NLP学习(5)----attention/ self-attention/ seq2seq/ transformer
目录:
(1)为什么使用attention
(2)attention的定义以及四种相似度计算方式
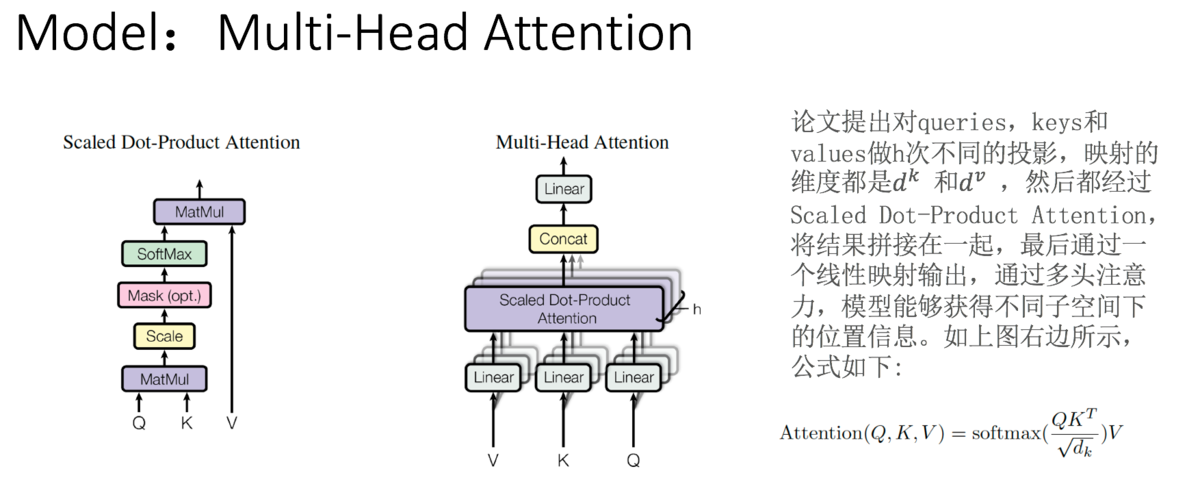
(3)attention类型(scaled dot-product attention \ multi-head attention)
(1)self-attention的计算
(2) self-attention如何并行
(3) self-attention的计算总结
(4) self-attention的类型(multi-head self-attention)
(1)传统的seq2seq
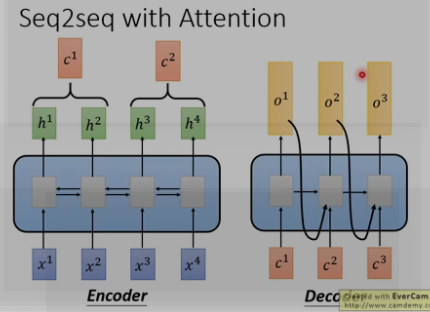
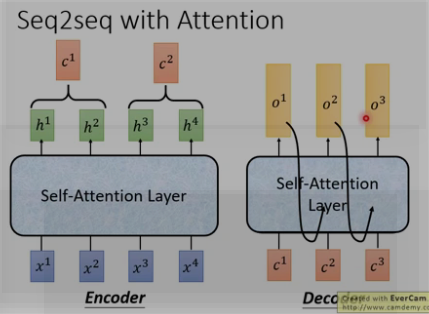
(2)seq2seq with attention
(1)整体结构
(2)细节:三种应用(encoder/decoder/encoder-decoder) + 位置encoding + 残差(Add) + Layer norm + 前馈神经网络(feed forward) + mask(decoder)
(3)实战
一. 前提:
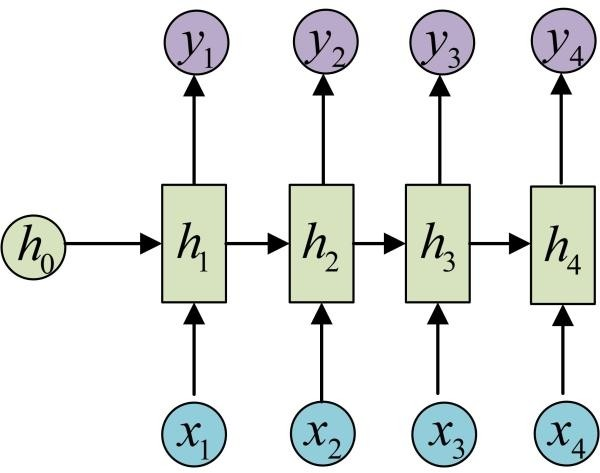
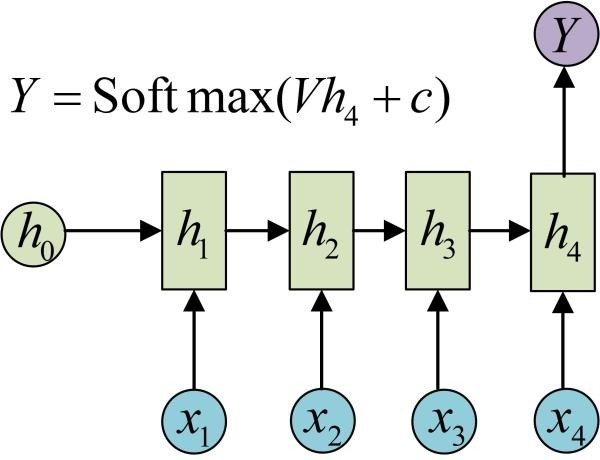
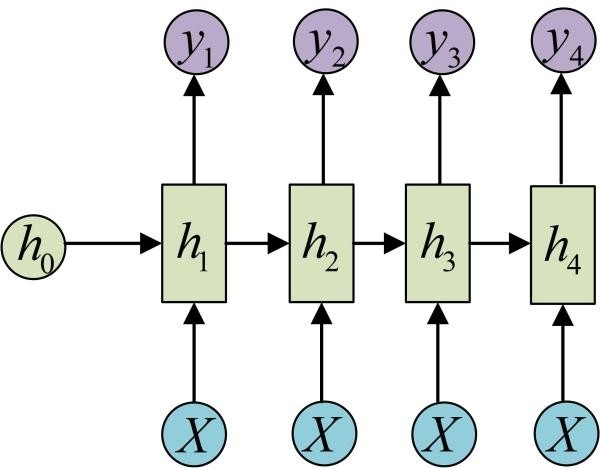
1. RNN : 解决INPUT是序列化的问题,但是RNN存在的缺陷是难以并行化处理.
| (1) RNN(N vs N) | (2) RNN (N vs 1) | ||
|
|
|
||
| (3) RNN (1 vs N) | (4) RNN (N vs M)---seq2seq | ||
 |
 |
||
2. CNN : 使用CNN来replaceRNN,可以并行,如下图每个黄色三角形都可以并行. 但是问题是难解决长依赖的序列, 解决办法是叠加多层的CNN,比如下图的CNN黄色三角形和蓝色三角形为两层CNN,
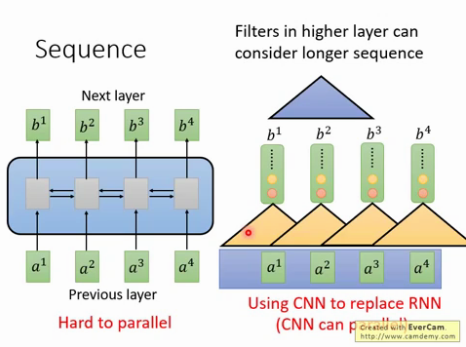
3. attention:
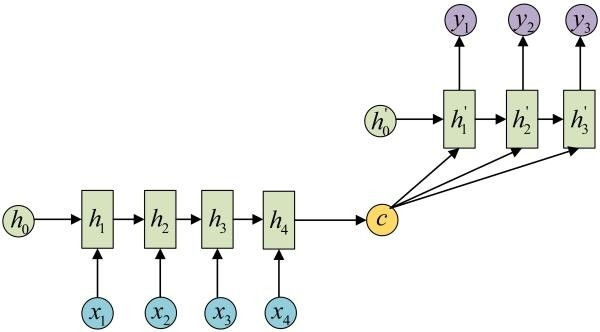
在Encoder-Decoder结构中,Encoder把所有的输入序列都编码成一个统一的语义特征c再解码,因此, c中必须包含原始序列中的所有信息,它的长度就成了限制模型性能的瓶颈。如机器翻译问题,当要翻译的句子较长时,一个c可能存不下那么多信息,就会造成翻译精度的下降。
Attention机制通过在每个时间输入不同的c来解决这个问题,下图是Attention机制的encoder and Decoder:
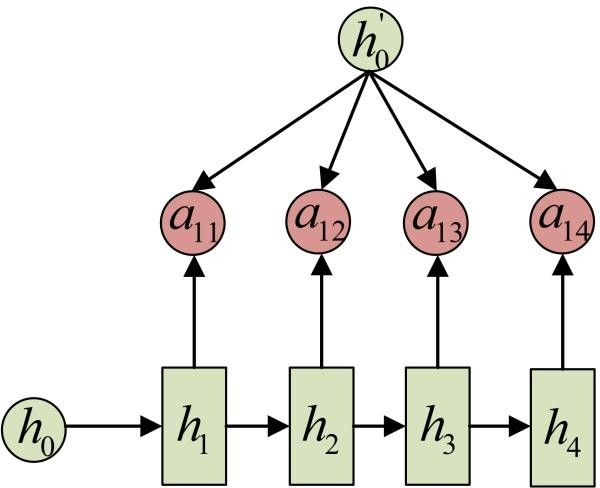
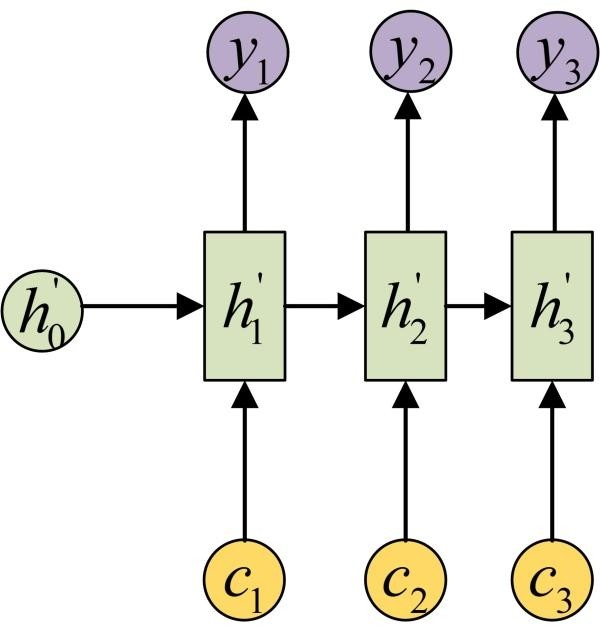
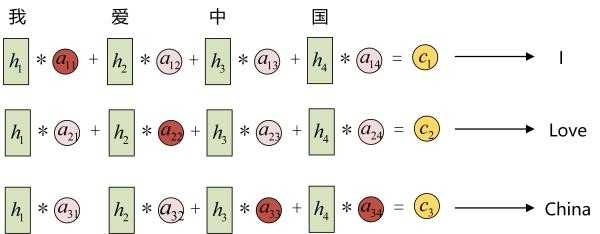
4. self-attention : 其输入和输出和RNN一样,就是中间不一样. 如下图, b1到b4是同时计算出来, RNN的b4必须要等到b1计算完.
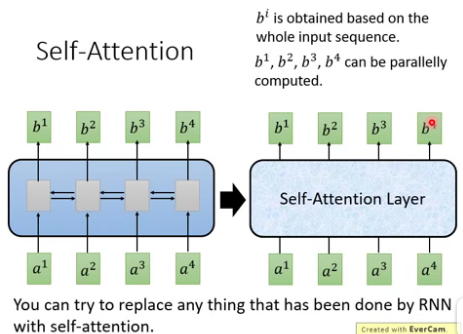
二.Attention
1. 为什么要用attention model?
The attention model用来帮助解决机器翻译在句子过长时效果不佳的问题。并且可以解决RNN难并行的问题.
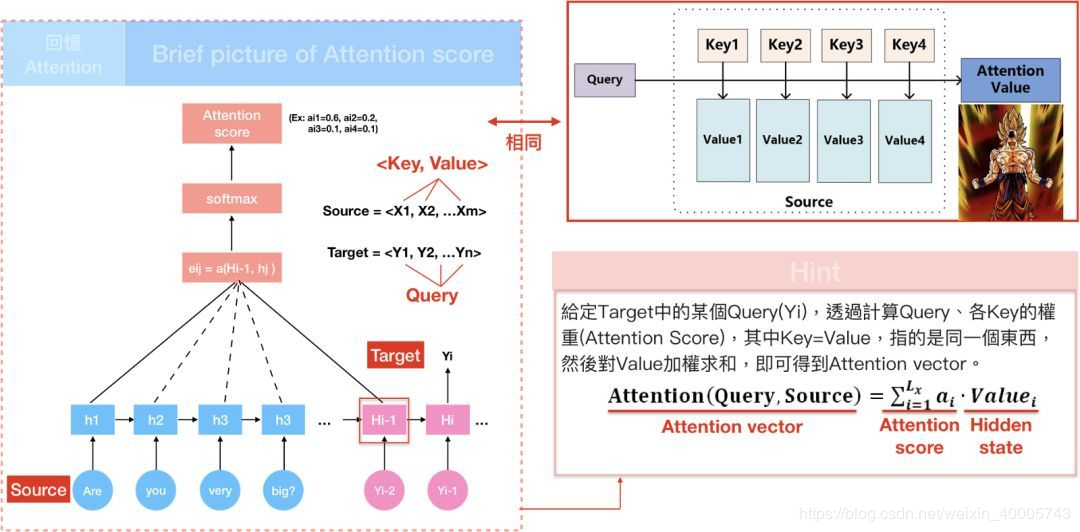

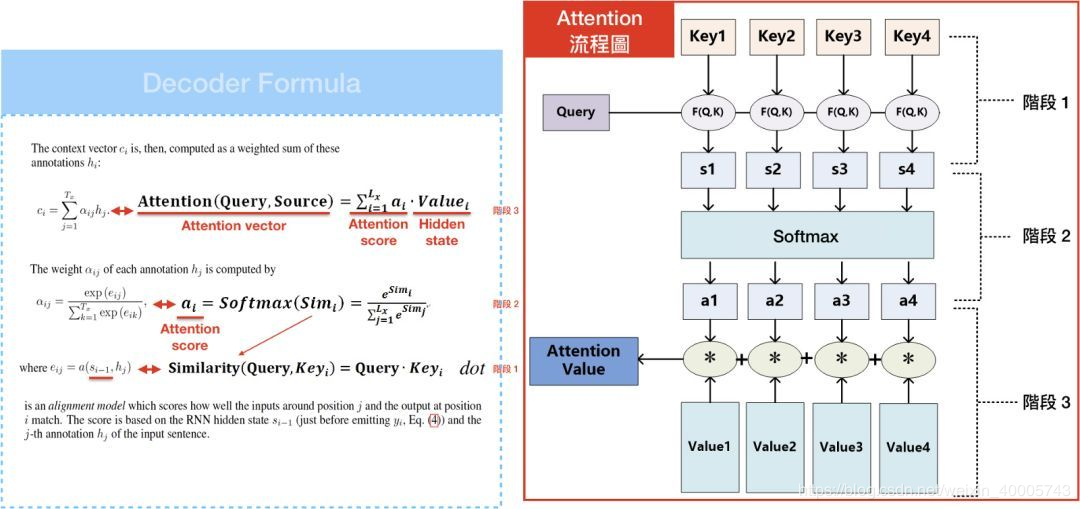
3. attentionl类型
点积注意力机制的优点是速度快、占用空间小。

三. self-attention
1. self-attention 的计算(Attention is all you need)

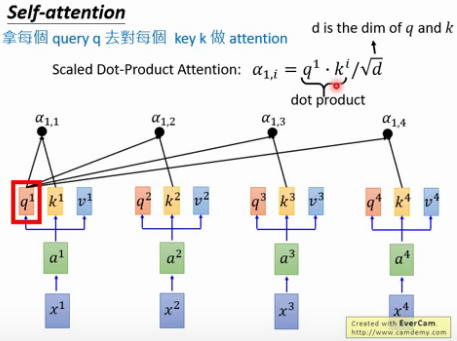
用每个query q去对每个key k做attention , 即计算得到α1,1 , α1,2 ……,
为什么要除以d [d等于q或k的维度,两者维度一样] ? 因为q和k的维度越大,dot product 之后值会更大,为了平衡值,相当于归一化这个值,除以一个d.

2. self-attention如何并行
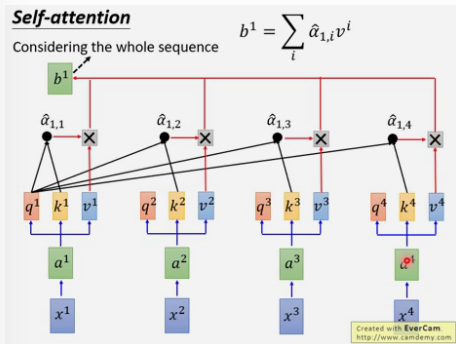
self-attention最终为一些矩阵相乘的形式,可以采用并行方式来计算.

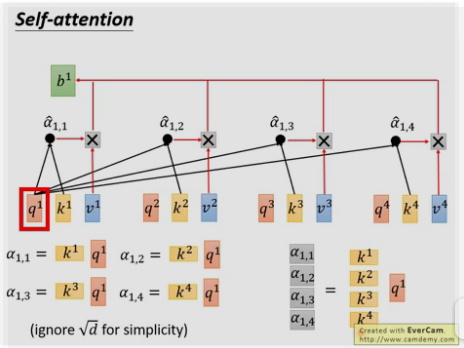
以上每个α都可以并行计算

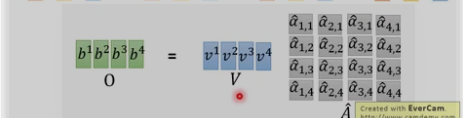
3. 计算总结:
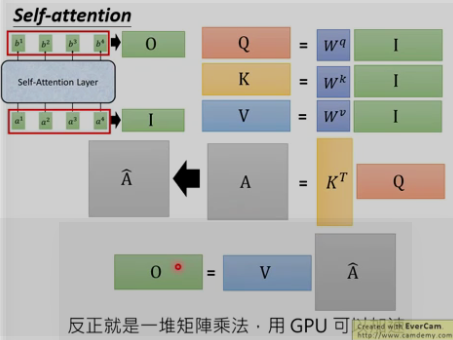
4. self_attention的类型
多头: 为何?因为不同的head可以关注不同的信息, 比如第一个head关注长时间的信息,第二个head关注短时间的信息.
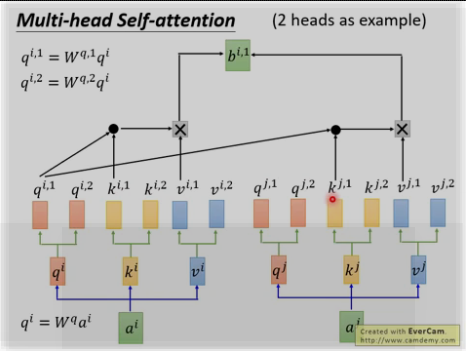
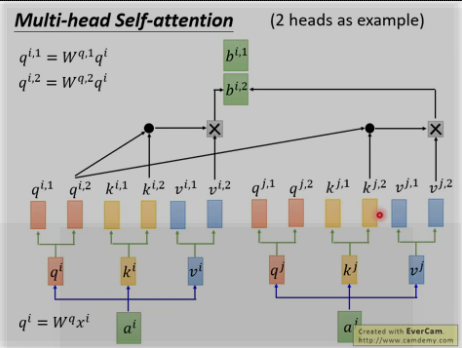
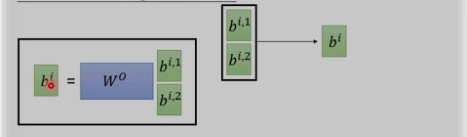
将两个bi,1和bi,2进行concat并乘以W0来降为成bi
四. seq2seq
传统的seq2seq: 中间用的是RNN
seq2seq with attention
五. Transformer
细扣 : https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/RLxWevVWHXgX-UcoxDS70w
1. 整体架构:
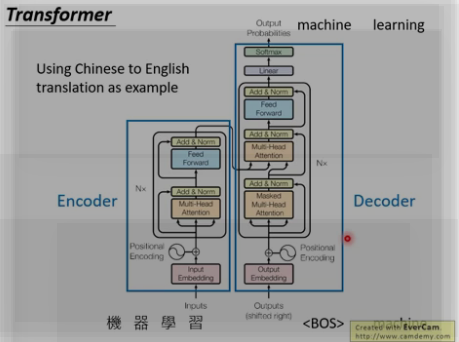
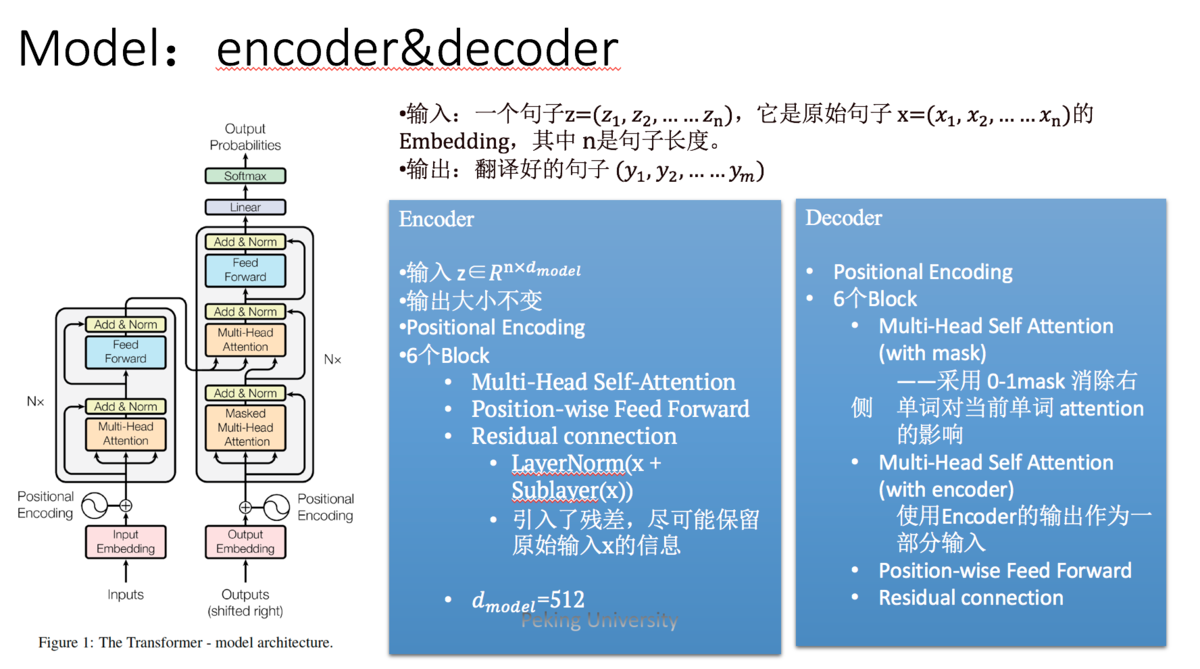
Transformer遵循这种结构,encoder和decoder都使用堆叠的self-attention和point-wise,fully connected layers。
Encoder: encoder由6个相同的层堆叠而成,每个层有两个子层。
第一个子层是多头自我注意力机制(multi-head self-attention mechanism),
第二层是简单的位置的全连接前馈网络(position-wise fully connected feed-forward network)。
中间: 两个子层中会使用一个残差连接,接着进行层标准化(layer normalization)。
也就是说每一个子层的输出都是LayerNorm(x + sublayer(x))。
网络输入是三个相同的向量q, k和v,是word embedding和position embedding相加得到的结果。为了方便进行残差连接,我们需要子层的输出和输入都是相同的维度。
Decoder:
三层: (多头self-attention + 多头attention + feed-forword )
decoder也是由N(N=6)个完全相同的Layer组成,decoder中的Layer由encoder的Layer中插入一个Multi-Head Attention + Add&Norm组成。
输入 : 输出的embedding与输出的position embedding求和做为decoder的输入,
MA-1层: 经过一个Multi-HeadAttention + Add&Norm((MA-1)层,MA-1层的输出做为下一Multi-Head Attention + Add&Norm(MA-2)的query(Q)输入,
MA-2层的Key和Value输入(从图中看,应该是encoder中第i(i = 1,2,3,4,5,6)层的输出对于decoder中第i(i = 1,2,3,4,5,6)层的输入)。
MA-2层的输出输入到一个前馈层(FF), 层与层之间使用的Position-wise feed forward network,经过AN(Add&norm)操作后,经过一个线性+softmax变换得到最后目标输出的概率。
mask : 对于decoder中的第一个多头注意力子层,需要添加masking,确保预测位置i的时候仅仅依赖于位置小于i的输出。
2. trip细节
(1) 三种应用
Transformer会在三个不同的方面使用multi-head attention:
1. encoder-decoder attention:使用multi-head
attention,输入为encoder的输出和decoder的self-attention输出,其中encoder的self-attention作为
key and value,decoder的self-attention作为query
2. encoder self-attention:使用 multi-head attention,输入的Q、K、V都是一样的(input embedding and positional embedding)
3. decoder self-attention:在decoder的self-attention层中,deocder 都能够访问当前位置前面的位置
(2)位置encoding


这样做的目的是因为正弦和余弦函数具有周期性,对于固定长度偏差k(类似于周期),post +k位置的PE可以表示成关于pos位置PE的一个线性变化(存在线性关系),这样可以方便模型学习词与词之间的一个相对位置关系。
上面的self-attention有个问题,q缺乏位置信息,因为近邻和长远的输入是同等的计算α.
位置encoding的ei是人工设置的,不是学习的.将其加入ai中.

为何是和ai相加,而不是concat?
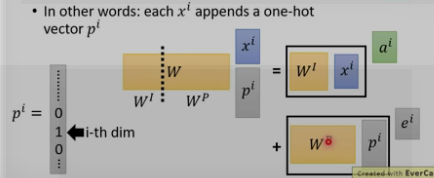
这里的Wp是通过别的方法计算的,如下图所示
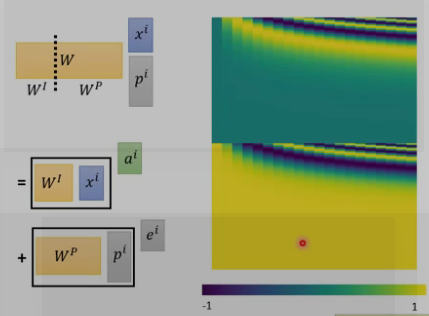
(3) 残差
对于每个encoder里面的每个sub-layer,它们都有一个残差的连接,理论上这可以回传梯度.
这种方式理论上可以很好的回传梯度
作者:收到一只叮咚
链接:https://www.imooc.com/article/67493
来源:慕课网
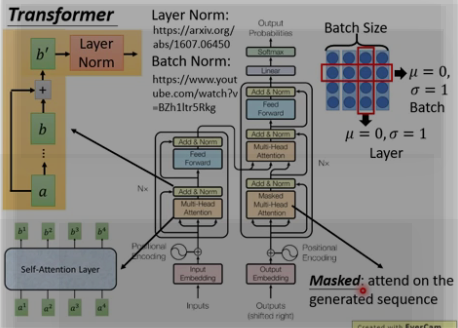
(4) Layer Norm
每个sub-layer后面还有一步 layer-normalization [layer Norm一般和RNN相接] 。可以加快模型收敛速度.
Batch Norm和Layer Norm 的区别, 下图右上角, 横向为batch size取均值为0, sigma = 1. 纵向 为layer Norm , 不需要batch size.
(5) Position-wise feed forward network 前馈神经网络
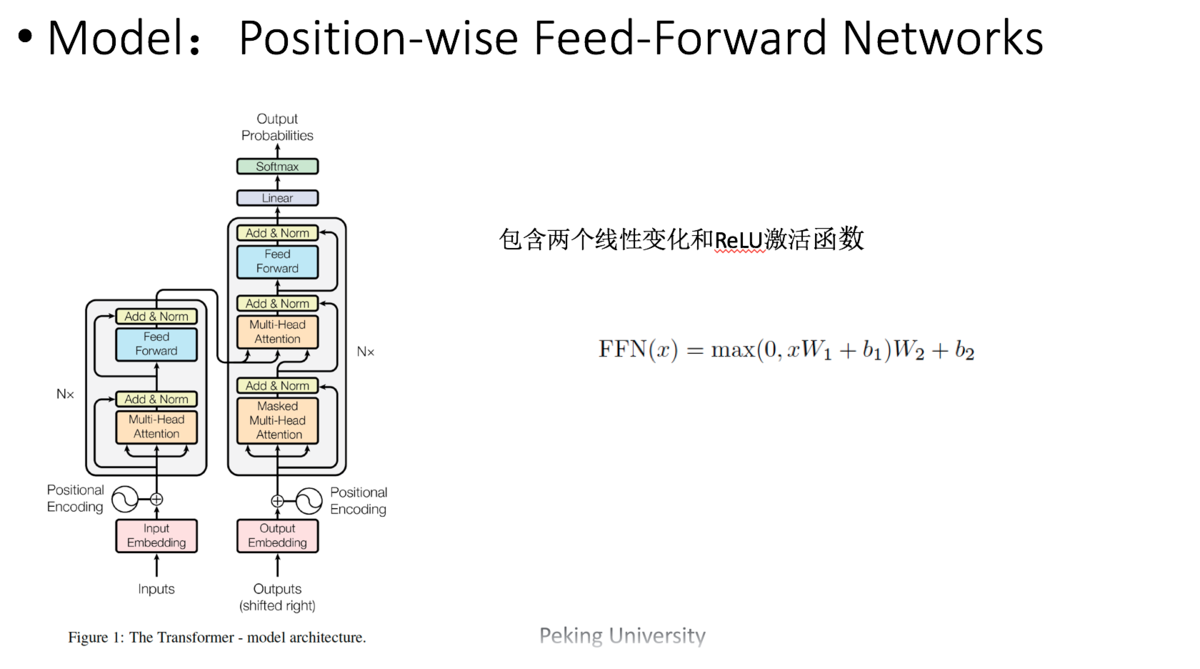
用了两层Dense层,activation用的都是Relu。
可以看成是两层的1*1的1d-convolution。hidden_size变化为:512->2048->512
Position-wise feed forward network,其实就是一个MLP 网络,1 的输出中,每个 d_model 维向量 x
在此先由 xW_1+b_1 变为 d_f $维的 x',再经过max(0,x')W_2+b_2 回归 d_model
维。之后再是一个residual connection。输出 size 仍是 $[sequence_length, d_model]$
(6) Masked : [decoder]
注意encoder里面是叫self-attention,decoder里面是叫masked self-attention。
这里的masked就是要在做language modelling(或者像翻译)的时候,不给模型看到未来的信息。

mask就是沿着对角线把灰色的区域用0覆盖掉,不给模型看到未来的信息。
(7) 优化

模型的训练采用了Adam方法,文章提出了一种叫warm up的学习率调节方法,如公式所示:
作者:收到一只叮咚
链接:https://www.imooc.com/article/67493
来源:慕课网
发展: universal transformer
应用: NLP \ self attention GAN (用在图像上)
3. 实战
https://www.jianshu.com/p/2b0a5541a17c
3.1 encoder
(1) 输入: encoder embedding和position embedding相加
(2) 两种attention
(3) Add & Normalize & FFN
3.2 decoder
(1)输入: decoder embedding和position embedding相加
(2)mask multi-head attention和encoder-decoder attention
(3)Add & Normalize & FFN & 输出
3.1 encoder
(1)输入: input embedding和position embedding相加
原始数据: word2vec [embedding表] + input_sentence [x] + output_sentence [y] + position embedding(固定)
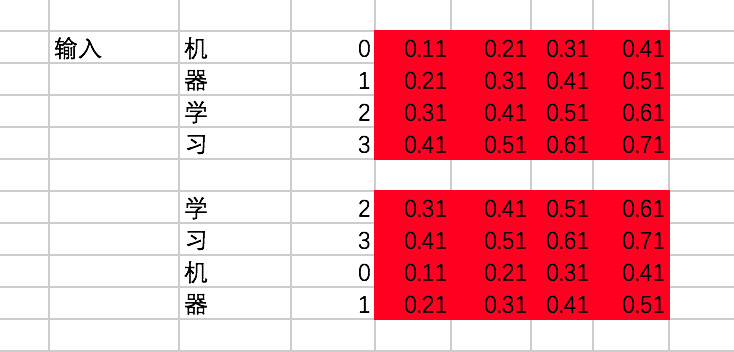
①输入input_sentence [x] 和 word2vec [embedding表]
假设我们有两条训练数据(input_sentence [x]):
[机、器、学、习] -> [ machine、learning]
[学、习、机、器] -> [learning、machine]
encoder的输入在转换成id后变为[[0,1,2,3],[2,3,0,1]]。
接下来,通过查找中文的embedding表(word2vec),转换为embedding为:
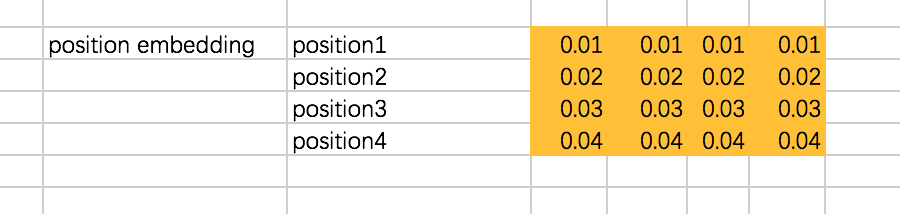
②将position embedding设为固定值,但实际是通过三角函数来计算得到的,这里为了方便设为固定值,注意这个position embedding是不用迭代训练的:
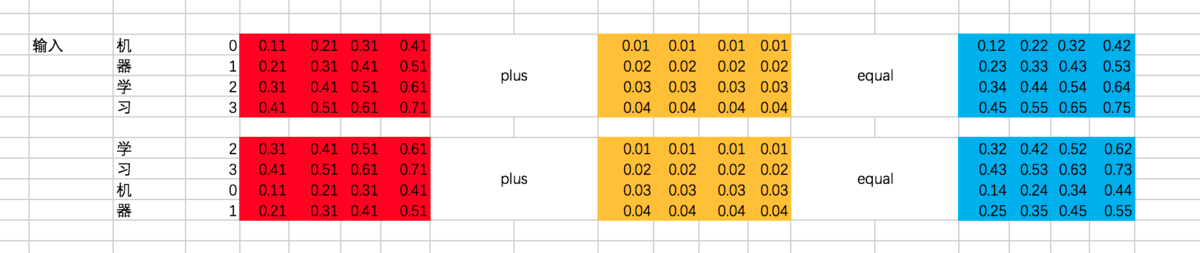
③对输入input_embedding加入位置偏置position_embedding,注意这里是两个向量的对位相加:
④output_sentence [y]和input_sentence做相同的处理
代码:
import tensorflow as tf chinese_embedding = tf.constant([[0.11,0.21,0.31,0.41],
[0.21,0.31,0.41,0.51],
[0.31,0.41,0.51,0.61],
[0.41,0.51,0.61,0.71]],dtype=tf.float32) english_embedding = tf.constant([[0.51,0.61,0.71,0.81],
[0.52,0.62,0.72,0.82],
[0.53,0.63,0.73,0.83],
[0.54,0.64,0.74,0.84]],dtype=tf.float32) position_encoding = tf.constant([[0.01,0.01,0.01,0.01],
[0.02,0.02,0.02,0.02],
[0.03,0.03,0.03,0.03],
[0.04,0.04,0.04,0.04]],dtype=tf.float32) encoder_input = tf.constant([[0,1,2,3],[2,3,0,1]],dtype=tf.int32) with tf.variable_scope("encoder_input"):
encoder_embedding_input = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(chinese_embedding,encoder_input)
encoder_embedding_input = encoder_embedding_input + position_encoding with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
print(sess.run([encoder_embedding_input]))
(2) attention
[scaled dot-product attention]
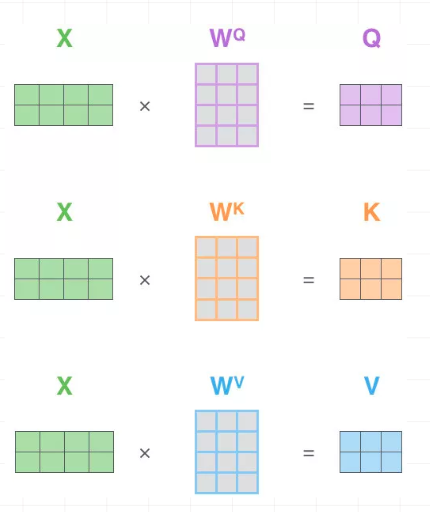
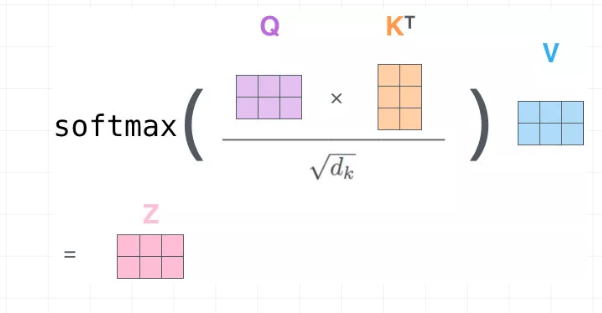
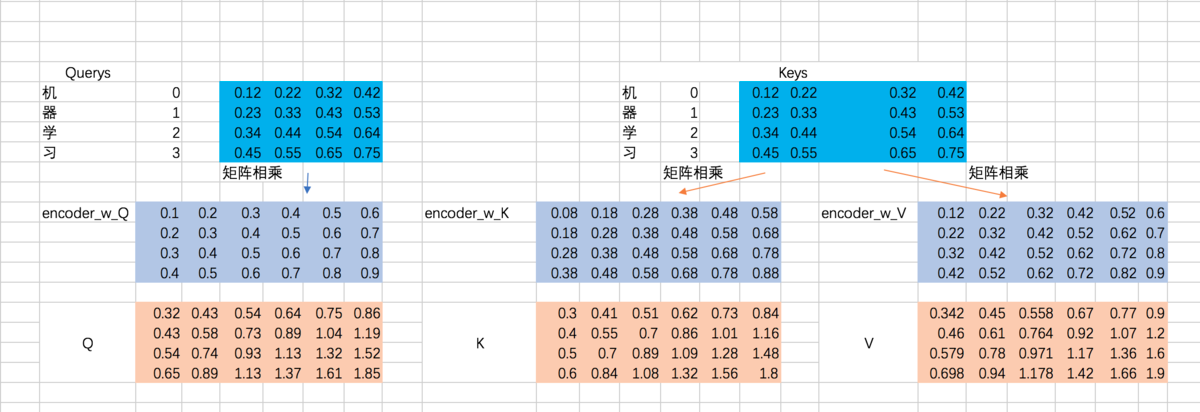
①计算Q . K . V [embedding × 三个W]
咱们先说说Q、K、V。比如我们想要计算上图中machine和机、器、学、习四个字的attention,并加权得到一个输出,那么Query由machine对应的embedding计算得到,K和V分别由机、器、学、习四个字对应的embedding得到。
在encoder的self-attention中,由于是计算自身和自身的相似度,所以Q、K、V都是由输入的embedding得到的,不过我们还是加以区分。
这里, Q、K、V分别通过一层全连接神经网络得到,同样,我们把对应的参数矩阵都写作常量。
接下来,以第一条输入为例, 将embedding 和 三个 W 矩阵相乘:
②计算α权重 [ softmax(Q * KT / sqrt(dk))]
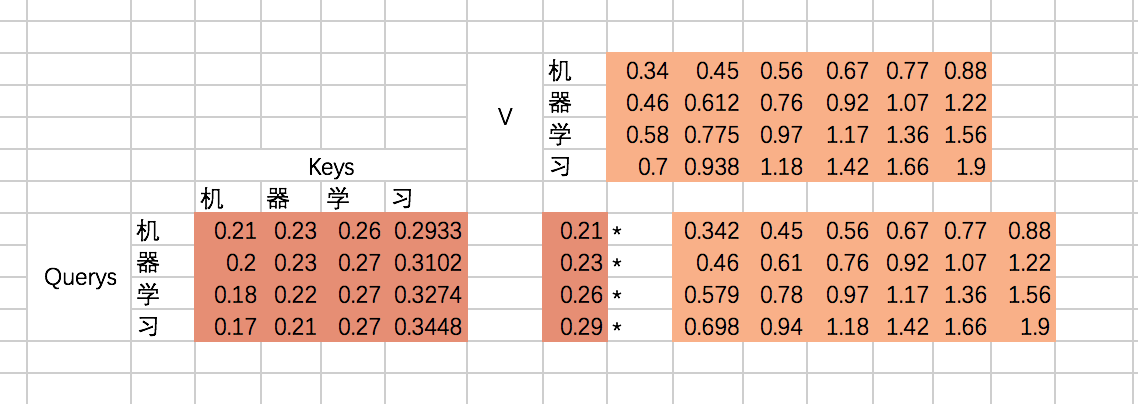
计算Q和K的相关性大小,这里使用内积的方式,相当于QKT: (下图中V应该改成K,不影响整个过程理解),得到结果为attention map
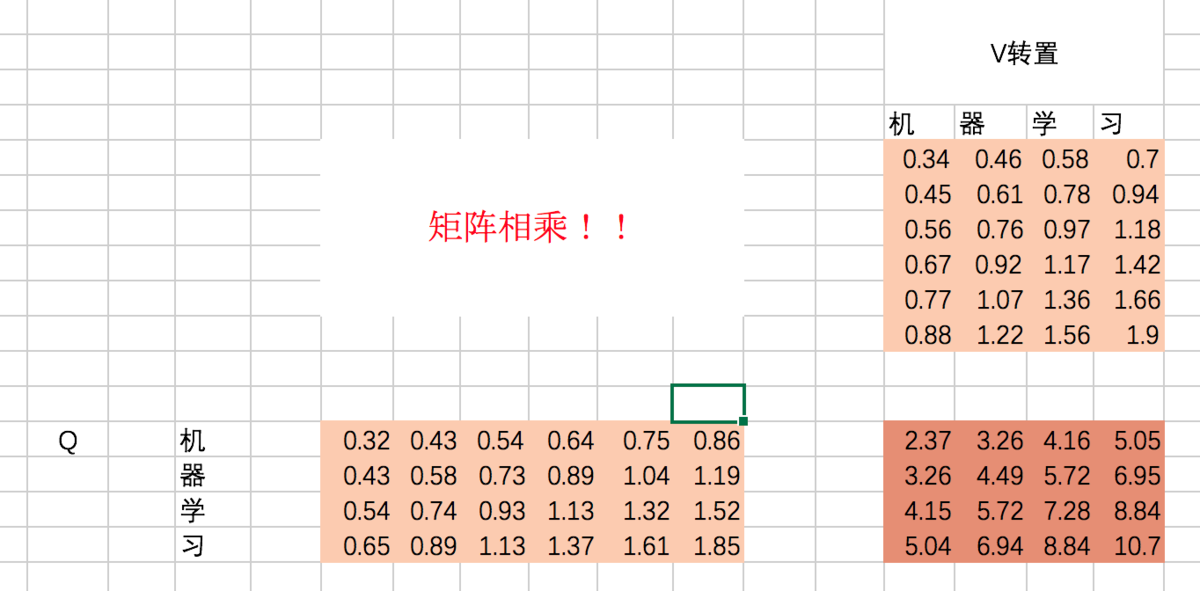
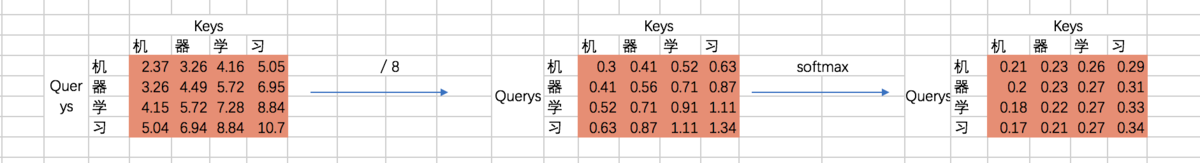
机和机自身的相关性是2.37(未进行归一化处理),机和器的相关性是3.26,依次类推。
接着除以一个规范化因子,然后进行softmax操作,这里的规范化因子选择除以8,然后每行进行一个softmax归一化操作(按行做归一化是因为attention的初衷是计算每个Query和所有的Keys之间的相关性):
③将α 与V加权求和:
最后就是得到每个输入embedding 对应的输出embedding,也就是基于attention map对V进行加权求和,以“机”这个输入为例,最后的输出应该是V对应的四个向量的加权求和:
代码:
with tf.variable_scope("encoder_scaled_dot_product_attention"):
encoder_Q = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(encoder_embedding_input,(-1,tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[2])),w_Q)
encoder_K = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(encoder_embedding_input,(-1,tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[2])),w_K)
encoder_V = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(encoder_embedding_input,(-1,tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[2])),w_V)
####① 计算Q K V
encoder_Q = tf.reshape(encoder_Q,(tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[0],tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[1],-1))
encoder_K = tf.reshape(encoder_K,(tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[0],tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[1],-1))
encoder_V = tf.reshape(encoder_V,(tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[0],tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[1],-1))
####②计算α , softmax( Q * KT / sqrt(dk) )
attention_map = tf.matmul(encoder_Q,tf.transpose(encoder_K,[0,2,1]))
attention_map = attention_map / 8
attention_map = tf.nn.softmax(attention_map)
###③ α * V ,自己补的,不一定对
#### weightedSumV = tf.matmul(attention_map,encoder_V)
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
print(sess.run(attention_map))
# print(sess.run(weightedSumV))
[multi-head attention]
Multi-Head Attention就是把Scaled Dot-Product Attention的过程做H次,然后把输出Z合起来。 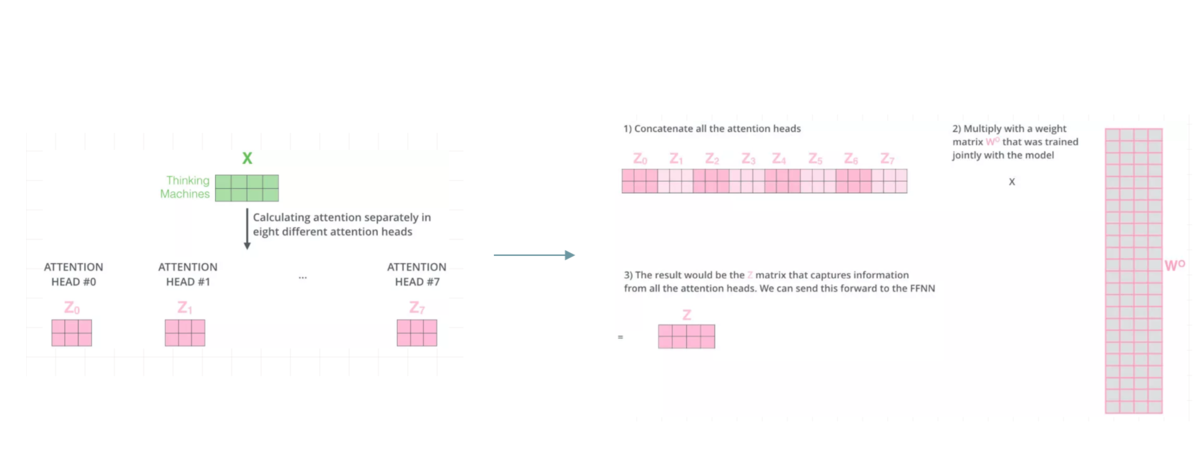
① 切分多个Head ( 即多个Q K V) , 并多次进行scaled dot-product attention
假设我们刚才计算得到的Q、K、V从中间切分,分别作为两个Head的输入:
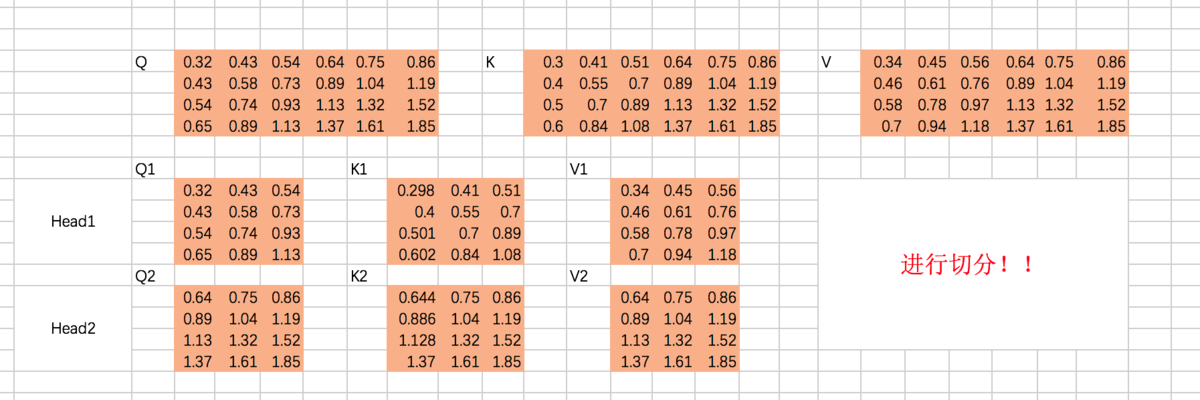
重复上面的Scaled Dot-Product Attention过程,我们分别得到两个Head的输出:

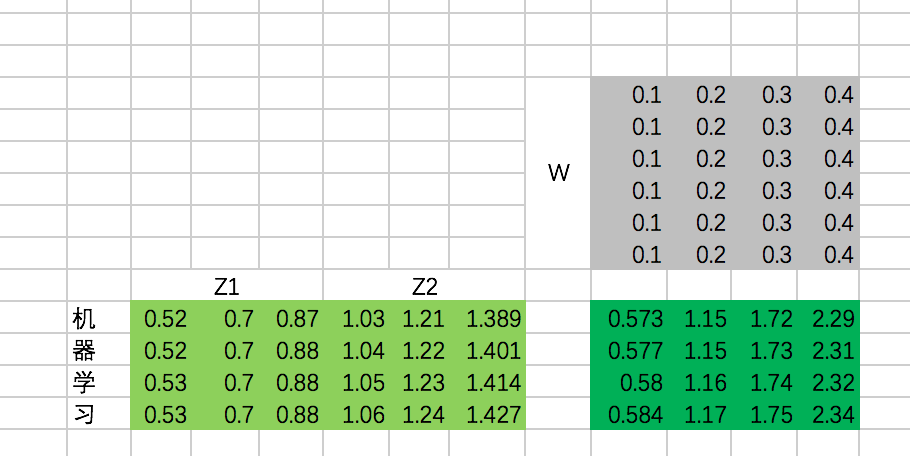
②concat多个Scaled Dot-Product Attention的结果 z , 并将其乘以W降维
接下来,我们需要通过一个权重矩阵,来得到最终输出。
为了我们能够进行后面的Add的操作,我们需要把输出的长度和输入保持一致,即每个单词得到的输出embedding长度保持为4。
同样,我们这里把转换矩阵W设置为常数:
代码:
w_Z = tf.constant([[0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4],
[0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4],
[0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4],
[0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4],
[0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4],
[0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4]],dtype=tf.float32) with tf.variable_scope("encoder_input"):
encoder_embedding_input = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(chinese_embedding,encoder_input)
encoder_embedding_input = encoder_embedding_input + position_encoding with tf.variable_scope("encoder_multi_head_product_attention"):
encoder_Q = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(encoder_embedding_input,(-1,tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[2])),w_Q)
encoder_K = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(encoder_embedding_input,(-1,tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[2])),w_K)
encoder_V = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(encoder_embedding_input,(-1,tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[2])),w_V) ###① 生成Q K V
encoder_Q = tf.reshape(encoder_Q,(tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[0],tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[1],-1))
encoder_K = tf.reshape(encoder_K,(tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[0],tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[1],-1))
encoder_V = tf.reshape(encoder_V,(tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[0],tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[1],-1)) ###②最后一维切分 成多个Head ---Q K V
encoder_Q_split = tf.split(encoder_Q,2,axis=2)
encoder_K_split = tf.split(encoder_K,2,axis=2)
encoder_V_split = tf.split(encoder_V,2,axis=2) ###第一维合并Q K V ,方便计算
encoder_Q_concat = tf.concat(encoder_Q_split,axis=0)
encoder_K_concat = tf.concat(encoder_K_split,axis=0)
encoder_V_concat = tf.concat(encoder_V_split,axis=0) ###计算attention α
attention_map = tf.matmul(encoder_Q_concat,tf.transpose(encoder_K_concat,[0,2,1]))
attention_map = attention_map / 8
attention_map = tf.nn.softmax(attention_map) ### α和V加权求和,结果为Z
weightedSumV = tf.matmul(attention_map,encoder_V_concat) ###③ 将多个head求出来的Z合并
outputs_z = tf.concat(tf.split(weightedSumV,2,axis=0),axis=2) ###④ 合并的Z与W相乘降维得到最终的Z
outputs = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(outputs_z,(-1,tf.shape(outputs_z)[2])),w_Z)
outputs = tf.reshape(outputs,(tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[0],tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[1],-1)) import numpy as np
with tf.Session() as sess:
# print(sess.run(encoder_Q))
# print(sess.run(encoder_Q_split))
#print(sess.run(weightedSumV))
#print(sess.run(outputs_z))
print(sess.run(outputs))
更详细的解释split函数和concat函数
split函数主要有三个参数,第一个是要split的tensor,第二个是分割成几个tensor,第三个是在哪一维进行切分。也就是说, encoder_Q_split = tf.split(encoder_Q,2,axis=2),执行这段代码的话,encoder_Q这个tensor会按照axis=2切分成两个同样大的tensor,这两个tensor的axis=0和axis=1维度的长度是不变的,但axis=2的长度变为了一半,我们在后面通过图示的方式来解释。
从代码可以看到,共有两次split和concat的过程,第一次是将Q、K、V切分为不同的Head:
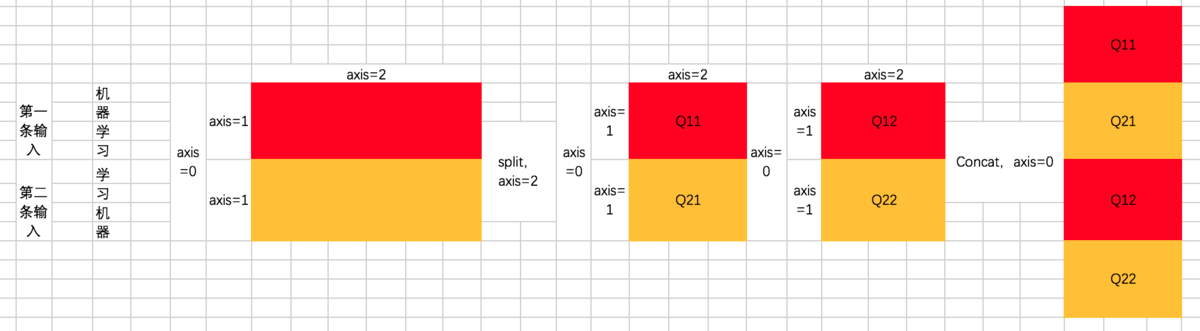
也就是说,原先每条数据的所对应的各Head的Q并非相连的,而是交替出现的,即 [Head1-Q11,Head1-Q21,Head2-Q12,Head2-Q22]
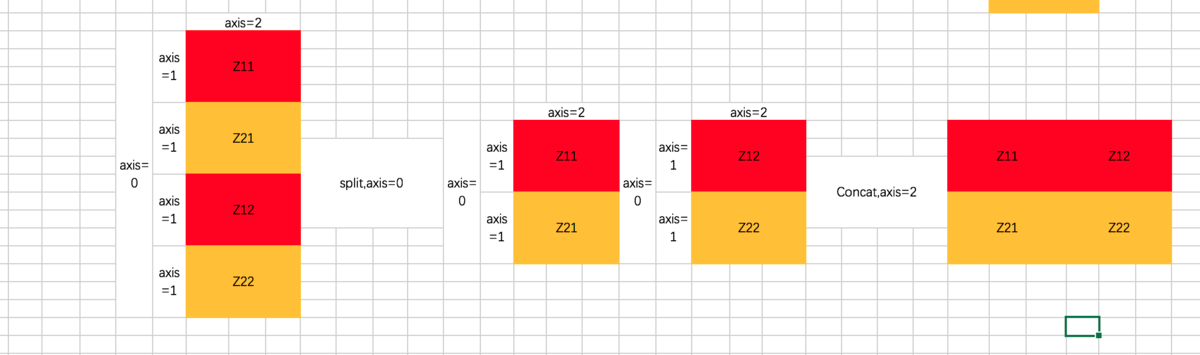
第二次是最后计算完每个Head的输出Z之后,通过split和concat进行还原,过程如下:
(3) Add & Normalize & FFN
第一次Add & Normalize:
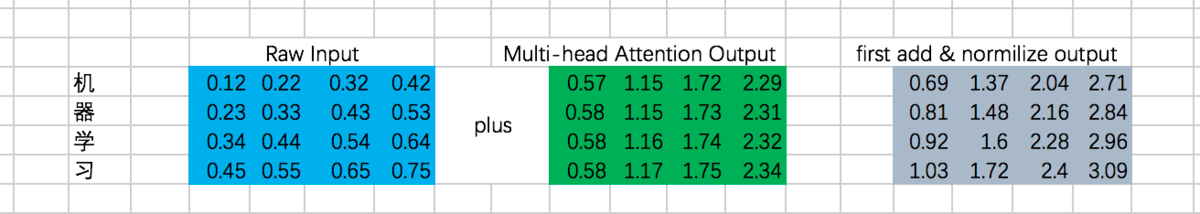
接下来是一个FFN,我们仍然假设是固定的参数,那么output是:
第二次Add & Normalize
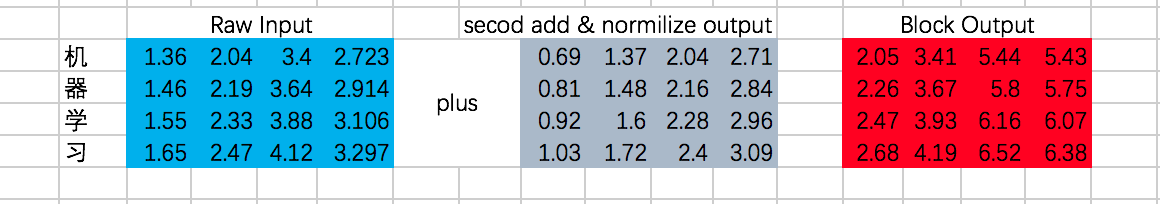
我们终于在经过一个Encoder的Block后得到了每个输入对应的输出,分别为:
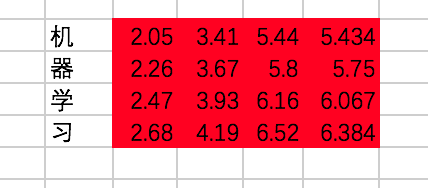
代码:
with tf.variable_scope("encoder_block"):
encoder_Q = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(encoder_embedding_input,(-1,tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[2])),w_Q)
encoder_K = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(encoder_embedding_input,(-1,tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[2])),w_K)
encoder_V = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(encoder_embedding_input,(-1,tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[2])),w_V)
encoder_Q = tf.reshape(encoder_Q,(tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[0],tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[1],-1))
encoder_K = tf.reshape(encoder_K,(tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[0],tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[1],-1))
encoder_V = tf.reshape(encoder_V,(tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[0],tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[1],-1))
encoder_Q_split = tf.split(encoder_Q,2,axis=2)
encoder_K_split = tf.split(encoder_K,2,axis=2)
encoder_V_split = tf.split(encoder_V,2,axis=2)
encoder_Q_concat = tf.concat(encoder_Q_split,axis=0)
encoder_K_concat = tf.concat(encoder_K_split,axis=0)
encoder_V_concat = tf.concat(encoder_V_split,axis=0)
attention_map = tf.matmul(encoder_Q_concat,tf.transpose(encoder_K_concat,[0,2,1]))
attention_map = attention_map / 8
attention_map = tf.nn.softmax(attention_map)
#multi-head attention的计算结果
weightedSumV = tf.matmul(attention_map,encoder_V_concat)
outputs_z = tf.concat(tf.split(weightedSumV,2,axis=0),axis=2)
#将多头结果的维度转为和encoder_embedding_input维度一样
sa_outputs = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(outputs_z,(-1,tf.shape(outputs_z)[2])),w_Z)
sa_outputs = tf.reshape(sa_outputs,(tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[0],tf.shape(encoder_embedding_input)[1],-1))
##第一次add
sa_outputs = sa_outputs + encoder_embedding_input
# todo :add BN
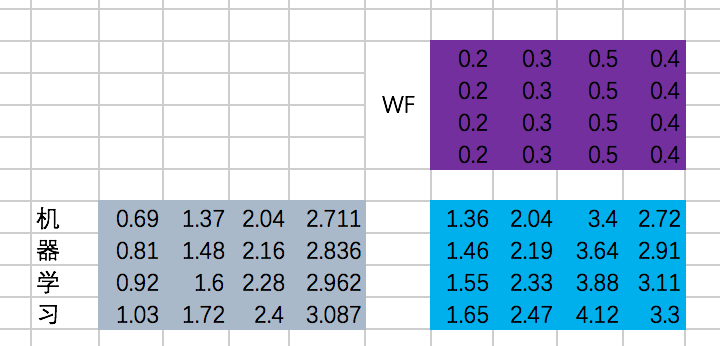
W_f = tf.constant([[0.2,0.3,0.5,0.4],
[0.2,0.3,0.5,0.4],
[0.2,0.3,0.5,0.4],
[0.2,0.3,0.5,0.4]])
##FFN
ffn_outputs = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(sa_outputs,(-1,tf.shape(sa_outputs)[2])),W_f)
ffn_outputs = tf.reshape(ffn_outputs,(tf.shape(sa_outputs)[0],tf.shape(sa_outputs)[1],-1))
#第二次add
encoder_outputs = ffn_outputs + sa_outputs
# todo :add BN
import numpy as np
with tf.Session() as sess:
# print(sess.run(encoder_Q))
# print(sess.run(encoder_Q_split))
#print(sess.run(weightedSumV))
#print(sess.run(outputs_z))
#print(sess.run(sa_outputs))
#print(sess.run(ffn_outputs))
print(sess.run(encoder_outputs))
3.2 decoder
相比Encoder,这里的过程分为6步,分别是 masked multi-head self attention、Add & Normalize、encoder-decoder attention、Add & Normalize、Feed Forward Network、Add & Normalize。
咱们还是重点来讲masked multi-head self attention和encoder-decoder attention。
(1) Decoder输入
总体input : [机、器、学、习] -> [ machine、learning]
因此,Decoder阶段的输入是:[ machine、learning]
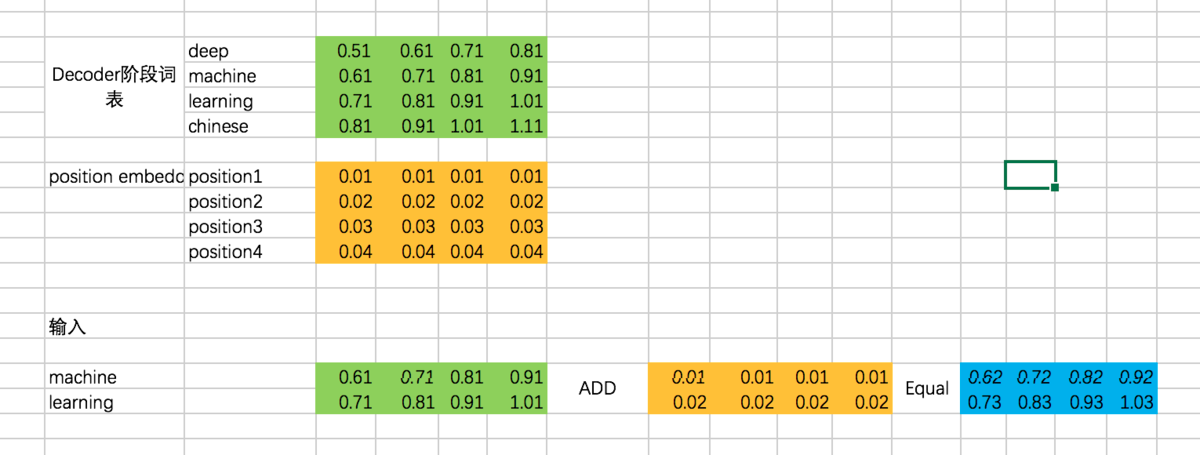
代码:
english_embedding = tf.constant([[0.51,0.61,0.71,0.81],
[0.61,0.71,0.81,0.91],
[0.71,0.81,0.91,1.01],
[0.81,0.91,1.01,1.11]],dtype=tf.float32) position_encoding = tf.constant([[0.01,0.01,0.01,0.01],
[0.02,0.02,0.02,0.02],
[0.03,0.03,0.03,0.03],
[0.04,0.04,0.04,0.04]],dtype=tf.float32) decoder_input = tf.constant([[1,2],[2,1]],dtype=tf.int32) with tf.variable_scope("decoder_input"):
decoder_embedding_input = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(english_embedding,decoder_input)
decoder_embedding_input = decoder_embedding_input + position_encoding[0:tf.shape(decoder_embedding_input)[1]]
(2) masked multi-head self attention
这个过程和multi-head self attention基本一致,只不过对于decoder来说,得到每个阶段的输出时,我们是看不到后面的信息的。举个例子,我们的第一条输入是:[机、器、学、习] -> [ machine、learning] ,decoder阶段两次的输入分别是machine和learning,在输入machine时,我们是看不到learning的信息的,因此在计算attention的权重的时候,machine和learning的权重是没有的。我们还是先通过excel来演示一下,再通过代码来理解:
计算Attention的权重矩阵是:
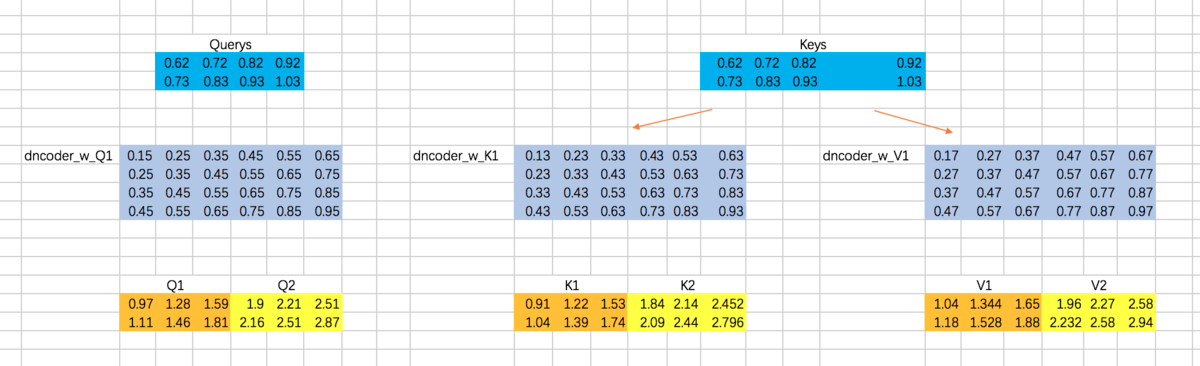
仍然以两个Head为例,计算Q、K、V:
分别计算两个Head的attention map
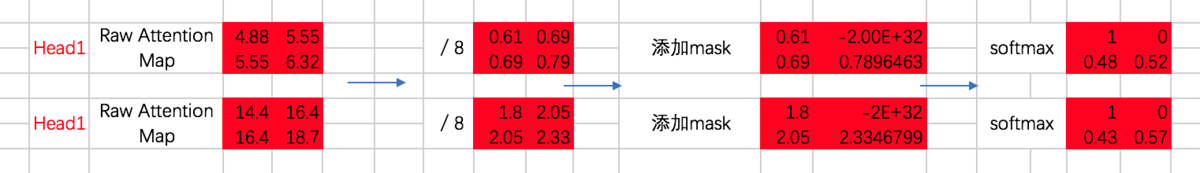
咱们先来实现这部分的代码,masked attention map的计算过程:
前两步和encoder一样,只是得到attention map [ Q*KT / sqrt(dk) ]之后加上masked.然后再softmax ,最后与V相乘.
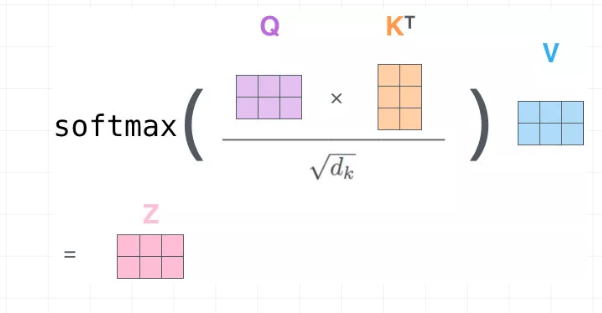
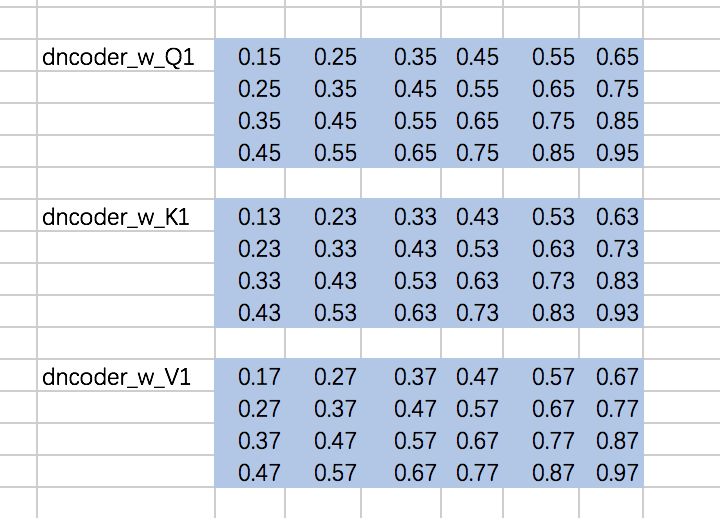
- 先定义下权重矩阵,同encoder一样,定义成常数:
w_Q_decoder_sa = tf.constant([[0.15,0.25,0.35,0.45,0.55,0.65],
[0.25,0.35,0.45,0.55,0.65,0.75],
[0.35,0.45,0.55,0.65,0.75,0.85],
[0.45,0.55,0.65,0.75,0.85,0.95]],dtype=tf.float32) w_K_decoder_sa = tf.constant([[0.13,0.23,0.33,0.43,0.53,0.63],
[0.23,0.33,0.43,0.53,0.63,0.73],
[0.33,0.43,0.53,0.63,0.73,0.83],
[0.43,0.53,0.63,0.73,0.83,0.93]],dtype=tf.float32) w_V_decoder_sa = tf.constant([[0.17,0.27,0.37,0.47,0.57,0.67],
[0.27,0.37,0.47,0.57,0.67,0.77],
[0.37,0.47,0.57,0.67,0.77,0.87],
[0.47,0.57,0.67,0.77,0.87,0.97]],dtype=tf.float32)
- 随后,计算添加mask之前的attention map:
with tf.variable_scope("decoder_sa_block"):
decoder_Q = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(decoder_embedding_input,(-1,tf.shape(decoder_embedding_input)[2])),w_Q_decoder_sa)
decoder_K = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(decoder_embedding_input,(-1,tf.shape(decoder_embedding_input)[2])),w_K_decoder_sa)
decoder_V = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(decoder_embedding_input,(-1,tf.shape(decoder_embedding_input)[2])),w_V_decoder_sa)
decoder_Q = tf.reshape(decoder_Q,(tf.shape(decoder_embedding_input)[0],tf.shape(decoder_embedding_input)[1],-1))
decoder_K = tf.reshape(decoder_K,(tf.shape(decoder_embedding_input)[0],tf.shape(decoder_embedding_input)[1],-1))
decoder_V = tf.reshape(decoder_V,(tf.shape(decoder_embedding_input)[0],tf.shape(decoder_embedding_input)[1],-1))
decoder_Q_split = tf.split(decoder_Q,2,axis=2)
decoder_K_split = tf.split(decoder_K,2,axis=2)
decoder_V_split = tf.split(decoder_V,2,axis=2)
decoder_Q_concat = tf.concat(decoder_Q_split,axis=0)
decoder_K_concat = tf.concat(decoder_K_split,axis=0)
decoder_V_concat = tf.concat(decoder_V_split,axis=0)
decoder_sa_attention_map_raw = tf.matmul(decoder_Q_concat,tf.transpose(decoder_K_concat,[0,2,1]))
decoder_sa_attention_map = decoder_sa_attention_map_raw / 8
- 随后,对attention map添加mask:
diag_vals = tf.ones_like(decoder_sa_attention_map[0,:,:])
tril = tf.contrib.linalg.LinearOperatorTriL(diag_vals).to_dense()
masks = tf.tile(tf.expand_dims(tril,0),[tf.shape(decoder_sa_attention_map)[0],1,1])
paddings = tf.ones_like(masks) * (-2 ** 32 + 1)
decoder_sa_attention_map = tf.where(tf.equal(masks,0),paddings,decoder_sa_attention_map)
#softmax
decoder_sa_attention_map = tf.nn.softmax(decoder_sa_attention_map)
这里我们首先构造一个全1的矩阵diag_vals,这个矩阵的大小同attention map。随后通过tf.contrib.linalg.LinearOperatorTriL方法把上三角部分变为0,该函数的示意如下:

基于这个函数生成的矩阵tril,我们便可以构造对应的mask了。不过需要注意的是,对于我们要加mask的地方,不能赋值为0,而是需要赋值一个很小的数,这里为-2^32 + 1。因为我们后面要做softmax,e^0=1,是一个很大的数啦。
- 补全multi-head attention得到attention map 后面的代码
weightedSumV = tf.matmul(decoder_sa_attention_map,decoder_V_concat) decoder_outputs_z = tf.concat(tf.split(weightedSumV,2,axis=0),axis=2) decoder_sa_outputs = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(decoder_outputs_z,(-1,tf.shape(decoder_outputs_z)[2])),w_Z_decoder_sa) decoder_sa_outputs = tf.reshape(decoder_sa_outputs,(tf.shape(decoder_embedding_input)[0],tf.shape(decoder_embedding_input)[1],-1)) with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run(decoder_sa_outputs))
(3)encoder-decoder attention
在encoder-decoder attention之间,还有一个Add & Normalize的过程,同样,我们忽略 Normalize,只做Add操作:
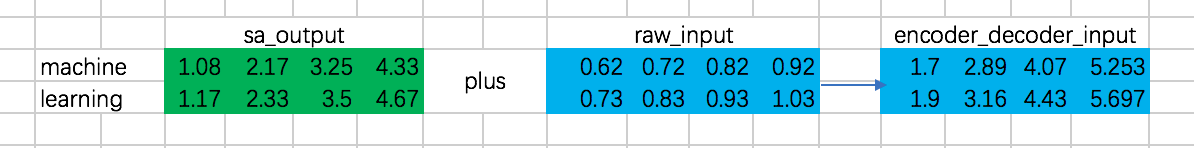
接下来,就是encoder-decoder了,这里跟multi-head attention相同,但是需要注意的一点是,我们这里想要做的是,计算decoder的每个阶段的输入和encoder阶段所有输出的attention,所以Q的计算通过decoder对应的embedding计算,而K和V通过encoder阶段输出的embedding来计算:
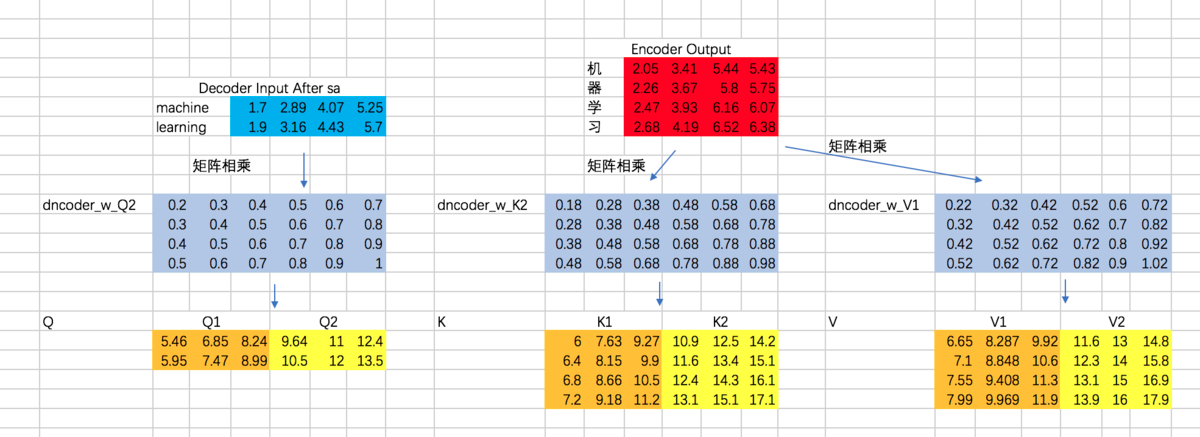
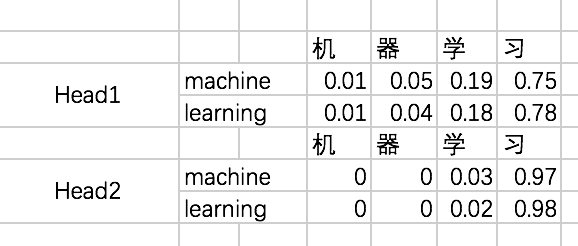
接下来,计算Attention Map,注意,这里attention map的大小为2 * 4的,每一行代表一个decoder的输入,与所有encoder输出之间的attention score。同时,我们不需要添加mask,因为decoder的输入是可以看到所有encoder的输出信息的。得到的attention map结果如下:
接下来,我们得到整个encoder-decoder阶段的输出为:
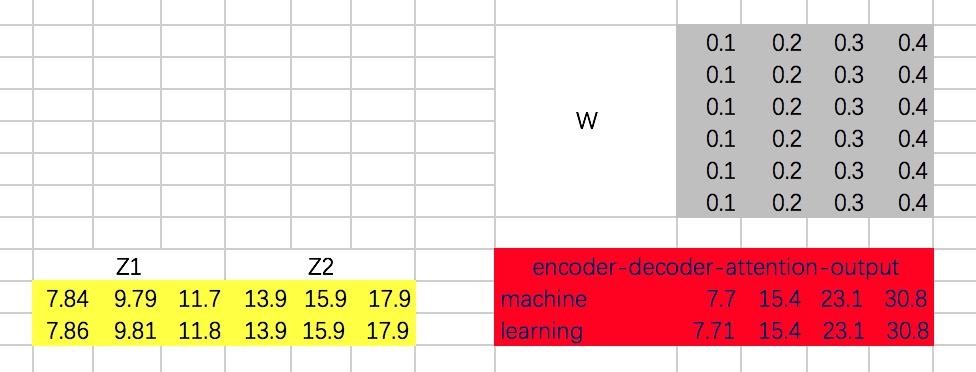
接下来,还有Add & Normalize、Feed Forward Network、Add & Normalize过程,咱们这里就省略了。encoder-decoder代码:
w_Q_decoder_sa2 = tf.constant([[0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5,0.6,0.7],
[0.3,0.4,0.5,0.6,0.7,0.8],
[0.4,0.5,0.6,0.7,0.8,0.9],
[0.5,0.6,0.7,0.8,0.9,1]],dtype=tf.float32) w_K_decoder_sa2 = tf.constant([[0.18,0.28,0.38,0.48,0.58,0.68],
[0.28,0.38,0.48,0.58,0.68,0.78],
[0.38,0.48,0.58,0.68,0.78,0.88],
[0.48,0.58,0.68,0.78,0.88,0.98]],dtype=tf.float32) w_V_decoder_sa2 = tf.constant([[0.22,0.32,0.42,0.52,0.62,0.72],
[0.32,0.42,0.52,0.62,0.72,0.82],
[0.42,0.52,0.62,0.72,0.82,0.92],
[0.52,0.62,0.72,0.82,0.92,1.02]],dtype=tf.float32) w_Z_decoder_sa2 = tf.constant([[0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4],
[0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4],
[0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4],
[0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4],
[0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4],
[0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4]],dtype=tf.float32) with tf.variable_scope("decoder_encoder_attention_block"): decoder_sa_outputs = decoder_sa_outputs + decoder_embedding_input encoder_decoder_Q = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(decoder_sa_outputs,(-1,tf.shape(decoder_sa_outputs)[2])),w_Q_decoder_sa2)
encoder_decoder_K = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(encoder_outputs,(-1,tf.shape(encoder_outputs)[2])),w_K_decoder_sa2)
encoder_decoder_V = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(encoder_outputs,(-1,tf.shape(encoder_outputs)[2])),w_V_decoder_sa2) encoder_decoder_Q = tf.reshape(encoder_decoder_Q,(tf.shape(decoder_embedding_input)[0],tf.shape(decoder_embedding_input)[1],-1))
encoder_decoder_K = tf.reshape(encoder_decoder_K,(tf.shape(encoder_outputs)[0],tf.shape(encoder_outputs)[1],-1))
encoder_decoder_V = tf.reshape(encoder_decoder_V,(tf.shape(encoder_outputs)[0],tf.shape(encoder_outputs)[1],-1)) encoder_decoder_Q_split = tf.split(encoder_decoder_Q,2,axis=2)
encoder_decoder_K_split = tf.split(encoder_decoder_K,2,axis=2)
encoder_decoder_V_split = tf.split(encoder_decoder_V,2,axis=2) encoder_decoder_Q_concat = tf.concat(encoder_decoder_Q_split,axis=0)
encoder_decoder_K_concat = tf.concat(encoder_decoder_K_split,axis=0)
encoder_decoder_V_concat = tf.concat(encoder_decoder_V_split,axis=0)
##注意,不用mask
encoder_decoder_attention_map_raw = tf.matmul(encoder_decoder_Q_concat,tf.transpose(encoder_decoder_K_concat,[0,2,1]))
encoder_decoder_attention_map = encoder_decoder_attention_map_raw / 8 encoder_decoder_attention_map = tf.nn.softmax(encoder_decoder_attention_map) weightedSumV = tf.matmul(encoder_decoder_attention_map,encoder_decoder_V_concat) encoder_decoder_outputs_z = tf.concat(tf.split(weightedSumV,2,axis=0),axis=2) encoder_decoder_outputs = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(encoder_decoder_outputs_z,(-1,tf.shape(encoder_decoder_outputs_z)[2])),w_Z_decoder_sa2) encoder_decoder_attention_outputs = tf.reshape(encoder_decoder_outputs,(tf.shape(decoder_embedding_input)[0],tf.shape(decoder_embedding_input)[1],-1)) encoder_decoder_attention_outputs = encoder_decoder_attention_outputs + decoder_sa_outputs # todo :add BN
W_f = tf.constant([[0.2,0.3,0.5,0.4],
[0.2,0.3,0.5,0.4],
[0.2,0.3,0.5,0.4],
[0.2,0.3,0.5,0.4]]) decoder_ffn_outputs = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(encoder_decoder_attention_outputs,(-1,tf.shape(encoder_decoder_attention_outputs)[2])),W_f)
decoder_ffn_outputs = tf.reshape(decoder_ffn_outputs,(tf.shape(encoder_decoder_attention_outputs)[0],tf.shape(encoder_decoder_attention_outputs)[1],-1)) decoder_outputs = decoder_ffn_outputs + encoder_decoder_attention_outputs
# todo :add BN with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run(decoder_outputs))
(4)全连接层及最终输出
最后的全连接层很简单了,对于decoder阶段的输出,通过全连接层和softmax之后,最终得到选择每个单词的概率,并计算交叉熵损失:
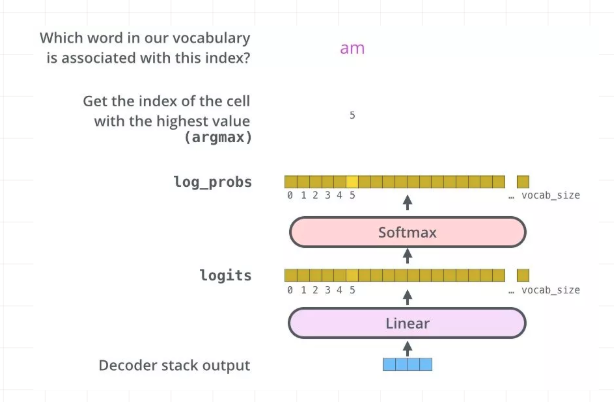
代码:
W_final = tf.constant([[0.2,0.3,0.5,0.4],
[0.2,0.3,0.5,0.4],
[0.2,0.3,0.5,0.4],
[0.2,0.3,0.5,0.4]]) logits = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(decoder_outputs,(-1,tf.shape(decoder_outputs)[2])),W_final)
logits = tf.reshape(logits,(tf.shape(decoder_outputs)[0],tf.shape(decoder_outputs)[1],-1)) logits = tf.nn.softmax(logits) y = tf.one_hot(decoder_input,depth=4) loss = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,labels=y) train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.0001).minimize(loss)
参考:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/3f2d4bc126e6
https://www.leiphone.com/news/201709/8tDpwklrKubaecTa.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/hellojamest/p/11128799.html
https://blog.csdn.net/longxinchen_ml/article/details/86533005
https://www.imooc.com/article/67493
李宏毅老师的课程
NLP 学习:http://www.shuang0420.com/categories/NLP/page/9/
NLP学习(5)----attention/ self-attention/ seq2seq/ transformer的更多相关文章
- [转] 用深度学习(CNN RNN Attention)解决大规模文本分类问题 - 综述和实践
转自知乎上看到的一篇很棒的文章:用深度学习(CNN RNN Attention)解决大规模文本分类问题 - 综述和实践 近来在同时做一个应用深度学习解决淘宝商品的类目预测问题的项目,恰好硕士毕业时论文 ...
- NLP教程(6) - 神经机器翻译、seq2seq与注意力机制
作者:韩信子@ShowMeAI 教程地址:http://www.showmeai.tech/tutorials/36 本文地址:http://www.showmeai.tech/article-det ...
- NLP学习(3)---Bert模型
一.BERT模型: 前提:Seq2Seq模型 前提:transformer模型 bert实战教程1 使用BERT生成句向量,BERT做文本分类.文本相似度计算 bert中文分类实践 用bert做中文命 ...
- TF-IDF与主题模型 - NLP学习(3-2)
分词(Tokenization) - NLP学习(1) N-grams模型.停顿词(stopwords)和标准化处理 - NLP学习(2) 文本向量化及词袋模型 - NLP学习(3-1) 在上一篇博文 ...
- 文本向量化及词袋模型 - NLP学习(3-1)
分词(Tokenization) - NLP学习(1) N-grams模型.停顿词(stopwords)和标准化处理 - NLP学习(2) 之前我们都了解了如何对文本进行处理:(1)如用NLTK文 ...
- [NLP/Attention]关于attention机制在nlp中的应用总结
原文链接: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41058526/article/details/80578932 attention 总结 参考:注意力机制(Attention Mec ...
- 用深度学习(CNN RNN Attention)解决大规模文本分类问题 - 综述和实践
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/25928551 近来在同时做一个应用深度学习解决淘宝商品的类目预测问题的项目,恰好硕士毕业时论文题目便是文本分类问题,趁此机会总结下文本分类 ...
- attention、self-attention、transformer和bert模型基本原理简述笔记
attention 以google神经机器翻译(NMT)为例 无attention: encoder-decoder在无attention机制时,由encoder将输入序列转化为最后一层输出state ...
- NLP学习(2)----文本分类模型
实战:https://github.com/jiangxinyang227/NLP-Project 一.简介: 1.传统的文本分类方法:[人工特征工程+浅层分类模型] (1)文本预处理: ①(中文) ...
随机推荐
- Boost Graph Library使用学习
Boost Graph Library,BGL 使用学习 探索 Boost Graph Library https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/aix/librar ...
- MySQL实战45讲学习笔记:第十二讲
一.引子 平时的工作中,不知道你有没有遇到过这样的场景,一条 SQL 语句,正常执行的时候特别快,但是有时也不知道怎么回事,它就会变得特别慢,并且这样的场景很难复现,它不只随机,而且持续时间还很短. ...
- [LeetCode] 34. Find First and Last Position of Element in Sorted Array 在有序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
Given an array of integers nums sorted in ascending order, find the starting and ending position of ...
- 官方一步解决各种Windows更新问题
原文部分: 修复 Windows 更新问题 适用于: Windows 8.1Windows 10Windows 7 此分布指南有什么作用? 此分步指南提供的步骤可修复 Windows 更新的问题, ...
- Codeforces 652F 解题报告
题意 有n只蚂蚁在长度为m个格子的环上,环上的格子以逆时针编号,每只蚂蚁每秒往它面向的方向移动一格.如果有两只蚂蚁相撞则相互调换方向,问t秒后每只蚂蚁的位置. 题解 首先通过观察可以发现 蚂蚁相撞产生 ...
- ROS-RouterOS KVM 安装 OpenWrt 旁路使用
原文: http://bbs.routerclub.com/thread-104864-1-1.html 这里所讲是X86架构的RouteROS的KVM虚拟机,其实RouterOS的KVM很早就有,大 ...
- Helm 常用命令及操作
Helm 常用命令 查看版本 #helm version 查看当前安装的charts #helm list 查询 charts #helm search redis 安装charts #helm in ...
- 【转】python实现Telnet操作
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import logging import telnetlib import time import sys import os host_ip = ' ...
- POJ 1306 暴力求组合数
Combinations Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 11049 Accepted: 5013 Des ...
- Rabbit MQ 学习参考
网上的教程虽然多,但是提供demo的比较少,或者没有详细的说明,因此,本人就照着网上的教程做了几个demo,并把代码托管在码云,供有需要的参考. 项目地址:https://gitee.com/dhcl ...