spark 中的RDD编程 -以下基于Java api
1.RDD介绍:
JavaRDD<String> lines=sc.textFile(inputFile);
(2)分发对象集合,这里以list为例
List<String> list=new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
JavaRDD<String> temp=sc.parallelize(list);
//上述方式等价于
JavaRDD<String> temp2=sc.parallelize(Arrays.asList("a","b","c"));
List<String> list=new ArrayList<String>();
//建立列表,列表中包含以下自定义表项
list.add("error:a");
list.add("error:b");
list.add("error:c");
list.add("warning:d");
list.add("hadppy ending!");
//将列表转换为RDD对象
JavaRDD<String> lines = sc.parallelize(list);
//将RDD对象lines中有error的表项过滤出来,放在RDD对象errorLines中
JavaRDD<String> errorLines = lines.filter(
new Function<String, Boolean>() {
public Boolean call(String v1) throws Exception {
return v1.contains("error");
}
}
);
//遍历过滤出来的列表项
List<String> errorList = errorLines.collect();
for (String line : errorList)
System.out.println(line);
JavaRDD<String> warningLines=lines.filter(new Function<String, Boolean>() {public Boolean call(String v1) throws Exception {return v1.contains("warning");}});JavaRDD<String> unionLines=errorLines.union(warningLines);for(String line :unionLines.collect())System.out.println(line);
/**
* Take the first num elements of the RDD. This currently scans the partitions *one by one*, so
* it will be slow if a lot of partitions are required. In that case, use collect() to get the
* whole RDD instead.
*/
def take(num: Int): JList[T]
程序示例:接上
JavaRDD<String> unionLines=errorLines.union(warningLines);
for(String line :unionLines.take(2))
System.out.println(line);
输出:
List<String> unions=unionLines.collect();
for(String line :unions)
System.out.println(line);
遍历输出RDD数据集unions的每一项
|
函数名
|
实现的方法
|
用途
|
|
Function<T,R>
|
R call(T)
|
接收一个输入值并返回一个输出值,用于类似map()和filter()的操作中 |
| Function<T1,T2,R> |
R call(T1,T2)
|
接收两个输入值并返回一个输出值,用于类似aggregate()和fold()等操作中
|
| FlatMapFunction<T,R> |
Iterable <R> call(T)
|
接收一个输入值并返回任意个输出,用于类似flatMap()这样的操作中
|
JavaRDD<String> errorLines=lines.filter(
new Function<String, Boolean>() {
public Boolean call(String v1)throws Exception {
return v1.contains("error");
}
}
);
List<String> strLine=new ArrayList<String>();
strLine.add("how are you");
strLine.add("I am ok");
strLine.add("do you love me")
JavaRDD<String> input=sc.parallelize(strLine);
JavaRDD<String> words=input.flatMap(
new FlatMapFunction<String, String>() {
public Iterable<String> call(String s) throws Exception {
return Arrays.asList(s.split(" "));
}
}
);
List<String> strLine=new ArrayList<String>();
strLine.add("how are you");
strLine.add("I am ok");
strLine.add("do you love me");
JavaRDD<String> input=sc.parallelize(strLine);
JavaRDD<String> words=input.flatMap(
new FlatMapFunction<String, String>() {
public Iterable<String> call(String s) throws Exception {
return Arrays.asList(s.split(" "));
}
}
);
JavaPairRDD<String,Integer> counts=words.mapToPair(
new PairFunction<String, String, Integer>() {
public Tuple2<String, Integer> call(String s) throws Exception {
return new Tuple2(s, 1);
}
}
);
JavaPairRDD <String,Integer> results=counts.reduceByKey(
new org.apache.spark.api.java.function.Function2<Integer, Integer, Integer>() {
public Integer call(Integer v1, Integer v2) throws Exception {
return v1 + v2;
}
}
) ;
class ContainError implements Function<String,Boolean>{
public Boolean call(String v1) throws Exception {
return v1.contains("error");
}
}
JavaRDD<String> errorLines=lines.filter(new ContainError());
for(String line :errorLines.collect())
System.out.println(line);
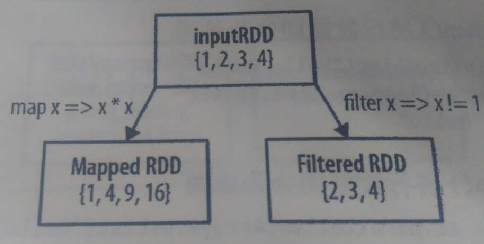
JavaRDD<Integer> rdd =sc.parallelize(Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4));
JavaRDD<Integer> result=rdd.map(
new Function<Integer, Integer>() {
public Integer call(Integer v1) throwsException {
return v1*v1;
}
}
);
System.out.println( StringUtils.join(result.collect(),","));
输出:
JavaRDD<Integer> rdd =sc.parallelize(Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4));
JavaRDD<Integer> results=rdd.filter(
new Function<Integer, Boolean>() {
public Boolean call(Integer v1) throws Exception {
return v1!=1;
}
}
);
System.out.println(StringUtils.join(results.collect(),","));
结果:
JavaRDD<String> rdd =sc.parallelize(Arrays.asList("hello world","hello you","world i love you"));
JavaRDD<String> words=rdd.flatMap(
new FlatMapFunction<String, String>() {
public Iterable<String> call(String s) throws Exception {
return Arrays.asList(s.split(" "));
}
}
);
System.out.println(StringUtils.join(words.collect(),'\n'));
输出:
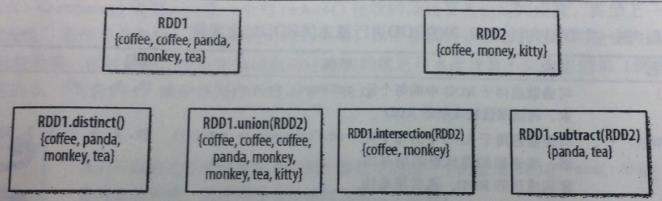
|
函数
|
用途
|
|
RDD1.distinct()
|
生成一个只包含不同元素的新RDD。需要数据混洗。 |
|
RDD1.union(RDD2)
|
返回一个包含两个RDD中所有元素的RDD |
|
RDD1.intersection(RDD2)
|
只返回两个RDD中都有的元素 |
|
RDD1.substr(RDD2)
|
返回一个只存在于第一个RDD而不存在于第二个RDD中的所有元素组成的RDD。需要数据混洗。 |
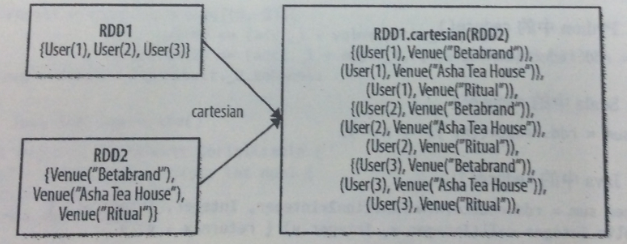
|
RDD1.cartesian(RDD2)
|
返回两个RDD数据集的笛卡尔集 |
JavaRDD<Integer> rdd1 = sc.parallelize(Arrays.asList(1,2));
JavaRDD<Integer> rdd2 = sc.parallelize(Arrays.asList(1,2));
JavaPairRDD<Integer ,Integer> rdd=rdd1.cartesian(rdd2);
for(Tuple2<Integer,Integer> tuple:rdd.collect())
System.out.println(tuple._1()+"->"+tuple._2());
输出:
JavaRDD<Integer> rdd = sc.parallelize(Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10));
Integer sum =rdd.reduce(
new Function2<Integer, Integer, Integer>() {
public Integercall(Integer v1, Integer v2) throws Exception {
return v1+v2;
}
}
);
System.out.println(sum.intValue());
输出:55
JavaRDD<Integer> rdd = sc.parallelize(Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10));
Integer sum =rdd.fold(0,
new Function2<Integer, Integer, Integer>() {
public Integer call(Integer v1, Integer v2) throws Exception {
return v1+v2;
}
}
);
System.out.println(sum);
②计算RDD数据集中所有元素的积:
JavaRDD<Integer> rdd = sc.parallelize(Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10));
Integer result =rdd.fold(1,
new Function2<Integer, Integer, Integer>() {
public Integer call(Integer v1, Integer v2) throws Exception {
return v1*v2;
}
}
);
System.out.println(result);
(3)aggregate()操作
public class AvgCount implements Serializable{
public int total;
public int num;
public AvgCount(int total,int num){
this.total=total;
this.num=num;
}
public double avg(){
return total/(double)num;
}
static Function2<AvgCount,Integer,AvgCount> addAndCount=
new Function2<AvgCount, Integer, AvgCount>() {
public AvgCount call(AvgCount a, Integer x) throws Exception {
a.total+=x;
a.num+=1;
return a;
}
};
static Function2<AvgCount,AvgCount,AvgCount> combine=
new Function2<AvgCount, AvgCount, AvgCount>() {
public AvgCount call(AvgCount a, AvgCount b) throws Exception {
a.total+=b.total;
a.num+=b.num;
return a;
}
};
public static void main(String args[]){
SparkConf conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("my app");
JavaSparkContext sc = new JavaSparkContext(conf);
AvgCount intial =new AvgCount(0,0);
JavaRDD<Integer> rdd =sc.parallelize(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6));
AvgCount result=rdd.aggregate(intial,addAndCount,combine);
System.out.println(result.avg());
}
}
这个程序示例可以实现求出RDD对象集的平均数的功能。其中addAndCount将RDD对象集中的元素合并起来放入AvgCount对象之中,combine提供两个AvgCount对象的合并的实现。我们初始化AvgCount(0,0),表示有0个对象,对象的和为0,最终返回的result对象中total中储存了所有元素的和,num储存了元素的个数,这样调用result对象的函数avg()就能够返回最终所需的平均数,即avg=tatal/(double)num。
| 级别 |
使用的空间
|
cpu时间
|
是否在内存
|
是否在磁盘
|
备注
|
|
MEMORY_ONLY
|
高 |
低
|
是
|
否
|
直接储存在内存 |
| MEMORY_ONLY_SER |
低
|
高
|
是
|
否
|
序列化后储存在内存里
|
|
MEMORY_AND_DISK
|
低 |
中等
|
部分
|
部分
|
如果数据在内存中放不下,溢写在磁盘上 |
|
MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER
|
低 |
高
|
部分
|
部分
|
数据在内存中放不下,溢写在磁盘中。内存中存放序列化的数据。 |
|
DISK_ONLY
|
低
|
高
|
否
|
是
|
直接储存在硬盘里面
|
JavaRDD<Integer> rdd =sc.parallelize(Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5));
rdd.persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_ONLY());
System.out.println(rdd.count());
System.out.println(StringUtils.join(rdd.collect(),','));
RDD还有unpersist()方法,调用该方法可以手动把持久化的RDD从缓存中移除。
JavaRDD<Integer> rdd =sc.parallelize(Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5));
JavaDoubleRDD result=rdd.mapToDouble(
new DoubleFunction<Integer>() {
public double call(Integer integer) throws Exception {
return (double) integer*integer;
}
}
);
System.out.println(result.max());
spark 中的RDD编程 -以下基于Java api的更多相关文章
- SpringMVC常用配置-Controller中的各种配置(基于Java API和注解)
- 02、体验Spark shell下RDD编程
02.体验Spark shell下RDD编程 1.Spark RDD介绍 RDD是Resilient Distributed Dataset,中文翻译是弹性分布式数据集.该类是Spark是核心类成员之 ...
- Spark学习之RDD编程(2)
Spark学习之RDD编程(2) 1. Spark中的RDD是一个不可变的分布式对象集合. 2. 在Spark中数据的操作不外乎创建RDD.转化已有的RDD以及调用RDD操作进行求值. 3. 创建RD ...
- Spark学习之RDD编程总结
Spark 对数据的核心抽象——弹性分布式数据集(Resilient Distributed Dataset,简称 RDD).RDD 其实就是分布式的元素集合.在 Spark 中,对数据的所有操作不外 ...
- Spark学习笔记——RDD编程
1.RDD——弹性分布式数据集(Resilient Distributed Dataset) RDD是一个分布式的元素集合,在Spark中,对数据的操作就是创建RDD.转换已有的RDD和调用RDD操作 ...
- Spark中的RDD和DataFrame
什么是DataFrame 在Spark中,DataFrame是一种以RDD为基础的分布式数据集,类似于传统数据库中的二维表格. RDD和DataFrame的区别 DataFrame与RDD的主要区别在 ...
- spark实验(四)--RDD编程(1)
一.实验目的 (1)熟悉 Spark 的 RDD 基本操作及键值对操作: (2)熟悉使用 RDD 编程解决实际具体问题的方法. 二.实验平台 操作系统:centos6.4 Spark 版本:1.5.0 ...
- spark中的RDD以及DAG
今天,我们就先聊一下spark中的DAG以及RDD的相关的内容 1.DAG:有向无环图:有方向,无闭环,代表着数据的流向,这个DAG的边界则是Action方法的执行 2.如何将DAG切分stage,s ...
- Spark学习(2) RDD编程
什么是RDD RDD(Resilient Distributed Dataset)叫做分布式数据集,是Spark中最基本的数据抽象,它代表一个不可变.可分区.弹性.里面的元素可并行计算的集合 RDD允 ...
随机推荐
- Struts1.x教程:配置文件总结
要想使用Struts,至少要依靠两个配置文件:web.xml和struts-config.xml.其中web.xml用来安装Struts框架.而struts-config.xml用来配置在Struts ...
- Exponential notation
Exponential notation You are given a positive decimal number x. Your task is to convert it to the &q ...
- Swaps in Permutation
Swaps in Permutation You are given a permutation of the numbers 1, 2, ..., n and m pairs of position ...
- j2ee常用包的作用
1.antlr-2.7.7.jar 呵呵 一句话,没有此包,hibernate不会执行hql语句 2.aopalliance-1.0.jar 这个包是AOP联盟的API包,里面包含了针对面向切面的 ...
- Java回调函数的理解
所谓回调,就是客户程序C调用服务程序S中的某个函数A,然后S又在某个时候反过来调用C中的某个函数B,对于C来说,这个B便叫做回调函数.例如Win32下的窗口过程函数就是一个典型的回调函数.一般说来,C ...
- Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare() 终极解决方法
非主线程中出现 在报错的方法前加Looper.prepare(); 方法末尾加Looper.loop(); 很简单吧
- Qt5:窗口居中显示
QDesktopWidget* desktop = QApplication::desktop(); // =qApp->desktop();也可以move((desktop->width ...
- sql server 行转列 Pivot UnPivot
SQL Server中行列转换 Pivot UnPivot 本文转自:张志涛 原文地址: http://www.cnblogs.com/zhangzt/archive/2010/07/29/17878 ...
- RSA非对称加密Java实现
原文 加密基础方法类 import java.security.MessageDigest; import sun.misc.BASE64Decoder; import sun.misc.BASE64 ...
- 在Ubuntu 14.04 64bit上安装StarUML 2.5版本
1,在“http://staruml.io/”下载: 2,sudo dpkg -i StarUML-v2.5.0-64-bit.deb安装. 3,注册 .在help中输入.name:maxiongyi ...
