Python基础之pytest参数化
上篇博文介绍过,pytest是目前比较成熟功能齐全的测试框架,使用率肯定也不断攀升。在实际
工作中,许多测试用例都是类似的重复,一个个写最后代码会显得很冗余。这里,我们来了解一下
@pytest.mark.parametrize装饰器,可以很好的解决上述问题。
源代码分析
def parametrize(self,argnames, argvalues, indirect=False, ids=None, scope=None):
""" Add new invocations to the underlying test function using the list
of argvalues for the given argnames. Parametrization is performed
during the collection phase. If you need to setup expensive resources
see about setting indirect to do it rather at test setup time. # 使用给定argnames的argValue列表向基础测试函数添加新的调用,在收集阶段执行参数化。 :arg argnames: a comma-separated string denoting one or more argument
names, or a list/tuple of argument strings. # 参数名:使用逗号分隔的字符串,列表或元祖,表示一个或多个参数名 :arg argvalues: The list of argvalues determines how often a
test is invoked with different argument values. If only one
argname was specified argvalues is a list of values. If N
argnames were specified, argvalues must be a list of N-tuples,
where each tuple-element specifies a value for its respective
argname. # 参数值:只有一个argnames,argvalues则是值列表。有N个argnames时,每个元祖对应一组argnames,所有元祖组合成一个列表 :arg indirect: The list of argnames or boolean. A list of arguments'
names (self,subset of argnames). If True the list contains all names from
the argnames. Each argvalue corresponding to an argname in this list will
be passed as request.param to its respective argname fixture
function so that it can perform more expensive setups during the
setup phase of a test rather than at collection time.
:arg ids: list of string ids, or a callable.
If strings, each is corresponding to the argvalues so that they are
part of the test id. If None is given as id of specific test, the
automatically generated id for that argument will be used.
If callable, it should take one argument (self,a single argvalue) and return
a string or return None. If None, the automatically generated id for that
argument will be used.
If no ids are provided they will be generated automatically from
the argvalues. # ids:字符串列表,可以理解成标题,与用例个数保持一致 :arg scope: if specified it denotes the scope of the parameters.
The scope is used for grouping tests by parameter instances.
It will also override any fixture-function defined scope, allowing
to set a dynamic scope using test context or configuration.
# 如果指定,则表示参数的范围。作用域用于按参数实例对测试进行分组。
它还将覆盖任何fixture函数定义的范围,允许使用测试上下文或配置设置动态范围。
"""
argnames
释义:参数名称
格式:字符串"arg1,arg2,arg3"
aegvalues
释义:参数值列表
格式:必须是列表,如[val1,val2,val3]
单个参数,里面是值的列表,如@pytest.mark.parametrize("name",["Jack","Locus","Bill"])
多个参数,需要用元祖来存放值,一个元祖对应一组参数的值,如@pytest.mark.parametrize("user,age",[("user1",15),("user2",24),("user3",25)])
ids
释义:可以理解为用例的id
格式:字符串列表,如["case1","case2","case3"]
indirect
释义:当indirect=True时,若传入的argnames是fixture函数名,此时fixture函数名将成为一个可执行的函数,
argvalues作为fixture的参数,执行fixture函数,最终结果再存入 request.param;当indirect=False时,fixture
函数只作为一个参数名给测试收集阶段调用。
备注:这里可以将the setup phase(测试设置阶段)理解为配置 conftest.py 阶段,将the collection phase(
测试收集阶段)理解为用例执行阶段。
装饰测试类
import pytest data = [
(2,2,4),
(3,4,12)
] def add(a,b):
return a * b @pytest.mark.parametrize('a,b,expect',data)
class TestParametrize(object):
def test_parametrize_1(self,a,b,expect):
print('\n测试函数1测试数据为\n{}-{}'.format(a,b))
assert add(a,b) == expect def test_parametrize_2(self,a,b,expect):
print('\n测试函数2测试数据为\n{}-{}'.format(a,b))
assert add(a,b) == expect if __name__ == "__main__":
pytest.main(["-s","test_07.py"])
============================= test session starts =============================
platform win32 -- Python 3.8.0, pytest-6.2.5, py-1.11.0, pluggy-1.0.0
rootdir: D:\AutoCode
plugins: html-3.1.1, metadata-1.11.0
collecting ... collected 4 items test_07.py::TestParametrize::test_parametrize_1[2-2-4]
测试函数1测试数据为
2-2
PASSED
test_07.py::TestParametrize::test_parametrize_1[3-4-12]
测试函数1测试数据为
3-4
PASSED
test_07.py::TestParametrize::test_parametrize_2[2-2-4]
测试函数2测试数据为
2-2
PASSED
test_07.py::TestParametrize::test_parametrize_2[3-4-12]
测试函数2测试数据为
3-4
PASSED ============================== 4 passed in 0.12s ============================== Process finished with exit code 0
由以上代码可以看到,当装饰器装饰测试类时,定义的数据集合会被传递给类的所有方法。
装饰测试函数
单个数据
import pytest
data = ["Rose","white"]
@pytest.mark.parametrize("name",data)
def test_parametrize(name):
print('\n列表中的名字为\n{}'.format(name))
if __name__ == "__main__":
pytest.main(["-s","test_07.py"])
============================= test session starts =============================
platform win32 -- Python 3.8.0, pytest-6.2.5, py-1.11.0, pluggy-1.0.0
rootdir: D:\AutoCode
plugins: html-3.1.1, metadata-1.11.0
collected 2 items test_07.py
列表中的名字为
Rose
.
列表中的名字为
white
. ============================== 2 passed in 0.09s ============================== Process finished with exit code 0
当测试用例只需要一个参数时,我们存放数据的列表无序嵌套序列,@pytest.mark.parametrize("name", data)
装饰器的第一个参数也只需要一个变量接收列表中的每个元素,第二个参数传递存储数据的列表,那么测试用
例需要使用同名的字符串接收测试数据(实例中的name)且列表有多少个元素就会生成并执行多少个测试用例。
一组数据
import pytest data = [
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 9]
] # 列表嵌套列表
# data_tuple = [
# (1, 2, 3),
# (4, 5, 9)
# ] # 列表嵌套元组 @pytest.mark.parametrize('a, b, expect', data)
def test_parametrize_1(a, b, expect): # 一个参数接收一个数据
print('\n测试数据为\n{},{},{}'.format(a, b, expect))
actual = a + b
assert actual == expect @pytest.mark.parametrize('value', data)
def test_parametrize_2(value): # 一个参数接收一组数据
print('\n测试数据为\n{}'.format(value))
actual = value[0] + value[1]
assert actual == value[2] if __name__ == "__main__":
pytest.main(["-s","test_07.py"])
============================= test session starts =============================
platform win32 -- Python 3.8.0, pytest-6.2.5, py-1.11.0, pluggy-1.0.0
rootdir: D:\AutoCode
plugins: html-3.1.1, metadata-1.11.0
collected 4 items test_07.py
测试数据为
1,2,3
.
测试数据为
4,5,9
.
测试数据为
[1, 2, 3]
.
测试数据为
[4, 5, 9]
. ============================== 4 passed in 0.09s ============================== Process finished with exit code 0
当测试用例需要多个数据时,我们可以使用嵌套序列(嵌套元组&嵌套列表)的列表来存放测试数据。
装饰器@pytest.mark.parametrize()可以使用单个变量接收数据,也可以使用多个变量接收,同样,测
试用例函数也需要与其保持一致。
当使用单个变量接收时,测试数据传递到测试函数内部时为列表中的每一个元素或者小列表,需
要使用索引的方式取得每个数据。
当使用多个变量接收数据时,那么每个变量分别接收小列表或元组中的每个元素列表嵌套多少个多
组小列表或元组,测生成多少条测试用例。
组合数据
import pytest data_1 = [1,2,3]
data_2 = ['a','b'] @pytest.mark.parametrize('a',data_1)
@pytest.mark.parametrize('b',data_2)
def test_parametrize_1(a,b):
print(f'笛卡尔积测试结果为:{a},{b}') if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main(["-vs","test_06.py"])
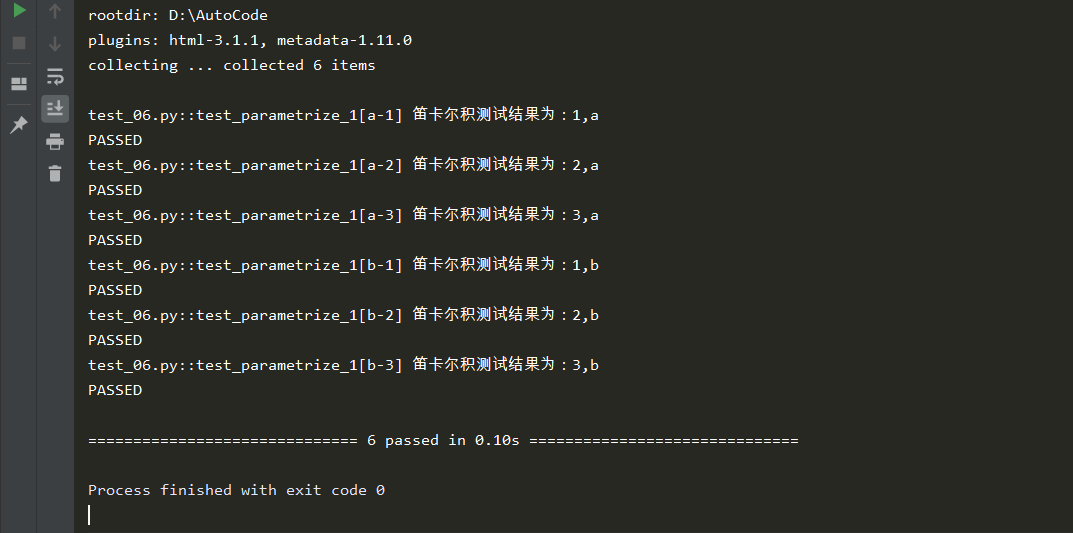
通过测试结果,我们不难分析,一个测试函数还可以同时被多个参数化装饰器装饰,那么多个
装饰器中的数据会进行交叉组合的方式传递给测试函数,进而生成n * n个测试用例。
标记用例
import pytest
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_input,expected",[
("3+5",8),
("2+4",6),
pytest.param("6 * 9",42,marks=pytest.mark.xfail),
pytest.param("6 * 6",42,marks=pytest.mark.skip)
])
def test_mark(test_input,expected):
assert eval(test_input) == expected
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main(["-vs","test_06.py"])
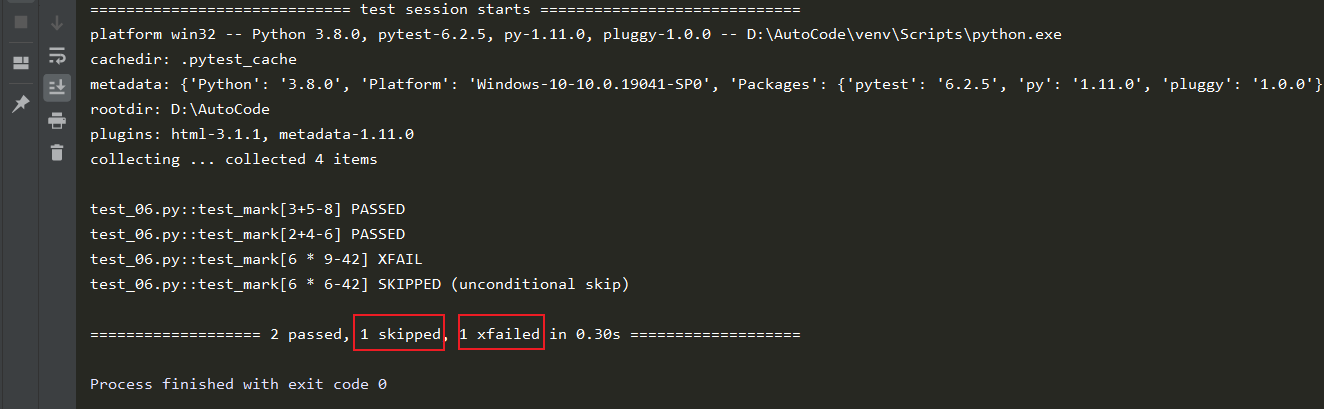
输出结果显示收集到4个用例,两个通过,一个被跳过,一个标记失败,当我们不想执行某组测试
数据时,我们可以标记skip或skipif;当我们预期某组数据会执行失败时,我们可以标记为xfail等。
嵌套字典
import pytest data = (
{
'user': "name1",
'pwd': 123
},
{
'user': "name2",
'pwd': 456
}
) @pytest.mark.parametrize('dic',data)
def test_parametrize(dic):
print('\n测试数据为\n{}'.format(dic)) if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main(["-vs","test_06.py"])

增加测试结果可读性
参数化装饰器有一个额外的参数ids,可以标识每一个测试用例,自定义测试数据结果的显示,
为了增加可读性,我们可以标记每一个测试用例使用的测试数据是什么,适当的增加一些说明。
在使用前你需要知道,ids参数应该是一个字符串列表,必须和数据对象列表的长度保持一致。
import pytest data_1 = [
(1, 2, 3),
(4, 5, 9)
] ids = ["a:{} + b:{} = expect:{}".format(a, b, expect) for a, b, expect in data_1] def add(a, b):
return a + b @pytest.mark.parametrize('a, b, expect', data_1, ids=ids)
class TestParametrize(object): def test_parametrize_1(self, a, b, expect):
print('\n测试函数1测试数据为\n{}-{}'.format(a, b))
assert add(a, b) == expect def test_parametrize_2(self, a, b, expect):
print('\n测试函数2数据为\n{}-{}'.format(a, b))
assert add(a, b) == expect if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main(["-v","test_06.py"])
不加ids参数的返回结果
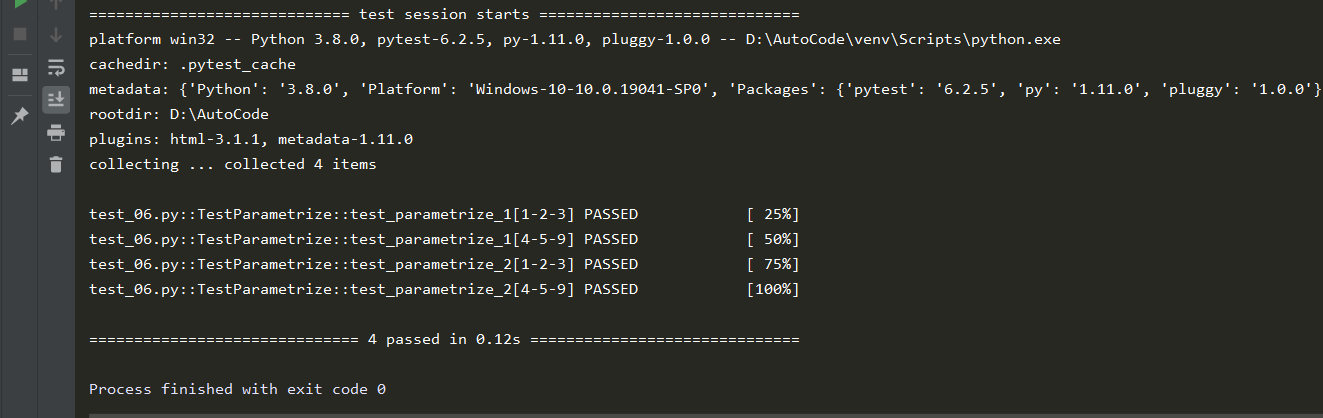
加ids参数的返回结果

我们可以看到带ids参数的返回结果中的用例都被一个列表明确的标记了,而且通过这种标记
可以更加直观的看出来,每个测试用例使用的数据名称及测试内容。
Python基础之pytest参数化的更多相关文章
- Python测试框架pytest入门基础
Pytest简介 Pytest is a mature full-featured Python testing tool that helps you write better programs.T ...
- Python基础-week05
本节大纲:Author:http://www.cnblogs.com/Jame-mei 模块介绍 time & datetime模块 random os sys shutil json &am ...
- Python基础(12)--模块
本文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/archimedes/p/python-modules.html,转载请注明源地址. 模块简介 如果你退出 Python 解释器重新进入,以前创 ...
- Python 中如何实现参数化测试?
Python 中如何实现参数化测试? 之前,我曾转过一个单元测试框架系列的文章,里面介绍了 unittest.nose/nose2 与 pytest 这三个最受人欢迎的 Python 测试框架. 本文 ...
- python基础全部知识点整理,超级全(20万字+)
目录 Python编程语言简介 https://www.cnblogs.com/hany-postq473111315/p/12256134.html Python环境搭建及中文编码 https:// ...
- pytest「conftest、pytest参数化、重运行、出测试报告」
文章总览图 一.conftest问题整理: 1.这个conftest.py分路径吗?如果在TestCases下建这个包可以直接用吗? TestCases这里有ModeA和ModeB,想在ModeA或M ...
- python测试框架-pytest
一.pytest 介绍.运行.参数化和数据驱动.Fixture pytest安装与介绍 官网 : pip install -U pytest 查看版本号:pytest --version 为何选择py ...
- python之最强王者(2)——python基础语法
背景介绍:由于本人一直做java开发,也是从txt开始写hello,world,使用javac命令编译,一直到使用myeclipse,其中的道理和辛酸都懂(请容许我擦干眼角的泪水),所以对于pytho ...
- Python开发【第二篇】:Python基础知识
Python基础知识 一.初识基本数据类型 类型: int(整型) 在32位机器上,整数的位数为32位,取值范围为-2**31-2**31-1,即-2147483648-2147483647 在64位 ...
随机推荐
- [源码解析] PyTorch 分布式(15) --- 使用分布式 RPC 框架实现参数服务器
[源码解析] PyTorch 分布式(15) --- 使用分布式 RPC 框架实现参数服务器 目录 [源码解析] PyTorch 分布式(15) --- 使用分布式 RPC 框架实现参数服务器 0x0 ...
- SQLserver 2014自定义备份数据库
一.管理-维护计划-维护计划向导-下一步 二.点击更改设置任务执行时间-确定-下一步 三.选择备份数据库完整-下一步 四.选择需要备份的数据库-然后确定 五.点目标自定义备份文件存储目录-下一步 六. ...
- 虚拟机快照和linux基础命令
虚拟机快照 磁盘"快照"是虚拟机磁盘文件(VMDK)在某个点及时的副本.可以通过使用恢复到快照来保持磁盘文件和系统存储. 1.拍摄快照 拍摄快照前先关机,然后右键点击虚拟机=> ...
- [Java Web 王者归来]读书笔记3
第四章 JSP JSP基本语法 1 JSP中嵌入Java 代码 <% Java code %> 2 JSP中输出 <%= num %> 3 JSP 中的注释 <%-- - ...
- Linux目录基础
一.解析映射文件 本地的DNS Linux: /etc/hosts Windows:C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts 二.磁盘挂载文件 /etc/fstab ...
- 电压-电流转换(一):4-20mA电流环
在仪表电路中,直流信号通常用作物理测量值的模拟表示,例如温度.压力.流量.重量和运动.最常见的是,直流电流信号优先于直流电压信号使用,因为在从电源(测量设备)到负载(指示器.记录仪或控制器)的整个串联 ...
- 如何在Uni-app中通过腾讯IM SDK实现社交应用和直播互动等功能
Uni-app想开发社交应用.IM.店铺客服.嵌入式社交模块.在线直播互动,这些功能Uni-app官方也没提供SDK,怎么办呢?找IM老大腾讯云啊,今天我们就在Uni-app中把腾讯云即时通讯TXIM ...
- echarts map 地图在react项目中的使用
需求 展示海南省地图,点击市高亮展示,并在右侧展示对应市的相关数据. 准备工作 Echarts 海南地图json 效果图 代码 index.tsx import React, { useRef, us ...
- JAVA判断字符串中某个字符存在的个数
/** * 判断字符串中某个字符存在的个数 * @param str1 完整字符串 * @param str2 要统计匹配个数的字符 * @return */ public static int co ...
- JAVAWEB导出word文档,遍历表格数据,导出图片
这是写的另一个导出word方法:https://www.cnblogs.com/pxblog/p/12790904.html 本次使用的是easypoi框架 官方教程:https://opensour ...
