python0301
1
、pycharm的使用


2、格式化输出
# name = input('请输入姓名')# age = input('请输入年龄')# hobby = input('请输入爱好')# msg = '我的姓名是' + name + '我今年' + age + '我的爱好是' + hobby# print(msg)# 字符串的拼接可以制作一个公共字符串模板,让某些位置变成动态的。"""msg = '''------------ info of Alex Li -----------Name : Alex LiAge : 73job : sbbossHobby: laddy_boy------------- end -----------------'''
msg1 = '''------------ info of 杨苏婷 -----------Name : 杨苏婷Age : 18job : student# name = input('请输入姓名:')# age = input('请输入年龄:')# job = input('请输入工作:')# hobby = input('请输入爱好:')# '''# 这样做很麻烦,用格式化输出# s1 = '------------ info of '+ name + ' -----------\n'# s2 = 'Name : ' + name + '\n'# '''# # % 占位符 s:字符串类型 d:数字 i:数字 # r 原形毕露# msg = '''------------ info of %s -----------# Name : %s# Age : %d# job : %s# Hobbie: %s# ------------- end -----------------''' % (name,name,int(age),job,hobby)# print(msg)
# 格式化输出 如果你只是想要表示百分号%,而不是占位符。# msg = '我叫%s,今年%s岁,学习进度为0.5%%' % ('高航', 40)# print(msg)Hobbie: movie------------- end -----------------'''"""
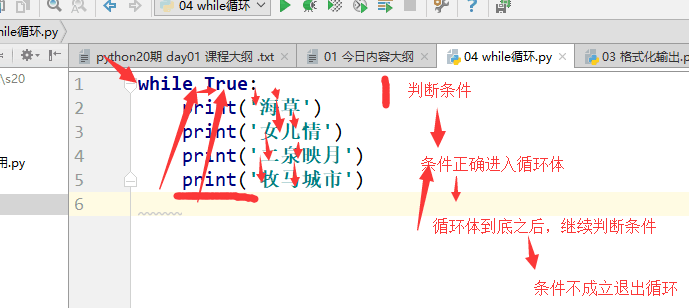
# 1,初识循环# while True:# print('海草')# print('女儿情')# print('二泉映月')# print('牧马城市')
# 如何终止循环'''1,改变条件。2,break3,调用系统命令:quit() exit() (不建议使用)'''
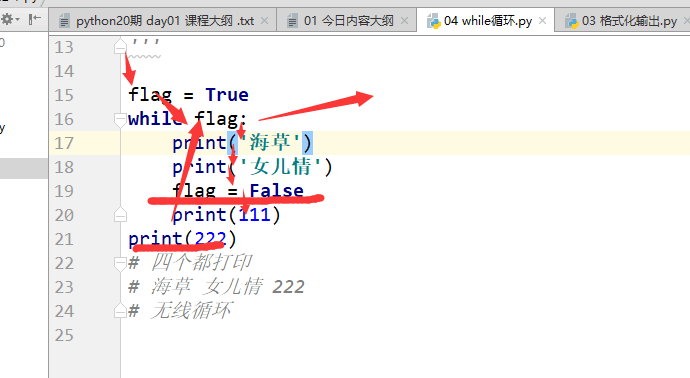
# flag = True# while flag:# print('海草')# print('女儿情')# flag = False# print(111)# print(222)# 四个都打印
# 从 1 ~ 100 利用while循环
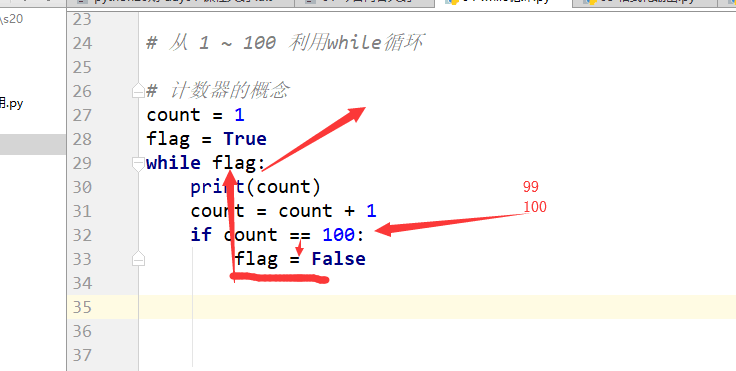
# 计数器的概念# count = 1# flag = True# while flag:# print(count)# count = count + 1# if count == 101:# flag = False
结果:1-100循环
# count = 1# while count < 101:# print(count)# count = count + 1
_____________________________________ # count = 1# count = 2# count = 3# print(count)# count = 1# count = count + 1# count = count + 1# print(count) 结果3 3# while break continue# break:循环中遇到break 直接退出循环,# print(111)# while True:# print(222)# print(333)# break# print(555)# print(666)

# 打印 1~100 所有的偶数。# 方法一# count = 2# while count < 101:# print(count)# count = count + 2 # count = 2# while True:# if count % 2 == 0:# print(count)# count = count + 1# if count > 100:# break
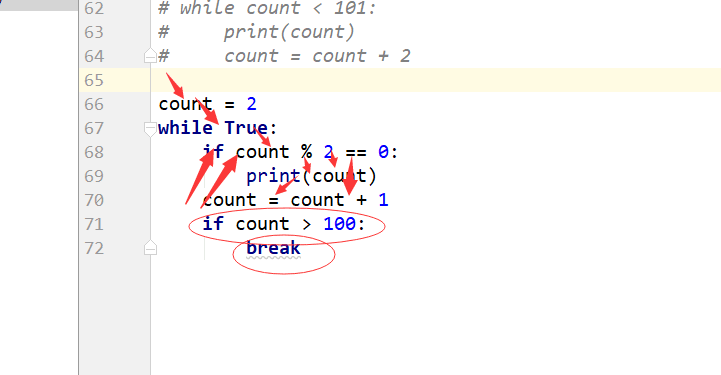
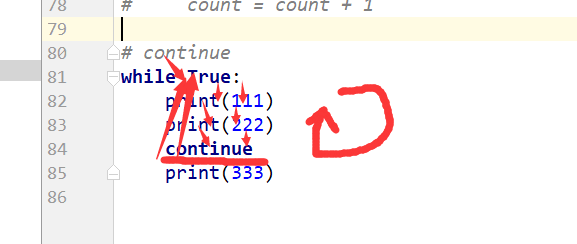
# count = 2# while count < 101:# if count % 2 == 0:# print(count)# count = count + 1 # continue# 结束本次循环,继续下一次循环# while True:# if# print(111)# print(222)# continue# print(333)
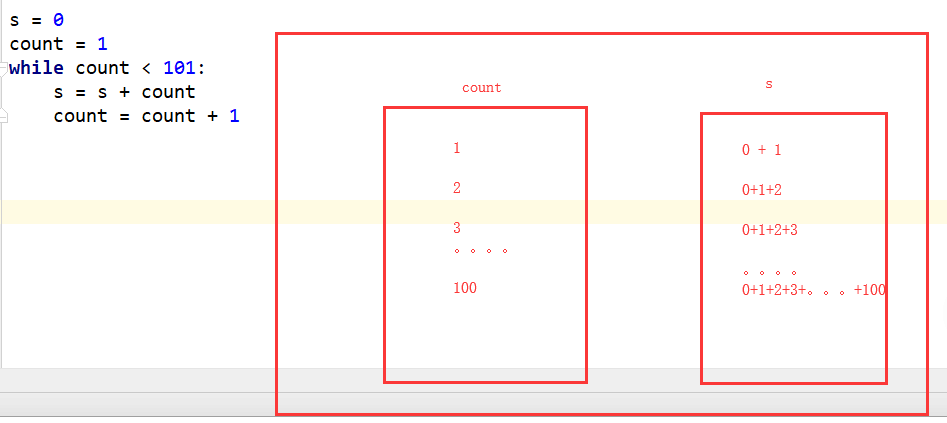
# 计算 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + ...100 结果## s = 0# count = 1# while count < 101:# s = s + count# count = count + 1# print(s)
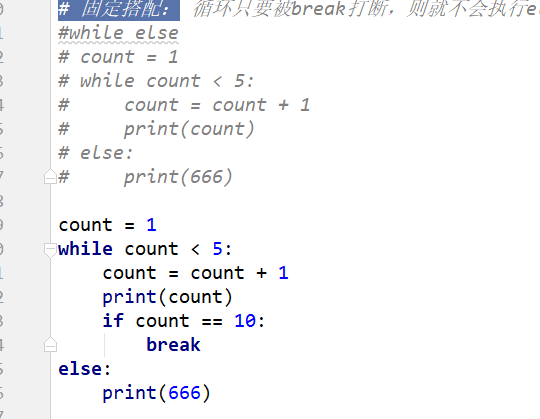
# 固定搭配: 循环只要被break打断,则就不会执行else的程序。#while else# count = 1# while count < 5:# count = count + 1# print(count)# else:# print(666)
count = 1while count < 5: count = count + 1 print(count) if count == 10: breakelse: print(666) 结果:2345666
# print(2**3)
# 逻辑运算
# 优先级# ()>not>and> or,同一个优先级从左至右一次计算。
# 1,运算符两边全部是比较运算。# print(1 > 2 or 3 < 4 and 1 < 2 or 3 > 7)
# print(1 > 2 or True or 3 > 7)
# print(2 > 1 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 < 1)# print(1 > 2 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 or 9 <10)
# 2 ,运算符两边全部是数字。'''x or y if x is True, return x,else y'''# print(1 or 3)# print(2 or 3)# print(10 or 3)# print(0 or 3)# print(-3 or 3)# print(1 and 3)# print(-1 and 3)# print(0 and 3)#int bool# int ---> bool 非0即True# print(bool(-2))# print(bool(2))# print(bool(0))# bool ---> int True 1 Flase 0# print(int(True))
# 面试题:# print(1 and 3 or 4 and 5)
# 第三种,思考题:# print(1 > 2 or 3 and 4 < 5 or 7)
# 成员运算:# s = 'alex 中'# s1 = 'a's = 'alexsb'# print('a' in s)# print('al' in s)# print('ae' in s) # False# print('alex' in s) # False# print('alexsb' in s) # False
# print('a' not in s)# print(2**16)print(2**32)
算数运算符arithmetic operator:
+ - * / %
% : 取余,取模。取的是第一个操作数和第二个操作数除法的余数。整除结果为0.
10 % 3 1
10 % 5 0
10 % -3 -1
10 % -5 ?
-10%3 ?
% 真正操作步骤:
- 用第一个数除以第二个数,得到最相近的两个商。取最小的数。
- 用第一个数减去第二个数和第一步的到的数的乘积。
赋值运算符assignment operator:
基本的赋值运算符:=
扩展的赋值运算符:
+= -= *= /= %=
例如:X += Y -> X = X + Y
比较运算符compare operator:
<= >= == !=
比较运算符的结果始终是布尔类型。
逻辑运算符logic operator:
python中只有三个逻辑运算符:
and or not
逻辑运算符的结果到底是什么类型???
结果取决于两个操作数的类型!!!
针对and操作:第一个操作数如果是可以转成False的话,那么第一个操作数的值,就是整个逻辑表达式的值。
如果第一个操作数可以转成True,第二个操作数的值就是整个表达式的值。
针对or操作:第一个操作数如果是可以转成False的话,第二个操作数的值就是整个表达式的值。
如果第一个操作数可以转成True, 第一个操作数的值,就是整个逻辑表达式的值。
成员运算符:
in not in
while循环:
[初始化部分一般是用来定义循环变量]
while 循环条件:
循环体语句
[循环变量更改部分]
[else :
语句体]
执行顺序:
- 初始化部分:一般是用来定义循环变量或新赋值
- 判断循环条件:
真:
执行循环体语句
是否执行了break语句
执行了:跳过else
没执行:当while正常执行完后,执行else
回到第二步条件判断
假:执行else
break:停止:直接停止当前的循环,不论还剩下多少次循环。
continue:跳过当前循环后面的语句,直接执行下一轮循环。
gbk:简体中文。一个中文编码成两个字节。
utf-8:中文一般是3个字节。
针对英文,始终是一个字节。
ascii –》 gbk
ascii–》 utf8
python0301的更多相关文章
随机推荐
- SQL游标在递归是的时候提示 "游标" 名称已经存在的问题
游标的语法: DECLARE cursor_name CURSOR [ LOCAL | GLOBAL ] [ FORWARD_ONLY | SCROLL ] [ STATIC | KEYSET | D ...
- haproxy监控页面添加及参数简介(转)
环境: [root@localhost 13:55:31 haproxy]# cat /etc/redhat-release CentOS release 6.8 (Final) [root@loca ...
- Go 指针
变量是存储值得地方. 借助声明变量时使用的名字来区分. 指针的值是一个变量的地址.一个指针指示值所保存的位置.不是所有的值都有地址,但是所有的变量都有.使用指针,可以在无需知道变量名字的情况下,间接读 ...
- SAP MM tables
Materials MARA - Material Master: General data MAKT - Material Master: Description MARM - Material M ...
- Python基础-python流程控制之顺序结构和分支结构(五)
流程控制 流程:计算机执行代码的顺序,就是流程 流程控制:对计算机代码执行顺序的控制,就是流程控制 流程分类:顺序结构.选择结构(分支结构).循环结构 顺序结构 一种代码自上而下执行的结构,是pyth ...
- WMI参数介绍
Win32_DiskDrive 硬盘 参数说明 vailability --设备的状态.BytesPerSector --在每个扇区的物理磁盘驱动器的字节数.Capabilities --媒体访 ...
- java实现单例模式
1.饿汉模式 public class Singleton{ private static Singleton instance = new Singleton(); private Singleto ...
- Zookeeper配置文件
zookeeper的默认配置文件为zookeeper/conf/zoo_sample.cfg,需要将其修改为zoo.cfg.其中各配置项的含义,解释如下: 1.tickTime:Client-Serv ...
- vue项目两级全选(多级原理也一样),感觉有点意思,随手一记
需求: 首先说一下思路:我首先把数据列表两级遍历了一下,增加了一个checked属性来控制勾选和不勾线 this.productList.forEach((item)=>{ this.$set( ...
- Ztree的onClick和onCheck事件
如下图所示,点击框选中,再点击框取消.现在需加上点击字体也能选中,再点击则取消 思路:点击事件是onClick,勾选的回调函数为onCheck,要实现上面需求,我们只需要在callback里新增一个点 ...
