Spring_Spring与AOP
一、传统编程使用代理解决目标类增强问题
//主业务接口
public interface ISomeService {
// 目标方法
void doFirst();
// 目标方法
void doSecond();
}
ISomeService
//目标类
public class SomeServiceImpl implements ISomeService { @Override
public void doFirst() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("执行doFirst()方法");
} @Override
public void doSecond() {
System.out.println("执行doSecond()方法");
} }
SomeServiceImpl
public class SystemService {
public static void doLog() {
System.out.println("执行日志代码");
}
public static void doTx() {
System.out.println("执行事务代码");
}
}
SystemService
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import com.jmu.service.ISomeService;
import com.jmu.service.SomeServiceImpl;
import com.jmu.utils.SystemService; public class MyTest { public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ISomeService target=new SomeServiceImpl();
ISomeService service=(ISomeService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.getClass().getClassLoader(),target.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() {
//织入weaving:将系统级服务切入到主业务逻辑中
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
SystemService.doTx();
//执行目标方法
Object result = method.invoke(target, args);
SystemService.doLog();
return result;
}
});
service.doFirst();
System.out.println("---------------");
service.doSecond();
} }
MyTest
二、AOP术语
(1)切面(Aspect)
切面泛指业务逻辑。常用的切面有通知(Advice)和顾问(Advisor)。实际上就是对主业务逻辑的一种增强。
(2)织入(Weaving)
织入指将切面代码插入到目标对象的过程。
(3)连接点(JoinPoint)
连接点指可以被切面织入的方法。通常业务接口中的方法均为连接点。
(4)切入点(Pointcut)
切入点指切面具体织入的方法。被标记为final的方法不能作为连接点和切点。
(5)目标对象(Target)
目标对象指将被增强的对象。
(6)通知(Advice)
通知是切面的一实现。,可以完成简单织入功能。通知定义了增强代码切入带目标代码的时间点,是目标方法执行之前执行,还是之后执行等。通知类型不同,切入的时间不同。
切入点定义切入的位置,通知定义切入的时间。
(7)顾问(Advisor)
顾问是切面的另一种实现,能够将通知以更为复杂的方式织入到目标对象中,是将通知包装为更复杂切面的装置器。
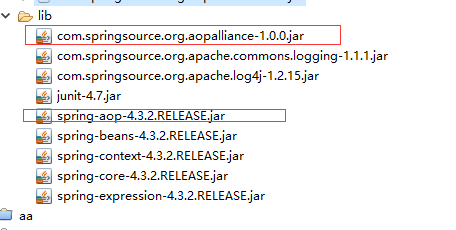
三、AOP编程环境的搭建
四、通知(Advice)的详解
(1)前置通知(MethodBeforeAdvice)
import java.lang.reflect.Method; import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice; //前置通知
public class MyMethodBeforeAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
// 当前方method:法在目标方法执行之前执行
// method:目标方法
// args:目标方法的参数列表
// target:目标对象
@Override
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// 对于目标方法增强的代码写于此
System.out.println("执行前置通知方法");
} }
MyMethodBeforeAdvice
<!-- 注册目标对象 -->
<bean id="someService" class="com.jmu.aop01.SomeServiceImpl" /> <!-- 注册切面:通知 -->
<bean id="myAdvice" class="com.jmu.aop01.MyMethodBeforeAdvice" /> <!-- 生成代理对象 -->
<bean id="serviceProxy" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">
<!-- <property name="targetName" ref="someService"></property> -->
<!-- 指定目标对象 -->
<property name="target" ref="someService"></property>
<!-- 指定切面 -->
<property name="interceptorNames" value="myAdvice"></property>
</bean>
applicationContext.xml
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class MyTest { @Test
public void test01() {
//创建容器对象
String resource = "com/jmu/aop01/applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(resource);
ISomeService service=(ISomeService) ac.getBean("serviceProxy");
service.doFirst();
System.out.println("----------");
service.doSecond();
} }
MyTest
输出:
执行前置通知方法
执行doFirst()方法
----------
执行前置通知方法
执行doSecond()方法
output
(2)后置通知(AfterReturningAdvice)
后置通知:可以获取到目标方法的返回结果,但无法改变目标方法的结果
//主业务接口
public interface ISomeService {
// 目标方法
void doFirst();
// 目标方法
String doSecond();
}
ISomeService
//目标类
public class SomeServiceImpl implements ISomeService { @Override
public void doFirst() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("执行doFirst()方法");
} @Override
public String doSecond() {
System.out.println("执行doSecond()方法");
return "ABCD";
} }
SomeServiceImpl
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
//后置通知:可以获取到目标方法的返回结果,但无法改变目标方法的结果
public class MyAfterReturningAdvice implements org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice {
// 在目标方法之后执行
// returnValue:目标方法的返回值
@Override
public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("执行后置通知方法 reurnValue= "+returnValue);
if (returnValue!=null) {
returnValue = ((String) returnValue).toLowerCase();
System.out.println("修改过的结果returnValue="+returnValue);
}
} }
MyAfterReturningAdvice
<!-- 注册目标对象 -->
<bean id="someService" class="com.jmu.aop02.SomeServiceImpl" /> <!-- 注册切面:通知 -->
<bean id="myAdvice" class="com.jmu.aop02.MyAfterReturningAdvice" /> <!-- 生成代理对象 -->
<bean id="serviceProxy" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="target" ref="someService"></property>
<property name="interceptorNames" value="myAdvice"></property>
</bean>
applicationContext.xml
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class MyTest { @Test
public void test01() {
//创建容器对象
String resource = "com/jmu/aop02/applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(resource);
ISomeService service=(ISomeService) ac.getBean("serviceProxy");
service.doFirst();
System.out.println("----------");
String result = service.doSecond();
System.out.println(result);
} }
MyTest
输出:
执行doFirst()方法
执行后置通知方法 reurnValue= null
----------
执行doSecond()方法
执行后置通知方法 reurnValue= ABCD
修改过的结果returnValue=abcd
output
(3)环绕通知(MethodInterceptor)
环绕通知:可以修改目标方法的返回结果
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
//环绕通知:可以修改目标方法的返回结果
public class MyMethodIntercepter implements MethodInterceptor { @Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("执行环绕通知:目标方法执行之前");
//执行目标方法
Object result = invocation.proceed();
System.out.println("执行环绕通知:目标方法执行之后");
if (result!=null) {
result=((String)result).toLowerCase();
}
return result;
} }
MyMethodIntercepter
输出:
执行环绕通知:目标方法执行之前
执行doFirst()方法
执行环绕通知:目标方法执行之后
----------
执行环绕通知:目标方法执行之前
执行doSecond()方法
执行环绕通知:目标方法执行之后
abcd
output
(4)异常通知(ThrowsAdvice)
a、
异常分2种:
- 运行时异常,不进行处理,也可以通过编译。若一个类继承自RunTimeException,则该异常就是运行时异常
- 编译时异常(受查异常 Checked Exception),不进行处理,不能通过编译。若一个类继承自Exception,则该异常就是受查异常
import org.springframework.aop.ThrowsAdvice;
public class MyThrowsAdvice implements ThrowsAdvice {
//当目标方法抛出与指定类型的异常具有is-a关系的异常时,执行当前方法
public void afterThrowing(Exception ex) {
System.out.println("执行异常通知方法");
}
}
MyThrowsAdvice
@Override
public void doFirst() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("执行doFirst()方法"+3/0);
}
SomeServiceImpl
输出:
执行异常通知方法
output
b、捕获自定义异常
public class UserException extends Exception {
public UserException() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public UserException(String message) {
super(message);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
}
UserException
public class UsernameException extends UserException {
public UsernameException() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public UsernameException(String message) {
super(message);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
}
UsernameException
public class PasswordException extends UserException {
public PasswordException() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public PasswordException(String message) {
super(message);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
}
PasswordException
//主业务接口
public interface ISomeService {
// 目标方法
boolean login(String username,String password)throws UserException; }
ISomeService
public class SomeServiceImpl implements ISomeService {
@Override
public boolean login(String username, String password) throws UserException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(!"Jane".equals(username)){
throw new UsernameException("用户名输入错误!");
}
if(!"aaa".equals(password)){
throw new PasswordException("密码输入错误!");
}
/* double a=3/0;*/
return true;
}
}
SomeServiceImpl
import org.springframework.aop.ThrowsAdvice;
public class MyThrowsAdvice implements ThrowsAdvice {
// 当目标方法抛出UsernameException异常时,执行当前方法
public void afterThrowing(UsernameException ex) {
System.out.println("发生用户名异常 ex=" + ex.getMessage());
}
// 当目标方法抛出PasswordException异常时,执行当前方法
public void afterThrowing(PasswordException ex) {
System.out.println("发生密码异常 ex=" + ex.getMessage());
}
// 当目标方法抛出其他异常时,执行当前方法
public void afterThrowing(Exception ex) {
System.out.println("发生异常 ex=" + ex.getMessage());
}
}
MyThrowsAdvice
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class MyTest { @Test
public void test01() throws UserException{
//创建容器对象
String resource = "com/jmu/aop05/applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(resource);
ISomeService service=(ISomeService) ac.getBean("serviceProxy");
service.login("gad", "aaa");
} }
MyTest
测试:
service.login("gad", "aaa");
输出:
发生用户名异常 ex=用户名输入错误!
在SomeServiceImpl中加入
double a=3/0;
输出:
发生异常 ex=/ by zero
c、异常的两种处理方式
控制台输出异常
public class MyTest {
@Test
public void test01() {
//创建容器对象
String resource = "com/jmu/aop05/applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(resource);
ISomeService service=(ISomeService) ac.getBean("serviceProxy");
try {
service.login("Jane", "111");
} catch (UserException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
MyTest
虚拟机不通过
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class MyTest { @Test
public void test01() throws UserException{
//创建容器对象
String resource = "com/jmu/aop05/applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(resource);
ISomeService service=(ISomeService) ac.getBean("serviceProxy");
service.login("Jane", "1111");
} }
MyTest
五、为目标方法织入多个通知
<!-- 注册目标对象 -->
<bean id="someService" class="com.jmu.aop06.SomeServiceImpl" /> <!-- 注册切面:通知 -->
<bean id="myBeforeAdvice" class="com.jmu.aop06.MyMethodBeforeAdvice" />
<bean id="myAfterAdvice" class="com.jmu.aop06.MyAfterReturningAdvice" /> <!-- 生成代理对象 -->
<bean id="serviceProxy" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="target" ref="someService"></property>
<property name="interceptorNames" value="myBeforeAdvice,myAfterAdvice"></property> <!-- <property name="interceptorNames">
<array>
<value>myBeforeAdvice</value>
<value>myAfterAdvice</value>
</array>
</property> -->
</bean>
applicationContext
六、无接口使用CGLIB代理
之前
改
//目标类
public class SomeService { public void doFirst() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("执行doFirst()方法");
} public String doSecond() {
System.out.println("执行doSecond()方法");
return "ABCD";
} }
SomeService
<!-- 注册目标对象 -->
<bean id="someService" class="com.jmu.aop07.SomeService" /> <!-- 注册切面:通知 -->
<bean id="myAdvice" class="com.jmu.aop07.MyAfterReturningAdvice" /> <!-- 生成代理对象 -->
<bean id="serviceProxy" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="target" ref="someService"></property>
<property name="interceptorNames" value="myAdvice"></property>
</bean>
applicationContext
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class MyTest { @Test
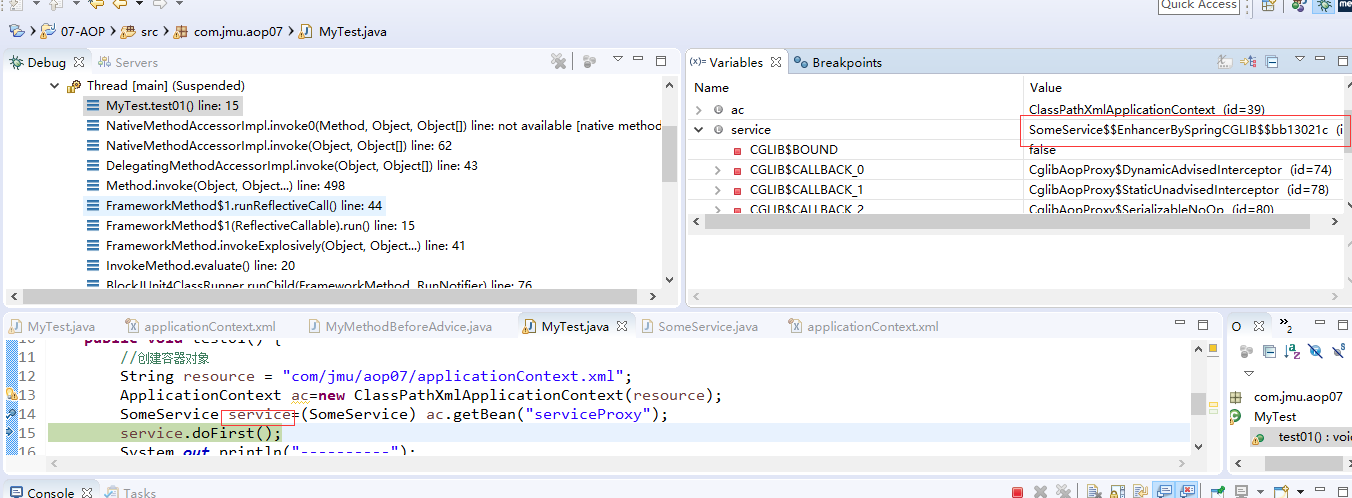
public void test01() {
//创建容器对象
String resource = "com/jmu/aop07/applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(resource);
SomeService service=(SomeService) ac.getBean("serviceProxy");
service.doFirst();
System.out.println("----------");
String result = service.doSecond();
System.out.println(result);
} }
MyTest
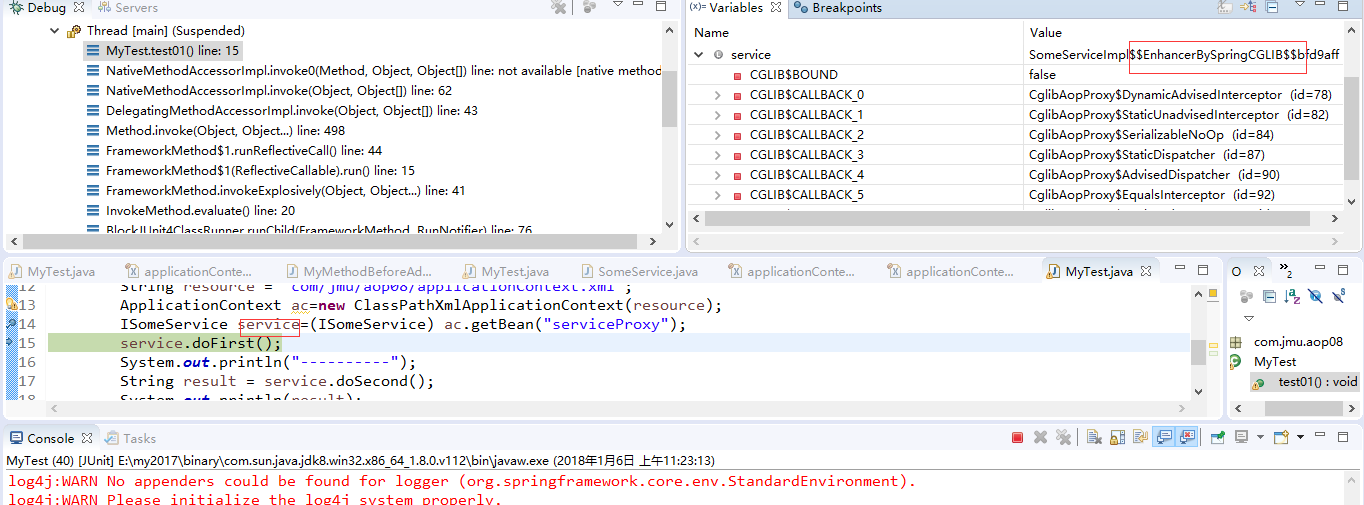
七、有接口(也可以)使用CGLIB
方法一:

方法二:
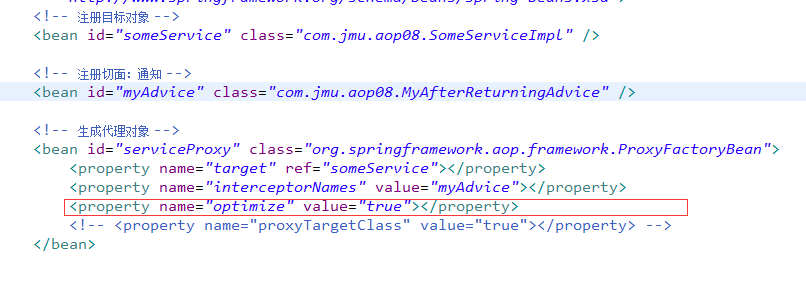
八、顾问 Advisor
通知是Spring提供的一种切面,只能将切面织入到目标方法的所有方法中。
顾问是Spring提供的另一种切面,其可以完成更为复杂的切面织入功能。
PointAdisor是顾问的一种,可以指定具体的切入点。顾问将通知进行了包装,会根据不同的通知类型,在不同的时间点,将切面织入到不同的切入点。
名称匹配方法切入点顾问
public class SomeServiceImpl implements ISomeService {
@Override
public void doFirst() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("执行doFirst()方法");
}
@Override
public String doSecond() {
System.out.println("执行doSecond()方法");
return "ABCD";
}
@Override
public void doThird() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("执行doThird()方法");
}
}
SomeServiceImpl
<!-- 注册目标对象 -->
<bean id="someService" class="com.jmu.aop09.SomeServiceImpl" /> <!-- 注册切面:通知-->
<bean id="myAdvice" class="com.jmu.aop09.MyAfterReturningAdvice" />
<!-- 注册切面:顾问-->
<bean id="myAdvisor" class="org.springframework.aop.support.NameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor">
<property name="advice" ref="myAdvice"></property>
<!-- 指定切入点 -->
<!-- <property name="mappedName" value="doFirst"></property> -->
<!-- <property name="mappedNames" value="doFirst,doSecond"></property> -->
<property name="mappedNames" value="*ir*"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="serviceProxy" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="target" ref="someService"></property>
<property name="interceptorNames" value="myAdvisor"></property>
</bean>
applicationContext
指定切入点:这里匹配的对象是简单方法名
<property name="mappedNames" value="*ir*"></property>
输出:
执行doFirst()方法
执行后置通知方法 reurnValue= null
----------
执行doSecond()方法
----------
执行doThird()方法
执行后置通知方法 reurnValue= null
output
正则表达式方法切入点顾问
| 运算符 | 名称 | 意义 |
| . | 点号 | 表示任意单个字符 |
| + | 加号 | 表示前一个字符出现一次或多次 |
| * | 星号 | 表示前一个字符出现0次或多次 |
<!-- 注册目标对象 -->
<bean id="someService" class="com.jmu.aop10.SomeServiceImpl" /> <!-- 注册切面:通知-->
<bean id="myAdvice" class="com.jmu.aop10.MyAfterReturningAdvice" />
<!-- 注册切面:顾问-->
<bean id="myAdvisor" class="org.springframework.aop.support.RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor">
<property name="advice" ref="myAdvice"></property>
<!-- 这里的正则表达式匹配的对象是全限定方法名 -->
<!-- <property name="pattern" value=".*doFirst"></property> -->
<!-- <property name="patterns" value=".*doFirst,.*doSecond"></property> -->
<property name="pattern" value=".*doFirst|.*doSecond"></property><!-- |为p右边的键,表示或 -->
</bean>
<bean id="serviceProxy" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="target" ref="someService"></property>
<property name="interceptorNames" value="myAdvisor"></property>
</bean>
applicationContext
这里正则表达式匹配的对象是全限定名
<property name="pattern" value=".*S.*"></property>
九、自动代理生成器
前面代码中所使用的代理对象,均是由ProxyFactoryBean代理工具类生成的。该代理工具类存在如下缺点:
1、一个代理对象只能代理一个Bean
2、在客户类中获取Bean时。使用的是代理类id,而非我们定义的模目标对象Bea的id。
Spring对此提供了自动代理生成器,常用的为以下2种:
默认advisor自动代理器
<!-- 注册自动代理生成器 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator"></bean>
public class MyTest {
@Test
public void test01() {
// 创建容器对象
String resource = "com/jmu/aop11/applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(resource);
ISomeService service = (ISomeService) ac.getBean("someService");
service.doFirst();
System.out.println("----------");
service.doSecond();
System.out.println("----------");
service.doThird();
System.out.println("--------------");
ISomeService service2 = (ISomeService) ac.getBean("someService2");
service2.doFirst();
System.out.println("----------");
service2.doSecond();
System.out.println("----------");
service2.doThird();
}
}
MyTest
输出:
执行doFirst()方法
执行后置通知方法 reurnValue= null
----------
执行doSecond()方法
----------
执行doThird()方法
执行后置通知方法 reurnValue= null
--------------
执行doFirst()方法
执行后置通知方法 reurnValue= null
----------
执行doSecond()方法
----------
执行doThird()方法
执行后置通知方法 reurnValue= null
output
DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator缺点:
- 不能选择目标对象
- 不能选择切面类型,切面只能是advisor
- 不能选择advisor,所有advisor均被作文切面织入到目标
Bean名称自动代理生成器
<!-- 注册目标对象 -->
<bean id="someService" class="com.jmu.aop12.SomeServiceImpl" />
<bean id="someService2" class="com.jmu.aop12.SomeServiceImpl" />
<!-- 注册切面:通知-->
<bean id="myAdvice" class="com.jmu.aop12.MyAfterReturningAdvice" />
<!-- 注册切面:顾问-->
<bean id="myAdvisor" class="org.springframework.aop.support.NameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor">
<property name="advice" ref="myAdvice"></property>
<property name="mappedNames" value="doFirst"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="myAdvisor2" class="org.springframework.aop.support.NameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor">
<property name="advice" ref="myAdvice"></property>
<property name="mappedNames" value="doSecond"></property>
</bean> <!-- 注册自动代理生成器 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.BeanNameAutoProxyCreator">
<property name="beanNames" value="someService"></property>
<!-- <property name="interceptorNames" value="myAdvice"></property> -->
<property name="interceptorNames" value="myAdvisor"></property>
</bean>
applicationContext
public class MyTest {
@Test
public void test01() {
// 创建容器对象
String resource = "com/jmu/aop12/applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(resource);
ISomeService service = (ISomeService) ac.getBean("someService");
service.doFirst();
System.out.println("----------");
service.doSecond();
System.out.println("----------");
service.doThird();
System.out.println("--------------");
ISomeService service2 = (ISomeService) ac.getBean("someService2");
service2.doFirst();
System.out.println("----------");
service2.doSecond();
System.out.println("----------");
service2.doThird();
}
}
MyTest
输出:
执行doFirst()方法
执行后置通知方法 reurnValue= null
----------
执行doSecond()方法
----------
执行doThird()方法
--------------
执行doFirst()方法
----------
执行doSecond()方法
----------
执行doThird()方法
output
Spring_Spring与AOP的更多相关文章
- Spring_Spring与AOP_AspectJ基于注解的AOP实现
一.AspectJ.Spring与AOP的关系 AspectJ是一个面向切面的框架,它扩展了Java语言.AspectJ定义了AOP语法,所以它有一个专门的编译器用来生成遵守Java字节编码规范的Cl ...
- 基于spring注解AOP的异常处理
一.前言 项目刚刚开发的时候,并没有做好充足的准备.开发到一定程度的时候才会想到还有一些问题没有解决.就比如今天我要说的一个问题:异常的处理.写程序的时候一般都会通过try...catch...fin ...
- Spring基于AOP的事务管理
Spring基于AOP的事务管理 事务 事务是一系列动作,这一系列动作综合在一起组成一个完整的工作单元,如果有任何一个动作执行失败,那么事务 ...
- 学习AOP之透过Spring的Ioc理解Advisor
花了几天时间来学习Spring,突然明白一个问题,就是看书不能让人理解Spring,一方面要结合使用场景,另一方面要阅读源代码,这种方式理解起来事半功倍.那看书有什么用呢?主要还是扩展视野,毕竟书是别 ...
- 学习AOP之深入一点Spring Aop
上一篇<学习AOP之认识一下SpringAOP>中大体的了解了代理.动态代理及SpringAop的知识.因为写的篇幅长了点所以还是再写一篇吧.接下来开始深入一点Spring aop的一些实 ...
- 学习AOP之认识一下Spring AOP
心碎之事 要说知道AOP这个词倒是很久很久以前了,但是直到今天我也不敢说非常的理解它,其中的各种概念即抽象又太拗口. 在几次面试中都被问及AOP,但是真的没有答上来,或者都在面上,这给面试官的感觉就是 ...
- .Net中的AOP系列之构建一个汽车租赁应用
返回<.Net中的AOP>系列学习总目录 本篇目录 开始一个新项目 没有AOP的生活 变更的代价 使用AOP重构 本系列的源码本人已托管于Coding上:点击查看. 本系列的实验环境:VS ...
- .NET里简易实现AOP
.NET里简易实现AOP 前言 在MVC的过滤器章节中对于过滤器的使用就是AOP的一个实现了吧,时常在工作学习中遇到AOP对于它的运用可以说是很熟练了,就是没想过如果自己来实现的话是怎么实现的,性子比 ...
- 在.Net中实现自己的简易AOP
RealProxy基本代理类 RealProxy类提供代理的基本功能.这个类中有一个GetTransparentProxy方法,此方法返回当前代理实例的透明代理.这是我们AOP实现的主要依赖. 新建一 ...
随机推荐
- Azure ARM (18) 将传统的ASM VM迁移到ARM VM (1)
<Windows Azure Platform 系列文章目录> 目前很多客户陆续的把传统ASM VM迁移至ARM VM.我这里简单介绍一下. 整个迁移过程分为: 1.Validate,Az ...
- 网络协议之ipv6
1. 地址分类 比較重要的主要有以下几种: 本地链路地址:用于链路之间相互通信 本地网站地址:用于子网内互相通信,类似于ipv4中的私有地址 全球单播地址:类似于ipv4中的公网地址 组播地址 2. ...
- google protocol buffer的原理和使用(四)
有个电子商务的系统(如果用C++实现).当中的模块A须要发送大量的订单信息给模块B.通讯的方式使用socket. 如果订单包含例如以下属性: ----------------------------- ...
- 【最短路】 ZOJ 1544 Currency Exchange 推断负圈
给出 N 种货币 M 条兑换关系 開始时全部的货币S 和有X 块钱 接下来M条关系 A B W1 W2 W3 W4 表示 A->B 所需的手续费为W2块钱 汇率为W1 B->A 所需的手 ...
- mysql还原数据库时,提示ERROR 1046 (3D000) No database selected 的解决方法
使用mysql数据库的朋友, 经常会使用mysqldump备案数据库, 然后到新服务器还原, 这个过程中, 有朋友会遇到ERROR 1046 (3D000) No database selected ...
- Bootstrap学习笔记(一)
用Laravel编写了一段时间程序,选择了bootstrap作为前段框架,现在已经有一段时间了,抽空总结一下: bootstrap是一个前端框架,所谓框架就是为满足特定需要在特定环境下提供的一 ...
- 《从Paxos到Zookeeper:分布式一致性原理与实践》【PDF】下载
内容简介 Paxos到Zookeeper分布式一致性原理与实践从分布式一致性的理论出发,向读者简要介绍几种典型的分布式一致性协议,以及解决分布式一致性问题的思路,其中重点讲解了Paxos和ZAB协议. ...
- 配置java项目的intellij idea的运行环境
才疏学浅,只懂一点点前端的皮毛东西,对于项目运行环境的配置一无所知,今天简单记录一下! 前提:装好了jdk.maven.intellij idea. 1. file菜单->Open...打开从S ...
- iOS tableView 数据处理,数据分类相同数据整合、合并计算总数总价
// 数据下载得到数组数据 modelArray = [MZPriceModel mj_objectArrayWithKeyValuesArray:data[@"info"]]; ...
- iOS 多线程 简单学习NSThread NSOperation GCD
1:首先简单介绍什么叫线程 可并发执行的,拥有最小系统资源,共享进程资源的基本调度单位. 共用堆,自有栈(官方资料说明iOS主线程栈大小为1M,其它线程为512K). 并发执行进度不可控,对非原子操作 ...
