MyBatis源码 核心配置解析 properties元素
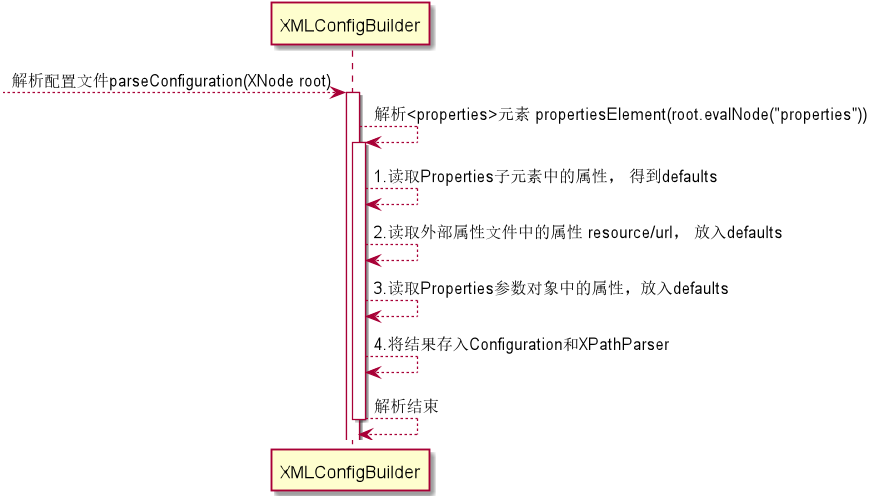
XMLConfigBuilder的parseConfiguration(XNode)方法,用于解析配置文件
XMLConfigBuilder的propertiesElement(XNode)方法,用于解析配置文件的properties标签。
private void propertiesElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
//1.读取 <property> 元素的内容
Properties defaults = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
String resource = context.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = context.getStringAttribute("url");
//不能同时设置 resource 和 url 属性
if (resource != null && url != null) {
throw new BuilderException("The properties element cannot specify both a URL and a resource based property file reference. Please specify one or the other.");
}
//2.读取外部属性文件中的内容
if (resource != null) {
defaults.putAll(Resources.getResourceAsProperties(resource));
} else if (url != null) {
defaults.putAll(Resources.getUrlAsProperties(url));
}
//3.读取创建 SqlSessionFactory 对象时,用户传入的 Properties 参数对象
Properties vars = configuration.getVariables();
if (vars != null) {
defaults.putAll(vars);
}
//将最终的结果存入Configuration和XPathParser
parser.setVariables(defaults);
configuration.setVariables(defaults);
/*
总结:
1.属性的读取顺序, property 元素先于外部属性文件先于 Properties 参数对象。后存入属性的将覆盖先前存入的同名属性。
因为:Properties 对象存入键值对时,键已存在,用新值覆盖旧值。
优先级:
Properties 参数对象 > 外部属性文件 > properties 元素
2.最终的结果存入了 Configuration 和 XPathParser
*/
}
}
解析 properties 元素时序图
官方对Properties的解释:

Properties的使用:
property元素
resource/url引用外部的properties文件
<properties resource="org/mybatis/example/jdbc.properties">
<property name="username" value="dev_user"/>
<property name="password" value="12345"/>
</properties>
#这是一个外部的 jdbc.properties
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3307/micro_message
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root
Properties参数对象
示例:
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("jdbc.username", "admin");
properties.setProperty("jdbc.password", "admin123");
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader, properties);
创建 SqlSessionFactory 对象时,可以传入 Properties 参数对象。
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, Properties properties);
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties);
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, Properties properties);
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties);
配置文件中通过 ${} 使用属性
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
MyBatis 源码中与 properties 元素解析相关的几个对象的数据关系:
XMLConfigBuilder BaseBuilder
XPathParser
Configuration
注意:箭头在这里仅表示引用关系。

XNode
public String getStringAttribute(String name) {
return getStringAttribute(name, null);
}
public String getStringAttribute(String name, String def) {
String value = attributes.getProperty(name);
if (value == null) {
return def;
} else {
return value;
}
}
public Properties getChildrenAsProperties() {
Properties properties = new Properties();
for (XNode child : getChildren()) {
String name = child.getStringAttribute("name");
String value = child.getStringAttribute("value");
if (name != null && value != null) {
properties.setProperty(name, value);
}
}
return properties;
}
public List<XNode> getChildren() {
List<XNode> children = new ArrayList<>();
NodeList nodeList = node.getChildNodes();
if (nodeList != null) {
for (int i = 0, n = nodeList.getLength(); i < n; i++) {
Node node = nodeList.item(i);
if (node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
children.add(new XNode(xpathParser, node, variables));
}
}
}
return children;
}

public XNode(XPathParser xpathParser, Node node, Properties variables) {
this.xpathParser = xpathParser;
this.node = node;
this.name = node.getNodeName();
this.variables = variables;
this.attributes = parseAttributes(node);
this.body = parseBody(node);
}
private Properties parseAttributes(Node n) {
Properties attributes = new Properties();
NamedNodeMap attributeNodes = n.getAttributes();
if (attributeNodes != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < attributeNodes.getLength(); i++) {
Node attribute = attributeNodes.item(i);
String value = PropertyParser.parse(attribute.getNodeValue(), variables);
attributes.put(attribute.getNodeName(), value);
}
}
return attributes;
}
private String parseBody(Node node) {
String data = getBodyData(node);
if (data == null) {
NodeList children = node.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
Node child = children.item(i);
data = getBodyData(child);
if (data != null) {
break;
}
}
}
return data;
}
private String getBodyData(Node child) {
if (child.getNodeType() == Node.CDATA_SECTION_NODE
|| child.getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE) {
String data = ((CharacterData) child).getData();
data = PropertyParser.parse(data, variables);
return data;
}
return null;
}
阅读源码 核心思想
修炼功法
按照功法修炼,可以不断突破瓶颈,提升实力。
无功法,难得道。
上层结构
界面,粒度,跟踪数据,这些都是在代码的细节上建造的上层知识结构,这种上层结构是理解和组织的产物,是处于缓慢消退的记忆,只有缓慢消退的记忆才具有价值。
概念性的东西:获取感性的认识,而非严格的定义。
功法残页1:粒度学习。
粒度由大到小才是一种合理的学习顺序。先了解下新类,再去关注新类中新方法的功能,再去关注新类中新方法的功能的实现。关注你需要了解的新类和需要了解的方法,不要看见一个新类,不看完它的方法不罢休。你一上来直奔新类新方法的功能的实现,结果整了一天看了2个方法。整个系统成千上万的方法,看到何年何月。而且没有上层建筑,你就会前学后忘。
目标1. 认识新类:先了解下新的类的基本作用。
目标2. 认识新类的新方法的功能:了解类的方法的功能
了解多个新方法的功能:先掌握认识的类的一个方法的功能,再了解需要了解的方法的功能。
目标3. 理解新方法的实现:认识类的方法的实现
举例:
系统十分复杂,我们通常不可能掌握每个细节。我们应该从大到小的分层次去认识这个复杂的系统。生活中,我们先知道了中国,然后才知道西安,然后知道了西安有个回民街,钟楼,大雁塔。系统中,类就是一个比较大的层次,而类的方法就是比较小的层次。
示例:
/*
分析:
读源码,必然遇到新的类,新的方法。
第1步,认识新类。了解这个类的基本作用。
第2步,认识新类的新方法的功能。大致的理解这个方法的作用,通过自己看实现或看别人的分析。
第3步,认识新类的新方法的实现。搞清楚这个方法的内部实现。
这个XNode中的构造方法涉及了新类:XPathParser Node XNode
认识新类:
1. XPathParser 通过XPath表达式解析xml文档的类。
2. Node 表示xml文档中节点的对象。
3. XNode MyBatis提供的对Node进行封装后对象。
认识新类的方法:XNode的构造方法
把传递的3个参数直接保存了起来。作为自己的状态。
进行处理,得到了3个处理结果,也保存了起来,作为自己的状态。
*/
public XNode(XPathParser xpathParser, Node node, Properties variables) {
this.xpathParser = xpathParser;
this.node = node;
this.name = node.getNodeName();
this.variables = variables;
this.attributes = parseAttributes(node);
this.body = parseBody(node);
}
功法残页2:跟踪数据
程序的核心就是数据,数据的处理逻辑和数据的存储,跟踪你关注的数据,你将会接触到系统内部与这个数据相关的新类和新方法,从而提升对系统的认识。对学习系统的的任务划分提供了一种方式。
这样将对把系统的学习拆分了。现在只需要了解这些与关注数据相关的新类和新方法,就能提升对系统的认识。而不是把一个新类的全部东西都学完也不一定能够提升对系统的认识。
示例:
MyBatis 中 build 方法的3个参数,reader environment properties,跟踪这3个数据。你将会对MyBatis系统有进一步的认识。
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
功法残页3:系统界面
示例: MyBatis 在插件方面,为开发人员提供了哪些东西呢?
MyBatis 为插件提供了 plugins 元素 plugin 元素 property 元素 Interceptor 接口,那么可以认为这是 MyBatis 提供的插件相关的界面。提出界面这个概念,一是为了将系统内部实现和用户操作部分分开。二是为了提供一个角度去认识系统。
个人认为:系统给开发提供的东西叫做这个系统的接口,而用于某个目的一组相关的接口,把这些东西当作系统的提供给开发人员的相关界面。界面,对学习系统的的任务划分提供了一种方式,每次关注系统的一个界面,学习系统的这个界面,获得对系统的认识的提升。
<!-- mybatis-config.xml -->
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="org.mybatis.example.ExamplePlugin">
<property name="someProperty" value="100"/>
</plugin>
</plugins>
MyBatis源码 核心配置解析 properties元素的更多相关文章
- MyBatis 源码分析 - 配置文件解析过程
* 本文速览 由于本篇文章篇幅比较大,所以这里拿出一节对本文进行快速概括.本篇文章对 MyBatis 配置文件中常用配置的解析过程进行了较为详细的介绍和分析,包括但不限于settings,typeAl ...
- Spring mybatis源码篇章-XMLLanguageDriver解析sql包装为SqlSource
前言:通过阅读源码对实现机制进行了解有利于陶冶情操,承接前文Spring mybatis源码篇章-MybatisDAO文件解析(二) 首先了解下sql mapper的动态sql语法 具体的动态sql的 ...
- mybatis源码核心代码
/** * mybatis源码测试类 * @param args * @throws IOException * @see org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuratio ...
- mybatis源码-原来resultMap解析完是这样
目录 1 两个基础类 1.1 列映射类ResultMapping 1.2 结果集映射类ResultMap 2. 解析 2.1 入口函数 2.2 解析流程 2.3 获取 id 2.4 解析结果集的类型 ...
- Mybatis源码解读-配置加载和Mapper的生成
问题 Mybatis四大对象的创建顺序? Mybatis插件的执行顺序? 工程创建 环境:Mybatis(3.5.9) mybatis-demo,参考官方文档 简单示例 这里只放出main方法的示例, ...
- MyBatis 源码分析——配置信息
MyBatis框架的启动前期需要加载相关的XML配置信息.从官网上我们可以了解到他具有十几个节点.其中笔者认为比较重要的节点是settings节点.properties节点.environments节 ...
- MyBatis 源码分析 - 映射文件解析过程
1.简介 在上一篇文章中,我详细分析了 MyBatis 配置文件的解析过程.由于上一篇文章的篇幅比较大,加之映射文件解析过程也比较复杂的原因.所以我将映射文件解析过程的分析内容从上一篇文章中抽取出来, ...
- Mybatis源码解读-SpringBoot中配置加载和Mapper的生成
本文mybatis-spring-boot探讨在springboot工程中mybatis相关对象的注册与加载. 建议先了解mybatis在spring中的使用和springboot自动装载机制,再看此 ...
- Mybatis源码解析-BoundSql
mybatis作为持久层,其操作数据库离不开sql语句.而BoundSql则是其保存Sql语句的对象 前提 针对mybatis的配置文件的节点解析,比如where/if/trim的节点解析可见文章Sp ...
随机推荐
- 黑苹果MacOS安装记录
https://blog.daliansky.net/macOS-Catalina-10.15-19A583-Release-version-with-Clover-5093-original-ima ...
- 利用SQL生成模型实体类
DECLARE @TableName sysname = 'TableName'; DECLARE @Result VARCHAR(MAX) = 'public class ' + @TableNam ...
- (五)golang--常用的一些玩意
\t--制表位 \n--换行符 \\--一个\ \"--一个” \r--回车 行注释://,一次性注释多行指令,选中代码后ctrl+/ 块注释:/* */ 代码规范: (1)官方推荐使用行注 ...
- mysql 基本操作 四
1.临时表 当绘画结束时,临时表会自动销毁,无法用show tables 查看 临时表. MariaDB [jason]> create temporary table tmp(pro ),ci ...
- nginx 安装ab小工具方法
nginx 安装ab小工具方法测试工具安装(以centos系统为例)yum -y install httpd-tools 然后测试下ab -V
- CSS属性相关知识
Css选择器 选择器的权重 在css中,哪个选择器的权重高,就走谁的样式. 标签选择器的权重是 1 Class选择器的权重是10 Id选择器的权重是100 行间样式的权重是1000 带有关键字 !im ...
- 固定定位导致$(window).scrollTop();获取滚动后到顶部距离总是为0
如下移动端索引列表页面(点击某元素后弹出的页面) 我想用 $(window).scrollTop(); 获取页面滚动后距离顶部的距离,但获取到的值总是0 期间查了很久,但都无疾而终,后来看到一篇 ...
- v8引擎详解(摘)-- V8引擎是一个JavaScript引擎实现
随着Web相关技术的发展,JavaScript所要承担的工作也越来越多,早就超越了“表单验证”的范畴,这就更需要快速的解析和执行JavaScript脚本.V8引擎就是为解决这一问题而生,在node中也 ...
- c#语法复习总结(2)-数据类型
C#数据类型可以分值类型和引用类型.值类型,先说说一个概念 c#栈和堆. 一,栈和堆. 堆:在c里面叫堆,在c#里面其实叫托管堆.为什么叫托管堆,我们往下看. 栈:就是堆栈,因为和堆一起叫着别扭,就简 ...
- aspx页面,后端通过Attributes.Add给textbox添加事件时,传参失效问题。
测试一:------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ...
