vuex源码分析3.0.1(原创)
前言
chapter1 store构造函数
1.constructor
2.get state和set state
3.commit
4.dispatch
5.subscribe和subscribeAction
6.watch和replaceState
7.registerModule和unregisterModule
8.hotUpdate和_withCommit
chapter2 export install
Q:Vuex如何实现装载的?
chapter3 辅助函数
1.registerMutation、registerAction、registerGetter
2.enableStrictMode、getNestedState
3.unifyObjectStyle(type, payload, options)
1.store构造函数 /part1
1.constructor
源码分析
constructor (options = {}) {
//安装Vue对象
if (!Vue && typeof window !== 'undefined' && window.Vue) {
console.log("window.vue");
install(window.Vue)
}
//开发环境对Vue、Promise和Store的判断
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
assert(Vue, `must call Vue.use(Vuex) before creating a store instance.`)
assert(typeof Promise !== 'undefined', `vuex requires a Promise polyfill in this browser.`)
assert(this instanceof Store, `store must be called with the new operator.`)
}
//options包括插件选项、严格模式选项
const {
plugins = [],
strict = false
} = options
// 存储内部的状态
this._committing = false
this._actions = Object.create(null)
this._actionSubscribers = []
this._mutations = Object.create(null)
this._wrappedGetters = Object.create(null)
this._modules = new ModuleCollection(options)
this._modulesNamespaceMap = Object.create(null)
this._subscribers = []
this._watcherVM = new Vue()
// 绑定commit和dispatch
const store = this
const { dispatch, commit } = this
this.dispatch = function boundDispatch (type, payload) {
return dispatch.call(store, type, payload)
}
this.commit = function boundCommit (type, payload, options) {
return commit.call(store, type, payload, options)
}
// 严格模式
this.strict = strict
const state = this._modules.root.state
// 初始化根模块,或者安装子模块
installModule(this, state, [], this._modules.root)
//初始化vm
resetStoreVM(this, state)
// 应用插件
plugins.forEach(plugin => plugin(this))
if (Vue.config.devtools) {
devtoolPlugin(this)
}
}
2.get state和set state
ES6的get和set是取值和存值的函数,这是是对属性state拦截存取行为。
示例1
E:\vuex>node
//类的声明,属性prop进行存取拦截
> class MyClass {
... constructor() {
..... // ...
..... }
... get prop() {
..... return 'getter';
..... }
... set prop(value) {
..... console.log('setter: ' + value);
..... }
... }
undefined
> let inst = new MyClass();
undefined
//设置prop时,根据程序逻辑会console.log
> inst.prop = ;
setter: //获取prop,根据return返回"getter"字符串
> inst.prop
'getter'
源码1
//取值返回的是this属性
get state () {
return this._vm._data.$$state
}
//如果在非生产环境,那么修改state就会使用assert打印错误信息
set state (v) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
assert(false, `use store.replaceState() to explicit replace store state.`)
}
}
3.commit
commit (_type, _payload, _options) {
// check object-style commit检查对象风格提交
const {
type,
payload,
options
} = unifyObjectStyle(_type, _payload, _options)
//mutation的type判断,也就是entry,如果不存在,那么打印错误信息“不存在的mutation type”
const mutation = { type, payload }
const entry = this._mutations[type]
if (!entry) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
console.error(`[vuex] unknown mutation type: ${type}`)
}
return;
}
//处理entry并订阅它
this._withCommit(() => {
entry.forEach(function commitIterator (handler) {
handler(payload)
})
})
this._subscribers.forEach(sub => sub(mutation, this.state))
//开发模式下的silent判断
if (
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
options && options.silent
) {
console.warn(
`[vuex] mutation type: ${type}. Silent option has been removed. ` +
'Use the filter functionality in the vue-devtools'
)
}
}
(1)const { type, payload,options}=unify..........这是ES6的解构赋值。(node环境执行的哦)
示例2
E:\vuex>node
> const person = {
... name: 'little bear',
... age: ,
... sex: '男'
... }
undefined
> let { name,age,sex } = person
undefined
> name
'little bear'
(2)this._withCommit(...)小括号内的部分总体上说是_withCommit的fn参数。
this._withCommit()中有对this._committing进行设置,首先this._committing = false赋值给中间变量,接下来提交前设为true,fn调用结束后再通过中间变量设为初始值。
接下来说说entry。entry就是mutations的type也就是某个函数。可是明明forEach方法是数组啊。其实通过this._mutations[type]获取到就是一个数组。那么对数组的元素handler进行调用。entry
类似如下内容:

(3)this._subscribers.forEach(sub => sub(mutation, this.state))是_subscribers遍历收集来的actions并执行。我们要注意到actions的使用也有commit提交,不过是异步的。所以这里的actions执行是为了补充刚刚同步提交的方式。
图示1

(4)process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&options && options.silent
检查选项,silent是静默选项,如果使用了silent,那么告知"silent已经被移除,请在dev-tool中使用过滤器功能。
4,dispatch
dispatch (_type, _payload) {
// 检查数组风格的分发
const {
type,
payload
} = unifyObjectStyle(_type, _payload)
const action = { type, payload }
//从this._actions拿到type对应的事件类型
const entry = this._actions[type]
//如果entry也就是事件类型不存在,那么打印信息"vuex不知道的action类型"
if (!entry) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
console.error(`[vuex] unknown action type: ${type}`)
}
return
}
//_actionSubscribers遍历每个订阅
this._actionSubscribers.forEach(sub => sub(action, this.state))
//如果entry.length大于1,那么返回promise
return entry.length >
? Promise.all(entry.map(handler => handler(payload)))
: entry[](payload)
}
5.subscribe和subscribeAction
subscribe订阅store的mutation。回调函数会在每个mutaion完成时触发。
示例
const myPlugin = store => {
// 当 store 初始化后订阅
store.subscribe((mutation, state) => {
//回调函数在每次mutation完成之后调用
state.count++;
})
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
count:
},
mutations:{
increment(state,payload){
state.count=state.count*payload;
}
},
plugins: [myPlugin]
})
//提交"increment"事件
store.commit("increment",)
//最终store.state.count等于5*20+1=101。
subscribeAction订阅action。回调函数会在每个action完成时触发。
const myPlugin2 = store => {
// 当 store 初始化后订阅
store.subscribeAction((action, state) => {
//每次action完成后回调函数都会被触发
state.huge--;
})
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
huge:
},
mutations:{
REDUCE(state,payload){
state.huge=state.huge-payload
}
},
actions:{
reduce({commit,state},payload){
commit("REDUCE",payload)
}
},
plugins: [myPlugin2]
})
store.dispatch("reduce",)
//store.state.huge结果2000-500-1等于1499
源码分析
subscribe (fn) {
//fn即刚才说的每次mutation之后的回调函数
return genericSubscribe(fn, this._subscribers)
}
subscribeAction (fn) {
return genericSubscribe(fn, this._actionSubscribers)
}
//subscribe和subscribeAction返回的是一个箭头函数
function genericSubscribe (fn, subs) {
//订阅fn,那么会push到this._subscribers或者this._actionSubscribers数组
if (subs.indexOf(fn) < ) {
subs.push(fn)
}
return () => {
//箭头函数在需要回调的时候再从数组里裁剪出fn元素
const i = subs.indexOf(fn)
if (i > -) {
subs.splice(i, )
}
}
}
可以看出,genericSubscribe功能是对订阅数组的处理,先存进数组,需要的时候再取出来。
6.watch和replaceState
源码分析
watch (getter, cb, options) {
//如果传入的getter不是function,那么打印信息"store.watch只接受一个函数"
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
assert(typeof getter === 'function', `store.watch only accepts a function.`)
}
//返回Vue.$watch方法,响应式监听() => getter(this.state, this.getters)返回的值
//如果发生变化,那么cb回调函数触发
//options包括选项:deep,选项:immediate
return this._watcherVM.$watch(() => getter(this.state, this.getters), cb, options)
}
示例
<!--Vue API中$watch的用法-->
<div id="app">
<button @click="addOne">加一</button>
</div>
<script>
let vm= new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
a:0
},
created:function(){
//$watch监听第一个函数返回的只,一旦发生变化,那么执行回调函数
this.$watch(function(){
return this.a;
},function(newValue,oldValue){
console.log(newValue)
})
},
methods:{
addOne(){
this.a=1;
}
}
}) </script>
示例
//replaceState整体替换state,变化引起回调发生
const store=new Vuex.Store({
state:{
count:0
}
}) store.watch(function(){
return store.state;
},function(){
console.log(store.state.count)//
})
store.replaceState({count:20})
示例
//通过mutation改变state,触发watch回调
const store2=new Vuex.Store({
state:{
count:100
},
mutations:{
ADDONE(state){
state.count++;
}
} })
store2.watch(function(){
return store2.state.count
},function(){
console.log(store2.state.count)
//
}
)
store2.commit("ADDONE");
源码分析
replaceState (state) {
this._withCommit(() => {
this._vm._data.$$state = state
})
}
通过传入一个新state对象,替换旧state。
示例
const store=new Vuex.Store({
state:{
count:,
num:
}
})
store.replaceState({count:});
//通过替换,旧的state不存在,只有更新后的state
store.state.count//等于0
store.state.num//undefined
7.registerModule和unregisterModule
示例
源码分析
registerModule (path, rawModule, options = {}) {
//传入的第一个参数要么是数组,要么是字符串,字符串会转化为字符串为元素的数组
if (typeof path === 'string') path = [path]
//开发环境下的调试信息
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
//如果path不能转为数组或者不是数组,那么打印"模块path必须是字符串或者数组"
assert(Array.isArray(path), `module path must be a string or an Array.`)
//如果传入的path为[]空数组,那么打印"不能使用registerModule来注册根模块"
assert(path.length > , 'cannot register the root module by using registerModule.')
}
//在store._modules上注册模块
this._modules.register(path, rawModule)
//安装模块
installModule(this, this.state, path, this._modules.get(path), options.preserveState)
// reset store to update getters...
//以当前state更新store.getters
resetStoreVM(this, this.state)
}
源码分析
function installModule (store, rootState, path, module, hot) {
const isRoot = !path.length
const namespace = store._modules.getNamespace(path)
// 注册命名空间的映射数组_modulesNamespaceMap
if (module.namespaced) {
store._modulesNamespaceMap[namespace] = module
}
//hot,即options 可以包含 preserveState: true 以允许保留之前的 state。用于服务端渲染。
if (!isRoot && !hot) {
const parentState = getNestedState(rootState, path.slice(, -))
const moduleName = path[path.length - ]
store._withCommit(() => {
Vue.set(parentState, moduleName, module.state)
})
}
const local = module.context = makeLocalContext(store, namespace, path)
//遍历mutation并注册mutation,会因为namespaced而不同
module.forEachMutation((mutation, key) => {
const namespacedType = namespace + key
registerMutation(store, namespacedType, mutation, local)
})
//遍历action并注册action
module.forEachAction((action, key) => {
//如果action.root为true,那么type等于key索引值,
//即全局action,无论是子模块还是子模块的子模块都如此
//如果action.root为false,那么type直接取namespacType
const type = action.root ? key : namespace + key
const handler = action.handler || action
registerAction(store, type, handler, local)
})
//遍历getter并注册getterts,会因为namespaced而不同
module.forEachGetter((getter, key) => {
const namespacedType = namespace + key
registerGetter(store, namespacedType, getter, local)
})
//遍历子模块,并递归调用installModule
module.forEachChild((child, key) => {
installModule(store, rootState, path.concat(key), child, hot)
})
}
源码分析
unregisterModule (path) {
if (typeof path === 'string') path = [path]
//如果传入参数不能转为数组,那么打印"模块路径必须是字符串或者数组"
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
assert(Array.isArray(path), `module path must be a string or an Array.`)
}
//取消注册,那么store._modules.root._children就不会定义myModule属性了
this._modules.unregister(path)
this._withCommit(() => {
//getNestedState获取到父级state
const parentState = getNestedState(this.state, path.slice(0, -1))
//Vue删除相应的module内容
Vue.delete(parentState, path[path.length - 1])
})
//以当前的this重置store
resetStore(this)
}
8.hotUpdate和_withCommit
源码分析
//热重载
hotUpdate (newOptions) {
this._modules.update(newOptions)
resetStore(this, true)
}
Vuex 支持在开发过程中热重载 mutation、module、action 和 getter。
_withCommit (fn) {
//每次提交的时候,内部代码都会传进来一个箭头函数
const committing = this._committing
this._committing = true
fn()
this._committing = committing
}
2.export install
示例
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<!--这行语句安装了window.Vue-->
<script>
let Vue;
if (!Vue && typeof window !== 'undefined' && window.Vue) {
console.log("window.vue");
install(window.Vue)
}
function install (_Vue) {
Vue = _Vue
console.log(Vue);
//applyMixin(Vue)是为了在Vue初始化之前(beforeCreate)来完成vuex的初始化
//因为2版本才提供了beforeCreate这个钩子函数
//applyMixin主要逻辑:if (version >= 2) {Vue.mixin({ beforeCreate: vuexInit })} else {}
}
</script>
从中可以看出vuex的初始化过程,以Vue2版本为为例:
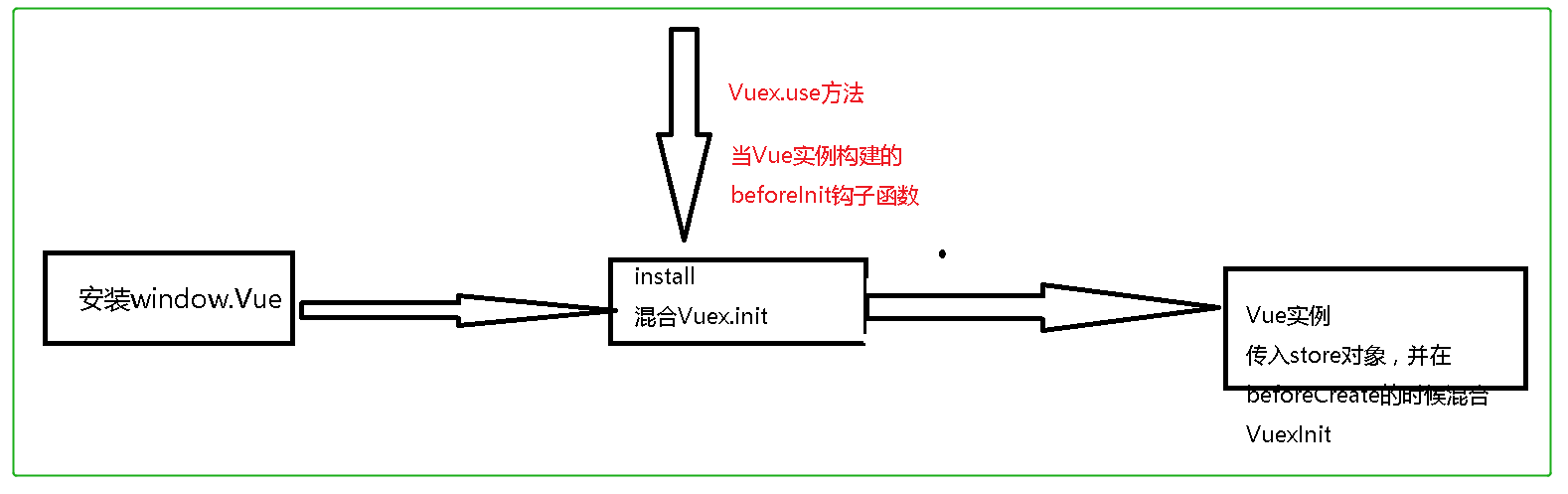
源码分析
export function install (_Vue) {
//那么问题来了,为什么要使用let Vue这个文件一个全局变量呢?主要是为了避免重复安装
if (Vue && _Vue === Vue) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
//如果已经安装过,那么Vue就等于window.Vue为什么呢?
//Vue.use(plugin)方法会调用export的install方法,那么调用中使用Vue=_Vue赋值语句
console.error(
'[vuex] already installed. Vue.use(Vuex) should be called only once.'
)
}
return
}
Vue = _Vue
applyMixin(Vue)
}
install调用逻辑分析:
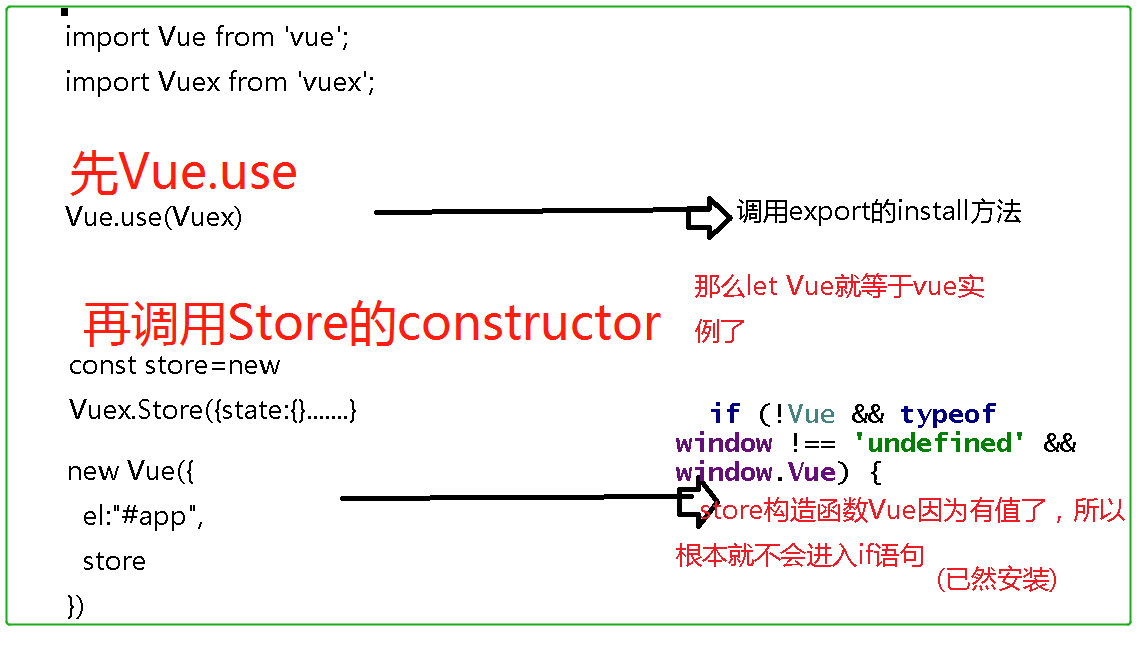
3.辅助函数
1.registerMutation、registerAction、registerGetter
function registerMutation (store, type, handler, local) {
//将type属性添加到_mutations对象,其初始值为空数组[]
const entry = store._mutations[type] || (store._mutations[type] = [])
//我们应该记得mutation是一个函数,那么function.call做一个继承,local.state和payload都应用于store对象
entry.push(function wrappedMutationHandler (payload) {
handler.call(store, local.state, payload)
})
}
........
registerMutation(store, namespacedType, mutation, local)
function registerAction (stobre, type, handler, local) {
//_actions具有type属性,其初始值为一个数组
const entry = store._actions[type] || (store._actions[type] = [])
entry.push(function wrappedActionHandler (payload, cb) {
//继承于store对象
let res = handler.call(store, {
dispatch: local.dispatch,
commit: local.commit,
getters: local.getters,
state: local.state,
rootGetters: store.getters,
rootState: store.state
}, payload, cb)
//如果res不是一个promise,那么相当于直接返回含有res内容的promise对象
if (!isPromise(res)) {
res = Promise.resolve(res)
}
//_devtoolHook判断
if (store._devtoolHook) {
//拦截promise错误
return res.catch(err => {
store._devtoolHook.emit('vuex:error', err)
throw err
})
} else {
//返回res
return res
}
})
}
.........
registerAction(store, type, handler, local)
我们应该还记得action是可以写异步操作的。
function registerGetter (store, type, rawGetter, local) {
//如果对应已getter存在,进入分支,打印说"vuex重复的getter键"
if (store._wrappedGetters[type]) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
console.error(`[vuex] duplicate getter key: ${type}`)
}
return
}
store._wrappedGetters[type] = function wrappedGetter (store) {
//通过当前local和store返回rawGetter对象
return rawGetter(
local.state, // local state
local.getters, // local getters
store.state, // root state
store.getters // root getters
)
}
}
2.enableStrictMode、getNestedState
if (store.strict) {
enableStrictMode(store)
}
//enableStrictMode功能是允许new vm的严格模式
function enableStrictMode (store) {
//侦听this._data.$$state也就是state
store._vm.$watch(function () { return this._data.$$state }, () => {
//state变化,回调函数触发
//store._committing为False,那么打印"不要在mutation处理器外部提交state
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
assert(store._committing, `do not mutate vuex store state outside mutation handlers.`)
}
//deep:true,跟踪对象内部属性的变化,sync:true,同步
}, { deep: true, sync: true })
}
首先,getNestedState的功能是父级state对象。
function getNestedState (state, path) {
return path.length
//state为初始值,接下来遍历path数组,并以state[key]取得state对象
? path.reduce((state, key) => state[key], state)
: state
}
那么为什么这个key比如state["myModule"]的索引就能拿到对应的state呢?这是因为state对象长这个样子。
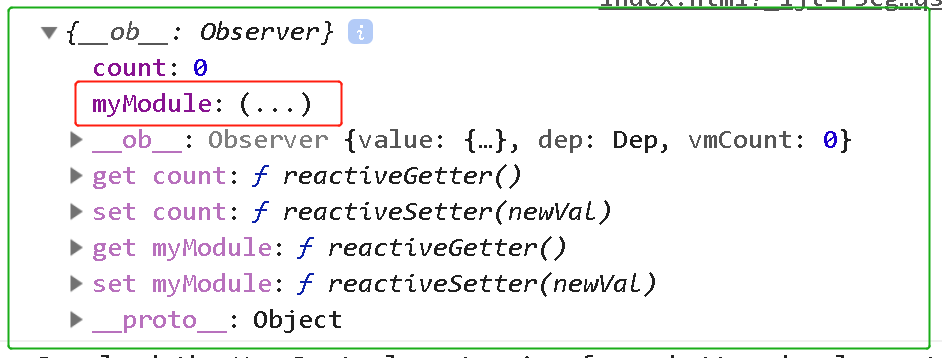
示例
let vm= new Vue({
el:"#app",
})
const store=new Vuex.Store({
state:{
count:
}
})
function getNestedState (state, path) {
return path.length
? path.reduce((state, key) => state[key], state)
: state
}
let myModule={
state:{
count:
}
}
store.registerModule("myModule",myModule)
//找到父级state对象
//["myModule"].slice(0,-1)等于[]
let parentState=getNestedState(store.state,["myModule"].slice(,-))
console.log(parentState)
结果如下:
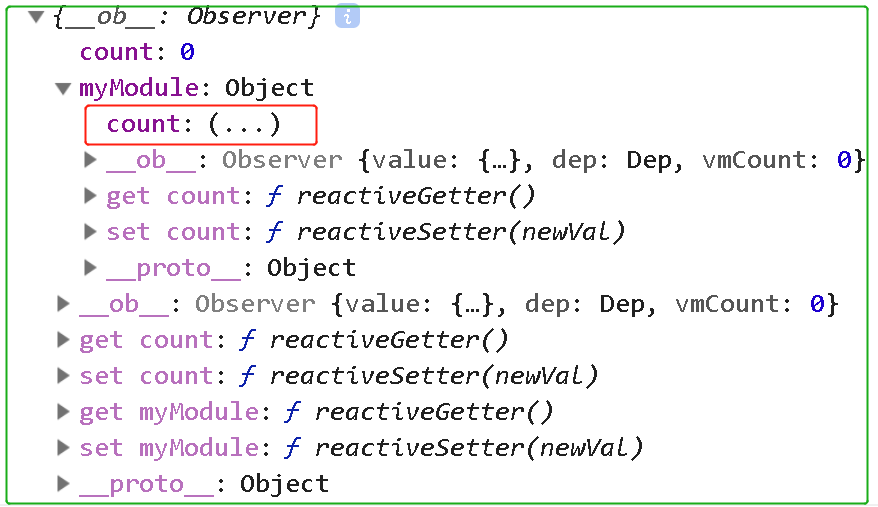
3.unifyObjectStyle(type, payload, options)
首先运行一下这个函数,它可以传入3个参数(payload)。由于process是nodejs环境的变量,那么在nodejs环境中运行。
它的功能是把提交数据对象风格化。
//nodejs环境输入function代码
E:\vuex>node
> function isObject (obj) {
... return obj !== null && typeof obj === 'object'
... }function unifyObjectStyle (type, payload, options) {
... if (isObject(type) && type.type) {
..... options = payload
..... payload = type
..... type = type.type
..... }
...
... if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
... assert(typeof type === 'string', `expects string as the type, but found ${typeof type}.`)
...
... }
...
... return { type, payload, options }
... }
undefined
//nodejs环境中调用刚刚定义的unifyObjectStyle。
> unifyObjectStyle("login",{name:"vicky",password:""})
{ type: 'login',
payload: { name: 'vicky', password: '' },
options: undefined }
> unifyObjectStyle({type:"login",payload:{name:"vicky",password:""}})
{ type: 'login',
payload: { type: 'login', payload: { name: 'vicky', password: '' } },
options: undefined }
它讨论了两种情况。(1)如果type.type不存在,那么就是以参数风格的提交,按照最终的对象格式return。(2)如果type.type存在,也就是对象风格的提交,那么就让对象的type和payload重新赋值。然后return。以最终实现对象风格的统一。
而process的部分是对type的值进行判断,如果不是string,那么assert一个报错信息。
写作不易,欢迎打赏!微信哦。

vuex源码分析3.0.1(原创)的更多相关文章
- VueX源码分析(5)
VueX源码分析(5) 最终也是最重要的store.js,该文件主要涉及的内容如下: Store类 genericSubscribe函数 resetStore函数 resetStoreVM函数 ins ...
- VueX源码分析(3)
VueX源码分析(3) 还剩余 /module /plugins store.js /plugins/devtool.js const devtoolHook = typeof window !== ...
- VueX源码分析(4)
VueX源码分析(4) /module store.js /module/module.js import { forEachValue } from '../util' // Base data s ...
- VueX源码分析(1)
VueX源码分析(1) 文件架构如下 /module /plugins helpers.js index.esm.js index.js store.js util.js util.js 先从最简单的 ...
- 逐行粒度的vuex源码分析
vuex源码分析 了解vuex 什么是vuex vuex是一个为vue进行统一状态管理的状态管理器,主要分为state, getters, mutations, actions几个部分,vue组件基于 ...
- VueX源码分析(2)
VueX源码分析(2) 剩余内容 /module /plugins helpers.js store.js helpers要从底部开始分析比较好.也即先从辅助函数开始再分析那4个map函数mapSta ...
- vuex 源码分析(七) module和namespaced 详解
当项目非常大时,如果所有的状态都集中放到一个对象中,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿. 为了解决这个问题,Vuex允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module).每个模块拥有自己的 state ...
- vuex 源码分析(六) 辅助函数 详解
对于state.getter.mutation.action来说,如果每次使用的时候都用this.$store.state.this.$store.getter等引用,会比较麻烦,代码也重复和冗余,我 ...
- vuex 源码分析(五) action 详解
action类似于mutation,不同的是Action提交的是mutation,而不是直接变更状态,而且action里可以包含任意异步操作,每个mutation的参数1是一个对象,可以包含如下六个属 ...
随机推荐
- ASP.NET MVC学习笔记(二)登陆验证
书上的验证时在配置文件中直接声明用户名和密码,想改成从数据验证账号和密码,搞了一下午都没高出来,不断的调试,发现 var table = userInfo.Tables.FirstOrDefault( ...
- python全栈开发_day31_OSI七层协议和c/s架构
一:OSI七层协议 应用层 =>表示层 =>会话层 =>传输层 =>网络层 =>数据链路层 =>物理连接层 二:c/s架构 b/s的本质也是c/s 手机端:好像cs ...
- 详解sizeof与strlen
一,sizeof是C语言的一种单目运算符,与C语言的其他运算符++,--一样,它并不是函数:sizeof()以字节为单位给出了操作数的大小:sizeof的值是无符号int. strlen是一个函数,只 ...
- Linux安装yum的痛苦路程(失败,慎入)
1,在网上下载了一个yum 的 rpm文件(yum-3.2.29-81.el6.centos.noarch.rpm),我在 http://www.rpmfind.net/linux/rpm2html/ ...
- 如何在CentOS 7安装Node.js
最近,我一直对学习Node.js比较感兴趣.这是一个Java平台的服务器端编程 ,它允许开发人员在服务器编写Java代码,并且有许多CentOS的用户正努力学习这个语言的开发环境.这正是我想做这个教程 ...
- ElasticSearch5.0——IK词库加载
Dictionary ConfigurationIKAnalyzer.cfg.xml can be located at {conf}/analysis-ik/config/IKAnalyzer.cf ...
- AWS 推出长期支持的 OpenJDK 免费分发版本 —— Amazon Corretto
简评:听说 Oracle JDK 要收费了,Oracle 要限制 Java 的商业或生产用途,针对这个问题,AWS 将会推出 Amazon Corretto. Java 是 AWS 用户使用的最流行的 ...
- select子句排列顺序与聚集函数
selcet 要返回的列或表达式 from 从中检索数据的表 where 行级过滤 group by 分组说明 having 组级过滤 order by 输出排列顺序 ASC正序排 ...
- Python中 '==' 与'is' 以及它们背后的故事
摘要 比较判断逻辑是在代码中经常使用的,在Python中常用 '==' 和 is 来做比较判断. == : 双等号是用来比较变量所指向内存单元中的值是否相等,它只关心值,并不在意值的内存地址,也就 ...
- HDU - 3085 Nightmare Ⅱ
HDU - 3085 Nightmare Ⅱ 双向BFS,建立两个队列,让男孩女孩一起走 鬼的位置用曼哈顿距离判断一下,如果该位置与鬼的曼哈顿距离小于等于当前轮数的两倍,则已经被鬼覆盖 #includ ...
