proc, activity, parent, aboveSystem, annotation);}});}return true;}
appNotResponding会输出现场的重要进程的trace等信息。 再回到【小节3.2】处理完ANR后再调用resumeAfterTargetsNotReadyTimeoutLocked。
3.8 resumeAfterTargetsNotReadyTimeoutLocked
[-> InputDispatcher.cpp]
void InputDispatcher::resumeAfterTargetsNotReadyTimeoutLocked(nsecs_t newTimeout,const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel) {if (newTimeout > 0) {//超时时间增加5smInputTargetWaitTimeoutTime = now() + newTimeout;} else {// Give up.mInputTargetWaitTimeoutExpired = true;// Input state will not be realistic. Mark it out of sync.if (inputChannel.get()) {ssize_t connectionIndex = getConnectionIndexLocked(inputChannel);if (connectionIndex >= 0) {sp<Connection> connection = mConnectionsByFd.valueAt(connectionIndex);sp<InputWindowHandle> windowHandle = connection->inputWindowHandle;if (windowHandle != NULL) {const InputWindowInfo* info = windowHandle->getInfo();if (info) {ssize_t stateIndex = mTouchStatesByDisplay.indexOfKey(info->displayId);if (stateIndex >= 0) {mTouchStatesByDisplay.editValueAt(stateIndex).removeWindow(windowHandle);}}}if (connection->status == Connection::STATUS_NORMAL) {CancelationOptions options(CancelationOptions::CANCEL_ALL_EVENTS,"application not responding");synthesizeCancelationEventsForConnectionLocked(connection, options);}}}}}
四. input死锁监测机制
4.1 IMS.start
[-> InputManagerService.java]
public void start() {...Watchdog.getInstance().addMonitor(this);...}
InputManagerService实现了Watchdog.Monitor接口, 并且在启动过程将自己加入到了Watchdog线程的monitor队列.
4.2 IMS.monitor
Watchdog便会定时调用IMS.monitor()方法.
public void monitor() {synchronized (mInputFilterLock) { }nativeMonitor(mPtr);}
nativeMonitor经过JNI调用,进如如下方法:
static void nativeMonitor(JNIEnv*, jclass, jlong ptr) {NativeInputManager* im = reinterpret_cast<NativeInputManager*>(ptr);im->getInputManager()->getReader()->monitor(); //见小节4.3im->getInputManager()->getDispatcher()->monitor(); //见小节4.4}
4.3 InputReader.monitor
[-> InputReader.cpp]
void InputReader::monitor() {//请求和释放一次mLock,来确保reader没有发生死锁的问题mLock.lock();mEventHub->wake();mReaderIsAliveCondition.wait(mLock);mLock.unlock();//监测EventHub[见小节4.3.1]mEventHub->monitor();}
获取mLock之后进入Condition类型的wait()方法,等待InputReader线程的loopOnce()中的broadcast()来唤醒.
void InputReader::loopOnce() {size_t count = mEventHub->getEvents(timeoutMillis, mEventBuffer, EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE);...{AutoMutex _l(mLock);mReaderIsAliveCondition.broadcast();if (count) {processEventsLocked(mEventBuffer, count);}}...mQueuedListener->flush();}
4.3.1 EventHub.monitor
[-> EventHub.cpp]
void EventHub::monitor() {//请求和释放一次mLock,来确保reader没有发生死锁的问题mLock.lock();mLock.unlock();}
4.4 InputDispatcher
[-> InputDispatcher.cpp]
void InputDispatcher::monitor() {mLock.lock();mLooper->wake();mDispatcherIsAliveCondition.wait(mLock);mLock.unlock();}
获取mLock之后进入Condition类型的wait()方法,等待IInputDispatcher线程的loopOnce()中的broadcast()来唤醒.
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() {nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;{AutoMutex _l(mLock);mDispatcherIsAliveCondition.broadcast();if (!haveCommandsLocked()) {dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime);}if (runCommandsLockedInterruptible()) {nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN;}}nsecs_t currentTime = now();int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime);mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis); //进入epoll_wait}
4.5 小节
通过将InputManagerService加入到Watchdog的monitor队列,定时监测是否发生死锁. 整个监测过涉及EventHub, InputReader, InputDispatcher, InputManagerService的死锁监测. 监测的原理很简单,通过尝试获取锁并释放锁的方式.
最后, 可通过adb shell dumpsys input来查看手机当前的input状态, 输出内容分别为EventHub.dump(), InputReader.dump(),InputDispatcher.dump()这3类,另外如果发生过input ANR,那么也会输出上一个ANR的状态.
其中mPendingEvent代表的当下正在处理的事件.
五. 总结
5.1 ANR分类
由小节[3.5] InputMonitor.notifyANR完成, 当发生ANR时system log中会出现以下信息, 并且TAG=WindowManager:
Input event dispatching timed out xxx. Reason: + reason, 其中xxx取值:
- 窗口类型: sending to
windowState.mAttrs.getTitle() - 应用类型: sending to application
appWindowToken.stringName - 其他类型: 则为空.
至于Reason主要有以下类型:
5.1.1 reason类型
由小节[2.3.1]checkWindowReadyForMoreInputLocked完成, ANR reason主要有以下几类:
- 无窗口, 有应用:Waiting because no window has focus but there is a focused application that may eventually add a window when it finishes starting up.
- 窗口暂停: Waiting because the
[targetType]window is paused. - 窗口未连接: Waiting because the
[targetType]window’s input channel is not registered with the input dispatcher. The window may be in the process of being removed. - 窗口连接已死亡:Waiting because the
[targetType]window’s input connection is[Connection.Status]. The window may be in the process of being removed. - 窗口连接已满:Waiting because the
[targetType]window’s input channel is full. Outbound queue length:[outboundQueue长度]. Wait queue length:[waitQueue长度]. - 按键事件,输出队列或事件等待队列不为空:Waiting to send key event because the
[targetType]window has not finished processing all of the input events that were previously delivered to it. Outbound queue length:[outboundQueue长度]. Wait queue length:[waitQueue长度]. - 非按键事件,事件等待队列不为空且头事件分发超时500ms:Waiting to send non-key event because the
[targetType]window has not finished processing certain input events that were delivered to it over 500ms ago. Wait queue length:[waitQueue长度]. Wait queue head age:[等待时长].
其中
- targetType: 取值为”focused”或者”touched”
- Connection.Status: 取值为”NORMAL”,”BROKEN”,”ZOMBIE”
另外, findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked, findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked这两个方法中可以通过实现 updateDispatchStatisticsLocked()来分析anr问题.
5.2 drop事件分类
由小节[2.1.2] dropInboundEventLocked完成,输出事件丢弃的原因:
- DROP_REASON_POLICY: “inbound event was dropped because the policy consumed it”;
- DROP_REASON_DISABLED: “inbound event was dropped because input dispatch is disabled”;
- DROP_REASON_APP_SWITCH: “inbound event was dropped because of pending overdue app switch”;
- DROP_REASON_BLOCKED: “inbound event was dropped because the current application is not responding and the user has started interacting with a different application””;
- DROP_REASON_STALE: “inbound event was dropped because it is stale”;
其他:
- doDispatchCycleFinishedLockedInterruptible的过程, 会记录分发时间超过2s的事件,
- findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked的过程, 可以统计等待时长信息.
转自:http://gityuan.com/2017/01/01/input-anr/
Input系统—ANR原理分析(转)的更多相关文章
- Android ANR原理分析
一.概述 ANR(Application Not responding),是指应用程序未响应,Android系统对于一些事件需要在一定的时间范围内完成,如果超过预定时间能未能得到有效响应或者响应时间过 ...
- Linux input系统数据上报流程【转】
转自:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000017255939 作为鸡生蛋系列文章,这里主要关注Linux input系统,主要为触摸事件上报流程. 读该文章最好有对li ...
- Android中Input型输入设备驱动原理分析(一)
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/eilianlau/article/details/6969361 话说Android中Event输入设备驱动原理分析还不如说Linux输入子系统呢,反 ...
- (转)Android 系统 root 破解原理分析
现在Android系统的root破解基本上成为大家的必备技能!网上也有很多中一键破解的软件,使root破解越来越容易.但是你思考过root破解的 原理吗?root破解的本质是什么呢?难道是利用了Lin ...
- Android中Input型输入设备驱动原理分析<一>
话说Android中Event输入设备驱动原理分析还不如说Linux输入子系统呢,反正这个是没变的,在android的底层开发中对于Linux的基本驱动程序设计还是没变的,当然Android底层机制也 ...
- ZT自老罗的博客 Android系统的智能指针(轻量级指针、强指针和弱指针)的实现原理分析
Android系统的智能指针(轻量级指针.强指针和弱指针)的实现原理分析 分类: Android 2011-09-23 00:59 31568人阅读 评论(42) 收藏 举报 androidclass ...
- Android 系统 root 破解原理分析 (续)
上文<Android系统root破解原理分析>介绍了Android系统root破解之后,应用程序获得root权限的原理.有一些网友提出对于root破解过程比较感兴趣,也提出了疑问.本文将会 ...
- 【Android漏洞复现】StrandHogg漏洞复现及原理分析_Android系统上的维京海盗
文章作者MG1937 CNBLOG博客:ALDYS4 QQ:3496925334 0x00 StrandHogg漏洞详情 StrandHogg漏洞 CVE编号:暂无 [漏洞危害] 近日,Android ...
- 老李推荐:第5章5节《MonkeyRunner源码剖析》Monkey原理分析-启动运行: 获取系统服务引用
老李推荐:第5章5节<MonkeyRunner源码剖析>Monkey原理分析-启动运行: 获取系统服务引用 上一节我们描述了monkey的命令处理入口函数run是如何调用optionP ...
随机推荐
- 【软件构造】第三章第三节 抽象数据型(ADT)
第三章第三节 抽象数据型(ADT) 3-1节研究了“数据类型”及其特性 ; 3-2节研究了方法和操作的“规约”及其特性:在本节中,我们将数据和操作复合起来,构成ADT,学习ADT的核心特征,以及如何设 ...
- Mapping (RESOURCE) not found :和BeanFactory not initialized or already closed - call 'refresh' before access记录
1.Mapping (RESOURCE) not found :cn/sxx/model/Supplier.hbm.xml : origin(cn/sxx/model/Supplier.hbm.xml ...
- UVa-1585-得分
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> int main() { char s[100]; int T; scanf("%d&q ...
- django扩展User模型(model),profile
from django.contrib.auth.models import User # Create your models here. class Profile(models.Model): ...
- 自定义ngCloak
场景: 一个非常复杂的表单页面,页面有5个标签,第五个标签中又有5个标签,也就是说一共有9个标签,每个标签中都有一个表单,表单之间相互关联.所有表单项(包括复合的),有80多个数据.全部东西写在一个h ...
- 洛谷 1196 [NOI2002]银河英雄传说【模板】带权并查集
[题解] 经典的带权并查集题目. 设cnt[i]表示i前面的点的数量,siz[i]表示第i个点(这个点是代表元)所处的联通块的大小:合并的时候更新siz.旧的代表元的cnt,路径压缩的时候维护cnt即 ...
- PS日记一
shift+alt 从中心开始画圆 PHOTOSHOP是处理位图的软件, 栅格化是将矢量图形如:(Illustrator,或者CoreIDRAW中绘画的图形), 包括文字,这些矢量图文转换(也叫栅格化 ...
- 【04】如何确定ruby安装好
[04]如何确定ruby安装好 命令行里输入 ruby -v 如果正确输出了 ruby 版本号,就OK了 是不是在Windows平台安装的?如果是,先按照楼上说得打开命令行 ...
- 大数据学习——Linux上常用软件安装
4.1 Linux系统软件安装方式 Linux上的软件安装有以下几种常见方式: 1.二进制发布包 软件已经针对具体平台编译打包发布,只要解压,修改配置即可 2.RPM发布包 软件已经按照redhat的 ...
- kafka直连方式消费多个topic
一个消费者组可以消费多个topic,以前写过一篇一个消费者消费一个topic的,这次的是一个消费者组通过直连方式消费多个topic,做了小测试,结果是正确的,通过查看zookeeper的客户端,zoo ...
