《FDTD electromagnetic field using MATLAB》读书笔记之 Figure 1.14
背景:
基于公式1.42(Ez分量)、1.43(Hy分量)的1D FDTD实现。
计算电场和磁场分量,该分量由z方向的电流片Jz产生,Jz位于两个理想导体极板中间,两个极板平行且向y和z方向无限延伸。
平行极板相距1m,差分网格Δx=1mm。
电流面密度导致分界面(电流薄层)磁场分量的不连续,在两侧产生Hy的波,每个强度为5×10^(-4)A/m。因为电磁波在自由空间中传播,本征阻抗为η0。
显示了从左右极板反射前后的传播过程。本例中是PEC边界,正切电场分量(Ez)在PEC表面消失。
观察图中step650到700的场的变换情况,经过PEC板的入射波和反射波的传播特征。经过PEC反射后,Ez的极性变反,这是因为反射系数等于-1;
而磁场分量Hy没有反向,反射系数等于1。
下面是书中的代码(几乎没动):
第1个是主程序:
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
%% Output Info about this m-file
fprintf('\n****************************************************************\n');
fprintf('\n <FDTD 4 ElectroMagnetics with MATLAB Simulations> \n');
fprintf('\n Listing A.1 \n\n'); time_stamp = datestr(now, 31);
[wkd1, wkd2] = weekday(today, 'long');
fprintf(' Now is %20s, and it is %7s \n\n', time_stamp, wkd2);
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % This program demonstrates a one-dimensional FDTD simulation.
% The problem geometry is composed of two PEC plates extending to
% infinity in y and z dimensions, parallel to each other with 1 meter
% separation. The space between the PEC plates is filled with air.
% A sheet of current source paralle to the PEC plates is placed
% at the center of the problem space. The current source excites fields
% in the problem space due to a z-directed current density Jz,
% which has a Gaussian waveform in time. % Define initial constants
eps_0 = 8.854187817e-12; % permittivity of free space
mu_0 = 4*pi*1e-7; % permeability of free space
c = 1/sqrt(mu_0*eps_0); % speed of light % Define problem geometry and parameters
domain_size = 1; % 1D problem space length in meters
dx = 1e-3; % cell size in meters, Δx=0.001m
dt = 3e-12; % duration of time step in seconds
number_of_time_steps = 2000; % number of iterations
nx = round(domain_size/dx); % number of cells in 1D problem space
source_position = 0.5; % position of the current source Jz % Initialize field and material arrays
Ceze = zeros(nx+1, 1);
Cezhy = zeros(nx+1, 1);
Cezj = zeros(nx+1, 1);
Ez = zeros(nx+1, 1);
Jz = zeros(nx+1, 1);
eps_r_z = ones (nx+1, 1); % free space
sigma_e_z = zeros(nx+1, 1); % free space Chyh = zeros(nx, 1);
Chyez = zeros(nx, 1);
Chym = zeros(nx, 1);
Hy = zeros(nx, 1);
My = zeros(nx, 1);
mu_r_y = ones (nx, 1); % free space
sigma_m_y = zeros(nx, 1); % free space % Calculate FDTD updating coefficients
Ceze = (2 * eps_r_z * eps_0 - dt * sigma_e_z) ...
./(2 * eps_r_z * eps_0 + dt * sigma_e_z); Cezhy = (2 * dt / dx) ...
./(2 * eps_r_z * eps_0 + dt * sigma_e_z); Cezj = (-2 * dt) ...
./(2 * eps_r_z * eps_0 + dt * sigma_e_z); Chyh = (2 * mu_r_y * mu_0 - dt * sigma_m_y) ...
./(2 * mu_r_y * mu_0 + dt * sigma_m_y); Chyez = (2 * dt / dx) ...
./(2 * mu_r_y * mu_0 + dt * sigma_m_y); Chym = (-2 *dt) ...
./(2 * mu_r_y * mu_0 + dt * sigma_m_y); % Define the Gaussian source waveform
time = dt * [0:number_of_time_steps-1].';
Jz_waveform = exp(-((time-2e-10)/5e-11).^2)*1e-3/dx;
source_position_index = round(nx * source_position/domain_size)+1; % Subroutine to initialize plotting
initialize_plotting_parameters; % FDTD loop
for time_step = 1:number_of_time_steps % Update Jz for the current time step
Jz(source_position_index) = Jz_waveform(time_step); % Update magnetic field
Hy(1:nx) = Chyh(1:nx) .* Hy(1:nx) ...
+ Chyez(1:nx) .* (Ez(2:nx+1) - Ez(1:nx)) ...
+ Chym(1:nx) .* My(1:nx); % Update electric field
Ez(2:nx) = Ceze (2:nx) .* Ez(2:nx) ...
+ Cezhy(2:nx) .* (Hy(2:nx) - Hy(1:nx-1)) ...
+ Cezj (2:nx) .* Jz(2:nx); Ez(1) = 0; % Apply PEC boundary condition at x = 0 m
Ez(nx+1) = 0; % Apply PEC boundary condition at x = 1 m % Subroutine to plot the current state of the fields
plot_fields;
end
第2个是initialize_plotting_parameters,看名字就知道是初始化参数:
% Subroutine used to initialize 1D plot Ez_positions = [0:nx]*dx;
Hy_positions = ([0:nx-1]+0.5)*dx;
v = [0 -0.1 -0.1; 0 -0.1 0.1; 0 0.1 0.1; 0 0.1 -0.1; ...
1 -0.1 -0.1; 1 -0.1 0.1; 1 0.1 0.1; 1 0.1 -0.1]; f = [1 2 3 4; 5 6 7 8];
axis([0 1 -0.2 0.2 -0.2 0.2]);
lez = line(Ez_positions, Ez*0, Ez, 'Color', 'b', 'linewidth', 1.5);
lhy = line(Hy_positions, 377*Hy, Hy*0, 'Color', 'r', 'LineWidth', 1.5, 'LineStyle','-.'); set(gca, 'fontsize', 12, 'fontweight', 'bold');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
axis square;
legend('E_{z}', 'H_{y} \times 377', 'location', 'northeast');
xlabel('x [m]');
ylabel('[A/m]');
zlabel('[V/m]');
grid on; p = patch('vertices', v, 'faces', f, 'facecolor', 'g', 'facealpha', 0.2);
text(0, 1, 1.1, 'PEC', 'horizontalalignment', 'center', 'fontweight', 'bold');
text(1, 1, 1.1, 'PEC', 'horizontalalignment', 'center', 'fontweight', 'bold');
第3个就是画图:
% Subroutine used to plot 1D transient field delete(lez);
delete(lhy);
lez = line(Ez_positions, Ez*0, Ez, 'Color', 'b', 'LineWidth', 1.5);
lhy = line(Hy_positions, 377*Hy, Hy*0, 'Color', 'r', 'LineWidth', 1.5, 'LineStyle', '-.');
ts = num2str(time_step);
ti = num2str(dt*time_step*1e9);
title(['time step = ' ts ' , time = ' ti ' ns']);
drawnow;
运行结果:
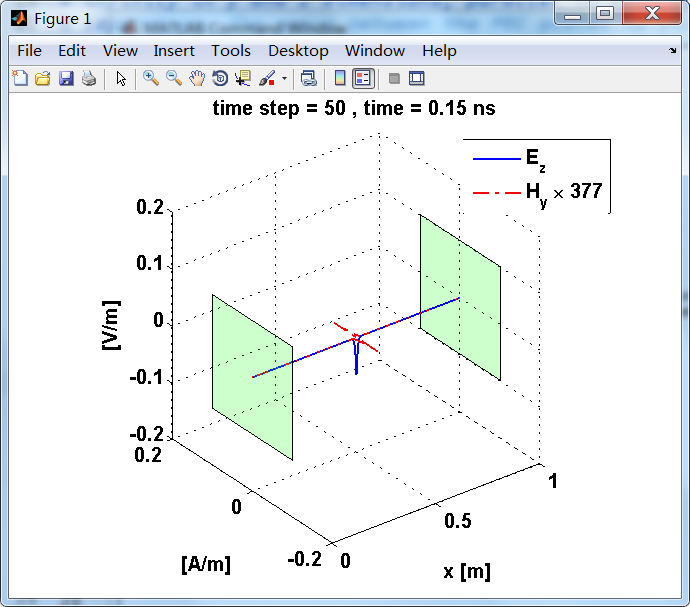
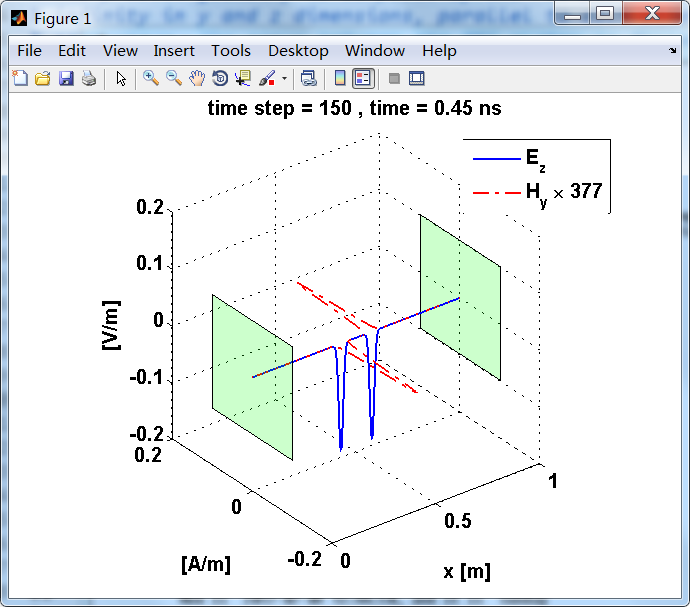
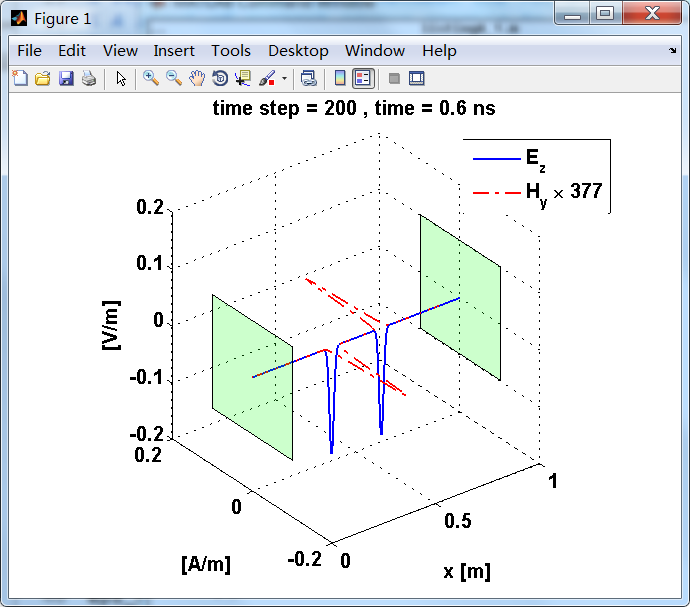
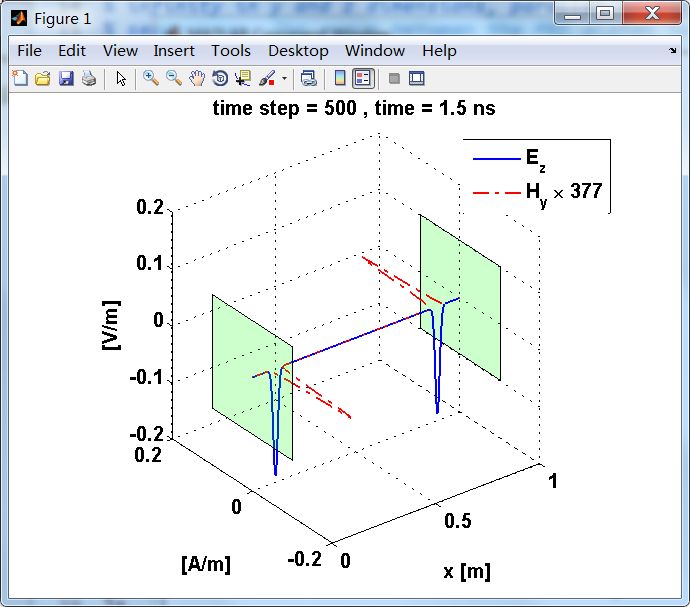
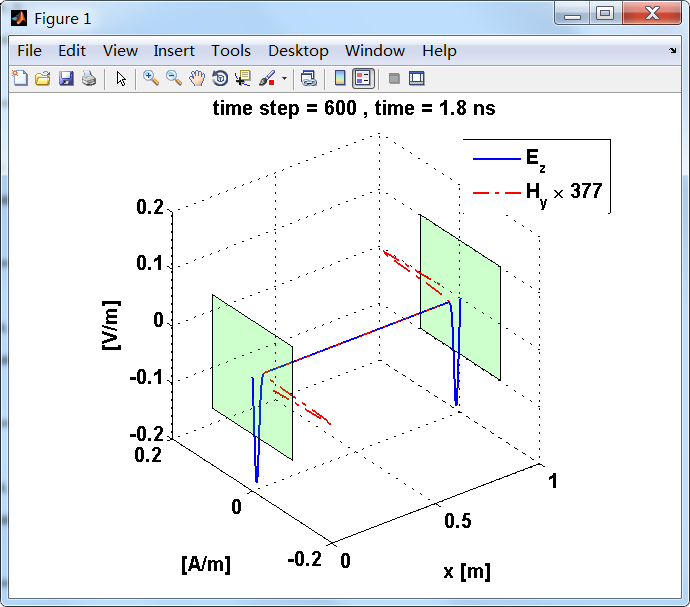
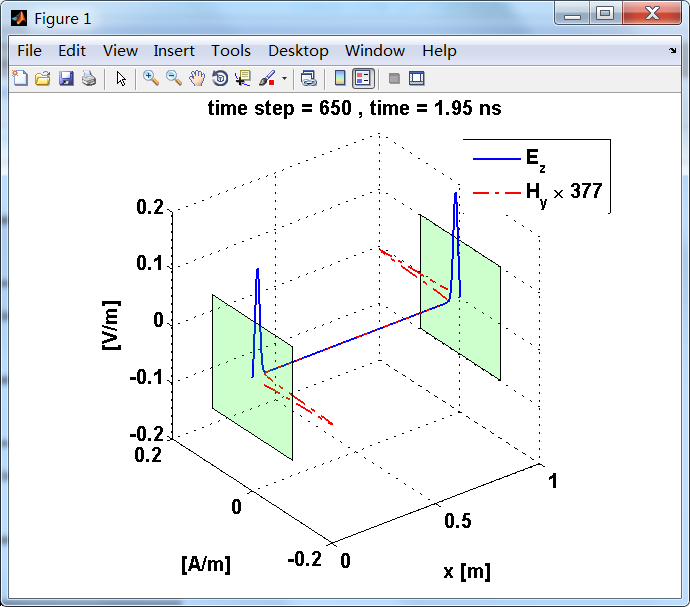
上图,从PEC板反射后,电场分量极性变反,磁场分量极性不变。
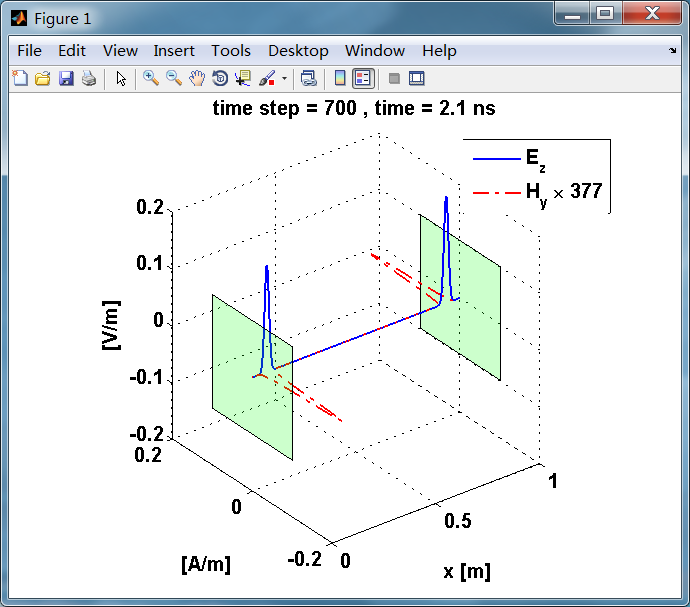
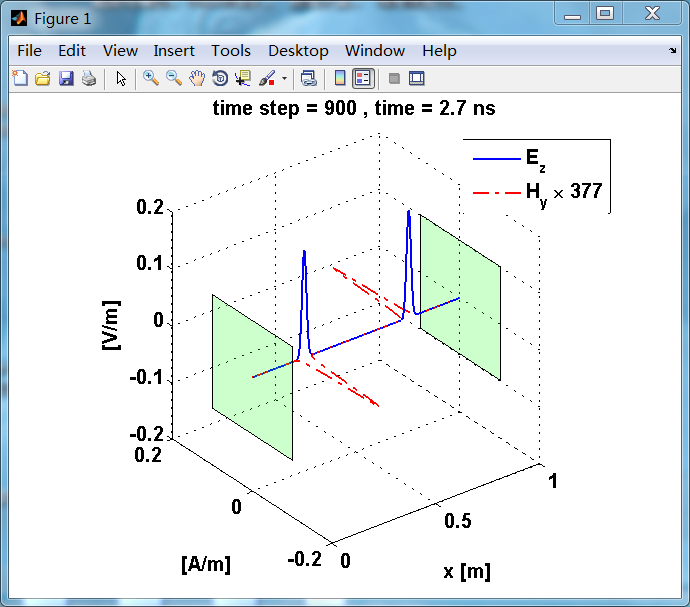
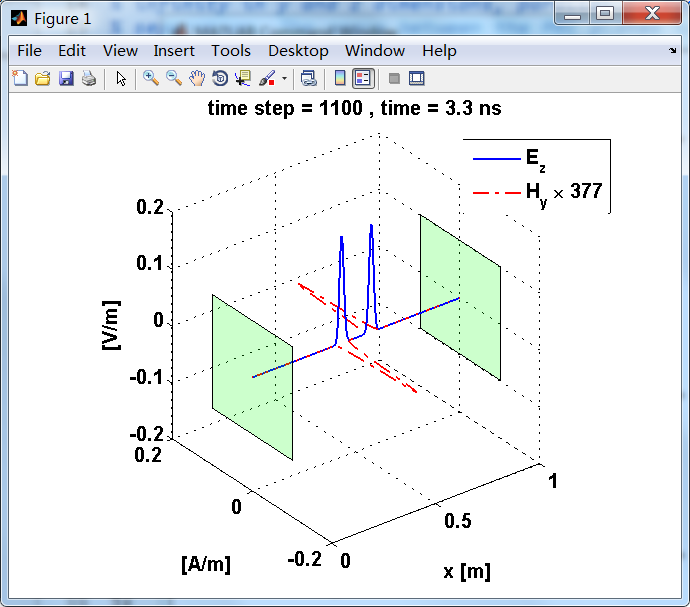

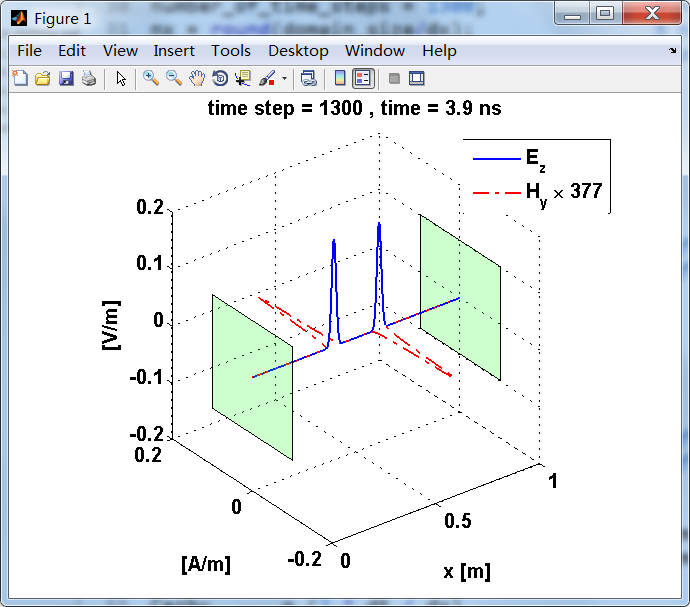
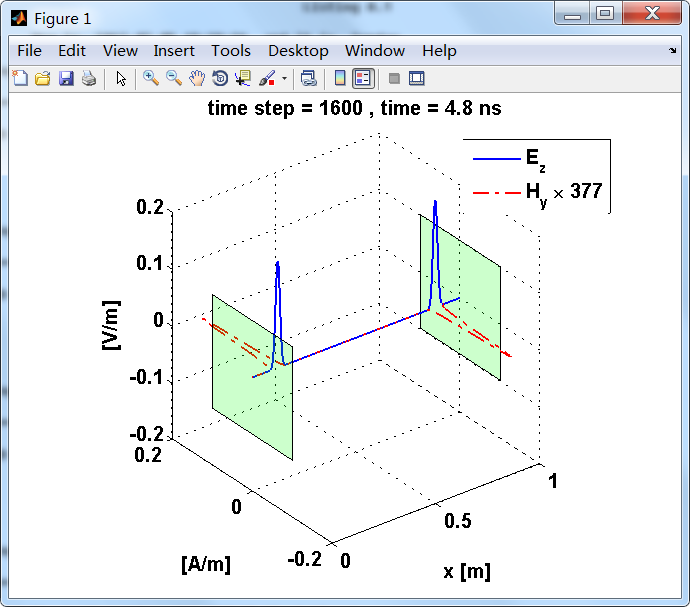
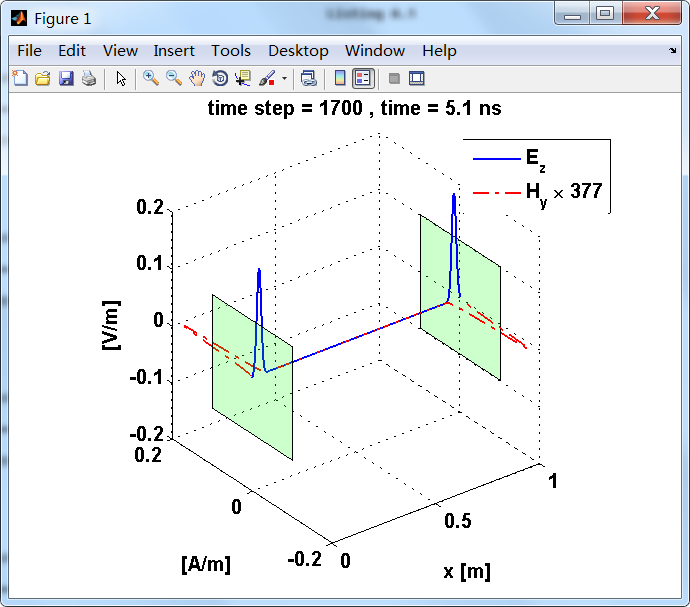
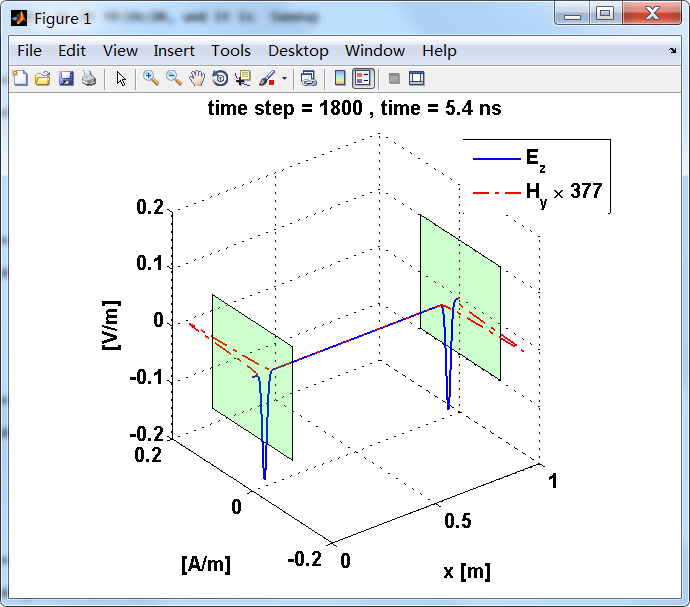
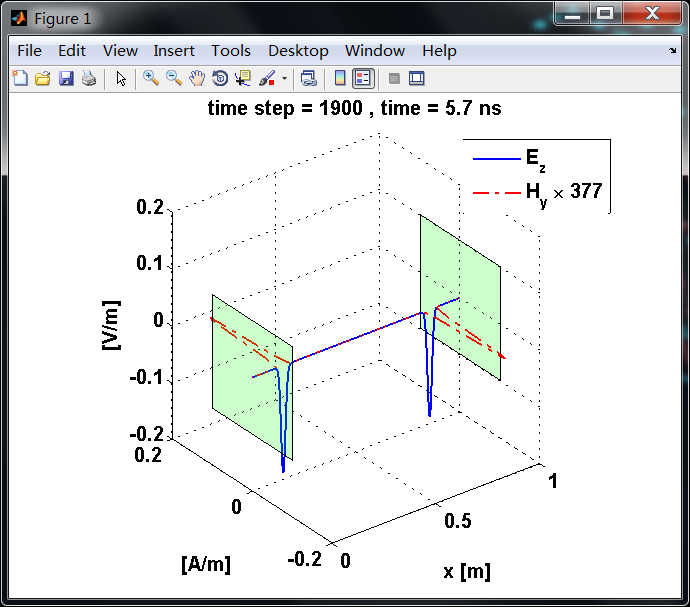
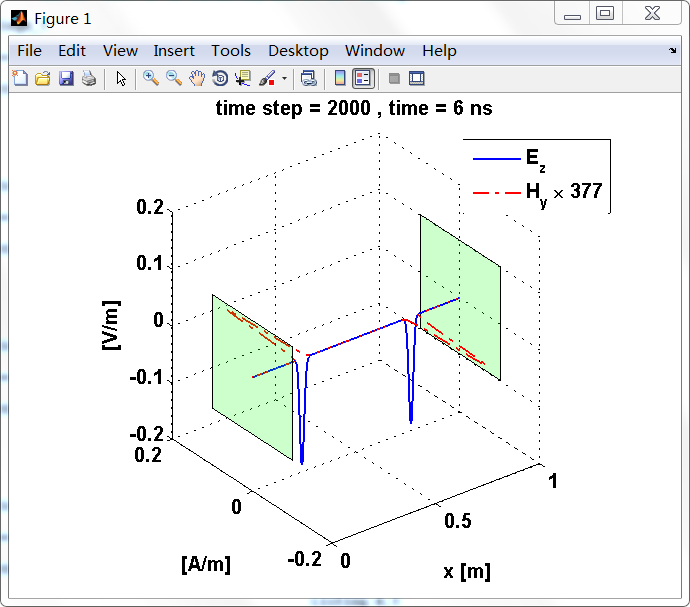
反射后,电场分量极性再次改变;
《FDTD electromagnetic field using MATLAB》读书笔记之 Figure 1.14的更多相关文章
- 《FDTD electromagnetic field using MATLAB》读书笔记 Figure 1.2
函数f(x)用采样间隔Δx=π/5进行采样,使用向前差商.向后差商和中心差商三种公式来近似一阶导数. 书中代码: %% ---------------------------------------- ...
- 《FDTD electromagnetic field using MATLAB》读书笔记之一阶、二阶偏导数差商近似
- 《FDTD electromagnetic field using MATLAB 》读书笔记001-差商种类
有限差分就是用差商代替微商,有3钟: 1.向前差商 2.向后差商 3.中心差商 上面三张途中虚线就是函数在x的精确微商(偏导数),直线就是用来代替精确 微商的差商格式.
- Python基础教程【读书笔记】 - 2016/7/14
希望通过博客园持续的更新,分享和记录Python基础知识到高级应用的点点滴滴! 第六波:第2章 列表和元组 [总览] 数据结构,是通过某种方式组织在一起的数据元素的集合,数据元素可以使数字或字符串 ...
- 读书笔记 effective c++ Item 14 对资源管理类的拷贝行为要谨慎
1. 自己实现一个资源管理类 Item 13中介绍了 “资源获取之时也是初始化之时(RAII)”的概念,这个概念被当作资源管理类的“脊柱“,也描述了auto_ptr和tr1::shared_ptr是如 ...
- TJI读书笔记17-字符串
TJI读书笔记17-字符串 不可变的String 重载”+”和StringBuilder toString()方法的一个坑 String上的操作 格式化输出 Formatter类 字符串操作可能是计算 ...
- 《Linux内核设计与实现》 Chapter4 读书笔记
<Linux内核设计与实现> Chapter4 读书笔记 调度程序负责决定将哪个进程投入运行,何时运行以及运行多长时间,进程调度程序可看做在可运行态进程之间分配有限的处理器时间资源的内核子 ...
- ANTLR3完全参考指南读书笔记[06]
前言 这段时间在公司忙的跟狗似的,但忙的是没多少技术含量的活儿. 终于将AST IR和tree grammar过了一遍,计划明天写完这部分的读书笔记. 内容 1 内部表示AST构建 2 树文法 ...
- 认识CLR [《CLR via C#》读书笔记]
认识CLR [<CLR via C#>读书笔记] <CLR via C#>读书笔记 什么是CLR CLR的基本概念 通用语言运行平台(Common Language Runti ...
随机推荐
- cocos-lua基础学习(八)Layer类学习笔记
创建 local layer = cc.Layer:create() local layer1 = cc.LayerColor:create(cc.c4b(192, 0, 0, 255), s.wid ...
- Java基础教程:IO流与文件基础
Java:IO流与文件基础 说明: 本章内容将会持续更新,大家可以关注一下并给我提供建议,谢谢啦. 走进流 什么是流 流:从源到目的地的字节的有序序列. 在Java中,可以从其中读取一个字节序列的对象 ...
- Bootstrap风格zTree树形菜单插件
这是一款bootstrap风格jQuery zTree树形菜单插件,支持自定义编辑.添加列表菜单.删除列表等功能的jQuery树形菜单代码.在线演示 具体代码实现: <!DOCTYPE html ...
- Django学习笔记之Ajax与文件上传
Ajax简介 AJAX(Asynchronous Javascript And XML)翻译成中文就是“异步Javascript和XML”.即使用Javascript语言与服务器进行异步交互,传输 ...
- 20145122《Java程序设计》第6周学习总结
教材学习内容总结 1.Java是以串流(Stream)的方式来处理输入与输出. 2.串流是一种抽象观念,从键盘输入资料,将处理结果输入档案,以及读取档案的内容等动作皆视为串流的处理. 3.在JAVA中 ...
- MSF基础攻击实践报告
MSF基础攻击实践 MSF的六个模块:exploit,encoder,payload,aux,post,nops exploit——渗透攻击模块 测试者利用它来攻击一个系统,程序,或服务,以获得开发者 ...
- 在 if 条件句中使用向量
上述例子的函数中,都只输入了单一值.如果我们提供一个向量,那么这个函数将产生警告,这是因为 if 语句不能与多值向量共存.check_ _positive(c(1,-1,0))## Warning i ...
- JavaScript权威指南--正则表达式
知识要点 正则表达式,是一个描述字符模式的对象.javascript的RegExp类表示正则表达式,String和RegExp都定义了方法,后者使用正则表达式进行强大的模式匹配和文本检索与替换功能. ...
- 获取和设置HTML标签中的数据
- ABP zero出现Default language is not defined!的错误的解决方法
打开程序包管理器控制台,把EntityFramework作为默认项目,并且执行Update-Database命令 再运行项目
