Tensorflow:DCGAN生成手写数字
参考地址:https://blog.csdn.net/miracle_ma/article/details/78305991
使用DCGAN(deep convolutional GAN):深度卷积GAN
网络结构如下:
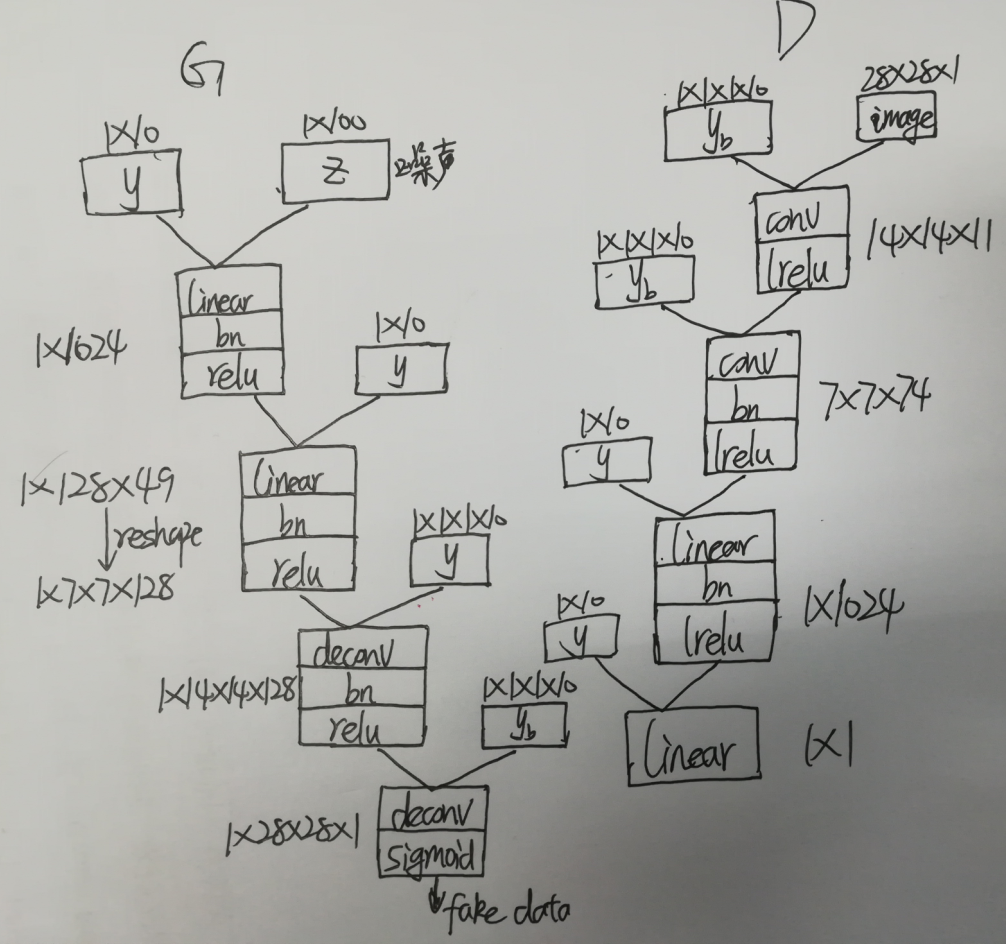
代码分成四个文件:
- 读入文件 read_data.py
- 配置线性层,卷积层,反卷积层 ops.py
- 构建生成器和判别器模型 model.py
- 训练模型 train.py
使用的layer种类有:
- conv(卷积层)
- deconv(反卷积层)
- linear(线性层)
- batch_norm(批量归一化层)
- lrelu/relu/sigmoid(非线性函数层)
一、读入文件(read_data.py)
import os
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf def read_data():
data_dir = "data\mnist"
#read training data
fd = open(os.path.join(data_dir,"train-images.idx3-ubyte"))
loaded = np.fromfile(file = fd, dtype = np.uint8)
trainX = loaded[16:].reshape((60000, 28, 28, 1)).astype(np.float) fd = open(os.path.join(data_dir,"train-labels.idx1-ubyte"))
loaded = np.fromfile(file = fd, dtype = np.uint8)
trainY = loaded[8:].reshape((60000)).astype(np.float) #read test data
fd = open(os.path.join(data_dir,"t10k-images.idx3-ubyte"))
loaded = np.fromfile(file = fd, dtype = np.uint8)
testX = loaded[16:].reshape((10000, 28, 28, 1)).astype(np.float) fd = open(os.path.join(data_dir,"t10k-labels.idx1-ubyte"))
loaded = np.fromfile(file = fd, dtype = np.uint8)
testY = loaded[8:].reshape((10000)).astype(np.float) # 将两个集合合并成70000大小的数据集
X = np.concatenate((trainX, testX), axis = 0)
y = np.concatenate((trainY, testY), axis = 0) print(X[:2])
#set the random seed
seed = 233
np.random.seed(seed)
np.random.shuffle(X)
np.random.seed(seed)
np.random.shuffle(y) return X/255, y
新建一个data文件夹,存放mnist数据集。读入训练集和测试集,将两个集合合并成一个70000的数据集,设置相同的随机种子,保证两个集合随机成相同的顺序。最后把X归一化到 [0, 1] 之间
二、配置线性层,卷积层,反卷积层 (ops.py)
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.contrib.layers.python.layers import batch_norm as batch_norm def linear_layer(value, output_dim, name = 'linear_connected'):
with tf.variable_scope(name):
try:
# 线性层的权重
# 名称:weights
# shape = [int(value.get_shape()[1]), output_dim], 我们需要传入最后输出多少维,也即是output_dim的值
# 初始化:使用标准正态截断函数 标准差是0.02
weights = tf.get_variable('weights',
[int(value.get_shape()[1]), output_dim],
initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev = 0.02))
# 线性层的偏置
# 名称:biases
# shape = [output_dim], 偏置与输出的维度相同
# 初始化:使用常量初始化 初始化为0
biases = tf.get_variable('biases',
[output_dim], initializer = tf.constant_initializer(0.0))
except ValueError:
tf.get_variable_scope().reuse_variables()
weights = tf.get_variable('weights',
[int(value.get_shape()[1]), output_dim],
initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev = 0.02))
biases = tf.get_variable('biases',
[output_dim], initializer = tf.constant_initializer(0.0))
return tf.matmul(value, weights) + biases def conv2d(value, output_dim, k_h = 5, k_w = 5, strides = [1,1,1,1], name = "conv2d"):
with tf.variable_scope(name):
try:
# 反卷积层的权重
# 名称:weights
# [5, 5, 输入的维度, 输出的维度]
# 初始化:使用标准正态截断函数 标准差是0.02
weights = tf.get_variable('weights',
[k_h, k_w, int(value.get_shape()[-1]), output_dim],
initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev = 0.02))
# 线性层的偏置
# 名称:biases
# shape = [output_shape[-1]], 偏置与输出的维度相同
# 初始化:使用常量初始化 初始化为0
biases = tf.get_variable('biases',
[output_dim], initializer = tf.constant_initializer(0.0))
except ValueError:
tf.get_variable_scope().reuse_variables()
weights = tf.get_variable('weights',
[k_h, k_w, int(value.get_shape()[-1]), output_dim],
initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev = 0.02))
biases = tf.get_variable('biases',
[output_dim], initializer = tf.constant_initializer(0.0))
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(value, weights, strides = strides, padding = "SAME")
conv = tf.reshape(tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases), conv.get_shape())
return conv def deconv2d(value, output_shape, k_h = 5, k_w = 5, strides = [1,1,1,1], name = "deconv2d"):
with tf.variable_scope(name):
try:
# 反卷积层的权重
# filter : [height, width, output_channels, in_channels]
# 名称:weights
# [5, 5, 输出的维度, 输入的维度]
# 初始化:使用标准正态截断函数 标准差是0.02
weights = tf.get_variable('weights',
[k_h, k_w, output_shape[-1], int(value.get_shape()[-1])],
initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev = 0.02))
# 线性层的偏置
# 名称:biases
# shape = [output_shape[-1]], 偏置与输出的维度相同
# 初始化:使用常量初始化 初始化为0
biases = tf.get_variable('biases',
[output_shape[-1]], initializer = tf.constant_initializer(0.0))
except ValueError:
tf.get_variable_scope().reuse_variables()
weights = tf.get_variable('weights',
[k_h, k_w, output_shape[-1], int(value.get_shape()[-1])],
initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev = 0.02))
biases = tf.get_variable('biases',
[output_shape[-1]], initializer = tf.constant_initializer(0.0))
deconv = tf.nn.conv2d_transpose(value, weights, output_shape, strides = strides)
deconv = tf.reshape(tf.nn.bias_add(deconv, biases), deconv.get_shape())
return deconv def conv_cond_concat(value, cond, name = 'concat'):
value_shapes = value.get_shape().as_list()
cond_shapes = cond.get_shape().as_list() with tf.variable_scope(name):
return tf.concat([value, cond * tf.ones(value_shapes[0:3] + cond_shapes[3:])], 3, name = name) # 批量归一化层
def batch_norm_layer(value, is_train = True, name = 'batch_norm'):
with tf.variable_scope(name) as scope:
if is_train:
return batch_norm(value, decay = 0.9, epsilon = 1e-5, scale = True,
is_training = is_train, updates_collections = None, scope = scope)
else :
return batch_norm(value, decay = 0.9, epsilon = 1e-5, scale = True,
is_training = is_train, reuse = True,
updates_collections = None, scope = scope) def lrelu(x, leak = 0.2, name = 'lrelu'):
with tf.variable_scope(name):
return tf.maximum(x, x*leak, name = name)
主要就是配置各个层的权重和参数,conv_cond_concat是为了用于卷积层计算的四维数据[batch_size, w, h, c]和约束条件y连接起来的操作,需要把两个数据的前三维转化到一样大小才能使用tf.concat(拼接函数)
lrelu是relu的改良版。代码中a = 0.2
三、构建生成器和判别器模型(model.py)
import tensorflow as tf
from ops import * BATCH_SIZE = 64 # 生成器模型
def generator(z, y,train = True):
with tf.variable_scope('generator', reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE):
# 生成器的输入,z是 1 * 100 维的噪声
yb = tf.reshape(y, [BATCH_SIZE, 1, 1, 10], name = 'g_yb')
# 将噪声 z 和 y 拼接起来
z_y = tf.concat([z,y], 1, name = 'g_z_concat_y') # 经过线性层,z_y 变成1024维
linear1 = linear_layer(z_y, 1024, name = 'g_linear_layer1')
# 先批量归一化,然后经过relu层,得 bn1
bn1 = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm_layer(linear1, is_train = True, name = 'g_bn1')) # 将 bn1 与 y 拼接在一起
bn1_y = tf.concat([bn1, y], 1 ,name = 'g_bn1_concat_y')
# 经过线性层,变成128 * 49
linear2 = linear_layer(bn1_y, 128*49, name = 'g_linear_layer2')
# 先批量归一化,然后经过relu层,得 bn2
bn2 = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm_layer(linear2, is_train = True, name = 'g_bn2'))
# reshape成 7 * 7 * 128
bn2_re = tf.reshape(bn2, [BATCH_SIZE, 7, 7, 128], name = 'g_bn2_reshape') # 将 bn2_re 与 yb 连接起来
bn2_yb = conv_cond_concat(bn2_re, yb, name = 'g_bn2_concat_yb')
# 经过反卷积 步长设为2,height和width 都翻倍
deconv1 = deconv2d(bn2_yb, [BATCH_SIZE, 14, 14, 128], strides = [1, 2, 2, 1], name = 'g_deconv1')
# 先批量归一化,然后经过relu层,得 bn3
bn3 = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm_layer(deconv1, is_train = True, name = 'g_bn3')) # 将 bn2_re 与 yb 连接起来
bn3_yb = conv_cond_concat(bn3, yb, name = 'g_bn3_concat_yb')
# 经过反卷积 步长设为2,height和width 都翻倍
deconv2 = deconv2d(bn3_yb, [BATCH_SIZE, 28, 28, 1], strides = [1, 2, 2, 1], name = 'g_deconv2') # 经过sigmoid层
return tf.nn.sigmoid(deconv2) # 判别器模型
def discriminator(image, y, reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE, train = True):
with tf.variable_scope('discriminator', reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE):
# 判别器有两个输入,一个是真实图片,另一个是生成的图片,都是 28 * 28
yb = tf.reshape(y, [BATCH_SIZE, 1, 1, 10], name = 'd_yb')
# 将 image 与 yb 连接起来
image_yb = conv_cond_concat(image, yb, name = 'd_image_concat_yb')
# 卷积:步长为2 14 * 14 * 11
conv1 = conv2d(image_yb, 11, strides = [1, 2, 2, 1], name = 'd_conv1')
# 经过 lrelu 层
lr1 = lrelu(conv1, name = 'd_lrelu1') # 将 lr1 与 yb 连接起来
lr1_yb = conv_cond_concat(lr1, yb, name = 'd_lr1_concat_yb')
# 卷积:步长为2 7 * 7 * 74
conv2 = conv2d(lr1_yb, 74, strides = [1, 2, 2, 1], name = 'd_conv2')
# 批量归一化
bn1 = batch_norm_layer(conv2, is_train = True, name = 'd_bn1')
# 经过 lrelu 层
lr2 = lrelu(bn1, name = 'd_lrelu2')
lr2_re = tf.reshape(lr2, [BATCH_SIZE, -1], name = 'd_lr2_reshape') # 将 lr2_re 与 y 连接起来
lr2_y = tf.concat([lr2_re, y], 1, name = 'd_lr2_concat_y')
# 经过线性层 变成 1 * 1024
linear1 = linear_layer(lr2_y, 1024, name = 'd_linear_layer1')
# 批量归一化
bn2 = batch_norm_layer(linear1, is_train = True, name = 'd_bn2')
# 经过 lrelu 层
lr3 = lrelu(bn2, name = 'd_lrelu3') lr3_y = tf.concat([lr3, y], 1, name = 'd_lr3_concat_y')
linear2 = linear_layer(lr3_y, 1, name = 'd_linear_layer2') return linear2 def sampler(z, y, train = True):
tf.get_variable_scope().reuse_variables()
return generator(z, y, train = train)
按照模型图实现生成器G,返回时用到了sigmoid,将输出值规范到(0, 1)与前面输入图像的范围一致。
判别器D:
1、 设置reuse变量(变量重复使用)。判别器有两个输入。对于同一个D,先喂给它real data(真实的图像),然后喂给它fake data(生成器生成的假图像)。在一次train_step里涉及到了两次D变量的重复使用,所以需要设置变量共享。
2、返回值没有使用sigmoid,因为训练中使用了sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits来计算loss
四、训练模型
import scipy.misc
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import os
from read_data import *
from ops import *
from model import * BATCH_SIZE = 64 # 保存图片,将图片拼接在一起
def save_images(images, size, path):
img = (images + 1.0)/2.0
h, w = img.shape[1], img.shape[2] merge_img = np.zeros((h * size[0], w * size[1], 3)) for idx, image in enumerate(images):
i = idx % size[1]
j = idx // size[1]
merge_img[j*h:j*h+h,i*w:i*w+w,:] = image return scipy.misc.imsave(path, merge_img) def train(): #read data
X, Y = read_data() #global_step to record the step of training
global_step = tf.Variable(0, name = 'global_step', trainable = True) # 创建placeholder
y = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [BATCH_SIZE], name = 'y')
_y = tf.one_hot(y, depth = 10, on_value=None, off_value=None, axis=None, dtype=None, name='one_hot')
z = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [BATCH_SIZE, 100], name = 'z')
images = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [BATCH_SIZE, 28, 28, 1], name = 'images') # 用噪声生成图片
G = generator(z, _y)
# 用真实图片训练判别器
D = discriminator(images, _y)
# 用生成的加图片G训练判别器
_D = discriminator(G, _y) # 计算损失值,使用 sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits
# 真实图片在判别器里产生的loss,我们希望真实图片在判别器里的label趋向于1
d_loss_real = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits = D, labels = tf.ones_like(D))) # 假图片在判别器里产生的loss,我们希望假图片在判别器里的label趋向于0
d_loss_fake = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits = _D, labels = tf.zeros_like(_D))) # 假图片在判别器上的结果,我们希望它以假乱真,希望它尽可能接近于1
g_loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits = _D, labels = tf.ones_like(_D))) # 判别器的总 loss
d_loss = d_loss_real + d_loss_fake t_vars = tf.trainable_variables()
d_vars = [var for var in t_vars if 'd_' in var.name]
g_vars = [var for var in t_vars if 'g_' in var.name] with tf.variable_scope(tf.get_variable_scope(), reuse = False):
# 优化判别器的 loss
d_optim = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.0002, beta1 = 0.5).minimize(d_loss, var_list = d_vars, global_step = global_step)
# 优化生成器的 loss
g_optim = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.0002, beta2 = 0.5).minimize(g_loss, var_list = g_vars, global_step = global_step) #tensorborad
train_dir = 'logs'
z_sum = tf.summary.histogram("z",z)
d_sum = tf.summary.histogram("d",D)
d__sum = tf.summary.histogram("d_",_D)
g_sum = tf.summary.histogram("g", G) d_loss_real_sum = tf.summary.scalar("d_loss_real", d_loss_real)
d_loss_fake_sum = tf.summary.scalar("d_loss_fake", d_loss_fake)
g_loss_sum = tf.summary.scalar("g_loss", g_loss)
d_loss_sum = tf.summary.scalar("d_loss", d_loss) g_sum = tf.summary.merge([z_sum, d__sum, g_sum, d_loss_fake_sum, g_loss_sum])
d_sum = tf.summary.merge([z_sum, d_sum, d_loss_real_sum, d_loss_sum]) #initial
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(train_dir, sess.graph) #save
saver = tf.train.Saver()
# 保存模型
check_path = "./save/model.ckpt" #sample
sample_z = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, size = (BATCH_SIZE, 100))
sample_labels = Y[0:BATCH_SIZE] #make sample
sample = sampler(z, _y) #run
sess.run(init)
#saver.restore(sess.check_path) #train
for epoch in range(10):
batch_idx = int(70000/64)
for idx in range(batch_idx):
batch_images = X[idx*64:(idx+1)*64]
batch_labels = Y[idx*64:(idx+1)*64]
batch_z = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, size = (BATCH_SIZE, 100)) _, summary_str = sess.run([d_optim, d_sum],
feed_dict = {images: batch_images,
z: batch_z,
y: batch_labels})
writer.add_summary(summary_str, idx+1) _, summary_str = sess.run([g_optim, g_sum],
feed_dict = {images: batch_images,
z: batch_z,
y: batch_labels})
writer.add_summary(summary_str, idx+1) d_loss1 = d_loss_fake.eval({z: batch_z, y: batch_labels})
d_loss2 = d_loss_real.eval({images: batch_images, y:batch_labels})
D_loss = d_loss1 + d_loss2
G_loss = g_loss.eval({z: batch_z, y: batch_labels}) #every 20 batch output loss
if idx % 20 == 0:
print("Epoch: %d [%4d/%4d] d_loss: %.8f, g_loss: %.8f" % (epoch, idx, batch_idx, D_loss, G_loss)) #every 100 batch save a picture
if idx % 100 == 0:
sap = sess.run(sample, feed_dict = {z: sample_z, y: sample_labels})
samples_path = './sample/'
save_images(sap, [8,8], samples_path+'test_%d_epoch_%d.png' % (epoch, idx)) #every 500 batch save model
if idx % 500 == 0:
saver.save(sess, check_path, global_step = idx + 1)
sess.close() if __name__ == '__main__':
train()
模型的训练顺序是先generator生成fake data,然后real data喂给D训练,再把fake data喂给D训练
分别计算生成器和判别器的loss,其中判别器的loss = real loss + fake loss
一个batch中,训练一次D训练一次G。按理说应该训练k次D,训练一次G(为了方便就没有这么做了)
生成的效果图如下:
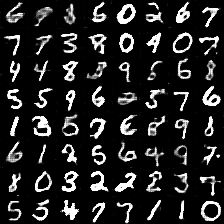
Tensorflow:DCGAN生成手写数字的更多相关文章
- Android+TensorFlow+CNN+MNIST 手写数字识别实现
Android+TensorFlow+CNN+MNIST 手写数字识别实现 SkySeraph 2018 Email:skyseraph00#163.com 更多精彩请直接访问SkySeraph个人站 ...
- 基于tensorflow的MNIST手写数字识别(二)--入门篇
http://www.jianshu.com/p/4195577585e6 基于tensorflow的MNIST手写字识别(一)--白话卷积神经网络模型 基于tensorflow的MNIST手写数字识 ...
- GAN实战笔记——第三章第一个GAN模型:生成手写数字
第一个GAN模型-生成手写数字 一.GAN的基础:对抗训练 形式上,生成器和判别器由可微函数表示如神经网络,他们都有自己的代价函数.这两个网络是利用判别器的损失记性反向传播训练.判别器努力使真实样本输 ...
- 基于TensorFlow的MNIST手写数字识别-初级
一:MNIST数据集 下载地址 MNIST是一个包含很多手写数字图片的数据集,一共4个二进制压缩文件 分别是test set images,test set labels,training se ...
- 卷积生成对抗网络(DCGAN)---生成手写数字
深度卷积生成对抗网络(DCGAN) ---- 生成 MNIST 手写图片 1.基本原理 生成对抗网络(GAN)由2个重要的部分构成: 生成器(Generator):通过机器生成数据(大部分情况下是图像 ...
- Tensorflow之MNIST手写数字识别:分类问题(1)
一.MNIST数据集读取 one hot 独热编码独热编码是一种稀疏向量,其中:一个向量设为1,其他元素均设为0.独热编码常用于表示拥有有限个可能值的字符串或标识符优点: 1.将离散特征的取值扩展 ...
- Tensorflow可视化MNIST手写数字训练
简述] 我们在学习编程语言时,往往第一个程序就是打印“Hello World”,那么对于人工智能学习系统平台来说,他的“Hello World”小程序就是MNIST手写数字训练了.MNIST是一个手写 ...
- GAN——生成手写数字
<Generative Adversarial Nets>是 GAN 系列的鼻祖.在这里通过 PyTorch 实现 GAN ,并且用于手写数字生成. 摘要: 我们提出了一个新的框架,通过对 ...
- TensorFlow(四):手写数字识别
一:数据集 采用MNIST数据集:-->官网 数据集被分成两部分:60000行的训练数据集和10000行的测试数据集. 其中每一张图片包含28*28个像素,我们把这个数组展开成一个向量,长度为2 ...
随机推荐
- ASP.NET Core中使用Unity5
⒈添加相关依赖 Install-Package Unity Install-Package Unity.RegistrationByConvention ⒉扫描项目接口实现类 using System ...
- ESD总结
设计人员完全可以让系统在经过ESD事件后不发生故障并仍能继续运行.将这个目标谨记在心,下面让我们更好地理解ESD冲击时到底发生了什么,然后介绍如何设计正确的系统架构来应对ESD. 简单模型 将一个电容 ...
- RefineDet网络简介(转载)
转载链接:https://blog.csdn.net/u014380165/article/details/79502308 思想:框架建立在FPN上,只不过在提取特征层(down-top)的时候就加 ...
- 【转】C++标准转换运算符const_cast
const_cast转换符是用来移除变量的const或volatile限定符. 对于const变量,我们不能修改它的值,这是这个限定符最直接的表现.但是我们就是想违背它的限定希望修改其内容怎么办呢? ...
- Css样式压缩、美化、净化工具 源代码
主要功能如下: /* 美化:格式化代码,使之容易阅读 */ /* 净化:将代码单行化,并去除注释 */ /* 压缩:将代码最小化,加快加载速度 */ /* 以下是演示代码 */ /*reset beg ...
- mariadb:分区自动创建与删除
参考文章:https://blog.csdn.net/xlxxcc/article/details/52486426 1.以日自动创建与删除分区 调用示例:CALL proc_day_partitio ...
- 转载:UML学习(一)-----用例图 (silent)
原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/silent2012/archive/2011/09/07/2169518.html 1.什么是用例图 用例图源于Jacobson的OOSE方法,用 ...
- __dict__(字典的另一种用法)
class Foo(): def __init__(self): self.name=None self.age=19 self.addr='上海' @property def dict(self): ...
- Confluence 6 数据收集隐私策略
为什么 Confluence 收集使用数据? 针对 Confluence 我们很自豪 Confluence 是这个星球上最高效和强大的协作工具,我们也计划继续保持这个特性,尽我们最大的努力提供更新的 ...
- Confluence 6 为登录失败编辑,禁用和配置验证码
在默认的情况下,验证码将会在失败登录次数达到的时候显示. 如果为登录失败编辑,禁用和配置验证码: 在屏幕的右上角单击 控制台按钮 ,然后选择 General Configuration 链接. 在左侧 ...
