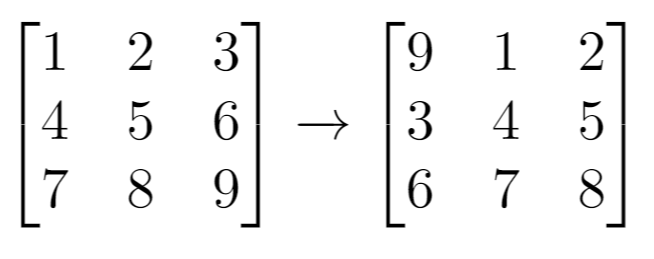【leetcode】1260. Shift 2D Grid
题目如下:
Given a 2D
gridof sizen*mand an integerk. You need to shift thegridktimes.In one shift operation:
- Element at
grid[i][j]becomes atgrid[i][j + 1].- Element at
grid[i][m - 1]becomes atgrid[i + 1][0].- Element at
grid[n - 1][m - 1]becomes atgrid[0][0].Return the 2D grid after applying shift operation
ktimes.Example 1:
Input:grid= [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]], k = 1
Output: [[9,1,2],[3,4,5],[6,7,8]]Example 2:
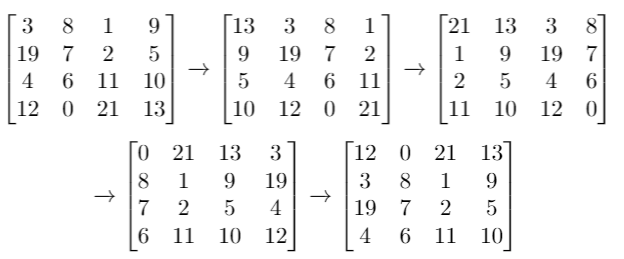
Input:grid= [[3,8,1,9],[19,7,2,5],[4,6,11,10],[12,0,21,13]], k = 4
Output: [[12,0,21,13],[3,8,1,9],[19,7,2,5],[4,6,11,10]]Example 3:
Input:grid= [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]], k = 9
Output: [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]Constraints:
1 <= grid.length <= 501 <= grid[i].length <= 50-1000 <= grid[i][j] <= 10000 <= k <= 100
解题思路:记grid的行数为row,列数为col,显然经过row*col次移动后和不移动效果是一样的,所以可以首先令k = k%(row*col)。剩下的k就是每一个元素需要移动的次数,我的方法是给grid的每个元素编号,从左到右,从上到下,依次为0,1,1....row*col - 1,这样方便计算。
代码如下:
class Solution(object):
def shiftGrid(self, grid, k):
"""
:type grid: List[List[int]]
:type k: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
row = len(grid)
col = len(grid[0])
k = k%(row * col)
res = [[0] * col for _ in range(row)]
for i in range(row):
for j in range(col):
inx = (i*col + j) + k
if inx >= (row*col):inx -= row*col
newrow = inx/col
newcol = inx%col
res[newrow][newcol] = grid[i][j]
return res
【leetcode】1260. Shift 2D Grid的更多相关文章
- 【leetcode】Search a 2D Matrix
Search a 2D Matrix Write an efficient algorithm that searches for a value in an m x n matrix. This m ...
- 【leetcode】 Search a 2D Matrix (easy)
Write an efficient algorithm that searches for a value in an m x n matrix. This matrix has the follo ...
- 【LeetCode】764. Largest Plus Sign 解题报告(Python)
[LeetCode]764. Largest Plus Sign 解题报告(Python) 作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn ...
- 【leetcode】657. Robot Return to Origin
Algorithm [leetcode]657. Robot Return to Origin https://leetcode.com/problems/robot-return-to-origin ...
- 【LeetCode】Permutations 解题报告
全排列问题.经常使用的排列生成算法有序数法.字典序法.换位法(Johnson(Johnson-Trotter).轮转法以及Shift cursor cursor* (Gao & Wang)法. ...
- 【LeetCode】分治法 divide and conquer (共17题)
链接:https://leetcode.com/tag/divide-and-conquer/ [4]Median of Two Sorted Arrays [23]Merge k Sorted Li ...
- 【LeetCode】1162. 地图分析 As Far from Land as Possible(Python)
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客:http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/ 目录 题目描述 题目大意 解题方法 这个题想考察什么? 剩下的任务就是套模板! 日期 题目 ...
- 【LeetCode】代码模板,刷题必会
目录 二分查找 排序的写法 BFS的写法 DFS的写法 回溯法 树 递归 迭代 前序遍历 中序遍历 后序遍历 构建完全二叉树 并查集 前缀树 图遍历 Dijkstra算法 Floyd-Warshall ...
- 【LeetCode】Island Perimeter 解题报告
[LeetCode]Island Perimeter 解题报告 [LeetCode] https://leetcode.com/problems/island-perimeter/ Total Acc ...
随机推荐
- 小米手机Toast带app名称
如果用小米手机做测试,会发现,Toast弹窗有可能会在前面带app名称.这是因为你传入的context是activity,如果是Application的话,就不会显示app名称.但是,我做测试时,一般 ...
- requests-html快速入门
昨天写了requests库好!最近requests库的作者又发布了一个新库,叫做requests-html,看名字也能猜出来,这是一个解析HTML的库,而且用起来和requests一样爽,下面就来介绍 ...
- [c++] SYSTEM_INFO
SYSTEM_INFO,Win32 API函数GetSystemInfo所使用的结构体. 说明 SYSTEM_INFO结构体包含了当前计算机的信息.这个信息包括计算机的体系结构.中央处理器的类型.系统 ...
- PTA(Basic Level)1048.数字加密
本题要求实现一种数字加密方法.首先固定一个加密用正整数 A,对任一正整数 B,将其每 1 位数字与 A 的对应位置上的数字进行以下运算:对奇数位,对应位的数字相加后对 13 取余--这里用 J 代表 ...
- MFC多线程的创建使用
最近学习了MFC多线程的使用, 写了一个继承CWinThread类的类MyThread: 在头文件开头用#define定义一个线程函数入口地址(会在下面定义代码中写出) 在类的开头加上IMPLEMEN ...
- 自动生成ID
public class IdUtil { /** * * @return 返回时间id,类似于20191217195622 */ public static String timeId(){ Dat ...
- Python 入门 之 面向对象的三大特性(封装 / 继承 / 多态)
Python 入门 之 面向对象的三大特性(封装 / 继承 / 多态) 1.面向对象的三大特性: (1)继承 继承是一种创建新类的方式,在Python中,新建的类可以继承一个或多个父类,父类又可以 ...
- idea 设置自动生成注释
idea新建类注释规则 /** @ProjectName: ${PROJECT_NAME} @Package: ${PACKAGE_NAME} @ClassName: ${NAME} @Descrip ...
- 今天发布MVC项目一直找不到页面
刚开始以为是framwork版本太高,服务器没安装. 后面想到应用池版本忘记选了
- 深入理解hive基础学习
Hive 是什么? 1.Hive 是基于 Hadoop处理结构化数据的一个数据仓库工具,可以将结构化的数据文件映射为一张数据库表,并提供类 SQL 查询功能. 2.Hive 利用 HDFS 存储数据 ...