XGBoost特征选择
1. 特征选择的思维导图
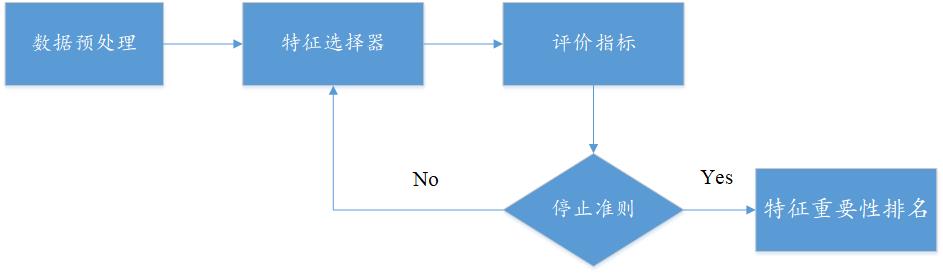
2. XGBoost特征选择算法
(1) XGBoost算法背景
2016年,陈天奇在论文《 XGBoost:A Scalable Tree Boosting System》中正式提出该算法。XGBoost的基本思想和GBDT相同,但是做了一些优化,比如二阶导数使损失函数更精准;正则项避免树过拟合;Block存储可以并行计算等。XGBoost具有高效、灵活和轻便的特点,在数据挖掘、推荐系统等领域得到广泛的应用。
(2) 算法原理

(3) 算法实现--python
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn import metrics
import xgboost as xgb
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
import pandas as pd, numpy as np
import matplotlib as mpl # mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['FangSong']
# mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False fpath = r".\processData\filter.csv"
Dataset = pd.read_csv(fpath) x = Dataset.loc[:, "nAcid":"Zagreb"]
y1 = Dataset.loc[:, "IC50_nM"]
y2 = Dataset.loc[:, "pIC50"] names = x.columns
names = list(names)
key = list(range(0, len(names)))
names_dict = dict(zip(key, names))
names_dicts = pd.DataFrame([names_dict]) x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y2, test_size=0.33, random_state=7)
"""
max_depth:树的最大深度
"""
model = xgb.XGBRegressor(max_depth=6, learning_rate=0.12, n_estimators=90, min_child_weight=6, objective="reg:gamma")
model.fit(x_train, y_train) feature_important = model.feature_importances_
rank_idx = np.argsort(feature_important)[::-1]
rank_idx30 = rank_idx[:30] rank_names30 = names_dicts.loc[:, rank_idx30]
label = rank_names30.values[0, :]
path1 = r"Xgboost排名前30的特征.csv"
pd.DataFrame(label).to_csv(path1, index=False) x_score = np.sort(feature_important)[::-1]
path = r"Xgboost排名前30的得分.csv"
pd.DataFrame(x_score[:30]).to_csv(path, index=False)
# xgboost网格搜索调参
gsCv = GridSearchCV(model,
{'max_depth':list(range(3, 10, 1)),
'learning_rate':[0.03, 0.04, 0.05, 0.06, 0.07, 0.08, 0.09, 0.1, 0.12, 0.13, 0.14, 0.15, 0.16, 0.17, 0.18, 0.19, 0.2],
'min_child_weight':list(range(2, 8, 2)),
'n_estimators':list(range(10, 101, 10))}) gsCv.fit(x_train, y_train)
print(gsCv.best_params_)
cv_results = pd.DataFrame(gsCv.cv_results_)
path = r"paramRank.csv"
cv_results.to_csv(path, index=False) # 可视化
plt.figure()
plt.bar(range(len(model.feature_importances_)), model.feature_importances_)
plt.xlabel("Feature")
plt.ylabel("Feature Score")
plt.title("Feature Importance")
plt.savefig("Xgboost") # 可视化
plt.figure()
plt.barh(label[::-1], x_score[:30][::-1], 0.6, align='center')
plt.grid(ls=':', color='gray', alpha=0.4)
plt.title("Xgboost Feature Importance")
# 添加数据标签
# for a, b in enumerate(rf_score[:30][::-1]):
# plt.text(b+0.1, a-0.6/2, '%s' % b, ha='center', va='bottom') plt.savefig("前30名特征")
plt.show()
注意:该算法没有数据是不能运行的,需要做适当的修改,后面使用网格调参,找到最优参数。
(4) 算法可视化


XGBoost特征选择的更多相关文章
- xgboost 特征选择,筛选特征的正要性
import pandas as pd import xgboost as xgb import operator from matplotlib import pylab as plt def ce ...
- 从信用卡欺诈模型看不平衡数据分类(1)数据层面:使用过采样是主流,过采样通常使用smote,或者少数使用数据复制。过采样后模型选择RF、xgboost、神经网络能够取得非常不错的效果。(2)模型层面:使用模型集成,样本不做处理,将各个模型进行特征选择、参数调优后进行集成,通常也能够取得不错的结果。(3)其他方法:偶尔可以使用异常检测技术,IF为主
总结:不平衡数据的分类,(1)数据层面:使用过采样是主流,过采样通常使用smote,或者少数使用数据复制.过采样后模型选择RF.xgboost.神经网络能够取得非常不错的效果.(2)模型层面:使用模型 ...
- XGBoost、LightGBM的详细对比介绍
sklearn集成方法 集成方法的目的是结合一些基于某些算法训练得到的基学习器来改进其泛化能力和鲁棒性(相对单个的基学习器而言)主流的两种做法分别是: bagging 基本思想 独立的训练一些基学习器 ...
- Stacking:Catboost、Xgboost、LightGBM、Adaboost、RF etc
python风控评分卡建模和风控常识(博客主亲自录制视频教程) https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005214003&am ...
- Xgboost总结
从决策树.随机森林.GBDT最终到XGBoost,每个热门算法都不是孤立存在的,而是基于一系列算法的改进与优化.决策树算法简单易懂可解释性强,但是过拟合风险很大,应用场景有限:随机森林采用Baggin ...
- Python机器学习笔记:XgBoost算法
前言 1,Xgboost简介 Xgboost是Boosting算法的其中一种,Boosting算法的思想是将许多弱分类器集成在一起,形成一个强分类器.因为Xgboost是一种提升树模型,所以它是将许多 ...
- 机器学习-树模型理论(GDBT,xgboost,lightBoost,随机森林)
tree based ensemble algorithms 主要介绍以下几种ensemble的分类器(tree based algorithms) xgboost lightGBM: 基于决策树算法 ...
- 随机森林RF、XGBoost、GBDT和LightGBM的原理和区别
目录 1.基本知识点介绍 2.各个算法原理 2.1 随机森林 -- RandomForest 2.2 XGBoost算法 2.3 GBDT算法(Gradient Boosting Decision T ...
- RF/GBDT/XGBoost/LightGBM简单总结(完结)
这四种都是非常流行的集成学习(Ensemble Learning)方式,在本文简单总结一下它们的原理和使用方法. Random Forest(随机森林): 随机森林属于Bagging,也就是有放回抽样 ...
随机推荐
- python实现分水岭算法
目录: 问题:分水岭算法对图像分割很有作用,怎么把对象分割开来的?分水岭算法是比较完美的分割,跟前面的讲的轮廓不一样! (一)原理 (二)实现 (一)原理 opencv中的分水岭算法是基于距离变换的, ...
- [loj3523]分糖果
做法1 将问题离线,并在左端点和右端点打上差分,之后即可以看作求$f(C,[a_{1},a_{2},...,a_{n}])$,其表示以$C$为上限(0为下限),从0开始不断加上$a_{i}$(可以为负 ...
- [loj2473]秘密袭击
容易发现答案即$\sum_{S}\sum_{u=1}^{W}[u\le val(S)]=\sum_{u=1}^{W}\sum_{S}[u\le val(S)]$,那么可以枚举权值$u$,并将点权$va ...
- [源码解析] PyTorch 分布式(12) ----- DistributedDataParallel 之 前向传播
[源码解析] PyTorch 分布式(12) ----- DistributedDataParallel 之 前向传播 目录 [源码解析] PyTorch 分布式(12) ----- Distribu ...
- 开源一个简单的react-native 菜单栏抽屉组件,带缩放效果
效果如图所示,源码地址:https://github.com/pofabs/PoSideMenu
- AI剪辑和自定义UI,打造更智能的剪辑体验
为满足开发者构建高效的应用内视频编辑能力,7月的HMS Core 6.0 推出了视频编辑服务(Video Editor Kit),一站式的视频处理能力获得了积极反响.同时,我们也关注到开发者需要集成丰 ...
- 洛谷 P4484 - [BJWC2018]最长上升子序列(状压 dp+打表)
洛谷题面传送门 首先看到 LIS 我们可以想到它的 \(\infty\) 种求法(bushi),但是对于此题而言,既然题目出这样一个数据范围,硬要暴搜过去也不太现实,因此我们需想到用某种奇奇怪怪的方式 ...
- Codeforces 1332G - No Monotone Triples(数据结构综合)
Codeforces 题目传送门 & 洛谷题目传送门 首先打表即可发现对于任意长度 \(\ge 5\) 的序列总存在一个 Monotone triple,证明不会实在不行直接 \(5^5\) ...
- Excel—在Excel中利用宏定义实现MD5对字符串(如:手机号)或者文件加密
下载宏文件[md5宏] 加载宏 试验md5加密 可能遇到的问题 解决办法 下载宏文件[md5宏] 下载附件,解压,得md5宏.xla md5宏.zip 加载宏 依次打开[文件]-[选项]-[自定义功能 ...
- jmeter非GUI(cmd命令行)模式的压测和输出测试报告
1.非GUI模式的压测,和GUI有啥不同? 2.非GUI模式怎么搞? 大家打开jmeter的时候,都会看到这个界面: 注意看这句话: Don't use GUI mode for load testi ...
