linux C 线程池(物不可穷也~)
Linux 多线程编程之 线程池 的原理和一个简单的C实现,提高对多线程编
程的认知,同步处理等操作,以及如何在实际项目中高效的利用多线程开
发。
1. 线程池介绍
为什么需要线程池???
目前的大多数网络服务器,包括Web服务器、Email服务器以及数据库服务
器等都具有一个共同点,就是单位时间内必须处理数目巨大的连接请求,
但处理时间却相对较短。
传统多线程方案中我们采用的服务器模型则是一旦接受到请求之后,即创
建一个新的线程,由该线程执行任务。任务执行完毕后,线程退出,这就
是是“即时创建,即时销毁”的策略。尽管与创建进程相比,创建线程的时
间已经大大的缩短,但是如果提交给线程的任务是执行时间较短,而且执
行次数极其频繁,那么服务器将处于不停的创建线程,销毁线程的状态,
这笔开销将是不可忽略的。
线程池为线程生命周期开销问题和资源不足问题提供了解决方案。通过对
多个任务重用线程,线程创建的开销被分摊到了多个任务上。其好处是,
因为在请求到达时线程已经存在,所以无意中也消除了线程创建所带来的
延迟。这样,就可以立即为请求服务,使应用程序响应更快。而且,通过
适当地调整线程池中的线程数目,也就是当请求的数目超过某个阈值时,
就强制其它任何新到的请求一直等待,直到获得一个线程来处理为止,从
而可以防止资源不足。
2. 线程池结构
2.1 线程池任务结点结构
线程池任务结点用来保存用户投递过来的的任务,并放入线程池中的线程来执行,任务结构如下:
// 线程池任务结点
struct worker_t {
void * (* process)(void * arg); /*回调函数*/
int paratype; /*函数类型(预留)*/
void * arg; /*回调函数参数*/
struct worker_t * next; /*链接下一个任务节点*/
};
2.2 线程池控制器
线程池控制器用来对线程池进行控制管理,描述当前线程池的最基本信息,包括任务的投递,线
程池状态的更新与查询,线程池的销毁等,其结构如下:
/*线程控制器*/
struct CThread_pool_t {
pthread_mutex_t queue_lock; /*互斥锁*/
pthread_cond_t queue_ready; /*条件变量*/ worker_t * queue_head; /*任务节点链表 保存所有投递的任务*/
int shutdown; /*线程池销毁标志 1-销毁*/
pthread_t * threadid; /*线程ID*/ int max_thread_num; /*线程池可容纳最大线程数*/
int current_pthread_num; /*当前线程池存放的线程*/
int current_pthread_task_num; /*当前已经执行任务和已分配任务的线程数目和*/
int current_wait_queue_num; /*当前等待队列的的任务数目*/
int free_pthread_num; /*线程池允许最大的空闲线程数/*/ /**
* function: ThreadPoolAddWorkUnlimit
* description: 向线程池投递任务
* input param: pthis 线程池指针
* process 回调函数
* arg 回调函数参数
* return Valr: 0 成功
* -1 失败
*/
int (* AddWorkUnlimit)(void * pthis, void * (* process)(void * arg), void * arg); /**
* function: ThreadPoolAddWorkLimit
* description: 向线程池投递任务,无空闲线程则阻塞
* input param: pthis 线程池指针
* process 回调函数
* arg 回调函数参数
* return Val: 0 成功
* -1 失败
*/
int (* AddWorkLimit)(void * pthis, void * (* process)(void * arg), void * arg); /**
* function: ThreadPoolGetThreadMaxNum
* description: 获取线程池可容纳的最大线程数
* input param: pthis 线程池指针
*/
int (* GetThreadMaxNum)(void * pthis); /**
* function: ThreadPoolGetCurrentThreadNum
* description: 获取线程池存放的线程数
* input param: pthis 线程池指针
* return Val: 线程池存放的线程数
*/
int (* GetCurrentThreadNum)(void * pthis); /**
* function: ThreadPoolGetCurrentTaskThreadNum
* description: 获取当前正在执行任务和已经分配任务的线程数目和
* input param: pthis 线程池指针
* return Val: 当前正在执行任务和已经分配任务的线程数目和
*/
int (* GetCurrentTaskThreadNum)(void * pthis); /**
* function: ThreadPoolGetCurrentWaitTaskNum
* description: 获取线程池等待队列任务数
* input param: pthis 线程池指针
* return Val: 等待队列任务数
*/
int (* GetCurrentWaitTaskNum)(void * pthis); /**
* function: ThreadPoolDestroy
* description: 销毁线程池
* input param: pthis 线程池指针
* return Val: 0 成功
* -1 失败
*/
int (* Destroy)(void * pthis);
};
2.3 线程池运行结构

解释:
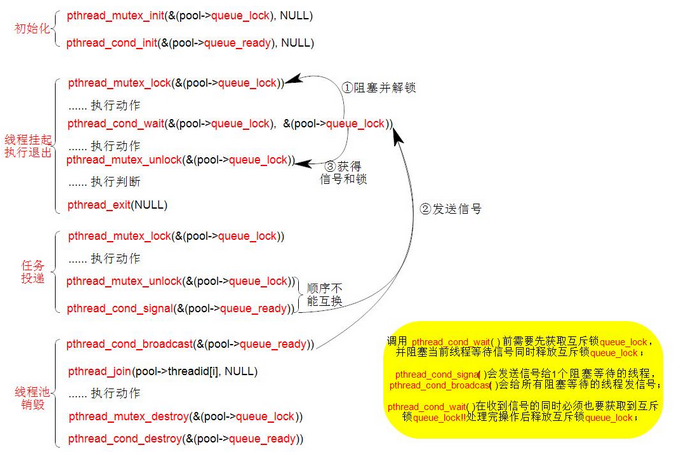
1) 图中的线程池中的"空闲"和"执行"分别表示空闲线程和执行线程,空闲线程指在正在等待任务的线程,
同样执行线程指正在执行任务的线程, 两者是相互转换的。当用户投递任务过来则用空闲线程来执行
该任务,且空闲线程状态转换为执行线程;当任务执行完后,执行线程状态转变为空闲线程。
2) 创建线程池时,正常情况会创建一定数量的线程, 所有线程初始化为空闲线程,线程阻塞等待用户
投递任务。
3) 用户投递的任务首先放入等待队列queue_head 链表中, 如果线程池中有空闲线程则放入空闲线程中
执行,否则根据条件选择继续等待空闲线程或者新建一个线程来执行,新建的线程将放入线程池中。
4) 执行的任务会从等待队列中脱离,并在任务执行完后释放任务结点worker_t
3. 线程池控制 / 部分函数解释
3.1 线程池创建
创建 max_num 个线程 ThreadPoolRoutine,即空闲线程
/**
* function: ThreadPoolConstruct
* description: 构建线程池
* input param: max_num 线程池可容纳的最大线程数
* free_num 线程池允许存在的最大空闲线程,超过则将线程释放回操作系统
* return Val: 线程池指针
*/
CThread_pool_t *
ThreadPoolConstruct(int max_num, int free_num)
{
int i = ; CThread_pool_t * pool = (CThread_pool_t *)malloc(sizeof(CThread_pool_t));
if(NULL == pool)
return NULL; memset(pool, , sizeof(CThread_pool_t)); /*初始化互斥锁*/
pthread_mutex_init(&(pool->queue_lock), NULL);
/*初始化条件变量*/
pthread_cond_init(&(pool->queue_ready), NULL); pool->queue_head = NULL;
pool->max_thread_num = max_num; // 线程池可容纳的最大线程数
pool->current_wait_queue_num = ;
pool->current_pthread_task_num = ;
pool->shutdown = ;
pool->current_pthread_num = ;
pool->free_pthread_num = free_num; // 线程池允许存在最大空闲线程
pool->threadid = NULL;
pool->threadid = (pthread_t *)malloc(max_num*sizeof(pthread_t));
/*该函数指针赋值*/
pool->AddWorkUnlimit = ThreadPoolAddWorkUnlimit;
pool->AddWorkLimit = ThreadPoolAddWorkLimit;
pool->Destroy = ThreadPoolDestroy;
pool->GetThreadMaxNum = ThreadPoolGetThreadMaxNum;
pool->GetCurrentThreadNum = ThreadPoolGetCurrentThreadNum;
pool->GetCurrentTaskThreadNum = ThreadPoolGetCurrentTaskThreadNum;
pool->GetCurrentWaitTaskNum = ThreadPoolGetCurrentWaitTaskNum; for(i=; i<max_num; i++) {
pool->current_pthread_num++; // 当前池中的线程数
/*创建线程*/
pthread_create(&(pool->threadid[i]), NULL, ThreadPoolRoutine, (void *)pool);
usleep();
} return pool;
}
3.2 投递任务
/**
* function: ThreadPoolAddWorkLimit
* description: 向线程池投递任务,无空闲线程则阻塞
* input param: pthis 线程池指针
* process 回调函数
* arg 回调函数参数
* return Val: 0 成功
* -1 失败
*/
int
ThreadPoolAddWorkLimit(void * pthis, void * (* process)(void * arg), void * arg)
{
// int FreeThreadNum = 0;
// int CurrentPthreadNum = 0; CThread_pool_t * pool = (CThread_pool_t *)pthis; /*为添加的任务队列节点分配内存*/
worker_t * newworker = (worker_t *)malloc(sizeof(worker_t));
if(NULL == newworker)
return -; newworker->process = process; // 回调函数,在线程ThreadPoolRoutine()中执行
newworker->arg = arg; // 回调函数参数
newworker->next = NULL; pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->queue_lock)); /*插入新任务队列节点*/
worker_t * member = pool->queue_head; // 指向任务队列链表整体
if(member != NULL) {
while(member->next != NULL) // 队列中有节点
member = member->next; // member指针往后移动 member->next = newworker; // 插入到队列链表尾部
} else
pool->queue_head = newworker; // 插入到队列链表头 assert(pool->queue_head != NULL);
pool->current_wait_queue_num++; // 等待队列加1 /*空闲的线程= 当前线程池存放的线程 - 当前已经执行任务和已分配任务的线程数目和*/
int FreeThreadNum = pool->current_pthread_num - pool->current_pthread_task_num;
/*如果没有空闲线程且池中当前线程数不超过可容纳最大线程*/
if(( == FreeThreadNum) && (pool->current_pthread_num < pool->max_thread_num)) { //-> 条件为真进行新线程创建
int CurrentPthreadNum = pool->current_pthread_num; /*新增线程*/
pool->threadid = (pthread_t *)realloc(pool->threadid,
(CurrentPthreadNum+) * sizeof(pthread_t)); pthread_create(&(pool->threadid[CurrentPthreadNum]),
NULL, ThreadPoolRoutine, (void *)pool);
/*当前线程池中线程总数加1*/
pool->current_pthread_num++; /*分配任务线程数加1*/
pool->current_pthread_task_num++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock)); /*发送信号给一个处与条件阻塞等待状态的线程*/
pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->queue_ready));
return ;
} pool->current_pthread_task_num++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock)); /*发送信号给一个处与条件阻塞等待状态的线程*/
pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->queue_ready));
// usleep(10); //看情况
return ;
}
投递任务时先创建一个任务结点保存回调函数和函数参数,并将任务结点放入等待队列中,在代码中
注释"//->条件为真创建新线程",realloc() 会在保存原始内存中的数据不变的基础上新增1个sizeof(pthread_t)
大小内存。之后更新current_pthread_num,和current_pthread_task_num;并发送信号
pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->queue_read)),给一个处于条件阻塞等待状态的线程,即线程ThreadPoolRoutin()
中的pthread_cond_wait(&(pool->queue_read), &(pool->queue_lock))阻塞等待接收信号,重点讲互
斥锁和添加变量:
pthread_mutex_t queue_lock; /**< 互斥锁*/
pthread_cond_t queue_ready; /**< 条件变量*/
这两个变量时线程池实现中很重要的点,这里简要介绍代码中会用到的相关函数功能;
3.3 执行线程
/**
* function: ThreadPoolRoutine
* description: 线程池中执行的线程
* input param: arg 线程池指针
*/
void *
ThreadPoolRoutine(void * arg)
{
CThread_pool_t * pool = (CThread_pool_t *)arg; while() {
/*上锁,pthread_cond_wait()调用会解锁*/
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->queue_lock)); /*队列没有等待任务*/
while((pool->current_wait_queue_num == ) && (!pool->shutdown)) {
/*条件锁阻塞等待条件信号*/
pthread_cond_wait(&(pool->queue_ready), &(pool->queue_lock));
} if(pool->shutdown) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock));
pthread_exit(NULL); // 释放线程
} assert(pool->current_wait_queue_num != );
assert(pool->queue_head != NULL); pool->current_wait_queue_num--; // 等待任务减1,准备执行任务
worker_t * worker = pool->queue_head; // 去等待队列任务节点头
pool->queue_head = worker->next; // 链表后移
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock)); (* (worker->process))(worker->arg); // 执行回调函数 pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->queue_lock));
pool->current_pthread_task_num--; // 函数执行结束
free(worker); // 释放任务结点
worker = NULL; if((pool->current_pthread_num - pool->current_pthread_task_num) > pool->free_pthread_num) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock));
break; // 当线程池中空闲线程超过 free_pthread_num 则将线程释放回操作系统
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock));
} pool->current_pthread_num--; // 当前线程数减1
pthread_exit(NULL); // 释放线程 return (void *)NULL;
}
这个就是用来执行任务的线程,在初始化创建线程时所有线程都全部阻塞在pthread_cond_wait()处
此时的线程就为空闲线程,也就是线程被挂起,当收到信号并取得互斥锁时, 表明任务投递过来
则获取等待队列里的任务结点并执行回调函数; 函数执行结束后回去判断当前等待队列是否还有任
务,有则接下去执行,否则重新阻塞回到空闲线程状态。
4. 完整代码实现
4.1 CThreadPool.h 文件
/**
* 线程池头文件
*
**/ #ifndef _CTHREADPOOL_H_
#define _CTHREADPOOL_H_ #include <pthread.h> /*线程池可容纳最大线程数*/
#define DEFAULT_MAX_THREAD_NUM 100 /*线程池允许最大的空闲线程,超过则将线程释放回操作系统*/
#define DEFAULT_FREE_THREAD_NUM 10 typedef struct worker_t worker_t;
typedef struct CThread_pool_t CThread_pool_t; /*线程池任务节点*/
struct worker_t {
void * (* process)(void * arg); /*回调函数*/
int paratype; /*函数类型(预留)*/
void * arg; /*回调函数参数*/
struct worker_t * next; /*链接下一个任务节点*/
}; /*线程控制器*/
struct CThread_pool_t {
pthread_mutex_t queue_lock; /*互斥锁*/
pthread_cond_t queue_ready; /*条件变量*/ worker_t * queue_head; /*任务节点链表 保存所有投递的任务*/
int shutdown; /*线程池销毁标志 1-销毁*/
pthread_t * threadid; /*线程ID*/ int max_thread_num; /*线程池可容纳最大线程数*/
int current_pthread_num; /*当前线程池存放的线程*/
int current_pthread_task_num; /*当前已经执行任务和已分配任务的线程数目和*/
int current_wait_queue_num; /*当前等待队列的的任务数目*/
int free_pthread_num; /*线程池允许最大的空闲线程数/*/ /**
* function: ThreadPoolAddWorkUnlimit
* description: 向线程池投递任务
* input param: pthis 线程池指针
* process 回调函数
* arg 回调函数参数
* return Valr: 0 成功
* -1 失败
*/
int (* AddWorkUnlimit)(void * pthis, void * (* process)(void * arg), void * arg); /**
* function: ThreadPoolAddWorkLimit
* description: 向线程池投递任务,无空闲线程则阻塞
* input param: pthis 线程池指针
* process 回调函数
* arg 回调函数参数
* return Val: 0 成功
* -1 失败
*/
int (* AddWorkLimit)(void * pthis, void * (* process)(void * arg), void * arg); /**
* function: ThreadPoolGetThreadMaxNum
* description: 获取线程池可容纳的最大线程数
* input param: pthis 线程池指针
*/
int (* GetThreadMaxNum)(void * pthis); /**
* function: ThreadPoolGetCurrentThreadNum
* description: 获取线程池存放的线程数
* input param: pthis 线程池指针
* return Val: 线程池存放的线程数
*/
int (* GetCurrentThreadNum)(void * pthis); /**
* function: ThreadPoolGetCurrentTaskThreadNum
* description: 获取当前正在执行任务和已经分配任务的线程数目和
* input param: pthis 线程池指针
* return Val: 当前正在执行任务和已经分配任务的线程数目和
*/
int (* GetCurrentTaskThreadNum)(void * pthis); /**
* function: ThreadPoolGetCurrentWaitTaskNum
* description: 获取线程池等待队列任务数
* input param: pthis 线程池指针
* return Val: 等待队列任务数
*/
int (* GetCurrentWaitTaskNum)(void * pthis); /**
* function: ThreadPoolDestroy
* description: 销毁线程池
* input param: pthis 线程池指针
* return Val: 0 成功
* -1 失败
*/
int (* Destroy)(void * pthis);
}; /**
* function: ThreadPoolConstruct
* description: 构建线程池
* input param: max_num 线程池可容纳的最大线程数
* free_num 线程池允许存在的最大空闲线程,超过则将线程释放回操作系统
* return Val: 线程池指针
*/
CThread_pool_t * ThreadPoolConstruct(int max_num, int free_num); /**
* function: ThreadPoolConstructDefault
* description: 创建线程池,以默认的方式初始化,未创建线程
*
* return Val: 线程池指针
*/
CThread_pool_t * ThreadPoolConstructDefault(void); #endif // _CTHREADPOOL_H_
4.2 CThreadPool.c 文件
/**
* 线程池实现
*
**/ #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <assert.h> #include "CThreadPool.h" void * ThreadPoolRoutine(void * arg); /**
* function: ThreadPoolAddWorkLimit
* description: 向线程池投递任务,无空闲线程则阻塞
* input param: pthis 线程池指针
* process 回调函数
* arg 回调函数参数
* return Val: 0 成功
* -1 失败
*/
int
ThreadPoolAddWorkLimit(void * pthis, void * (* process)(void * arg), void * arg)
{
// int FreeThreadNum = 0;
// int CurrentPthreadNum = 0; CThread_pool_t * pool = (CThread_pool_t *)pthis; /*为添加的任务队列节点分配内存*/
worker_t * newworker = (worker_t *)malloc(sizeof(worker_t));
if(NULL == newworker)
return -; newworker->process = process; // 回调函数,在线程ThreadPoolRoutine()中执行
newworker->arg = arg; // 回调函数参数
newworker->next = NULL; pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->queue_lock)); /*插入新任务队列节点*/
worker_t * member = pool->queue_head; // 指向任务队列链表整体
if(member != NULL) {
while(member->next != NULL) // 队列中有节点
member = member->next; // member指针往后移动 member->next = newworker; // 插入到队列链表尾部
} else
pool->queue_head = newworker; // 插入到队列链表头 assert(pool->queue_head != NULL);
pool->current_wait_queue_num++; // 等待队列加1 /*空闲的线程= 当前线程池存放的线程 - 当前已经执行任务和已分配任务的线程数目和*/
int FreeThreadNum = pool->current_pthread_num - pool->current_pthread_task_num;
/*如果没有空闲线程且池中当前线程数不超过可容纳最大线程*/
if(( == FreeThreadNum) && (pool->current_pthread_num < pool->max_thread_num)) {
int CurrentPthreadNum = pool->current_pthread_num; /*新增线程*/
pool->threadid = (pthread_t *)realloc(pool->threadid,
(CurrentPthreadNum+) * sizeof(pthread_t)); pthread_create(&(pool->threadid[CurrentPthreadNum]),
NULL, ThreadPoolRoutine, (void *)pool);
/*当前线程池中线程总数加1*/
pool->current_pthread_num++; /*分配任务线程数加1*/
pool->current_pthread_task_num++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock)); /*发送信号给一个处与条件阻塞等待状态的线程*/
pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->queue_ready));
return ;
} pool->current_pthread_task_num++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock)); /*发送信号给一个处与条件阻塞等待状态的线程*/
pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->queue_ready));
// usleep(10); //看情况
return ;
} /**
* function: ThreadPoolAddWorkUnlimit
* description: 向线程池投递任务
* input param: pthis 线程池指针
* process 回调函数
* arg 回调函数参数
* return Valr: 0 成功
* -1 失败
*/
int
ThreadPoolAddWorkUnlimit(void * pthis, void * (* process)(void * arg), void * arg)
{
// int FreeThreadNum = 0;
// int CurrentPthreadNum = 0; CThread_pool_t * pool = (CThread_pool_t *)pthis; /*给新任务队列节点分配内存*/
worker_t * newworker = (worker_t *)malloc(sizeof(worker_t));
if(NULL == newworker)
return -; newworker->process = process; // 回调函数
newworker->arg = arg; // 回调函数参数
newworker->next = NULL; pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->queue_lock)); /*新节点插入任务队列链表操作*/
worker_t * member = pool->queue_head;
if(member != NULL) {
while(member->next != NULL)
member = member->next; member->next = newworker; // 插入队列链表尾部
} else
pool->queue_head = newworker; // 插入到头(也就是第一个节点,之前链表没有节点) assert(pool->queue_head != NULL);
pool->current_wait_queue_num++; // 当前等待队列的的任务数目+1 int FreeThreadNum = pool->current_pthread_num - pool->current_pthread_task_num;
/*只判断是否没有空闲线程*/
if( == FreeThreadNum) {
int CurrentPthreadNum = pool->current_pthread_num;
pool->threadid = (pthread_t *)realloc(pool->threadid,
(CurrentPthreadNum+)*sizeof(pthread_t));
pthread_create(&(pool->threadid[CurrentPthreadNum]),NULL,
ThreadPoolRoutine, (void *)pool);
pool->current_pthread_num++;
if(pool->current_pthread_num > pool->max_thread_num)
pool->max_thread_num = pool->current_pthread_num; pool->current_pthread_task_num++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock));
pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->queue_ready));
return ;
} pool->current_pthread_task_num++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock));
pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->queue_ready));
// usleep(10);
return ;
} /**
* function: ThreadPoolGetThreadMaxNum
* description: 获取线程池可容纳的最大线程数
* input param: pthis 线程池指针
* return val: 线程池可容纳的最大线程数
*/
int
ThreadPoolGetThreadMaxNum(void * pthis)
{
int num = ;
CThread_pool_t * pool = (CThread_pool_t *)pthis; pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->queue_lock));
num = pool->max_thread_num;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock)); return num;
} /**
* function: ThreadPoolGetCurrentThreadNum
* description: 获取线程池存放的线程数
* input param: pthis 线程池指针
* return Val: 线程池存放的线程数
*/
int
ThreadPoolGetCurrentThreadNum(void * pthis)
{
int num = ;
CThread_pool_t * pool = (CThread_pool_t *)pthis; pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->queue_lock));
num = pool->current_pthread_num;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock)); return num;
} /**
* function: ThreadPoolGetCurrentTaskThreadNum
* description: 获取当前正在执行任务和已经分配任务的线程数目和
* input param: pthis 线程池指针
* return Val: 当前正在执行任务和已经分配任务的线程数目和
*/
int
ThreadPoolGetCurrentTaskThreadNum(void * pthis)
{
int num = ;
CThread_pool_t * pool = (CThread_pool_t *)pthis; pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->queue_lock));
num = pool->current_pthread_task_num;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock)); return num;
} /**
* function: ThreadPoolGetCurrentWaitTaskNum
* description: 获取线程池等待队列任务数
* input param: pthis 线程池指针
* return Val: 等待队列任务数
*/
int
ThreadPoolGetCurrentWaitTaskNum(void * pthis)
{
int num = ;
CThread_pool_t * pool = (CThread_pool_t *)pthis; pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->queue_lock));
num = pool->current_wait_queue_num;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock)); return num;
} /**
* function: ThreadPoolDestroy
* description: 销毁线程池
* input param: pthis 线程池指针
* return Val: 0 成功
* -1 失败
*/
int
ThreadPoolDestroy(void * pthis)
{
int i;
CThread_pool_t * pool = (CThread_pool_t *)pthis; if(pool->shutdown) // 已销毁
return -; pool->shutdown = ; // 销毁标志置位 /*唤醒所有pthread_cond_wait()等待线程*/
pthread_cond_broadcast(&(pool->queue_ready));
for(i=; i<pool->current_pthread_num; i++)
pthread_join(pool->threadid[i], NULL); // 等待所有线程执行结束 free(pool->threadid); // 释放 /*销毁任务队列链表*/
worker_t * head = NULL;
while(pool->queue_head != NULL) {
head = pool->queue_head;
pool->queue_head = pool->queue_head->next;
free(head);
} /*销毁锁*/
pthread_mutex_destroy(&(pool->queue_lock));
pthread_cond_destroy(&(pool->queue_ready)); free(pool);
pool = NULL; return ;
} /**
* function: ThreadPoolRoutine
* description: 线程池中运行的线程
* input param: arg 线程池指针
*/
void *
ThreadPoolRoutine(void * arg)
{
CThread_pool_t * pool = (CThread_pool_t *)arg; while() {
/*上锁,pthread_cond_wait()调用会解锁*/
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->queue_lock)); /*队列没有等待任务*/
while((pool->current_wait_queue_num == ) && (!pool->shutdown)) {
/*条件锁阻塞等待条件信号*/
pthread_cond_wait(&(pool->queue_ready), &(pool->queue_lock));
} if(pool->shutdown) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock));
pthread_exit(NULL); // 释放线程
} assert(pool->current_wait_queue_num != );
assert(pool->queue_head != NULL); pool->current_wait_queue_num--; // 等待任务减1,准备执行任务
worker_t * worker = pool->queue_head; // 去等待队列任务节点头
pool->queue_head = worker->next; // 链表后移
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock)); (* (worker->process))(worker->arg); // 执行回调函数 pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->queue_lock));
pool->current_pthread_task_num--; // 函数执行结束
free(worker); // 释放任务结点
worker = NULL; if((pool->current_pthread_num - pool->current_pthread_task_num) > pool->free_pthread_num) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock));
break; // 当线程池中空闲线程超过 free_pthread_num 则将线程释放回操作系统
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->queue_lock));
} pool->current_pthread_num--; // 当前线程数减1
pthread_exit(NULL); // 释放线程 return (void *)NULL;
} /**
* function: ThreadPoolConstruct
* description: 构建线程池
* input param: max_num 线程池可容纳的最大线程数
* free_num 线程池允许存在的最大空闲线程,超过则将线程释放回操作系统
* return Val: 线程池指针
*/
CThread_pool_t *
ThreadPoolConstruct(int max_num, int free_num)
{
int i = ; CThread_pool_t * pool = (CThread_pool_t *)malloc(sizeof(CThread_pool_t));
if(NULL == pool)
return NULL; memset(pool, , sizeof(CThread_pool_t)); /*初始化互斥锁*/
pthread_mutex_init(&(pool->queue_lock), NULL);
/*初始化条件变量*/
pthread_cond_init(&(pool->queue_ready), NULL); pool->queue_head = NULL;
pool->max_thread_num = max_num; // 线程池可容纳的最大线程数
pool->current_wait_queue_num = ;
pool->current_pthread_task_num = ;
pool->shutdown = ;
pool->current_pthread_num = ;
pool->free_pthread_num = free_num; // 线程池允许存在最大空闲线程
pool->threadid = NULL;
pool->threadid = (pthread_t *)malloc(max_num*sizeof(pthread_t));
/*该函数指针赋值*/
pool->AddWorkUnlimit = ThreadPoolAddWorkUnlimit;
pool->AddWorkLimit = ThreadPoolAddWorkLimit;
pool->Destroy = ThreadPoolDestroy;
pool->GetThreadMaxNum = ThreadPoolGetThreadMaxNum;
pool->GetCurrentThreadNum = ThreadPoolGetCurrentThreadNum;
pool->GetCurrentTaskThreadNum = ThreadPoolGetCurrentTaskThreadNum;
pool->GetCurrentWaitTaskNum = ThreadPoolGetCurrentWaitTaskNum; for(i=; i<max_num; i++) {
pool->current_pthread_num++; // 当前池中的线程数
/*创建线程*/
pthread_create(&(pool->threadid[i]), NULL, ThreadPoolRoutine, (void *)pool);
usleep();
} return pool;
} /**
* function: ThreadPoolConstructDefault
* description: 创建线程池,以默认的方式初始化,未创建线程
*
* return Val: 线程池指针
*/
CThread_pool_t *
ThreadPoolConstructDefault(void)
{
CThread_pool_t * pool = (CThread_pool_t *)malloc(sizeof(CThread_pool_t));
if(NULL == pool)
return NULL; memset(pool, , sizeof(CThread_pool_t)); pthread_mutex_init(&(pool->queue_lock), NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&(pool->queue_ready), NULL); pool->queue_head = NULL;
pool->max_thread_num = DEFAULT_MAX_THREAD_NUM; // 默认值
pool->current_wait_queue_num = ;
pool->current_pthread_task_num = ;
pool->shutdown = ;
pool->current_pthread_num = ;
pool->free_pthread_num = DEFAULT_FREE_THREAD_NUM; // 默认值
pool->threadid = NULL;
/*该函数指针赋值*/
pool->AddWorkUnlimit = ThreadPoolAddWorkUnlimit;
pool->AddWorkLimit = ThreadPoolAddWorkLimit;
pool->Destroy = ThreadPoolDestroy;
pool->GetThreadMaxNum = ThreadPoolGetThreadMaxNum;
pool->GetCurrentThreadNum = ThreadPoolGetCurrentThreadNum;
pool->GetCurrentTaskThreadNum = ThreadPoolGetCurrentTaskThreadNum;
pool->GetCurrentWaitTaskNum = ThreadPoolGetCurrentWaitTaskNum; return pool;
}
4.3 测试 main.c 文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h> #include "CThreadPool.h" void * thread_1(void * arg);
void * thread_2(void * arg);
void * thread_3(void * arg);
void DisplayPoolStatus(CThread_pool_t * pPool); int nKillThread = ; int main()
{
CThread_pool_t * pThreadPool = NULL; pThreadPool = ThreadPoolConstruct(, );
int nNumInput = ;
char LogInput[] = "OK!"; DisplayPoolStatus(pThreadPool);
/*可用AddWorkLimit()替换看执行的效果*/
pThreadPool->AddWorkUnlimit((void *)pThreadPool, (void *)thread_1, (void *)NULL);
/*
* 没加延迟发现连续投递任务时pthread_cond_wait()会收不到信号pthread_cond_signal() !!
* 因为AddWorkUnlimit()进去后调用pthread_mutex_lock()把互斥锁锁上,导致pthread_cond_wait()
* 收不到信号!!也可在AddWorkUnlimit()里面加个延迟,一般情况可能也遇不到这个问题
*/
usleep();
pThreadPool->AddWorkUnlimit((void *)pThreadPool, (void *)thread_2, (void *)nNumInput);
usleep();
pThreadPool->AddWorkUnlimit((void *)pThreadPool, (void *)thread_3, (void *)LogInput);
usleep();
DisplayPoolStatus(pThreadPool); nKillThread = ;
usleep(); /**< 先让线程退出 */
DisplayPoolStatus(pThreadPool);
nKillThread = ;
usleep();
DisplayPoolStatus(pThreadPool);
nKillThread = ;
usleep();
DisplayPoolStatus(pThreadPool); pThreadPool->Destroy((void*)pThreadPool);
return ;
} void *
thread_1(void * arg)
{
printf("Thread 1 is running !\n");
while(nKillThread != )
usleep();
return NULL;
} void *
thread_2(void * arg)
{
int nNum = (int)arg; printf("Thread 2 is running !\n");
printf("Get Number %d\n", nNum);
while(nKillThread != )
usleep();
return NULL;
} void *
thread_3(void * arg)
{
char * pLog = (char *)arg; printf("Thread 3 is running !\n");
printf("Get String %s\n", pLog);
while(nKillThread != )
usleep();
return NULL;
} void
DisplayPoolStatus(CThread_pool_t * pPool)
{
static int nCount = ; printf("****************************\n");
printf("nCount = %d\n", nCount++);
printf("max_thread_num = %d\n", pPool->GetThreadMaxNum((void *)pPool));
printf("current_pthread_num = %d\n", pPool->GetCurrentThreadNum((void *)pPool));
printf("current_pthread_task_num = %d\n", pPool->GetCurrentTaskThreadNum((void *)pPool));
printf("current_wait_queue_num = %d\n", pPool->GetCurrentWaitTaskNum((void *)pPool));
printf("****************************\n");
}
4.4 Makefile
简单写一个makefile
CC = gcc
CFLAGS = -g -Wall -o2
LIB = -lpthread RUNE = $(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(object) -o $(exe) $(LIB)
RUNO = $(CC) $(CFLAGS) -c $< -o $@ $(LIB) .RHONY:clean object = main.o CThreadPool.o
exe = CThreadpool $(exe):$(object)
$(RUNE) %.o:%.c CThreadPool.h
$(RUNO)
%.o:%.c
$(RUNO) clean:
-rm -rf *.o CThreadpool *~
注意:使用模式规则,能引入用户自定义变量,为多个文件建立相同的规则,规则中的相关
文件前必须用“%”表明。关于Makefile的一些规则解释见另一篇
5. 参考
感谢下面博主的贡献,特别致谢(死去的龙7)博主!!! 天行健,君子以自强不息~ 祝诸位幸福安好!!!Thanks again.
死去的龙7:https://www.cnblogs.com/deadlong7/p/4155663.html
青山小和尚:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36359022/article/details/78796784
developerWorks:https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/l-cn-mthreadps/
6. 后记
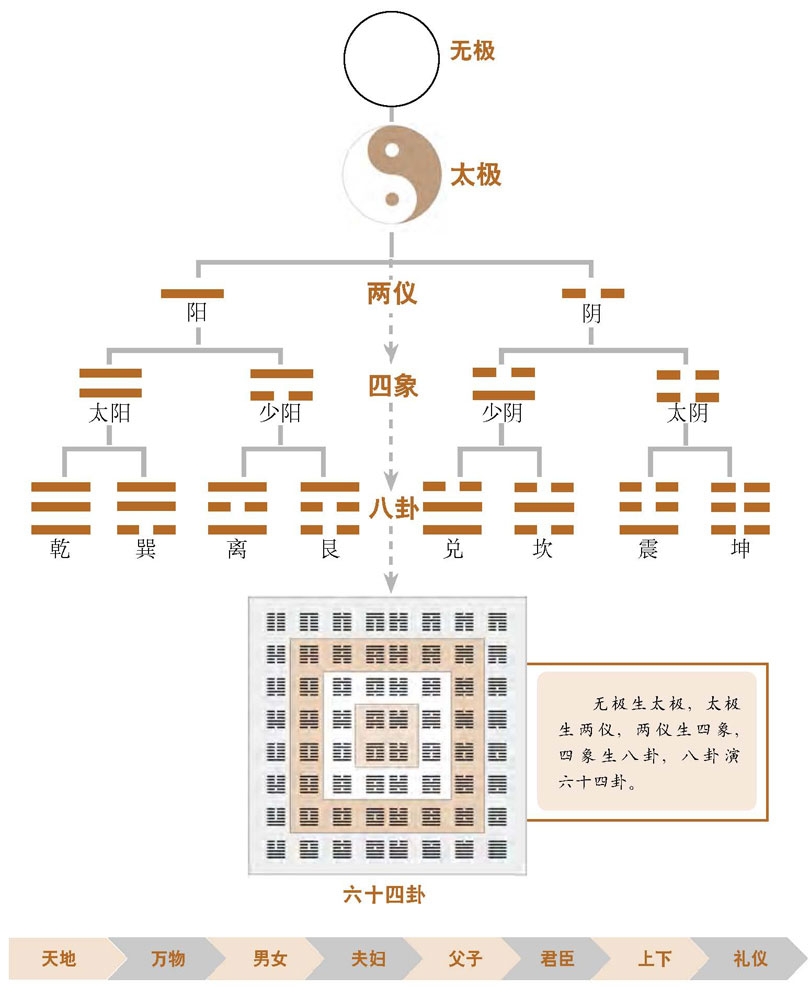
无极生太极
太极生两仪
两仪生四象
四象生八卦
八卦:qian乾 xun巽 li离 gen艮 dui兑 kan坎 zhen震 kun坤
宇宙从混沌未分的“无极”而来,无极动而生太极,太极分阴阳两仪,在由
阴阳分化出太阴、太阳、少阴、少阳这四象,四象分化而为八卦, 八卦
代表着世界的八种基本属性,可以用“天地风山水火雷泽”来概括《说卦》
认为:
乾,键也
坤,顺也
震,动也
巽,入也
坎,陷也
离,丽也
艮,止也
兑,说也
八卦又分出六十四卦,但六十四卦并不代表事务演化过程的终结。六十四
卦最后两卦为“既济” 和 “未济”,象征事务发展到最后必然有一个结果,但
这个结果作为一个"节点“,以它为开始将展开另一次全新的演变, 所以
“物不可穷也,故受之以未济终焉",
linux C 线程池(物不可穷也~)的更多相关文章
- Linux C++线程池实例
想做一个多线程服务器测试程序,因此参考了github的一些实例,然后自己动手写了类似的代码来加深理解. 目前了解的线程池实现有2种思路: 第一种: 主进程创建一定数量的线程,并将其全部挂起,此时线程状 ...
- 基于linux与线程池实现文件管理
项目要求 1.基本 用线程池实现一个大文件夹的拷贝,大文件夹嵌套很多小文件:实现复制到指定文件夹的全部文件夹. 2.扩充功能 显示进度条:拷贝耗时统计:类似linux的tree,不能直接用system ...
- Linux C++线程池
.为什么需要线程池? 部分应用程序需要执行很多细小的任务,对于每个任务都创建一个线程来完成,任务完成后销毁线程,而这就会产生一个问题:当执行的任务所需要的时间T1小于等于创建线程时间T2和销毁线程时间 ...
- Linux下线程池的理解与简单实现
首先,线程池是什么?顾名思义,就是把一堆开辟好的线程放在一个池子里统一管理,就是一个线程池. 其次,为什么要用线程池,难道来一个请求给它申请一个线程,请求处理完了释放线程不行么?也行,但是如果创建线程 ...
- Linux简单线程池实现(带源码)
这里给个线程池的实现代码,里面带有个应用小例子,方便学习使用,代码 GCC 编译可用.参照代码看下面介绍的线程池原理跟容易接受,百度云下载链接: http://pan.baidu.com/s/1i3z ...
- linux中线程池【转】
本文转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/yusiguyuan/article/details/18401277 一.线程池 大多数的网络服务器,包括Web服务器都具有一个特点,就是单位时 ...
- Linux pthread 线程池实现
基于pthread封装了一个简易的ThreadPool,具有以下特性: 1.具有优先级的任务队列 2.线程池大小可以二次调整,增加线程或者删除空闲线程 3.任务两种重写方式,重写run或者使用函数回调 ...
- 【Linux】线程池
首先,线程池是什么?顾名思义,就是把一堆开辟好的线程放在一个池子里统一管理,就是一个线程池. 其次,为什么要用线程池,难道来一个请求给它申请一个线程,请求处理完了释放线程不行么?也行,但是如果创建线程 ...
- linux 条件变量与线程池
条件变量Condition Variables 概述 1. 条件变量提供了另外一种线程同步的方式.如果没有条件变量,程序需要使用线程连续轮询(可能在临界区critical section内)方式检查条 ...
随机推荐
- UVa 12219 公共表达式消除
https://vjudge.net/problem/UVA-12219 题意: 用表达式树来表示一个表达式. 思路: 用map来记录出现过的子树.如(b,3,6)表示这棵子树的根为b,左子树为编号为 ...
- WPF基础学习笔记整理 (七) Binding绑定
基础知识: 数据绑定是一种关系,该关系告诉WPF从源对象提取一些信息,并用这些信息设置目标对象的属性:目标对象始终是依赖属性,而源对象则可以是任何内容. BindingOperations类,提供静态 ...
- xinwenti
angularjs angular2脏检查机制和数据双向绑定远离 angular2 aot编译
- php将中文符号全部替换为英文符号
php将中文符号全部替换为英文符号 一.总结 一句话总结:可以用简单替换和规律替换 简单替换 str_replace() 规律替换 均相差 65248 方法一:简单替换(php代码) $val1=st ...
- 发票查验---异步处理多条记录---demo代码
/// 窗体加载事件 /// </summary> /// <param name="obj"></param> ...
- 关于一致性hash详细
一致性哈希算法在1997年由麻省理工学院提出的一种分布式哈希(DHT)实现算法,设计目标是为了解决因特网中的热点(Hot spot)问题,初衷和CARP十分类似.一致性哈希修正了CARP使用的简 单哈 ...
- Python解析Wav文件并绘制波形的方法
资源下载 #本文PDF版下载 Python解析Wav文件并绘制波形的方法 #本文代码下载 Wav波形绘图代码 #本文实例音频文件night.wav下载 音频文件下载 (石进-夜的钢琴曲) 前言 在现在 ...
- python-day33--互斥锁
锁的意思就是:一个一个的执行 from multiprocessing import Process,Lock import os import time def work(mutex): mutex ...
- 3n+1问题中的几个小的注意点
3038 3n+1问题 时间限制: 1 s 空间限制: 32000 KB 题目等级 : 白银 Silver 题解 题目描述 Description 3n+1问题是一个简单有趣而又没有 ...
- Vue--Vue.nextTick()的使用
Vue.nextTick()是比较常用到的API Vue官网对它的解释是:在下次 DOM 更新循环结束之后执行延迟回调.在修改数据之后立即使用这个方法,获取更新后的 DOM. 首先要明白Vue的响应式 ...
