Matrices and Vectors
Matrices and Vectors
Matrices are 2-dimensional arrays:

A vector is a matrix with one column and many rows:The above matrix has four rows and three columns, so it is a 4 x 3 matrix.

Notation and terms:So vectors are a subset of matrices. The above vector is a 4 x 1 matrix.
- Aij refers to the element in the ith row and jth column of matrix A.
- A vector with 'n' rows is referred to as an 'n'-dimensional vector.
- vi refers to the element in the ith row of the vector.
- In general, all our vectors and matrices will be 1-indexed. Note that for some programming languages, the arrays are 0-indexed.
- Matrices are usually denoted by uppercase names while vectors are lowercase.
- "Scalar" means that an object is a single value, not a vector or matrix.
- R refers to the set of scalar real numbers.
- Rn refers to the set of n-dimensional vectors of real numbers.
Run the cell below to get familiar with the commands in Octave/Matlab. Feel free to create matrices and vectors and try out different things.
% The ; denotes we are going back to a new row.
A = [1, 2, 3; 4, 5, 6; 7, 8, 9; 10, 11, 12] % Initialize a vector
v = [1;2;3] % Get the dimension of the matrix A where m = rows and n = columns
[m,n] = size(A) % You could also store it this way
dim_A = size(A) % Get the dimension of the vector v
dim_v = size(v) % Now let's index into the 2nd row 3rd column of matrix A
A_23 = A(2,3)
Addition and Scalar Multiplication
Addition and subtraction are element-wise, so you simply add or subtract each corresponding element:
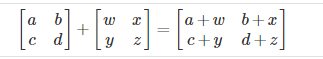
Subtracting Matrices:
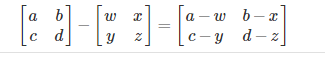
In scalar multiplication, we simply multiply every element by the scalar value:To add or subtract two matrices, their dimensions must be the same.
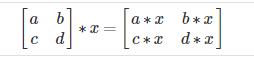
Experiment below with the Octave/Matlab commands for matrix addition and scalar multiplication. Feel free to try out different commands. Try to write out your answers for each command before running the cell below.In scalar division, we simply divide every element by the scalar value:
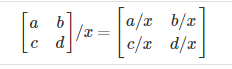
Experiment below with the Octave/Matlab commands for matrix addition and scalar multiplication. Feel free to try out different commands. Try to write out your answers for each command before running the cell below.
% Initialize matrix A and B
A = [1, 2, 4; 5, 3, 2]
B = [1, 3, 4; 1, 1, 1] % Initialize constant s
s = 2 % See how element-wise addition works
add_AB = A + B % See how element-wise subtraction works
sub_AB = A - B % See how scalar multiplication works
mult_As = A * s % Divide A by s
div_As = A / s % What happens if we have a Matrix + scalar?
add_As = A + s
Matrix-Vector Multiplication
We map the column of the vector onto each row of the matrix, multiplying each element and summing the result.
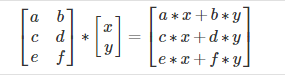
An m x n matrix multiplied by an n x 1 vector results in an m x 1 vector.The result is a vector. The number of columns of the matrix must equal the number of rows of the vector.
Below is an example of a matrix-vector multiplication. Make sure you understand how the multiplication works. Feel free to try different matrix-vector multiplications.
% Initialize matrix A
A = [1, 2, 3; 4, 5, 6;7, 8, 9] % Initialize vector v
v = [1; 1; 1] % Multiply A * v
Av = A * v
Matrix-Matrix Multiplication
We multiply two matrices by breaking it into several vector multiplications and concatenating the result.
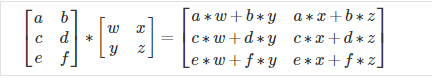
To multiply two matrices, the number of columns of the first matrix must equal the number of rows of the second matrix.An m x n matrix multiplied by an n x o matrix results in an m x o matrix. In the above example, a 3 x 2 matrix times a 2 x 2 matrix resulted in a 3 x 2 matrix.
For example:
% Initialize a 3 by 2 matrix
A = [1, 2; 3, 4;5, 6] % Initialize a 2 by 1 matrix
B = [1; 2] % We expect a resulting matrix of (3 by 2)*(2 by 1) = (3 by 1)
mult_AB = A*B % Make sure you understand why we got that result
Matrix Multiplication Properties
- Matrices are not commutative: A∗B≠B∗A
- Matrices are associative: (A∗B)∗C=A∗(B∗C)
The identity matrix, when multiplied by any matrix of the same dimensions, results in the original matrix. It's just like multiplying numbers by 1. The identity matrix simply has 1's on the diagonal (upper left to lower right diagonal) and 0's elsewhere.
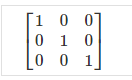
When multiplying the identity matrix after some matrix (A∗I), the square identity matrix's dimension should match the other matrix's columns. When multiplying the identity matrix before some other matrix (I∗A), the square identity matrix's dimension should match the other matrix's rows
.
% Initialize random matrices A and B
A = [1,2;4,5]
B = [1,1;0,2] % Initialize a 2 by 2 identity matrix
I = eye(2) % The above notation is the same as I = [1,0;0,1] % What happens when we multiply I*A ?
IA = I*A % How about A*I ?
AI = A*I % Compute A*B
AB = A*B % Is it equal to B*A?
BA = B*A % Note that IA = AI but AB != BA
Inverse and Transpose
The inverse of a matrix A is denoted A−1. Multiplying by the inverse results in the identity matrix.
A non square matrix does not have an inverse matrix. We can compute inverses of matrices in octave with the pinv(A) function and in Matlab with the inv(A) function. Matrices that don't have an inverse are singular or degenerate.
The transposition of a matrix is like rotating the matrix 90° in clockwise direction and then reversing it. We can compute transposition of matrices in matlab with the transpose(A) function or A':
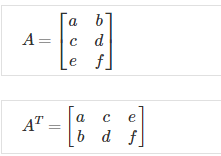
In other words:
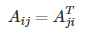
% Initialize matrix A
A = [1,2,0;0,5,6;7,0,9] % Transpose A
A_trans = A' % Take the inverse of A
A_inv = inv(A) % What is A^(-1)*A?
A_invA = inv(A)*A
Matrices and Vectors的更多相关文章
- RNN 入门教程 Part 2 – 使用 numpy 和 theano 分别实现RNN模型
转载 - Recurrent Neural Networks Tutorial, Part 2 – Implementing a RNN with Python, Numpy and Theano 本 ...
- [zt]矩阵求导公式
今天推导公式,发现居然有对矩阵的求导,狂汗--完全不会.不过还好网上有人总结了.吼吼,赶紧搬过来收藏备份. 基本公式:Y = A * X --> DY/DX = A'Y = X * A --&g ...
- Applying Eigenvalues to the Fibonacci Problem
http://scottsievert.github.io/blog/2015/01/31/the-mysterious-eigenvalue/ The Fibonacci problem is a ...
- 图像处理之image stitching
背景介绍 图像拼接是一项应用广泛的图像处理技术.根据特征点的相互匹配,可以将多张小视角的图像拼接成为一张大视角的图像,在广角照片合成.卫星照片处理.医学图像处理等领域都有应用.早期的图像拼接主要是运用 ...
- 对于fmri的设计矩阵构造的一个很直观的解释-by 西南大学xulei教授
本程序意在解释这样几个问题:完整版代码在本文的最后. 1.实验的设计如何转换成设计矩阵? 2.设计矩阵的每列表示一个刺激条件,如何确定它们? 3.如何根据设计矩阵和每个体素的信号求得该体素对刺激的敏感 ...
- Introduction to Gaussian Processes
Introduction to Gaussian Processes Gaussian processes (GP) are a cornerstone of modern machine learn ...
- The Model Complexity Myth
The Model Complexity Myth (or, Yes You Can Fit Models With More Parameters Than Data Points) An oft- ...
- SparkMLlib-----GMM算法
Gaussian Mixture Model(GMM)是一个很流行的聚类算法.它与K-Means的很像,但是K-Means的计算结果是算出每个数据点所属的簇,而GMM是计算出这些数据点分配到各个类别的 ...
- Machine-learning of Andrew Ng(Stanford University)
1.基础概念 机器学习是一门研究在非特定编程条件下让计算机采取行动的学科.最近二十年,机器学习为我们带来了自动驾驶汽车.实用的语音识别.高效的网络搜索,让我们对人类基因的解读能力大大提高.当今机器学习 ...
随机推荐
- webservice07#契约优先#webservice实现简单的动态web项目
1, 用户管理 User{username,password,nickname} 属性. 2,契约优先[ 先用schema做标准来写wsdl.再生成服务器端的接口,再编写接口的类] 在src下创建目录 ...
- Linux下安全证书申请以及配置到Nginx
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/xdtianyu/scripts/master/lets-encrypt/letsencrypt.shchmod +x l ...
- Windows下chm转换为html的超简单方法
摘要:通过调用Windows命令,将chm 文件转换为html 文件 概述:很多程序员朋友都会遇到这样的问题,看一个离线版的帮助文档(chm文件),总会产生一个索引文件(该文件的chw文件), 而且有 ...
- CentOS7的一些初始化
默认最小化安装 [root@GVMCET001 ~]# nmtui 设置网络,主机名等 [root@GVMCET001 ~]# yum update 更新系统 SSH [root@GVMCET001 ...
- oracle pl/sql 变量
一.变量介绍在编写pl/sql程序时,可以定义变量和常量:在pl/sql程序中包括有:1).标量类型(scalar)2).复合类型(composite) --用于操作单条记录3).参照类型(refer ...
- Android在 普通类(非Activity,多数为Adapter) 中 传输数据为空值 解决方法 :在startActivity 用 intent传输数据
这是bundle是传输不了数据的,获取到 出现这种情况的原因是非activity类中不存在Context,而在活动中传输数据时需要Context. 我收集到了两种解决方法. 1. 在调用该Adapte ...
- BGP协议
BGP属于自治系统间路由协议.BGP的主要目标是为处于不同AS中的路由器之间进行路由信息通信提供保障.BGP既不是纯粹的矢量距离协议,也不是纯粹的链路状态协议,通常被称为通路向量路由协议.这是因为BG ...
- 用ESP8266+android,制作自己的WIFI小车(Android 软件)
先说一下这篇文章里面的内容:TCP 客户端, 自定义对话框, 自定义按钮, ProgressBar竖直显示, 重力感应传感器,手机返回键新开启界面的问题(返回上次的界面),数据保存 软件的通信是配合 ...
- fitnesse - Variables and Symbols
fitnesse - Variables and Symbols 2017-09-30 目录 1 Variables(静态变量) 1.1 定义及使用 1.2 Variable作用域 1.2. ...
- js-异步机制与同步机制
Javascript的优势之一是其如何处理异步代码.异步代码会被放入一个事件队列,等到所有其他代码执行后才进行,而不会阻塞线程 1 理解异步代码: 1.1 JavaScript最基础的异步函数是set ...
