标签传播算法(llgc 或 lgc)
动手实践标签传播算法
复现论文:Learning with Local and Global Consistency[1]
lgc 算法可以参考:DecodePaper/notebook/lgc
初始化算法
载入一些必备的库:
from IPython.display import set_matplotlib_formats%matplotlib inline#set_matplotlib_formats('svg', 'pdf')import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom scipy.spatial.distance import cdistfrom sklearn.datasets import make_moonssave_dir = '../data/images'
创建一个简单的数据集
利用 make_moons 生成一个半月形数据集。
n = 800 # 样本数n_labeled = 10 # 有标签样本数X, Y = make_moons(n, shuffle=True, noise=0.1, random_state=1000)X.shape, Y.shape
((800, 2), (800,))
def one_hot(Y, n_classes):'''对标签做 one_hot 编码参数=====Y: 从 0 开始的标签n_classes: 类别数'''out = Y[:, None] == np.arange(n_classes)return out.astype(float)
color = ['red' if l == 0 else 'blue' for l in Y]plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], color=color)plt.savefig(f"{save_dir}/bi_classification.pdf", format='pdf')plt.show()Y_input = np.concatenate((one_hot(Y[:n_labeled], 2), np.zeros((n-n_labeled, 2))))
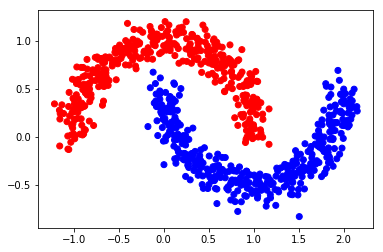
算法过程:
Step 1: 创建相似度矩阵 W
def rbf(x, sigma):return np.exp((-x)/(2* sigma**2))
sigma = 0.2dm = cdist(X, X, 'euclidean')W = rbf(dm, sigma)np.fill_diagonal(W, 0) # 对角线全为 0
Step 2: 计算 S
\]
向量化编程:
def calculate_S(W):d = np.sum(W, axis=1)D_ = np.sqrt(d*d[:, np.newaxis]) # D_ 是 np.sqrt(np.dot(diag(D),diag(D)^T))return np.divide(W, D_, where=D_ != 0)S = calculate_S(W)
迭代一次的结果
alpha = 0.99F = np.dot(S, Y_input)*alpha + (1-alpha)*Y_inputY_result = np.zeros_like(F)Y_result[np.arange(len(F)), F.argmax(1)] = 1Y_v = [1 if x == 0 else 0 for x in Y_result[0:,0]]color = ['red' if l == 0 else 'blue' for l in Y_v]plt.scatter(X[0:,0], X[0:,1], color=color)#plt.savefig("iter_1.pdf", format='pdf')plt.show()
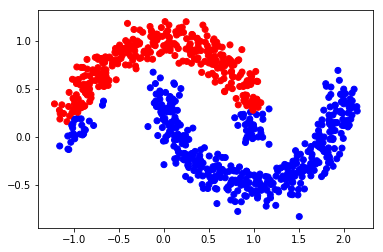
Step 3: 迭代 F "n_iter" 次直到收敛
n_iter = 150F = Y_inputfor t in range(n_iter):F = np.dot(S, F)*alpha + (1-alpha)*Y_input
Step 4: 画出最终结果
Y_result = np.zeros_like(F)Y_result[np.arange(len(F)), F.argmax(1)] = 1Y_v = [1 if x == 0 else 0 for x in Y_result[0:,0]]color = ['red' if l == 0 else 'blue' for l in Y_v]plt.scatter(X[0:,0], X[0:,1], color=color)#plt.savefig("iter_n.pdf", format='pdf')plt.show()

from sklearn import metricsprint(metrics.classification_report(Y, F.argmax(1)))acc = metrics.accuracy_score(Y, F.argmax(1))print('准确度为',acc)
precision recall f1-score support0 1.00 0.86 0.92 4001 0.88 1.00 0.93 400micro avg 0.93 0.93 0.93 800macro avg 0.94 0.93 0.93 800weighted avg 0.94 0.93 0.93 800准确度为 0.92875
sklearn 实现 lgc
参考:https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/label_propagation.html
在 sklearn 里提供了两个 lgc 模型:LabelPropagation 和 LabelSpreading,其中后者是前者的正则化形式。\(W\) 的计算方式提供了 rbf 与 knn。
rbf核由参数gamma控制(\(\gamma=\frac{1}{2{\sigma}^2}\))knn核 由参数n_neighbors(近邻数)控制
def pred_lgc(X, Y, F, numLabels):from sklearn import preprocessingfrom sklearn.semi_supervised import LabelSpreadingcls = LabelSpreading(max_iter=150, kernel='rbf', gamma=0.003, alpha=.99)# X.astype(float) 为了防止报错 "Numerical issues were encountered "cls.fit(preprocessing.scale(X.astype(float)), F)ind_unlabeled = np.arange(numLabels, len(X))y_pred = cls.transduction_[ind_unlabeled]y_true = Y[numLabels:].astype(y_pred.dtype)return y_true, y_pred
Y_input = np.concatenate((Y[:n_labeled], -np.ones(n-n_labeled)))y_true, y_pred = pred_lgc(X, Y, Y_input, n_labeled)print(metrics.classification_report(Y, F.argmax(1)))
precision recall f1-score support0 1.00 0.86 0.92 4001 0.88 1.00 0.93 400micro avg 0.93 0.93 0.93 800macro avg 0.94 0.93 0.93 800weighted avg 0.94 0.93 0.93 800
networkx 实现 lgc
参考:networkx.algorithms.node_classification.lgc.local_and_global_consistency 具体的细节,我还没有研究!先放一个简单的例子:
G = nx.path_graph(4)G.node[0]['label'] = 'A'G.node[3]['label'] = 'B'G.nodes(data=True)G.edges()predicted = node_classification.local_and_global_consistency(G)predicted
['A', 'A', 'B', 'B']
更多精彩内容见:DecodePaper 觉得有用,记得给个 star !(@DecodePaper)
Zhou D, Bousquet O, Lal T N, et al. Learning with Local and Global Consistency[C]. neural information processing systems, 2003: 321-328. ↩︎
标签传播算法(llgc 或 lgc)的更多相关文章
- 标签传播算法(Label Propagation)及Python实现
众所周知,机器学习可以大体分为三大类:监督学习.非监督学习和半监督学习.监督学习可以认为是我们有非常多的labeled标注数据来train一个模型,期待这个模型能学习到数据的分布,以期对未来没有见到的 ...
- 标签传播算法(Label Propagation Algorithm, LPA)初探
0. 社区划分简介 0x1:非重叠社区划分方法 在一个网络里面,每一个样本只能是属于一个社区的,那么这样的问题就称为非重叠社区划分. 在非重叠社区划分算法里面,有很多的方法: 1. 基于模块度优化的社 ...
- Label Propagation Algorithm LPA 标签传播算法解析及matlab代码实现
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/bethansy/p/6953625.html LPA算法的思路: 首先每个节点有一个自己特有的标签,节点会选择自己邻居中出现次数最多的标 ...
- lpa标签传播算法解说及代码实现
package lpa; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class L ...
- 神经网络训练中的Tricks之高效BP(反向传播算法)
神经网络训练中的Tricks之高效BP(反向传播算法) 神经网络训练中的Tricks之高效BP(反向传播算法) zouxy09@qq.com http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09 ...
- (3)Deep Learning之神经网络和反向传播算法
往期回顾 在上一篇文章中,我们已经掌握了机器学习的基本套路,对模型.目标函数.优化算法这些概念有了一定程度的理解,而且已经会训练单个的感知器或者线性单元了.在这篇文章中,我们将把这些单独的单元按照一定 ...
- [2] TensorFlow 向前传播算法(forward-propagation)与反向传播算法(back-propagation)
TensorFlow Playground http://playground.tensorflow.org 帮助更好的理解,游乐场Playground可以实现可视化训练过程的工具 TensorFlo ...
- 反向传播算法 Backpropagation Algorithm
假设我们有一个固定样本集,它包含 个样例.我们可以用批量梯度下降法来求解神经网络.具体来讲,对于单个样例(x,y),其代价函数为:这是一个(二分之一的)方差代价函数.给定一个包含 个样例的数据集,我们 ...
- 神经网络之反向传播算法(BP)公式推导(超详细)
反向传播算法详细推导 反向传播(英语:Backpropagation,缩写为BP)是"误差反向传播"的简称,是一种与最优化方法(如梯度下降法)结合使用的,用来训练人工神经网络的常见 ...
随机推荐
- 前端学习 -- Css -- 有序列表和无序列表
列表就相当于去超市购物时的那个购物清单, 在HTML也可以创建列表,在网页中一共有三种列表: 1.无序列表 2.有序列表 3.定义列表 无序列表 - 使用ul标签来创建一个无序列表 - 使用li在ul ...
- Spark记录-spark报错Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform
解决方案一: #cp $HADOOP_HOME/lib/native/libhadoop.so $JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/amd64 #源码编译snappy---./configure ...
- SQL记录-PLSQL游标
PL/SQL游标 Oracle会创建一个存储区域,被称为上下文区域,用于处理SQL语句,其中包含需要处理的语句,例如所有的信息,行数处理,等等. 游标是指向这一上下文的区域. PL/SQL通过控制光标 ...
- bzoj千题计划283:bzoj4516: [Sdoi2016]生成魔咒(后缀数组)
http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=4516 考虑在后面新加一个字母产生的影响 假设是第i个 如果不考虑重复,那么会增加i个不同的字符串 考 ...
- HTML5 移动开发 (HTML5标签和属性)
第一阶 1.如何使用HTML5中的新标签及属性 2.HTML5中的其它变化 3.HTML5的移动支持 4.使用HTML5开发移动WEB引用的理由 第二阶 HTML5 ...
- 第8月第16天 django pil
1. https://github.com/chaonet/forum/ sudo easy_install --find-links http://www.pythonware.com/produ ...
- 游程编码(Run Length Code)
一.什么是游程编码 游程编码是一种比较简单的压缩算法,其基本思想是将重复且连续出现多次的字符使用(连续出现次数,某个字符)来描述. 比如一个字符串: AAAAABBBBCCC 使用游程编码可以将其描述 ...
- Spark笔记之使用UDF(User Define Function)
一.UDF介绍 UDF(User Define Function),即用户自定义函数,Spark的官方文档中没有对UDF做过多介绍,猜想可能是认为比较简单吧. 几乎所有sql数据库的实现都为用户提供了 ...
- pt-table-checksum 3.0.4检测不出主从差异数据
群里好几位同学问 pt-table-checksum 3.0.4, 主从两个表数据是不一致,为啥检测不出来?前段时间自己也测试过,只是没整理成随笔^_- 一.基本环境 VMware10.0+CentO ...
- FPGA学习笔记. 二分频和三分频
二分频和三分频 二分频:将输入频率CLK分为原来的 1/2 . 实现:在每次CLK的上升沿或下降沿将输出翻转. 三分频: 1/3占空比. 实现:可使用上升沿或下降沿计数生成输出.需要一个两位计数器. ...
