CS:APP3e 深入理解计算机系统_3e CacheLab实验
详细的题目要求和实验资源可以到教材官网 或者 课程官网 获取。 本次实验难点在Part B的64 * 64部分,主要介绍这一部分。
Part A: 编写缓存模拟器
前期准备:
getopt和fscanf系列库函数对于这次实验很重要,不太明白的可以man一下,或者参考这两篇文章:
注意事项:
1.由于我们的模拟器必须适应不同的s, E, b,所以数据结构必须动态申请(malloc系列),注意初始化。
2.测试数据中以“I”开头的行是对指令缓存(i-cache)进行读写,我们编写的是数据缓存(d-cache),这些行直接忽略。
3.这次实验假设内存全部对齐,即数据不会跨越block,所以测试数据里面的数据大小也可以忽略。
4.为了使得评分程序正常运行,main函数最后需要加上:
printSummary(hit_count, miss_count, eviction_count);
5.建议把-v这个选项也实现了,这样自己debug的时候也方便一些。另外,可以先从规模小的测试数据开始,然后用大的。
思路要点及其实现:
1.这次实验只要求我们测试hit/miss/eviction的次数,并没有实际的数据存储 ,所以我们不用实现line中的block部分。
2.这次实验要求使用LRU(least recently used),即没有空模块(valid为0)时替换最早使用的那一个line。所以我们应该在line中实现一个能够记录当前line最后一次写入的时间参量,每次”写入“line的时候就更新一下该参量。(这一点csapp上没有详细说)
3.综上,结合书上对cache的描述,我们可以得到如下数据结构:
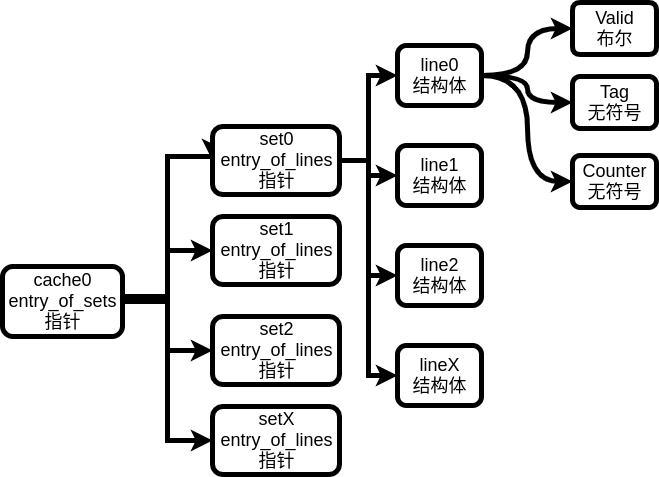
注意到cache(sets的入口)和set(lines的入口)都是用指针实现的,sets构成一个指针数组,因为它们不含任何数据,唯一的用处就是通过偏移量寻找到指定的line。
下面结合代码执行的顺序对我实现的程序进行解释,由于写了很多注释,就不详细的说了(我的sublime写不了中文,就用的英文注释的,语法有错还请指出)
更新:一航介绍了一个插件,可以解决Ubuntu下sublime中文输入的问题
头文件:
#include "cachelab.h"
#include <stdio.h> /* fopen freopen perror */
#include <stdint.h> /* uintN_t */
#include <unistd.h> /* getopt */
#include <getopt.h> /* getopt -std=c99 POSIX macros defined in <features.h> prevents <unistd.h> from including <getopt.h>*/
#include <stdlib.h> /* atol exit*/
#include <errno.h> /* errno */
为什么要包含该头文件的原因在右侧注释中写出来了。由于我们实验使用的64位地址,所以将tag和set的索引用64位保存就足够了,我这里使用了C99中的固定长度类型uintN_t,可移植性好一些。另外要注意的是,C99必须包含unistd.h和getopt.h两个头文件才能正常使用getopt 。
宏定义:
#define false 0
#define true 1
我喜欢用_Bool+宏定义true和false,你也可以使用stdbool.h。
数据结构类型定义:
typedef struct
{
_Bool valid; /* flag whether this line/block is valid, zero at first*/
uint64_t tag; /* identifier to choose line/block */
uint64_t time_counter; /* LRU strategy counter, we should evict the block who has the min time_counter, zero at first */
/* We don't need to simulate the block, since we just requested to count hit/miss/eviction */
}line;
typedef line *entry_of_lines;
typedef entry_of_lines *entry_of_sets;
time_counter初始化的时候都是0,其值越大代表这个line最近刚刚被写入——我们不应该替换它——所以valid为0的line的time_counter一定也是0(最小值),因为他们连使用都没有被使用过,即我们一定会先替换valid为0的line,这符合书上的策略。
typedef struct
{
int hit;
int miss;
int eviction;
}result;
我将结果设计成了一个结构体,这样函数方便返回一些。(少用全局变量)
main函数的数据类型:
result Result = {0, 0, 0};
const char *help_message = "Usage: \"Your complied program\" [-hv] -s <s> -E <E> -b <b> -t <tracefile>\n" \
"<s> <E> <b> should all above zero and below 64.\n" \
"Complied with std=c99\n";
const char *command_options = "hvs:E:b:t:";
FILE* tracefile = NULL;
entry_of_sets cache = NULL;
_Bool verbose = false; /* flag whether switch to verbose mode, zero for default */
uint64_t s = 0; /* number of sets ndex's bits */
uint64_t b = 0; /* number of blocks index's bits */
uint64_t S = 0; /* number of sets */
uint64_t E = 0; /* number of lines */
注释已经写的很清楚了,我解释一下help_message的写法,有的同学可能不知道C中字符串的写法:两个字符串中间只有空格,C编译器会自动将它们合并。例如:
char* test_string = "hello" " world"
那么test_string就会是“hello world”。
另外,在C中,一行写不下的时候可以使用\字符隔开,编译器会自动合并的。
main函数读取参数:
char ch; /* command options */
while((ch = getopt(argc, argv, command_options)) != -1)
{
switch(ch)
{
case 'h':
{
printf("%s", help_message);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
case 'v':
{
verbose = true;
break;
}
case 's':
{
if (atol(optarg) <= 0) /* We assume that there are at least two sets */
{
printf("%s", help_message);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
s = atol(optarg);
S = 1 << s;
break;
}
case 'E':
{
if (atol(optarg) <= 0)
{
printf("%s", help_message);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
E = atol(optarg);
break;
}
case 'b':
{
if (atol(optarg) <= 0) /* We assume that there are at least two sets */
{
printf("%s", help_message);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
b = atol(optarg);
break;
}
case 't':
{
if ((tracefile = fopen(optarg, "r")) == NULL)
{
perror("Failed to open tracefile");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
break;
}
default:
{
printf("%s", help_message);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
}
关于getopt的用法可以参考文章开头的文章;perror和fopen的用法请man一下,fopen失败后会设置errno的。
if (s == 0 || b ==0 || E == 0 || tracefile == NULL)
{
printf("%s", help_message);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
如果读取的参数中没有s或者b或者E或者文件,那么那他们将会是对应的初始值。
main函数调用函数并结束程序:
cache = InitializeCache(S, E);
Result = ReadAndTest(tracefile, cache, S, E, s, b, verbose);
RealseMemory(cache, S, E); /* Don't forget this in C/C++, and do not double release which causes security problem */
//printf("hits:%d misses:%d evictions:%d\n", Result.hit, Result.miss, Result.eviction);
printSummary(Result.hit, Result.miss, Result.eviction);
return 0;
InitializeCache是用来动态申请数据结构的,ReadAndTest是本程序的核心,用来测试hit/miss/eviction的次数。另外不要忘记或者重复释放内存。下面分别介绍这三个函数。
entry_of_sets InitializeCache(uint64_t S, uint64_t E)
{
entry_of_sets cache;
/* use calloc instead of malloc to match the default situation we designed */
if ((cache = calloc(S, sizeof(entry_of_lines))) == NULL) /* initialize the sets */
{
perror("Failed to calloc entry_of_sets");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
for(int i = 0; i < S; ++i) /* initialize the lines in set */
{
if ((cache[i] = calloc(E, sizeof(line))) == NULL)
{
perror("Failed to calloc line in sets");
}
}
return cache;
}
我们首先根据S(set的数目)申请一个数组,该数组元素是lines的入口的指针。接着循环S次每次申请E个line数据结构,并让刚刚的指针数组的元素指向它们:
+-----+
+-----+ +-->Valid|
+---->line0+---+ +-----+
| +-----+ |
+---------------+ | | +---+
| set0 | | +-----+ +-->Tag|
+--> entry_of_lines+------>line1| | +---+
| +---------------+ | +-----+ |
| | | +-------+
| +---------------+ | +-----+ +-->Counter|
| | set1 | +---->line2| +-------+
+--> entry_of_lines| | +-----+
+--------------+ | +---------------+ |
| cache0 +------+ | +-----+
| entry_of_sets| | +---------------+ +---->lineX|
+--------------+ | | set2 | +-----+
+--> entry_of_lines|
| +---------------+
|
| +---------------+
| | setX |
+--> entry_of_lines|
+---------------+
释放之前申请的内存:
void RealseMemory(entry_of_sets cache, uint64_t S, uint64_t E)
{
for (uint64_t i = 0; i < S; ++i)
{
free(cache[i]);
}
free(cache);
}
不解释。
核心部分,测试hit/miss/eviction的次数:
result ReadAndTest(FILE *tracefile, entry_of_sets cache, uint64_t S, uint64_t E, uint64_t s, uint64_t b, _Bool verbose)
{
result Result = {0, 0, 0};
char ch;
uint64_t address;
while((fscanf(tracefile, " %c %lx%*[^\n]", &ch, &address)) == 2) /* read instruction and address from tracefile and ignore the size */
/* address is represented by hexadecimal, use %lx instead of %lu */
{
if (ch == 'I')
{
continue; /* we don't care about 'I' */
}
else
{
uint64_t set_index_mask = (1 << s) - 1;
uint64_t set_index = (address >> b) & set_index_mask;
uint64_t tag = (address >> b) >> s;
entry_of_lines search_line = cache[set_index];
if (ch == 'L' || ch == 'S') /* load/store can cause at most one cache miss */
{
if (verbose) printf("%c %lx ", ch, address);
Result = HitMissEviction(search_line, Result, E, tag, verbose);
}
else if (ch == 'M') /* data modify (M) is treated as a load followed by a store to the same address.
Hence, an M operation can result in two cache hits, or a miss and a hit plus an possible eviction. */
{
if (verbose) printf("%c %lx ", ch, address);
Result = HitMissEviction(search_line, Result, E, tag, verbose); /* load, hit/miss(+eviction) */
Result = HitMissEviction(search_line, Result, E, tag, verbose); /* store, must hit */
}
else /* ignore other cases */
{
continue;
}
}
}
return Result;
}
如果命令是“L”或者“M”,我们就进入HitMissEviction一次判断其是否hit或者miss以及是否发生替换,如果是M就相当于一次“L”和一次“M”,需要进入HitMissEviction两次,其结果可能为两次hit,也可能为一次miss+(eviction)一次hit。我们在ReadAndTest里通过一些位运算找到对应的set(即entry_of_lines),然后以此作为参数调用HitMissEviction 判断到底是miss(有没有eviction)还是hit。
result HitMissEviction(entry_of_lines search_line, result Result, uint64_t E, uint64_t tag, _Bool verbose)
{
uint64_t oldest_time = UINT64_MAX;
uint64_t youngest_time = 0;
uint64_t oldest_block = UINT64_MAX;
_Bool hit_flag = false;
for (uint64_t i = 0; i < E; ++ i)
{
if (search_line[i].tag == tag && search_line[i].valid) /* hit */
{
if (verbose) printf("hit\n");
hit_flag = true;
++Result.hit;
++search_line[i].time_counter; /* update the time counter */
break;
}
}
if (!hit_flag) /* miss */
{
if (verbose) printf("miss");
++Result.miss;
uint64_t i;
for (i = 0; i < E; ++i) /* search for the oldest modified block (invalid blocks are oldest as we designed) */
{
if (search_line[i].time_counter < oldest_time)
{
oldest_time = search_line[i].time_counter;
oldest_block = i;
}
if (search_line[i].time_counter > youngest_time) /* search for the youngest modified block to update the new block's time counter */
{
youngest_time = search_line[i].time_counter;
}
}
search_line[oldest_block].time_counter = youngest_time + 1;
search_line[oldest_block].tag = tag;
if (search_line[oldest_block].valid) /* It's a valid block, ++eviction */
{
if (verbose) printf(" and eviction\n");
++Result.eviction;
}
else
{
if (verbose) printf("\n");
search_line[oldest_block].valid = true;
}
}
return Result;
}
HitMissEviction里面需要注意的地方是时间参量的更新,我们既要找到最“老”的line,也要同时记住最“新”的line的时间参量(我这里是遍历搜索,也可以在设计set的数据类型时设计为结构体,其中放一个最新的时间参量),以此来更新时间参量。如果我们要替换的line的valid为1,则发生了一次eviction。
partA完整代码下载
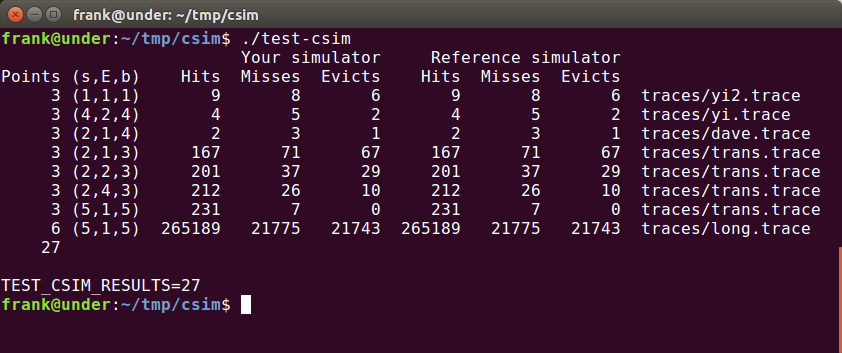
运行结果:
Part B: 优化矩阵转置
前期准备:
最简单的转置实现:
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < M; ++j)
{
dst[j][i] = src[i][j]
}
}
注意事项:
1.最多只能定义12个局部变量。
2.不允许使用位运算,不允许使用数组或者malloc。
3.不能改变原数组A,但是可以修改转置数组B。
思路要点及其实现:
1.block的大小为32byte,即可以放下8个int,即miss的最低限度是1/8。
2.cache的大小为32*32,即32个block,128个int。
3.blocking是一种很好的优化技术,这次实验基本就靠他了;)其大致概念为以数据块的形式读取数据,完全利用后丢弃,然后读取下一个,这样防止block利用的不全面。可以参考卡耐基梅隆的一篇文章:waside-blocking
4.尽量将一个block读入完全或者写入完全,例如假设一个block可以放两个数,进行如下转置操作,其读取时“尽力”读取,完全利用了一个block,但是在写入的时候浪费了1/2的空间。

5.尽量使用刚刚使用的block(还是“热乎的”),因为它们很可能还没有被替换,hit的概率会很大。
6.读出和写入的时候注意判断这两个位置映射在cache中的位置是否相同,(我们这个cache是直接映射,一个set只有一个block,所以绝大部分的miss伴随着替换),也可以说,我们要尽量避免替换的发生。
下面我结合实验要求的三个例子具体讲。
32 × 32 (M = 32, N = 32)
由于我们的block能存8个int,所以blocking的数据块最好是以它为单位的,这样能尽可能利用block,例如8 * 8或者16 * 16。
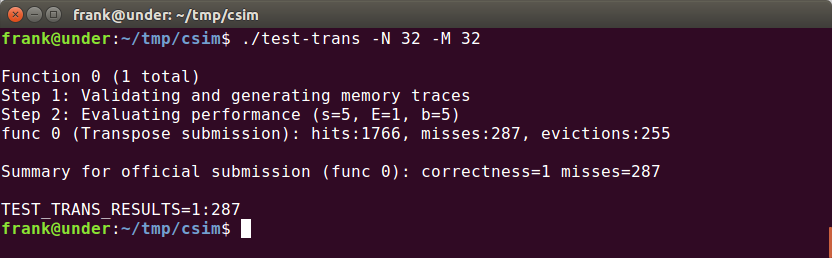
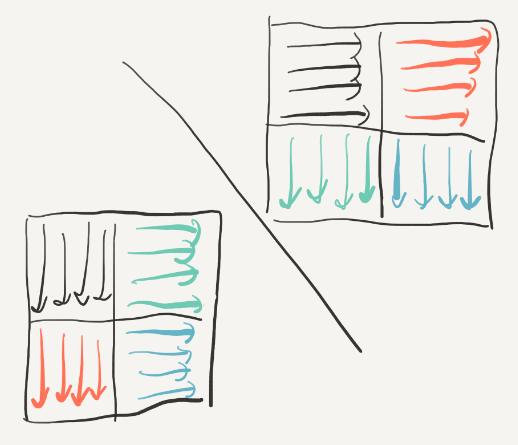
在32*32的情况中,一行是32个int,也就是4个block,所以cache可以存8行,由此可以推出映射冲突的情况:只要两个int之间相差8行的整数倍,那么读取这两个元素所在的block就会发生替换,再读后面连续的元素也会不断发生抖动(thrashing)下图中标出了与一个元素冲突的位置(包括他自己本身的位置,因为我们A,B两个数组在内存中是相邻的,而32*32又是cache的整数倍。):
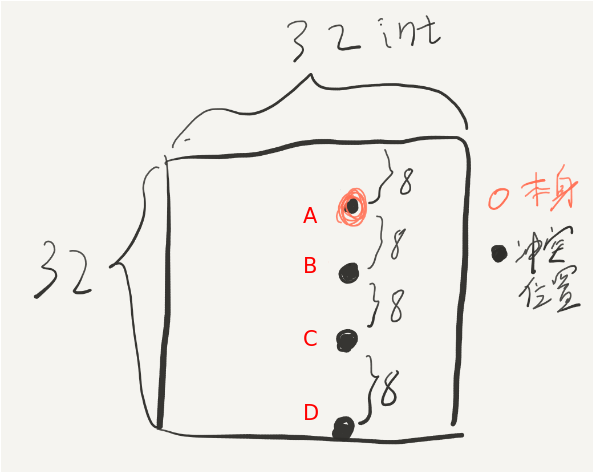
但是转置的过程中这样的情况会发生吗?图中的BCD三点对于A来说仅仅是行差了8K,这在转置中是不可能发生的!因为转置是将A[i][j]送到B[j][i],不会有B[i][j+8k]的情况出现。
但是对于A点而言,如果A[i][j]中i = j,那么B也会是B[i][j],即映射遇到同一个block中,而当i = j的时候,就是对角线的情况:
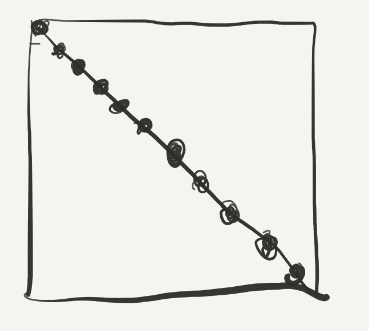
所以现在我们只要单独处理对角线的情况就可以啦,这里有两种处理方法:
- 由于我们可以使用12个局部变量,所以我们可以用8个局部变量一次性将包含对角线int的block全部读出,这样即使写入的时候替换了之前的block也不要紧,因为我们已经全部读出了。
- 我们用一个局部变量暂时先保存这个对角线元素,并用另一个变量记录它的位置,待block的其他7个元素写完以后,我们再将这个会引起替换的元素写到目的地。
下面的代码使用第一种方法,另外,由于相差8行就会有冲突,所以我们blocking的时候用8*8的数据块。
for (int i = 0; i < N; i += 8)
{
for (int j = 0; j < M; j += 8)
{
for (int k = i; k < i + 8; ++k)
{
int temp_value0 = A[k][j];
int temp_value1 = A[k][j+1];
int temp_value2 = A[k][j+2];
int temp_value3 = A[k][j+3];
int temp_value4 = A[k][j+4];
int temp_value5 = A[k][j+5];
int temp_value6 = A[k][j+6];
int temp_value7 = A[k][j+7];
B[j][k] = temp_value0;
B[j+1][k] = temp_value1;
B[j+2][k] = temp_value2;
B[j+3][k] = temp_value3;
B[j+4][k] = temp_value4;
B[j+5][k] = temp_value5;
B[j+6][k] = temp_value6;
B[j+7][k] = temp_value7;
}
}
}
运行结果:
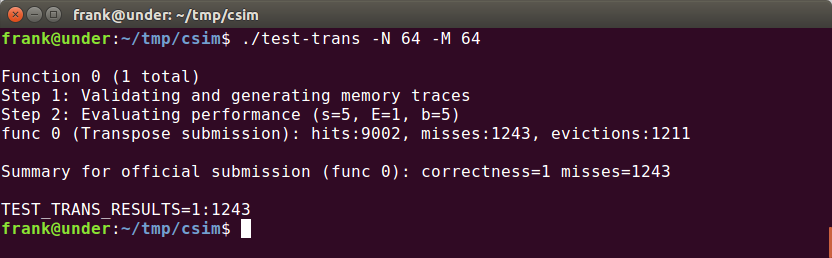
64 × 64 (M = 64, N = 64)
此时,数组一行有64个int,即8个block,所以每四行就会填满一个cache,即两个元素相差四行就会发生冲突。
如果我们使用4*4的blocking,这样固然可以成功,但是每次都会有1/2的损失,优化不够。如果使用刚刚的8*8的blocking,那么在写入的时候就会发生冲突:
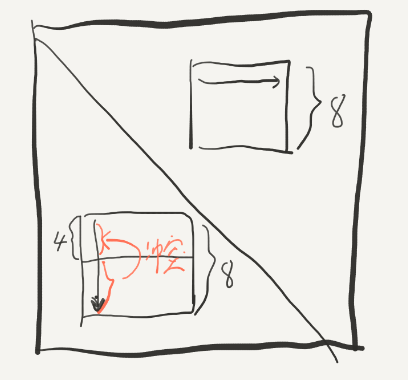
这个时候可以使用一下“divide and conquer”的思想,我们先将8*8的块分成四部分:
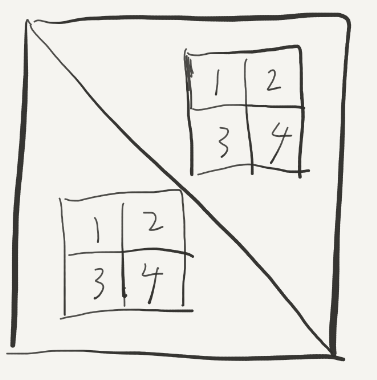
本来我们是要将右上角的2移动到左下角的3的(转置),但是为了防止冲突我们先把他们移动到2的位置,以后再来处理:
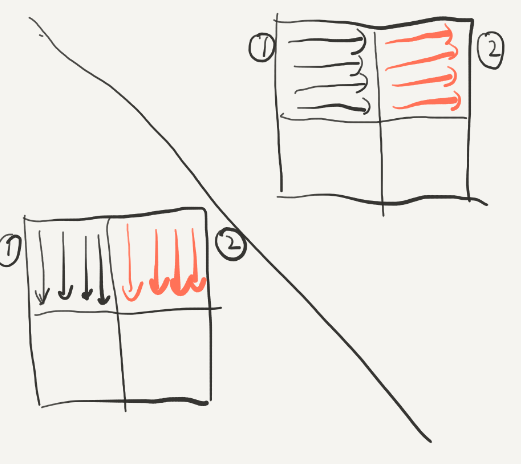
对于3和4,我们采取一样的策略,就可以得到如下结果,在这个过程中没有抖动的发生:
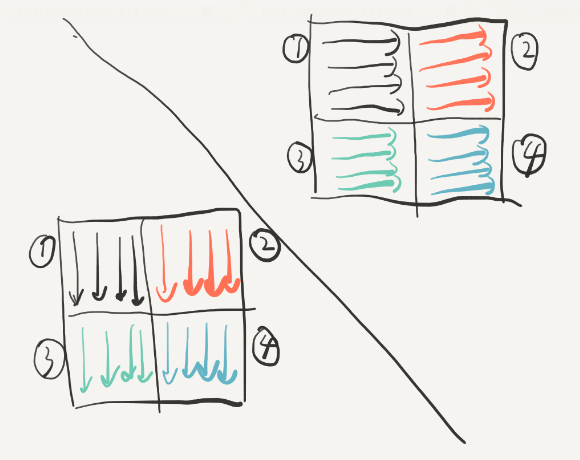
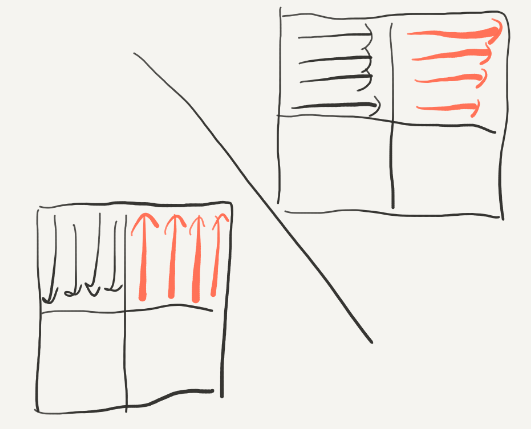
这个时候再将23互换就可以啦。
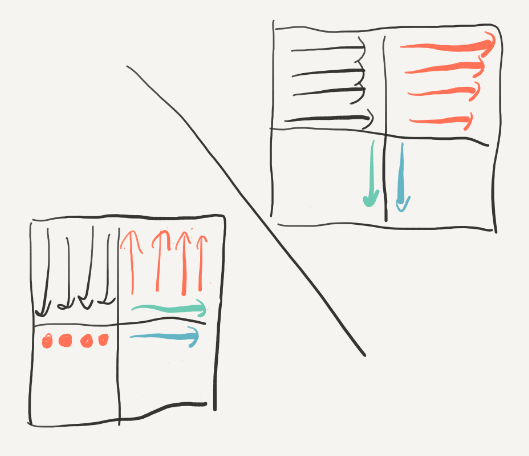
但是,测试以后并不能满足优化的要求,说明我们将23转换的时候(或是之后)又发生很多miss,所以我们应该在将右上角的34转换的过程中将2的位置复原,这里的复原是整个实验中最具技巧性的,由前面的要点5:尽量使用刚刚使用的block(还是“热乎的”),因为它们很可能还没有被替换,hit的概率会很大。我们在转换2的时候逆序转换:
同时在读取右上角34的时候按列来读,这样的好处就是把2换到3的过程中是从下到上按行换的,因为这样可以先使用“最热乎”的block:
接着转换:
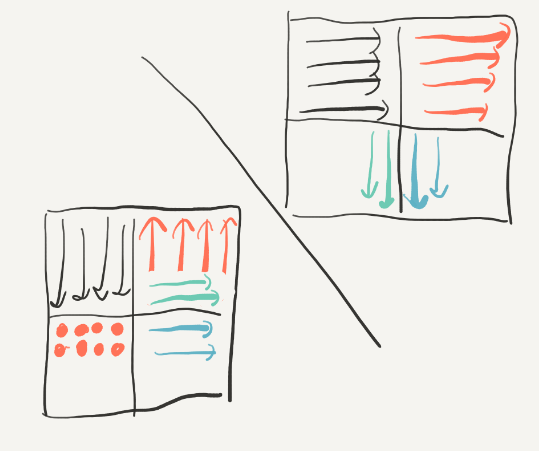
最后的效果:
for (int i = 0; i < N; i += 8)
{
for (int j = 0; j < M; j += 8)
{
for (int k = i; k < i + 4; ++k)
{
/* 读取1 2,暂时放在左下角1 2 */
int temp_value0 = A[k][j];
int temp_value1 = A[k][j+1];
int temp_value2 = A[k][j+2];
int temp_value3 = A[k][j+3];
int temp_value4 = A[k][j+4];
int temp_value5 = A[k][j+5];
int temp_value6 = A[k][j+6];
int temp_value7 = A[k][j+7];
B[j][k] = temp_value0;
B[j+1][k] = temp_value1;
B[j+2][k] = temp_value2;
B[j+3][k] = temp_value3;
/* 逆序放置 */
B[j][k+4] = temp_value7;
B[j+1][k+4] = temp_value6;
B[j+2][k+4] = temp_value5;
B[j+3][k+4] = temp_value4;
}
for (int l = 0; l < 4; ++l)
{
/* 按列读取 */
int temp_value0 = A[i+4][j+3-l];
int temp_value1 = A[i+5][j+3-l];
int temp_value2 = A[i+6][j+3-l];
int temp_value3 = A[i+7][j+3-l];
int temp_value4 = A[i+4][j+4+l];
int temp_value5 = A[i+5][j+4+l];
int temp_value6 = A[i+6][j+4+l];
int temp_value7 = A[i+7][j+4+l];
/* 从下向上按行转换2到3 */
B[j+4+l][i] = B[j+3-l][i+4];
B[j+4+l][i+1] = B[j+3-l][i+5];
B[j+4+l][i+2] = B[j+3-l][i+6];
B[j+4+l][i+3] = B[j+3-l][i+7];
/* 将3 4放到正确的位置 */
B[j+3-l][i+4] = temp_value0;
B[j+3-l][i+5] = temp_value1;
B[j+3-l][i+6] = temp_value2;
B[j+3-l][i+7] = temp_value3;
B[j+4+l][i+4] = temp_value4;
B[j+4+l][i+5] = temp_value5;
B[j+4+l][i+6] = temp_value6;
B[j+4+l][i+7] = temp_value7;
}
}
}
运行结果:
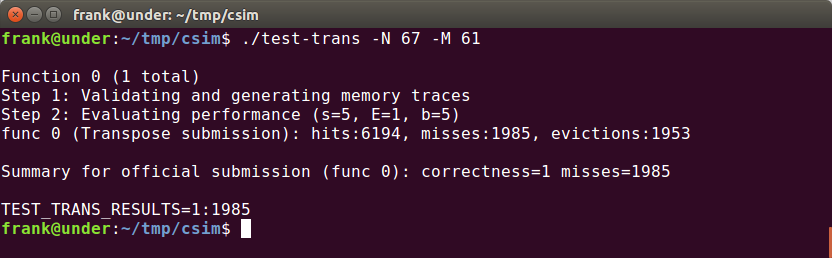
61 × 67 (M = 61, N = 67)
这个题只要求miss < 2000,比较宽松。
这个时候由于不对称,所以也不存在相差4行就必定冲突的情况,我们可以试一下16 * 16这种blocking。但是“对角线”的元素(横坐标等于纵坐标)肯定还是会冲突的(其实这个时候不是对角线了,因为不是正方形)。我们在这里用32*32分析中的第二种方法。
for (int i = 0; i < N; i += 16)
{
for (int j = 0; j < M; j += 16)
{
for (int k = i; k < i + 16 && k < N; ++k)
{
int temp_position = -1;
int temp_value = 0;
int l;
for (l = j; l < j + 16 && l < M; ++l)
{
if (l == k) /* 横坐标等于纵坐标,局部变量暂存,整个block读完再处理 */
{
temp_position = k;
temp_value = A[k][k];
}
else
{
B[l][k] = A[k][l];
}
}
if (temp_position != -1) /* 遇到了冲突元素 */
{
B[temp_position][temp_position] = temp_value;
}
}
}
}
运行结果:
partB完整代码下载
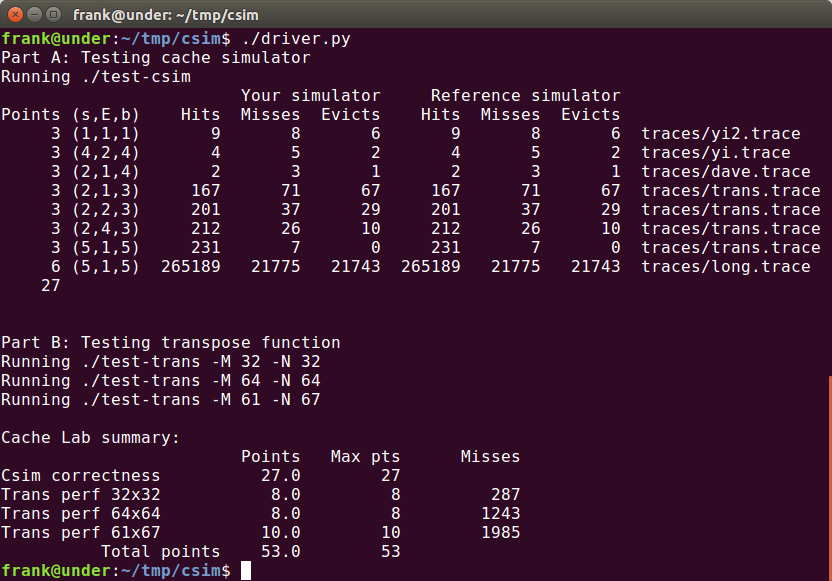
最终结果为满分:
CS:APP3e 深入理解计算机系统_3e CacheLab实验的更多相关文章
- CS:APP3e 深入理解计算机系统_3e MallocLab实验
详细的题目要求和资源可以到 http://csapp.cs.cmu.edu/3e/labs.html 或者 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~./213/schedule.html 获取. ...
- CS:APP3e 深入理解计算机系统_3e bomblab实验
bomb.c /*************************************************************************** * Dr. Evil's Ins ...
- CS:APP3e 深入理解计算机系统_3e Attacklab 实验
详细的题目要求和资源可以到 http://csapp.cs.cmu.edu/3e/labs.html 或者 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~./213/schedule.html 获取. ...
- CS:APP3e 深入理解计算机系统_3e Datalab实验
由于http://csapp.cs.cmu.edu/并未完全开放实验,很多附加实验做不了,一些环境也没办法搭建,更没有标准答案.做了这个实验的朋友可以和我对对答案:) 实验内容和要求可在http:// ...
- CS:APP3e 深入理解计算机系统_3e ShellLab(tsh)实验
详细的题目要求和资源可以到 http://csapp.cs.cmu.edu/3e/labs.html 或者 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~./213/schedule.html 获取. ...
- CS:APP3e 深入理解计算机系统_3e C Programming Lab实验
queue.h: /* * Code for basic C skills diagnostic. * Developed for courses 15-213/18-213/15-513 by R. ...
- CS:APP3e 深入理解计算机系统_3e Y86-64模拟器指南
详细的题目要求和资源可以到 http://csapp.cs.cmu.edu/3e/labs.html 或者 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~./213/schedule.html 获取. ...
- 深入理解计算机系统_3e 第九章家庭作业 CS:APP3e chapter 9 homework
9.11 A. 00001001 111100 B. +----------------------------+ | Parameter Value | +--------------------- ...
- 深入理解计算机系统_3e 第八章家庭作业 CS:APP3e chapter 8 homework
8.9 关于并行的定义我之前写过一篇文章,参考: 并发与并行的区别 The differences between Concurrency and Parallel +---------------- ...
随机推荐
- 老的工程移植到AndroidStudio需要修改的注意事项
之前老的工程用android-apt编译,如果要在新的AndroidStudio编译至少需要修改一下几部分: 1. 修改project里的build.gradle dependencies { cla ...
- mvc4 实现自己的权限验证 仿Authorize与AllowAnonymous原理
参考文章 :http://www.cosdiv.com/page/M0/S878/878978.html 实现的效果:在控制器上(Controller)验证权限,在动作(Action)上不验证. 用M ...
- OOA、OOD、OOP分别是什么?
什么是面向对象分析(OOA)? "面向对象分析是一种分析方法,这种方法利用从问题域的词汇表中找到的类和对象来分析需求." 什么是面向对象设计(OOD)? "面向对象设计是 ...
- 通用的contain函数
用来检测节点所属关系:document.documentElement.contains(document.body) function contains(refNode, otherNode) {i ...
- display: run-in
If a sibling block box (that does not float and is not absolutely positioned) follows the run-in box ...
- Spring IOC容器分析(2) -- BeanDefinition
上文对Spring IOC容器的核心BeanFactory接口分析发现:在默认Bean工厂DefaultListableBeanFactory中对象不是以Object形成存储,而是以BeanDefin ...
- KODExplorer可道云-轻松搭建属于自己/团队的私有云网盘服务
如今国内各大网盘关停的也快差不多,百度网盘限速严重.国外大牌的如 Dropbox 或 Google Drive又在长城之外,在各种VPN都被封禁的大背景下,科学上网也困难重重,麻烦到要死.那么,除了购 ...
- 一:Spring Boot、Spring Cloud
上次写了一篇文章叫Spring Cloud在国内中小型公司能用起来吗?介绍了Spring Cloud是否能在中小公司使用起来,这篇文章是它的姊妹篇.其实我们在这条路上已经走了一年多,从16年初到现在. ...
- [标]ORACLE常用的一些语句记录
--查询实际的统计信息select num_rows,blocks,empty_blocks,avg_space,avg_row_len,sample_size, last_analyzed ...
- File signature analysis failed to recognize .old file
My friend May she found a strange file called "bkp.old" as below in the evidence files. Sh ...
