Codeforces Round #394 (Div. 2) A,B,C,D,E
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
On her way to programming school tiger Dasha faced her first test — a huge staircase!

The steps were numbered from one to infinity. As we know, tigers are very fond of all striped things, it is possible that it has something to do with their color. So on some interval of her way she calculated two values — the number of steps with even and odd numbers.
You need to check whether there is an interval of steps from the l-th to the r-th (1 ≤ l ≤ r), for which values that Dasha has found are correct.
In the only line you are given two integers a, b (0 ≤ a, b ≤ 100) — the number of even and odd steps, accordingly.
In the only line print "YES", if the interval of steps described above exists, and "NO" otherwise.
2 3
YES
3 1
NO
In the first example one of suitable intervals is from 1 to 5. The interval contains two even steps — 2 and 4, and three odd: 1, 3 and 5.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
#define eps 1e-14
#define bug(x) cout<<"bug"<<" "<<x<<endl;
const int N=1e5+,M=1e6+,inf=1e9+,mod=1e9+;
const ll INF=1e18+;
int main()
{
int a,b;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
if(a==&&b==)
return puts("NO");
if(abs(a-b)<=)
printf("YES\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Running with barriers on the circle track is very popular in the country where Dasha lives, so no wonder that on her way to classes she saw the following situation:
The track is the circle with length L, in distinct points of which there are n barriers. Athlete always run the track in counterclockwise direction if you look on him from above. All barriers are located at integer distance from each other along the track.
Her friends the parrot Kefa and the leopard Sasha participated in competitions and each of them ran one lap. Each of the friends started from some integral point on the track. Both friends wrote the distance from their start along the track to each of the n barriers. Thus, each of them wrote n integers in the ascending order, each of them was between 0 and L - 1, inclusively.
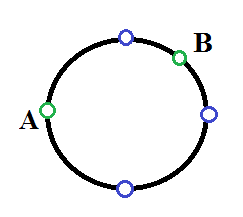 Consider an example. Let L = 8, blue points are barriers, and green points are Kefa's start (A) and Sasha's start (B). Then Kefa writes down the sequence[2, 4, 6], and Sasha writes down [1, 5, 7].
Consider an example. Let L = 8, blue points are barriers, and green points are Kefa's start (A) and Sasha's start (B). Then Kefa writes down the sequence[2, 4, 6], and Sasha writes down [1, 5, 7].
There are several tracks in the country, all of them have same length and same number of barriers, but the positions of the barriers can differ among different tracks. Now Dasha is interested if it is possible that Kefa and Sasha ran the same track or they participated on different tracks.
Write the program which will check that Kefa's and Sasha's tracks coincide (it means that one can be obtained from the other by changing the start position). Note that they always run the track in one direction — counterclockwise, if you look on a track from above.
The first line contains two integers n and L (1 ≤ n ≤ 50, n ≤ L ≤ 100) — the number of barriers on a track and its length.
The second line contains n distinct integers in the ascending order — the distance from Kefa's start to each barrier in the order of its appearance. All integers are in the range from 0 to L - 1 inclusively.
The second line contains n distinct integers in the ascending order — the distance from Sasha's start to each barrier in the order of its overcoming. All integers are in the range from 0 to L - 1 inclusively.
Print "YES" (without quotes), if Kefa and Sasha ran the coinciding tracks (it means that the position of all barriers coincides, if they start running from the same points on the track). Otherwise print "NO" (without quotes).
3 8
2 4 6
1 5 7
YES
4 9
2 3 5 8
0 1 3 6
YES
2 4
1 3
1 2
NO
The first test is analyzed in the statement.
暴力;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
#define eps 1e-14
#define bug(x) cout<<"bug"<<" "<<x<<endl;
const int N=1e5+,M=1e6+,inf=1e9+,mod=1e9+;
const ll INF=1e18+;
int a[N],b[N];
int p[N],q[N];
int check(int n,int st)
{
int en=;
for(int i=st;i<=n;i++)
if(q[i]!=p[en++])
return ;
for(int i=;i<st;i++)
if(q[i]!=p[en++])
return ;
return ;
}
int main()
{
int n,l;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&l);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&b[i]);
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
p[i]=a[i+]-a[i];
p[n]=l-a[n]+a[];
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
q[i]=b[i+]-b[i];
q[n]=l-b[n]+b[];
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(check(n,i))
{
return puts("YES\n");
}
}
puts("NO\n");
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
After overcoming the stairs Dasha came to classes. She needed to write a password to begin her classes. The password is a string of length n which satisfies the following requirements:
- There is at least one digit in the string,
- There is at least one lowercase (small) letter of the Latin alphabet in the string,
- There is at least one of three listed symbols in the string: '#', '*', '&'.

Considering that these are programming classes it is not easy to write the password.
For each character of the password we have a fixed string of length m, on each of these n strings there is a pointer on some character. The i-th character displayed on the screen is the pointed character in the i-th string. Initially, all pointers are on characters with indexes1 in the corresponding strings (all positions are numbered starting from one).
During one operation Dasha can move a pointer in one string one character to the left or to the right. Strings are cyclic, it means that when we move the pointer which is on the character with index 1 to the left, it moves to the character with the index m, and when we move it to the right from the position m it moves to the position 1.
You need to determine the minimum number of operations necessary to make the string displayed on the screen a valid password.
The first line contains two integers n, m (3 ≤ n ≤ 50, 1 ≤ m ≤ 50) — the length of the password and the length of strings which are assigned to password symbols.
Each of the next n lines contains the string which is assigned to the i-th symbol of the password string. Its length is m, it consists of digits, lowercase English letters, and characters '#', '*' or '&'.
You have such input data that you can always get a valid password.
Print one integer — the minimum number of operations which is necessary to make the string, which is displayed on the screen, a valid password.
3 4
1**2
a3*0
c4**
1
5 5
#*&#*
*a1c&
&q2w*
#a3c#
*&#*&
3
In the first test it is necessary to move the pointer of the third string to one left to get the optimal answer.

In the second test one of possible algorithms will be:
- to move the pointer of the second symbol once to the right.
- to move the pointer of the third symbol twice to the right.

思路:打表找到每行可以到三种不同字符的最小距离;暴力枚举三种出现的情况
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
#define eps 1e-14
#define bug(x) cout<<"bug"<<" "<<x<<endl;
const int N=1e5+,M=1e6+,inf=1e8+,mod=1e9+;
const ll INF=1e18+;
char mp[][];
int n,m;
int dis[][];
void init()
{
for(int i=;i<;i++)
{
for(int j=;j<;j++)
dis[i][j]=inf;
}
}
int ans[];
int check(int x,int y,int z)
{
if(x==y||x==z||y==z)
return -;
ans[]=dis[x][]+dis[y][]+dis[z][];
ans[]=dis[x][]+dis[y][]+dis[z][];
ans[]=dis[x][]+dis[y][]+dis[z][];
ans[]=dis[x][]+dis[y][]+dis[z][];
ans[]=dis[x][]+dis[y][]+dis[z][];
ans[]=dis[x][]+dis[y][]+dis[z][];
int minn=ans[];
for(int i=;i<=;i++)
minn=min(minn,ans[i]);
return minn;
}
int main()
{
init();
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%s",mp[i]+);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=;j<=m;j++)
{
int dis1=j-;
int dis2=m+-j;
if(mp[i][j]>=''&&mp[i][j]<='')
dis[i][]=min(dis1,min(dis2,dis[i][]));
else if(mp[i][j]=='*'||mp[i][j]=='&'||mp[i][j]=='#')
dis[i][]=min(dis1,min(dis2,dis[i][]));
else
dis[i][]=min(dis1,min(dis2,dis[i][]));
}
}
int ans=inf;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=;j<=n;j++)
{
for(int k=;k<=n;k++)
{
int v=check(i,j,k);
if(v!=-)
{
ans=min(ans,v);
}
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Dasha logged into the system and began to solve problems. One of them is as follows:
Given two sequences a and b of length n each you need to write a sequence c of length n, the i-th element of which is calculated as follows: ci = bi - ai.
About sequences a and b we know that their elements are in the range from l to r. More formally, elements satisfy the following conditions: l ≤ ai ≤ r and l ≤ bi ≤ r. About sequence c we know that all its elements are distinct.

Dasha wrote a solution to that problem quickly, but checking her work on the standard test was not so easy. Due to an error in the test system only the sequence a and the compressed sequence of the sequence c were known from that test.
Let's give the definition to a compressed sequence. A compressed sequence of sequence c of length n is a sequence p of length n, so that pi equals to the number of integers which are less than or equal to ci in the sequence c. For example, for the sequencec = [250, 200, 300, 100, 50] the compressed sequence will be p = [4, 3, 5, 2, 1]. Pay attention that in c all integers are distinct. Consequently, the compressed sequence contains all integers from 1 to n inclusively.
Help Dasha to find any sequence b for which the calculated compressed sequence of sequence c is correct.
The first line contains three integers n, l, r (1 ≤ n ≤ 105, 1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ 109) — the length of the sequence and boundaries of the segment where the elements of sequences a and b are.
The next line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (l ≤ ai ≤ r) — the elements of the sequence a.
The next line contains n distinct integers p1, p2, ..., pn (1 ≤ pi ≤ n) — the compressed sequence of the sequence c.
If there is no the suitable sequence b, then in the only line print "-1".
Otherwise, in the only line print n integers — the elements of any suitable sequence b.
5 1 5
1 1 1 1 1
3 1 5 4 2
3 1 5 4 2
4 2 9
3 4 8 9
3 2 1 4
2 2 2 9
6 1 5
1 1 1 1 1 1
2 3 5 4 1 6
-1
Sequence b which was found in the second sample is suitable, because calculated sequencec = [2 - 3, 2 - 4, 2 - 8, 9 - 9] = [ - 1, - 2, - 6, 0] (note that ci = bi - ai) has compressed sequence equals to p = [3, 2, 1, 4].
思路:模拟,排个序;
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000")
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<string>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
#include<stack>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<list>
#include<set>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
#define eps 1e-14
#define bug(x) cout<<"bug"<<x<<endl;
const int N=2e5+,M=1e6+;
const ll INF=1e18+,mod=;
int n,l,r;
struct is
{
int a,p,pos;
bool operator <(const is &b)const
{
return p<b.p;
}
}a[N];
int ans[N];
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&l,&r);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i].a),a[i].pos=i;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i].p);
sort(a+,a++n);
int st=l-a[].a+ ;
ans[a[].pos]=l;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
st=max(st,l-a[i].a);
if(st+a[i].a>r)return puts("-1");
ans[a[i].pos]=st+a[i].a;
st++;
}
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
printf("%d ",ans[i]);
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Dasha decided to have a rest after solving the problem. She had been ready to start her favourite activity — origami, but remembered the puzzle that she could not solve.

The tree is a non-oriented connected graph without cycles. In particular, there always are n - 1 edges in a tree with n vertices.
The puzzle is to position the vertices at the points of the Cartesian plane with integral coordinates, so that the segments between the vertices connected by edges are parallel to the coordinate axes. Also, the intersection of segments is allowed only at their ends. Distinct vertices should be placed at different points.
Help Dasha to find any suitable way to position the tree vertices on the plane.
It is guaranteed that if it is possible to position the tree vertices on the plane without violating the condition which is given above, then you can do it by using points with integral coordinates which don't exceed 1018 in absolute value.
The first line contains single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 30) — the number of vertices in the tree.
Each of next n - 1 lines contains two integers ui, vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n) that mean that the i-th edge of the tree connects vertices ui and vi.
It is guaranteed that the described graph is a tree.
If the puzzle doesn't have a solution then in the only line print "NO".
Otherwise, the first line should contain "YES". The next n lines should contain the pair of integers xi, yi (|xi|, |yi| ≤ 1018) — the coordinates of the point which corresponds to the i-th vertex of the tree.
If there are several solutions, print any of them.
7
1 2
1 3
2 4
2 5
3 6
3 7
YES
0 0
1 0
0 1
2 0
1 -1
-1 1
0 2
6
1 2
2 3
2 4
2 5
2 6
NO
4
1 2
2 3
3 4
YES
3 3
4 3
5 3
6 3
In the first sample one of the possible positions of tree is:
题意:给你一棵树,平铺在二维坐标中,边平行x,y轴;
思路:利用类似二进制的思路;
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000")
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<string>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
#include<stack>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<list>
#include<set>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
#define eps 1e-14
#define bug(x) cout<<"bug"<<x<<endl;
const int N=2e5+,M=1e6+;
const ll INF=1e18+,mod=;
int n;
struct is
{
int v,next;
}edge[N<<];
int edg,head[N];
int du[N];
pair<ll,ll>ans[N];
int c(int x)
{
if(x&)return x+;
return x-;
}
void init()
{
memset(head,-,sizeof(head));
edg=;
}
int flag[N][];
void add(int u,int v)
{
edg++;
edge[edg].v=v;
edge[edg].next=head[u];
head[u]=edg;
}
void dfs(int u,int fa,ll len)
{
for(int i=head[u];i!=-;i=edge[i].next)
{
int v=edge[i].v;
if(v==fa)continue;
//cout<<u<<" "<<v<<endl;
for(int i=;i<=;i++)
{
if(flag[u][i])continue;
flag[v][c(i)]=;
flag[u][i]=;
//cout<<u<<" "<<v<<" "<<i<<" "<<len<<endl;
if(i==)
ans[v]=make_pair(ans[u].first,ans[u].second+len);
else if(i==)
ans[v]=make_pair(ans[u].first,ans[u].second-len);
else if(i==)
ans[v]=make_pair(ans[u].first-len,ans[u].second);
else if(i==)
ans[v]=make_pair(ans[u].first+len,ans[u].second);
break;
}
dfs(v,u,len>>);
}
}
int check()
{
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
if(du[i]>)
return ;
return ;
}
int main()
{
init();
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
int u,v;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
add(u,v),add(v,u);
du[u]++,du[v]++;
}
if(check()==)return puts("NO\n");
ans[]=make_pair(0LL,0LL);
dfs(,-,(1LL<<));
printf("YES\n");
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
printf("%lld %lld\n",ans[i].first,ans[i].second);
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
On her way to programming school tiger Dasha faced her first test — a huge staircase!

The steps were numbered from one to infinity. As we know, tigers are very fond of all striped things, it is possible that it has something to do with their color. So on some interval of her way she calculated two values — the number of steps with even and odd numbers.
You need to check whether there is an interval of steps from the l-th to the r-th (1 ≤ l ≤ r), for which values that Dasha has found are correct.
In the only line you are given two integers a, b (0 ≤ a, b ≤ 100) — the number of even and odd steps, accordingly.
In the only line print "YES", if the interval of steps described above exists, and "NO" otherwise.
2 3
YES
3 1
NO
In the first example one of suitable intervals is from 1 to 5. The interval contains two even steps — 2 and 4, and three odd: 1, 3 and 5.
Codeforces Round #394 (Div. 2) A,B,C,D,E的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #394 (Div. 2) E. Dasha and Puzzle(分形)
E. Dasha and Puzzle time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
- Codeforces Round #394 (Div. 2) 颓废记
昨天晚上(今天凌晨),又忍不住去打CF.(本蒟弱到只能打Div.2)... 我觉得我可以用一个词概括我这次的CF: 呵呵 刚一开赛,我就codeforces访问失败.. 后来好不容易能上了,两三分钟才 ...
- Codeforces Round #394 (Div. 2) E. Dasha and Puzzle 构造
E. Dasha and Puzzle 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/761/problem/E Description Dasha decided to h ...
- Codeforces Round #394 (Div. 2) D. Dasha and Very Difficult Problem 贪心
D. Dasha and Very Difficult Problem 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/761/problem/D Description Da ...
- Codeforces Round #394 (Div. 2) C. Dasha and Password 暴力
C. Dasha and Password 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/761/problem/C Description After overcoming ...
- Codeforces Round #394 (Div. 2) B. Dasha and friends 暴力
B. Dasha and friends 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/761/problem/B Description Running with barr ...
- Codeforces Round #394 (Div. 2) A. Dasha and Stairs 水题
A. Dasha and Stairs 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/761/problem/A Description On her way to prog ...
- Codeforces Round #394 (Div. 2) E. Dasha and Puzzle(dfs)
http://codeforces.com/contest/761/problem/E 题意:给出一棵树,现在要把这棵树上的结点放置在笛卡尔坐标上,使得每一条边与x轴平行或者与y轴平行.输出可行解,即 ...
- Codeforces Round #394 (Div. 2) C.Dasha and Password(暴力)
http://codeforces.com/contest/761/problem/C 题意:给出n个串,每个串的初始光标都位于0(列)处,怎样移动光标能够在凑出密码(每个串的光标位置表示一个密码的字 ...
- Codeforces Round #394 (Div. 2) B. Dasha and friends(暴力)
http://codeforces.com/contest/761/problem/B 题意: 有一个长度为l的环形跑道,跑道上有n个障碍,现在有2个人,给出他们每过多少米碰到障碍,判断他们跑的是不是 ...
随机推荐
- 170721、springboot编程之注解(annotation)列表
(1)@SpringBootApplication 申明让spring boot自动给程序进行必要的配置,这个配置等同于: @Configuration ,@EnableAutoConfigurati ...
- LightOj 1422 Halloween Costumes(区间DP)
B - Halloween Costumes Time Limit:2000MS Memory Limit:32768KB 64bit IO Format:%lld & %llu Submit ...
- 【Maven学习】Nexus私服代理其他第三方的Maven仓库
一.背景 [Maven学习]Nexus OSS私服仓库的安装和配置 http://blog.csdn.net/ouyang_peng/article/details/78793038 [Maven学习 ...
- mysql 大表优化
当MySQL单表记录数过大时,增删改查性能都会急剧下降,可以参考以下步骤来优化: 转自:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000006158186 单表优化 除非单表数据未 ...
- JavaScript类库汇总
日期处理Moment.js http://momentjs.cn/ http://momentjs.com/ nodejslinq,jslinq http://jslinq.codepl ...
- hive两大表关联优化试验
呼叫结果(call_result)与销售历史(sale_history)的join优化: CALL_RESULT: 32亿条/444G SALE_HISTORY:17亿条/439G 原逻辑 Map: ...
- stringbuffer 和 stringbuilder区别
stringbuffer 和 stringbuilder速度 小于 线程安全 线程非安全 单线程操作大量数据用stringbui ...
- C语言中exit函数的使用
exit() 结束当前进程/当前程序/,在整个程序中,只要调用 exit ,就结束 return() 是当前函数返回,当然如果是在主函数main, 自然也就结束当前进程了,如果不是,那就是退回上一 ...
- 在GUI程序中使用控制台的两种方法
win32程序启用控制台(控制台文件名:conout$,conin$,conerr$) //添加控制台,加入在程序构造函数中 AllocConsole(); freopen("conin$& ...
- zw版【转发·台湾nvp系列Delphi例程】HALCON SetIcon2
zw版[转发·台湾nvp系列Delphi例程]HALCON SetIcon2 procedure TForm1.Button1Click(Sender: TObject);var img : HUnt ...
