c++ stl源码剖析学习笔记(二)iterator
ITERATOR 迭代器
template<class InputIterator,class T>
InputIterator find(InputIterator first,InputIterator last,const T& value)
{
while(first != last && *first != value)
++first;
return first;
}
代码示例
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
const int arraySize = ;
int ia[arraySize] = {,,,,,,}; vector<int> ivect(ia,ia+arraySize);
list<int> ilist(ia,ia+arraySize);
deque<int> ideque(ia,ia+arraySize); vector<int>::iterator it1 = find(ivect.begin(),ivect.end(),);
if(it1 == ivect.end())
cout << "4 not found." << endl;
else
cout << "4 found. " << * it1 << endl; list<int>::iterator it2 = find(ilist.begin(),ilist.end(),);
if(it2 == ilist.end())
cout << "6 not found. " << endl;
else
cout << "6 found. " << *it2 << endl; deque<int>::iterator it3 = find(ideque.begin(),ideque.end(),);
if(it3 == ideque.end())
cout << "8 not found. " << endl;
else
cout << "8 find " << *it3 << endl; return ;
}
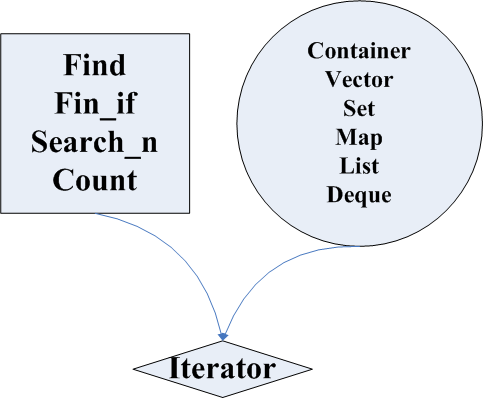
stl中容器有vector\set\list等等等等
算法有find\count等
两者独立 而他们之间的联系便是由iterator进行连接 将两者粘合起来
iterator类似智能指针
智能指针auto_ptr 除了拥有平常指针概念的功能 还具有引用计数功能
通过对该指针指向的元素的引用计数 自动释放元素内存资源 而不必手动调用delete
(auto_ptr 在c++11之后已经被智能指针shared_ptr unique_ptr取代)
示例代码如下
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template<class T>
class auto_ptr{
public:
explicit auto_ptr(T* p = 0):pointer(p){}
template<typename U>
auto_ptr(auto_ptr<U>& rhs):pointer(rhs.release()){}
~auto_ptr(){ cout << "enter delete status\n";delete pointer;} template<class U>
auto_ptr<T>& operator=(auto_ptr<U>& rhs){
if(this != &rhs) reset(rhs.release());
return *this;
}
T& operator*()const{return *pointer;}
T* operator->()const{return pointer;}
T* get()const{return pointer;} private:
T* pointer;
}; int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
auto_ptr<string> ps(new string("test"));
cout << *ps << endl;
cout << ps->size() << endl;
return 0;
}
要使用iterator这个智能指针 就需要识别指向的元素的相关信息,比如类别、引用等
代码使用了trait技巧将元素信息提取出来
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo> using namespace std; struct INT{
typedef int value_type;
typedef int difference_type;
typedef int* pointer;
typedef int& reference;
}; struct FLOAT{
typedef float value_type;
typedef float difference_type;
typedef float* pointer;
typedef float& reference;
}; template<class I>
struct Iterator_Traits{
//typedef typename I::iterator_category iterator_category;
typedef typename I::value_type value_type;
typedef typename I::difference_type difference_type;
typedef typename I::pointer pointer;
typedef typename I::reference reference;
}; int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
std::cout << typeid(Iterator_Traits<INT>::reference).name() << std::endl;
std::cout << typeid(Iterator_Traits<FLOAT>::reference).name() << std::endl; return 0;
}
至此 除了
//typedef typename I::iterator_category iterator_category;
还没解决 其他都解决完毕
iterator_category是什么东西呢?
iterator迭代器也是有类型区分的

那么在实际代码中是如何进行识别呢?
在代码执行时才识别区分 效率太低

#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo> using namespace std; //申请五个作为迭代器iterator类别的结构
struct input_iterator_tag_{};
struct output_iterator_tag_{};
struct forward_iterator_tag_:public input_iterator_tag_{};
struct bidirectional_iterator_tag_:public forward_iterator_tag_{};
struct random_access_iterator_tag_:public bidirectional_iterator_tag_{}; struct INT{
typedef input_iterator_tag_ iterator_category;
typedef int value_type;
typedef int difference_type;
typedef int* pointer;
typedef int& reference;
}; struct FLOAT{
typedef output_iterator_tag_ iterator_category;
typedef float value_type;
typedef float difference_type;
typedef float* pointer;
typedef float& reference;
}; template<class I>
struct MyIterator_Traits{
typedef typename I::iterator_category iterator_category;
typedef typename I::value_type value_type;
typedef typename I::difference_type difference_type;
typedef typename I::pointer pointer;
typedef typename I::reference reference;
};
template<typename T,typename Distance>
void test(T t,Distance n){
typename MyIterator_Traits<T>::iterator_category SELECT_TYPE;
test_(t,n,SELECT_TYPE);
} template<typename InputIterator,typename Distance>
void test_(InputIterator i,Distance j,input_iterator_tag_){
cout << "input_iterator_tag_" << endl;
} template<typename InputIterator,typename Distance>
void test_(InputIterator i,Distance j,output_iterator_tag_){
cout << "output_iterator_tag_" << endl;
} int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
INT i;
FLOAT f;
char c;
test(i,c);
test(f,c); return 0;
}
我们对不同的迭代器 指定不同的tag 这样就会进入到不同的函数中去了
c++ stl源码剖析学习笔记(二)iterator的更多相关文章
- c++ stl源码剖析学习笔记(一)uninitialized_copy()函数
template <class InputIterator, class ForwardIterator>inline ForwardIterator uninitialized_copy ...
- c++ stl源码剖析学习笔记(三)容器 vector
stl中容器有很多种 最简单的应该算是vector 一个空间连续的数组 他的构造函数有多个 以其中 template<typename T> vector(size_type n,cons ...
- STL源码剖析 学习笔记 MiniSTL
https://github.com/joeyleeeeeee97 目录: 第二章 空间适配器 第三章 迭代器 第四章 序列式容器(vector,list,deque,stack,heap,prior ...
- STL源码剖析-学习笔记
1.模板是一个公式或是蓝图,本身不是类或是函数,需进行实例化的过程.这个过程是在编译期完成的,编译器根据传递的实参,推断出形参的类型,从而实例化相应的函数 2. 后续补充-.
- STL源码剖析读书笔记之vector
STL源码剖析读书笔记之vector 1.vector概述 vector是一种序列式容器,我的理解是vector就像数组.但是数组有一个很大的问题就是当我们分配 一个一定大小的数组的时候,起初也许我们 ...
- 重温《STL源码剖析》笔记 第三章
源码之前,了无秘密. --侯杰 第三章:迭代器概念与traits编程技法 迭代器是一种smart pointer auto_Ptr 是一个用来包装原生指针(native pointer)的对象,声明狼 ...
- STL源码剖析读书笔记--第四章--序列式容器
1.什么是序列式容器?什么是关联式容器? 书上给出的解释是,序列式容器中的元素是可序的(可理解为可以按序索引,不管这个索引是像数组一样的随机索引,还是像链表一样的顺序索引),但是元素值在索引顺序的方向 ...
- 重温《STL源码剖析》笔记 第五章
源码之前,了无秘密 ——侯杰 序列式容器 关联式容器 array(build in) RB-tree vector set heap map priority-queue multiset li ...
- 重温《STL源码剖析》笔记 第六、七、八章 next_permutation (字典序)
源码之前,了无秘密 ——侯杰 第六章算法 next_permutation 比如:01342 -> 01423 -> 01432 方法:从尾端开始往前寻找两个相邻的元素,令第一个元素为* ...
随机推荐
- Can't parse message of type "gazebo.msgs.Packet" because it is missing required fields: stamp, type
在gazebo的仿真环境中,采用强化学习HER算法训练baxter执行reach.slide和pick and place任务. 运行HER算法,此时尚未启动gazebo仿真环境,出现如下报错: [l ...
- Tomcat性能调优后, 启动出现警告问题 [did not find a matching property.]
http://blog.csdn.net/dracotianlong/article/details/8963594 Tomcat性能调优后, 启动出现警告问题 [did not find a mat ...
- [转]Oracle left join \ right join
select 1 from a,b where a.id=b.id(+) 等同于 a left join b on a.id=b.id select 1 from a,b where a.id(+)= ...
- Python循环语句之break与continue的用法
摘自原文章: http://www.jb51.net/article/73383.htm Python break 语句Python break语句,就像在C语言中,打破了最小封闭for或while循 ...
- Java中常用类(包装类扩展知识)
Java常用类有哪些? 八大基本数据类型的包装类 包装类均位于java.lang包中,包装类和基本数据类型的对应关系如下表: 基本数据类型 包装类 byte Byte boolean Boolean ...
- [UE4]Spin Box,数字输入,可拖动
一.Spin Box在Input组下 二.Spin Box的文字样式可以在Spin Box.Display中修改 三.Spin Box事件 1.On Value Changed:值改变时触发 2.On ...
- atop 分析小记
atop分析小记 atop这个工具相当NB 项目中需要用到它的磁盘使用率统计值,为了一探究竟,挖了下它的代码 atopsar atopsar实际就是atop的一个链接指向. 从atop.c的main源 ...
- tp5 (layui )excel导入
1.composer安装PHPExcel 下载安装composer 其次 cmd切换到项目根目录 运行命令:composer require phpoffice/phpexcel 注意: 1.运行可能 ...
- 一入爬虫深似海,从此游戏是路人!总结我的python爬虫学习笔记!
前言 还记得是大学2年级的时候,偶然之间看到了学长在学习python:我就坐在旁边看他敲着代码,感觉很好奇.感觉很酷,从那之后,我就想和学长一样的厉害,就想让学长教我,请他吃了一周的饭,他答应了.从此 ...
- python3:实现字符串的全排列(有重复字符)
抛出问题 求任意一个字符串的全排列组合,例如a='123',输出 123,132,213,231,312,321. 解决方案 #字符串任意两个位置字符交换 def str_replace(str, x ...
