verilog 和system verilog 文件操作
1. 文件操作
Verilog具有系统任务和功能,可以打开文件、将值输出到文件、从文件中读取值并加 载到其他变量和关闭文件。
1.1 Verilog文件操作
1.1.1 打开和关闭文件
module tb;
// 声明一个变量存储 file handler
integer fd;
initial begin
// 以写权限打开一个文件名为 "my_file.txt" 的新文件,并将文件柄指针存储在变量"fd"中
fd = $fopen("my_file.txt", "w");
// 关闭指向 "fd"的文件柄
$fclose(fd);
end
endmodule
|
Argument |
Description |
|
"r" or "rb" |
可读方式打开 |
|
"w" or "wb" |
创建用于写入的新文件。如果文件存在,则将其截断为零长度并覆盖 |
|
"a" or "ab" |
如果文件存在,追加(在EOF时打开以写入),否则创建一个新文件 |
|
"r+", "r+b" or "rb+" |
可读可写方式打开 |
|
"w+", "w+b" or "wb+" |
截断或创建以进行更新 |
|
"a+", "a+b", or "ab+" |
在EOF处追加或创建新文件进行更新 |
1.1.2 写文件
|
Function |
Description |
|
$fdisplay |
Similar to $display, writes out to file instead |
|
$fwrite |
Similar to $write, writes out to file instead |
|
$fstrobe |
Similar to $strobe, writes out to file instead |
|
$fmonitor |
Similar to $monitor, writes out to file instead |
上述每个系统函数都以基数十进制打印值。它们还有其他三个版本,可以以二进制、八进制 和十六进制打印值。
|
Function |
Description |
|
$fdisplay() |
Prints in decimal by default |
|
$fdisplayb() |
Prints in binary |
|
$fdisplayo() |
Prints in octal |
|
$fdisplayh() |
Prints in hexadecimal |
module tb;
integer fd;
integer i;
reg [7:0] my_var;
initial begin
// Create a new file
fd = $fopen("my_file.txt", "w");
my_var = 0;
$fdisplay(fd, "Value displayed with $fdisplay");
#10 my_var = 8'h1A;
$fdisplay(fd, my_var); // Displays in decimal
$fdisplayb(fd, my_var); // Displays in binary
$fdisplayo(fd, my_var); // Displays in octal
$fdisplayh(fd, my_var); // Displays in hex
// $fwrite does not print the newline char '
' automatically at
// the end of each line; So we can predict all the values printed
// below to appear on the same line
$fdisplay(fd, "Value displayed with $fwrite");
#10 my_var = 8'h2B;
$fwrite(fd, my_var);
$fwriteb(fd, my_var);
$fwriteo(fd, my_var);
$fwriteh(fd, my_var);
// Jump to new line with '
', and print with strobe which takes
// the final value of the variable after non-blocking assignments
// are done
$fdisplay(fd, "
Value displayed with $fstrobe");
#10 my_var <= 8'h3C;
$fstrobe(fd, my_var);
$fstrobeb(fd, my_var);
$fstrobeo(fd, my_var);
$fstrobeh(fd, my_var);
#10 $fdisplay(fd, "Value displayed with $fmonitor");
$fmonitor(fd, my_var);
for(i = 0; i < 5; i= i+1) begin
#5 my_var <= i;
end
#10 $fclose(fd);
end
endmodule

1.1.3 读取文件
读取一行
系统函数 $fgets 从 [hl]fd[/hd] 指定的文件中将字符读入变量 str 直到 str 被填满,或者读
取换行符并传输到 str,或者遇到 EOF 条件。
如果在读取过程中发生错误,则返回代码零。否则返回读取的字符数。
1.1.3.1 检测 EOF
当找到 EOF 时,系统函数 $feof 返回一个非零值,否则对于给定的文件描述符作为参数返回零。
module tb;
reg[8*45:1] str;
integer fd;
initial begin
fd = $fopen("my_file.txt", "r");
// Keep reading lines until EOF is found
while (! $feof(fd)) begin
// Get current line into the variable 'str'
$fgets(str, fd);
// Display contents of the variable
$display("%0s", str);
end
$fclose(fd);
end
endmodule
1.1.3.2 fdisplay 的多个参数
当给$fdisplay多个变量时,它只是按给定的顺序一个接一个地打印所有变量,没有空格。
module tb;
reg [3:0] a, b, c, d;
reg [8*30:0] str;
integer fd;
initial begin
a = 4'ha;
b = 4'hb;
c = 4'hc;
d = 4'hd;
fd = $fopen("my_file.txt", "w");
$fdisplay(fd, a, b, c, d);
$fclose(fd);
end
endmodule

1.1.4 将数据格式化为字符串
系统函数中的第一个参数 $sformat 是放置结果的变量名。第二个参数是format_string,它告诉如何将以下参数格式化为字符串。
module tb;
reg [8*19:0] str;
reg [3:0] a, b;
initial begin
a = 4'hA;
b = 4'hB;
// Format 'a' and 'b' into a string given
// by the format, and store into 'str' variable
$sformat(str, "a=%0d b=0x%0h", a, b);
$display("%0s", str);
end
endmodule

1.2 sv文件操作
System Verilog 允许我们读取和写入磁盘中的文件。
1.2.1 打开关闭文件
可以使用 $fopen() 系统任务打开文件进行读取或写入。该任务将返回一个称为文件描述符的 32位整数句柄。这个句柄应该用于读取和写入该文件,直到它被关闭。文件描述符可以用$fclose() 系统任务关闭。一旦文件描述符关闭,就不允许进一步读取或写入文件描述符。
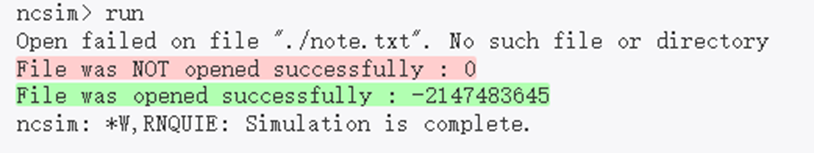
例子:在下面显示的代码中,我们将声明一个名为 fd的int变量来保存文件描述符。 fd 最初为零,并从$fopen()中获取有效值,可以检查文件是否成功打开。该文件最终在执行$fclose()时关闭。
module tb;
initial begin
// 1. Declare an integer variable to hold the file descriptor
int fd;
// 2. Open a file called "note.txt" in the current folder with a "read permission
// If the file does not exist, then fd will be zero
fd = $fopen ("./note.txt", "r");
if (fd) $display("File was opened successfully : %0d", fd);
else $display("File was NOT opened successfully : %0d", fd);
// 2. Open a file called "note.txt" in the current folder with a "write permission
// "fd" now points to the same file, but in write mode
fd = $fopen ("./note.txt", "w");
if (fd) $display("File was opened successfully : %0d", fd);
else $display("File was NOT opened successfully : %0d", fd);
// 3. Close the file descriptor
$fclose(fd);
end
endmodule
在仿真结束之前关闭所有打开的文件以将内容完全写入文件很重要。
1.2.2 以读取和附加模式打开
默认情况下,文件以写入 w 模式打开。通过提供正确的模式类型,也可以在其他模式下打开文件。下表显示了可以打开文件的所有不同模式。
例子:在下面的代码中,我们将看到如何使用上表中描述的不同文件访问模式。
module tb;
initial begin
int fd_w, fd_r, fd_a, fd_wp, fd_rp, fd_ap;
fd_w = $fopen ("./todo.txt", "w"); // Open a new file in write mode a
fd_r = $fopen ("./todo.txt", "r"); // Open in read mode
fd_a = $fopen ("./todo.txt", "a"); // Open in append mode
if (fd_w) $display("File was opened successfully : %0d", fd_w);
else $display("File was NOT opened successfully : %0d", fd_w)
if (fd_r) $display("File was opened successfully : %0d", fd_r);
else $display("File was NOT opened successfully : %0d", fd_r)
if (fd_a) $display("File was opened successfully : %0d", fd_a);
else $display("File was NOT opened successfully : %0d", fd_a)
// Close the file descriptor
$fclose(fd_w);
$fclose(fd_r);
$fclose(fd_a);
end
endmodule
从下面的日志可以看出,这三个变量都有不同的值,每个变量都指向同一个文件,但访问权限不同。

1.2.3 读取和写入文件
文件应以写入 w 模式或附加 a 模式打开。系统任务如 $fdisplay() 和 $fwrite() 可用于将格式化字符串写入文件。这些任务的第一个参数是文件描述符句柄,第二个参数是要存储的数据。 要读取文件,必须以读取 r 模式或读写 r+ 模式打开它。 $fgets() 是一个系统任务,它 将从文件中读取一行。如果这个任务被调用 10 次,那么它将读取 10 行。
例子:下面显示的代码演示了如何使用 $fdisplay() . 然后以读取模式打开文件,并使用 $fgets() 本地变量将内容读回。然后使用标准显示任务$display()打印出来。
module tb;
int fd; // Variable for file descriptor handle
string line; // String value read from the file
initial begin
// 1. Lets first open a new file and write some contents into it
fd = $fopen ("trial", "w");
// Write each index in the for loop to the file using $fdisplay
// File handle should be the first argument
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) begin
$fdisplay (fd, "Iteration = %0d", i);
end
// Close this file handle
$fclose(fd);
// 2. Let us now read back the data we wrote in the previous step
fd = $fopen ("trial", "r");
// Use $fgets to read a single line into variable "line"
$fgets(line, fd);
$display ("Line read : %s", line);
// Get the next line and display
$fgets(line, fd);
$display ("Line read : %s", line);
// Close this file handle
$fclose(fd);
end
endmodule

1.2.4 阅读直到文件结束
在前面的示例中,我们 $fgets() 两次使用系统任务从文件中读取两行。SystemVerilog 有 另一个任务调用 $feof() ,当到达文件末尾时返回 true。这可以在循环中使用,如下所示以读取文件的全部内容。
例子
module tb;
int fd; // Variable for file descriptor handle
string line; // String value read from the file
initial begin
// 1. Lets first open a new file and write some contents into it
fd = $fopen ("trial", "w");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) begin
$fdisplay (fd, "Iteration = %0d", i);
end
$fclose(fd);
// 2. Let us now read back the data we wrote in the previous step
fd = $fopen ("trial", "r");
while (!$feof(fd)) begin
$fgets(line, fd);
$display ("Line: %s", line);
end
// Close this file handle
$fclose(fd);
end
endmodule

1.2.5 解析值的行
SystemVerilog 有另一个名为的系统任务 $fscanf() ,它允许我们扫描并获取某些值。
例子
module tb;
int fd; // Variable for file descriptor handle
int idx;
string str;
initial begin
// 1. Lets first open a new file and write some contents into it
fd = $fopen ("trial", "w");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
$fdisplay (fd, "Iteration = %0d", i);
$fclose(fd);
// 2. Let us now read back the data we wrote in the previous step
fd = $fopen ("trial", "r");
// fscanf returns the number of matches
while ($fscanf (fd, "%s = %0d", str, idx) == 2) begin
$display ("Line: %s = %0d", str, idx);
end
// Close this file handle
$fclose(fd);
end
endmodule
1.2.6 多通道文件描述符
mcd是一个 32 位压缩数组值,其中设置了一个位,指示打开哪个文件。mcd 的 LSB 总是指 标准输出。输出被定向到使用多通道描述符打开的两个或多个文件,方法是将它们的mcd按 位或运算在一起,并写入结果值。
1.3 范围解析运算符::
范围解析运算符 :: 用于引用类范围内的标识符。 范围解析运算符 :: 的左侧应该是类类型名称、包名称、覆盖组类型名称、覆盖点或交叉名称、 typedef 名称。运算符的右侧应该是一个标识符,如变量或方法名称。
1.3.1 使用范围解析运算符原因
类和其他作用域可以具有相同的标识符名称,并且如果在未指定作用域的情况下被引用,则可能会产生命名空间冲突。范围解析运算符 :: 唯一标识给定类的成员或参数。 它们还用于从类外部访问类的静态变量和方法、参数和局部参数。它还允许从子类中访问基类的公共和受保护成员。
1.3.2 例子
1.3.2.1 定义外部函数
class ABC;
int data;
extern virtual function void display();
endclass
// Definition of an external function using scope
// resolution operator
function void ABC::display();
$display("data = 0x%0h", data);
endfunction
module tb;
initial begin
ABC abc = new();
abc.data = 32'hface_cafe;
abc.display();
end
endmodule

1.3.2.2 访问静态方法和函数
class ABC;
static int data;
static function void display();
$display("data = 0x%0h", data);
endfunction
endclass
module tb;
initial begin
ABC a1, a2;
// Assign to static variable before creating
// class objects, and display using class_type and
// scope resolution operator
ABC::data = 32'hface_cafe;
ABC::display();
a1 = new();
a2 = new();
$display ("a1.data=0x%0h a2.data=0x%0h", a1.data, a2.data);
end
endmodule

1.3.2.3 使用包
package my_pkg;
typedef enum bit {FALSE, TRUE} e_bool;
endpackage
module tb;
bit val;
initial begin
// Refer to types that have been declared
// in a package. Note that package has to
// be included in compilation but not
// necessarily "imported"
val = my_pkg::TRUE;
$display("val = 0x%0h", val);
end
endmodule

1.3.2.4 避免命名空间冲突
package my_pkg;
typedef enum bit {FALSE, TRUE} e_bool;
endpackage
import my_pkg::*;
module tb;
typedef enum bit {TRUE, FALSE} e_bool;
initial begin
e_bool val;
// Be explicit and say that TRUE from my_pkg
// should be assigned to val
val = my_pkg::TRUE;
$display("val = 0x%0h", val);
// TRUE from current scope will be assigned to
// val
val = TRUE;
$display("val = 0x%0h", val);
end
endmodule

verilog 和system verilog 文件操作的更多相关文章
- system verilog中的跳转操作
在verilog中,使用disable声明来从执行流程中的某一点跳转到另一点.特别地,disable声明使执行流程跳转到标注名字的声明组末尾,或者一个任务的末尾. verilog中的disable命令 ...
- system verilog中的类型转换(type casting)、位宽转换(size casting)和符号转换(sign casting)
类型转换 verilog中,任何类型的任何数值都用来给任何类型赋值.verilog使用赋值语句自动将一种类型的数值转换为另一种类型. 例如,当一个wire类型赋值给一个reg类型的变量时,wire类型 ...
- System Verilog基础(一)
学习文本值和基本数据类型的笔记. 1.常量(Literal Value) 1.1.整型常量 例如:8‘b0 32'd0 '0 '1 'x 'z 省略位宽则意味着全位宽都被赋值. 例如: :] sig1 ...
- System Verilog随笔(1)
测试文件该怎么写? 首先看一个简单代码案例: `timescale 1ns/10ps //1 module test; //2 intput wire[15:0] a; output reg[15 ...
- 一段比较有意思的代码——介绍system verilog中的新增幅值语句
system verilog中新加了很多幅值语句,虽然都只适用于阻塞幅值,但是在某些场合中非常实用. 下面是一段有意思的代码,覆盖了一些用法. package definitions; typedef ...
- 【转】uvm 与 system verilog的理解
http://www.cnblogs.com/loves6036/p/5779691.html 数字芯片和FPGA的验证.主要是其中的功能仿真和时序仿真. 验证中通常要搭建一个完整的测试平台和写所需要 ...
- (转)新手学习System Verilog & UVM指南
从刚接触System Verilog以及后来的VMM,OVM,UVM已经有很多年了,随着电子工业的逐步发展,国内对验证人才的需求也会急剧增加,这从各大招聘网站贴出的职位上也可以看出来,不少朋友可能想尽 ...
- nodejs文件操作模块FS(File System)常用函数简明总结(转)
件系统操作相关的函数挺多的.首先可以分为两大类. 一类是异步+回调的. 一类是同步的. 在这里只对异步的进行整理,同步的只需要在函数名称后面加上Sync即可 1. 首先是一类最常规的读写函数,函数名称 ...
- 【.NET深呼吸】Zip文件操作(1):创建和读取zip文档
.net的IO操作支持对zip文件的创建.读写和更新.使用起来也比较简单,.net的一向作风,东西都准备好了,至于如何使用,请看着办. 要对zip文件进行操作,主要用到以下三个类: 1.ZipFile ...
- 野路子出身PowerShell 文件操作实用功能
本文出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/wy123/p/6129498.html 因工作需要,处理一批文件,本想写C#来处理的,后来想想这个是PowerShell的天职,索性就网上各种 ...
随机推荐
- LOJ.数列分块入门3
题目 分析 由大题目知此题分块 注意处理前驱下标的合法性 \(Code\) #include<cstdio> #include<cmath> #include<algor ...
- 从零开始使用阿里云OSS服务(白嫖)
阿里云对象存储服务OSS使用记录 1 新人免费开通OSS服务 访问 阿里云官网,登录账号(个人新用户账号),首页搜索 对象存储OSS,点击下方的直达. 点击立即开通,此时会在一个新网页中完成开通 完成 ...
- 跳板攻击之:reGeorg 代理转发
跳板攻击之:reGeorg 代理转发 郑重声明: 本笔记编写目的只用于安全知识提升,并与更多人共享安全知识,切勿使用笔记中的技术进行违法活动,利用笔记中的技术造成的后果与作者本人无关.倡导维护网络安全 ...
- 代码随想录算法训练营day06 | leetcode 242、349 、202、1
基础知识 哈希 常见的结构(不要忘记数组) 数组 set (集合) map(映射) 注意 哈希冲突 哈希函数 LeetCode 242 分析1.0 HashMap<Character, Inte ...
- 为什么不建议使用 @Autowired 注解进行注入
在Spring中,Bean的注入一般有三种方式:属性注入.set方法注入.构造器注入. 1.Autowired注入的原理 @Autowired属于属性注入,默认按照类型装配,默认情况下要求依赖的对象必 ...
- day05-mybatis配置文件和SQL映射文件
Mybatis配置文件&SQL映射文件 1.配置文件-mybatis-config.xml 1.1基本说明 mybatis的核心配置文件(mybatis-config.xml),它的作用如配置 ...
- 认识 C 的编译器和编译流程
GCC 的编译流程 我们写的 C 代码保存在扩展名是 .c 的文件,其实是一个纯文本文件. GCC(C 编译器之一)通过预处理器(Pre-Processing)把头文件展开到hello.i文件中. 编 ...
- [{"morpherRegistry":{},"dynaClass":{"dynaProperties":[{"indexed":false,"mapp
将list存到json中后,json返回的内容是[{"morpherRegistry":{},"dynaClass":{"dynaProperties ...
- element ui 浏览器表单自动填充默认样式
::v-deep .el-input__inner { -webkit-text-fill-color: #000000; caret-color: #0a0a0a; box- ...
- maven上传jar包或pom文件到远程仓库
一. 步骤 有时候,项目中打好的jar包或pom文件需要上传到远程仓库,步骤总结如下: 安装好maven,网上有很多教程,默认已安装 工程中的settings.xml增加相应的server账号密码: ...
