使用C#实现数据结构堆
一、 堆的介绍:
堆是用来排序的,通常是一个可以被看做一棵树的数组对象。堆满足已下特性:
1. 堆中某个节点的值总是不大于或不小于其父节点的值
任意节点的值小于(或大于)它的所有后裔,所以最小元(或最大元)在堆的根节点上(堆序性)。堆有大根堆和小根堆,将根节点最大的堆叫做最大堆或大根堆,根节点最小的堆叫做最小堆或小根堆。
2. 堆总是一棵完全二叉树
除了最底层,其他层的节点都被元素填满,且最底层尽可能地从左到右填入。
堆示意图:

将堆元素从上往下从左到右放进数组对象中,子父节点索引满足关系:
parentIndex = (index+1)/ 2 - 1;
childLeftIndex = parentIndex * 2 + 1;
childRightIndex = (parentIndex + 1) * 2;
其中:index为任一节点索引;parentIndex该节点父索引;childLeftIndex该父节点下的子左节点;childRightIndex该父节点下的子右节点。
创建堆的大概思路:
1. 向堆中添加元素:
加到数组尾处,循环比对其父节点值(大根堆和小根堆比对策略不一样),比对结果的目标索引不是父节点索引则交换子父节点元素,继续向上比对其父父节点…;直至比对过程中目标索引为父节点索引或达到根节点结束,新堆创建完成。
2. 向堆中取出元素:
取出根节点元素,并将堆末尾元素插入根节点(为了保证堆的完全二叉树特性),从根部再循环向下比对父节点、子左节点、子右节点值,比对结果目标索引不为父节点交换目标索引和父节点的值,向下继续比对;直至比对过程中目标索引为父节点索引或达到堆尾部结束,新堆创建完成。
二、 代码实现:
因为大根堆和小根堆只是比较策略不同,所以整合了两者,用的时候可以直接设置堆的类别;默认小根堆,默认比较器。实现代码如下:


1 public class Heap<T>
2 {
3 private T[] _array;//数组,存放堆数据
4 private int _count;//堆数据数量
5 private HeapType _typeName;//堆类型
6 private const int _DefaultCapacity = 4;//默认数组容量/最小容量
7 private const int _ShrinkThreshold = 50;//收缩阈值(百分比)
8 private const int _MinimumGrow = 4;//最小扩容量
9 private const int _GrowFactor = 200; // 数组扩容百分比,默认2倍
10 private IComparer<T> _comparer;//比较器
11 private Func<T, T, bool> _comparerFunc;//比较函数
12
13
14 //堆数据数量
15 public int Count => _count;
16 //堆类型
17 public HeapType TypeName => _typeName;
18
19
20 public Heap() : this(_DefaultCapacity, HeapType.MinHeap, null) { }
21 public Heap(int capacity) : this(capacity, HeapType.MinHeap, null) { }
22 public Heap(HeapType heapType) : this(_DefaultCapacity, heapType, null) { }
23 public Heap(int capacity, HeapType heapType, IComparer<T> comparer)
24 {
25 Init(capacity, heapType, comparer);
26 }
27 public Heap(IEnumerable<T> collection, HeapType heapType, IComparer<T> comparer)
28 {
29 if (collection == null)
30 throw new IndexOutOfRangeException();
31 Init(collection.Count(), heapType, comparer);
32 using (IEnumerator<T> en = collection.GetEnumerator())//避免T在GC堆中有非托管资源,GC不能释放,需手动
33 {
34 while (en.MoveNext())
35 Enqueue(en.Current);
36 }
37 }
38 private void Init(int capacity, HeapType heapType, IComparer<T> comparer)
39 {
40 if (capacity < 0)
41 throw new IndexOutOfRangeException();
42 _count = 0;
43 _array = new T[capacity];
44 _comparer = comparer ?? Comparer<T>.Default;
45 _typeName = heapType;
46 switch (heapType)
47 {
48 default:
49 case HeapType.MinHeap:
50 _comparerFunc = (T t1, T t2) => _comparer.Compare(t1, t2) > 0;//目标对象t2小
51 break;
52 case HeapType.MaxHeap:
53 _comparerFunc = (T t1, T t2) => _comparer.Compare(t1, t2) < 0;//目标对象t2大
54 break;
55 }
56 }
57
58
59 public T Dequeue()
60 {
61 if (_count == 0)
62 throw new InvalidOperationException();
63 T result = _array[0];
64 _array[0] = _array[--_count];
65 _array[_count] = default(T);
66
67 if (_array.Length > _DefaultCapacity && _count * 100 <= _array.Length * _ShrinkThreshold)//缩容
68 {
69 int newCapacity = Math.Max(_DefaultCapacity, (int)((long)_array.Length * (long)_ShrinkThreshold / 100));
70 SetCapacity(newCapacity);
71 }
72 AdjustHeap(_array, 0, _count);
73 return result;
74 }
75 public void Enqueue(T item)
76 {
77 if (_count >= _array.Length)//扩容
78 {
79 int newCapacity = Math.Max(_array.Length+_MinimumGrow, (int)((long)_array.Length * (long)_GrowFactor / 100));
80 SetCapacity(newCapacity);
81 }
82
83 _array[_count++] = item;
84 int parentIndex;
85 int targetIndex;
86 int targetCount = _count;
87 while (targetCount > 1)
88 {
89 parentIndex = targetCount / 2 - 1;
90 targetIndex = targetCount - 1;
91 if (!_comparerFunc.Invoke(_array[parentIndex], _array[targetIndex]))
92 break;
93 Swap(_array, parentIndex, targetIndex);
94 targetCount = parentIndex + 1;
95 }
96 }
97 private void AdjustHeap(T[] array, int parentIndex, int count)
98 {
99 if (_count < 2)
100 return;
101 int childLeftIndex = parentIndex * 2 + 1;
102 int childRightIndex = (parentIndex + 1) * 2;
103
104 int targetIndex = parentIndex;
105 if (childLeftIndex < count && _comparerFunc.Invoke(array[parentIndex], array[childLeftIndex]))
106 targetIndex = childLeftIndex;
107 if (childRightIndex < count && _comparerFunc.Invoke(array[targetIndex], array[childRightIndex]))
108 targetIndex = childRightIndex;
109 if (targetIndex != parentIndex)
110 {
111 Swap(_array, parentIndex, targetIndex);
112 AdjustHeap(_array, targetIndex, _count);
113 }
114 }
115
116 private void SetCapacity(int capacity)
117 {
118 T[] newArray = new T[capacity];
119 Array.Copy(_array, newArray, _count);
120 _array = newArray;
121 }
122
123 private void Swap(T[] array, int index1, int index2)
124 {
125 T temp = array[index1];
126 array[index1] = array[index2];
127 array[index2] = temp;
128 }
129
130 public void Clear()
131 {
132 Array.Clear(_array, 0, _count);
133 Init(_DefaultCapacity, HeapType.MinHeap, null);
134 }
135 }
136
137 public enum HeapType { MinHeap, MaxHeap }
三、 使用测试:
建一个Person类用来测试,例子中Person比较规则是:先按年龄比较,年龄相同再按身高比较。具体比较大小是由选择堆的类别进行不同的排序规则:如Person类中小根堆先按年龄小者排序,年龄相同者按身高大者排序;而使用大根堆则相反。两种比较器写法,前者直接使用默认比较器;后者需要将比较器注入到堆中。


1 public class Person : IComparable<Person>
2 {
3 public string name { get; set; }
4 public int Age { get; set; }
5
6 public int Height { get; set; }
7 public override string ToString()
8 {
9 return $"我叫{name},年龄{Age},身高{Height}";
10 }
11
12 //小根堆:先排年龄小,年龄相同,按身高大的先排;大根堆相反
13 public int CompareTo(Person other)
14 {
15 if (this.Age.CompareTo(other.Age) != 0)
16 return this.Age.CompareTo(other.Age);
17 else if (this.Height.CompareTo(other.Height) != 0)
18 return ~this.Height.CompareTo(other.Height);
19 else
20 return 0;
21 }
22 }
23
24 public class personComparer : IComparer<Person>
25 {
26 //大根堆:先排年龄大,年龄相同,按身高大的先排;小根堆相反
27 public int Compare(Person x, Person y)
28 {
29 if (x.Age.CompareTo(y.Age) != 0)
30 return x.Age.CompareTo(y.Age);
31 else if (x.Height.CompareTo(y.Height) != 0)
32 return x.Height.CompareTo(y.Height);
33 else
34 return 0;
35 }
36 }
主函数调用:


1 static void Main(string[] args)
2 {
3 int[] array = { 3, 5, 8, 3, 7, 1 };
4 Heap<int> heap0 = new Heap<int>(array, HeapType.MaxHeap, null);
5 Console.WriteLine(heap0.TypeName);
6 Console.WriteLine(heap0.Dequeue());
7 Console.WriteLine(heap0.Dequeue());
8 Console.WriteLine(heap0.Dequeue());
9 Console.WriteLine(heap0.Dequeue());
10 int length = heap0.Count;
11 for (int count = 0; count < length; count++)
12 {
13 Console.WriteLine(heap0.Dequeue());
14 }
15
16
17
18 Person person1 = new Person() { Age = 12, Height = 158, name = "张三" };
19 Person person2 = new Person() { Age = 13, Height = 160, name = "李四" };
20 Person person3 = new Person() { Age = 10, Height = 150, name = "王二" };
21 Person person4 = new Person() { Age = 10, Height = 152, name = "麻子" };
22 Person person5 = new Person() { Age = 12, Height = 150, name = "刘五" };
23 List<Person> people = new List<Person>();
24 people.Add(person1);
25 people.Add(person2);
26 people.Add(person3);
27 people.Add(person4);
28 people.Add(person5);
29 Heap<Person> heap2 = new Heap<Person>(people, HeapType.MinHeap, null);
30 Person person6 = new Person() { Age = 9, Height = 145, name = "赵六" };
31 heap2.Enqueue(person6);
32 Console.WriteLine(heap2.TypeName);
33 Console.WriteLine(heap2.Dequeue());
34 Console.WriteLine(heap2.Dequeue());
35 Console.WriteLine(heap2.Dequeue());
36 Console.WriteLine(heap2.Dequeue());
37
38
39 PersonComparer personComparer = new PersonComparer();
40 Heap<Person> heap3 = new Heap<Person>(1,HeapType.MaxHeap,personComparer);
41 heap3.Enqueue(person1);
42 heap3.Enqueue(person2);
43 heap3.Enqueue(person3);
44 heap3.Enqueue(person4);
45 heap3.Enqueue(person5);
46 heap3.Enqueue(person6);
47 Console.WriteLine(heap3.TypeName);
48 Console.WriteLine(heap3.Dequeue());
49 Console.WriteLine(heap3.Dequeue());
50 Console.WriteLine(heap3.Dequeue());
51 Console.WriteLine(heap3.Dequeue());
52
53
54
55 Console.ReadKey();
56 }
57
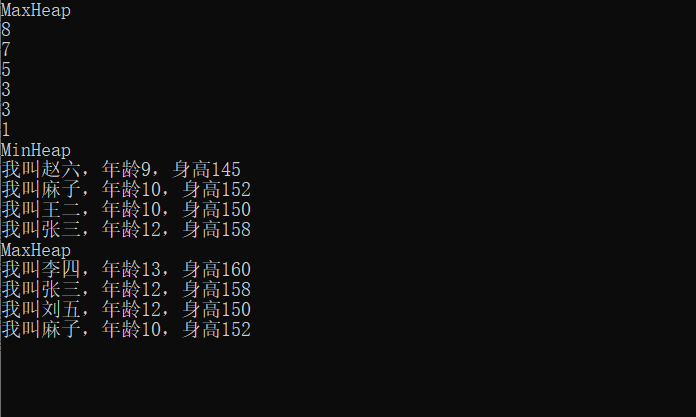
输出结果:
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq826364410/article/details/79770791
https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/dotnet/api/system.collections.generic.comparer-1?view=net-5.0
使用C#实现数据结构堆的更多相关文章
- 基本数据结构——堆(Heap)的基本概念及其操作
基本数据结构――堆的基本概念及其操作 小广告:福建安溪一中在线评测系统 Online Judge 在我刚听到堆这个名词的时候,我认为它是一堆东西的集合... 但其实吧它是利用完全二叉树的结构来维护一组 ...
- 数据结构-堆 Java实现
数据结构-堆 Java实现. 实现堆自动增长 /** * 数据结构-堆. 自动增长 * */ public class Heap<T extends Comparable> { priva ...
- C 数据结构堆
引言 - 数据结构堆 堆结构都很耳熟, 从堆排序到优先级队列, 我们总会看见它的身影. 相关的资料太多了, 堆 - https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%A0%86%E7 ...
- java数据结构----堆
1.堆:堆是一种树,由它实现的优先级队列的插入和删除的时间复杂度都是O(logn),用堆实现的优先级队列虽然和数组实现相比较删除慢了些,但插入的时间快的多了.当速度很重要且有很多插入操作时,可以选择堆 ...
- 数据结构 - 堆(Heap)
数据结构 - 堆(Heap) 1.堆的定义 堆的形式满足完全二叉树的定义: 若 i < ceil(n/2) ,则节点i为分支节点,否则为叶子节点 叶子节点只可能在最大的两层出现,而最大层次上的叶 ...
- [数据结构]——堆(Heap)、堆排序和TopK
堆(heap),是一种特殊的数据结构.之所以特殊,因为堆的形象化是一个棵完全二叉树,并且满足任意节点始终不大于(或者不小于)左右子节点(有别于二叉搜索树Binary Search Tree).其中,前 ...
- 数据结构&堆&heap&priority_queue&实现
目录 什么是堆? 大根堆 小根堆 堆的操作 STL queue 什么是堆? 堆是一种数据结构,可以用来实现优先队列 大根堆 大根堆,顾名思义就是根节点最大.我们先用小根堆的建堆过程学习堆的思想. 小根 ...
- 基本数据结构 —— 堆以及堆排序(C++实现)
目录 什么是堆 堆的存储 堆的操作 结构体定义 判断是否为空 往堆中插入元素 从堆中删除元素 取出堆中最大的元素 堆排序 测试代码 例题 参考资料 什么是堆 堆(英语:heap)是计算机科学中一类特殊 ...
- 数据结构——堆(Heap)大根堆、小根堆
目录 Heap是一种数据结构具有以下的特点: 1)完全二叉树: 2)heap中存储的值是偏序: Min-heap: 父节点的值小于或等于子节点的值: Max-heap: 父节点的值大于或等于子节点的值 ...
- 第二十八篇 玩转数据结构——堆(Heap)和有优先队列(Priority Queue)
1.. 优先队列(Priority Queue) 优先队列与普通队列的区别:普通队列遵循先进先出的原则:优先队列的出队顺序与入队顺序无关,与优先级相关. 优先队列可以使用队列的接口,只是在 ...
随机推荐
- Python之 time 与 datetime模块
time与datetime模块 一.time 在Python中,通常有这几种方式来表示时间: 时间戳(timestamp):通常来说,时间戳表示的是从1970年1月1日00:00:00开始按秒计算的偏 ...
- dede 织梦的安装 出现dir
安装dede系统.(如果您已经安装,请跳过本步.)直接运行:http://您的域名/install如果没有出现该页面,而是出现了一个空白页面写着dir 那么请删除install文件夹中的 instal ...
- Spring Cloud Gateway 跨域 CORS 配置方式实现
网上找了一堆文章全是说这样写无效 globalcors: cors-configurations: '[/**]': allowCredentials: true allowedOriginPatte ...
- Jmeter(三十五) - 从入门到精通进阶篇 - 关联(详解教程)
1.简介 上一篇中介绍了如果想要同时发送多条请求,那么怎样才能让每条数据某些请求参数改变呢.这就用到了jMeter参数化.在实际测试场景中,我们往往还有这样的需求,登录后服务器响应的token作为下次 ...
- 【IMPDP】ORA-31655
出现ora-31655错误的情况是因为不是同一个schema,导致的问题产生 解决的方法; 在导入语句最后添加上remap_schema=old:new 着old是原schema,也就是导出的用户名, ...
- Spring-AOP为类增加新的功能
适配器的简单应用实现: 比如:有一个类Car,在类中有两个属性一个为汽车名name,另一个为速度speed.其行为为run(). 现在有一辆车BMWCar 增加了GPS功能.如下实现: 基本类: pu ...
- Ubuntu18.04完全卸载mysql5.7并安装mysql8.0的安装方法
Ubuntu18.04版本下,如果直接输入: sudo apt install mysql-server 命令,会默认安装mysql5.7版本,安装过程并没有提示输入密码,安装完成后也无法正常登录,这 ...
- Markdown里常用的HTML元素
转义:\ 换行:<br/> 红色文字:<font color=#FF0000>字体改成红色了</font> A标签 新窗口:<a href="xxx ...
- 03. struts2中Action配置的各项默认值
Action中的各项默认值 Action各项配置 <action name="helloworld" class="com.liuyong666.action.He ...
- C++中输出变量类型的方法
C++中输出变量类型的方法 在c++中输出变量或者数据类型,使用typeid().name()的方法.如下例子: #include <iostream> #include <stri ...
