[ Python ] 基本数据类型及属性(上篇)
1. 基本数据类型
(1) 数字 - int
(2) 字符串 - str
(3) 布尔值 - bool
2. int 类型中重要的方法
(1) int
将字符串转换为数字类型:
# 将字节为数字的字符串转换为 int 类型
- # 将字节为数字的字符串转换为 int 类型
- a = '123'
- b = int(a)
- print(type(a), a)
- print(type(b), b)
- # 用 十六进制的方式将 num 转换为十进制
- num = '0011'
- v = int(num, base=16)
- print(v)
3. 字符串主要的方法

实例详细介绍:
(1) capitalize()
首字母大写
- test = 'hkey'
- v = test.capitalize()
- print(v)
- # 执行结果:
- Hkey
(2) lower() casefold()
将字符串大写字母变小写,casefold() 可将其他国家的一些字母变小写
- test = 'HkEy'
- v1 = test.casefold()
- v2 = test.lower()
- print(v1, v2)
- # 执行结果:
- hkey hkey
(3) center()
设置宽度,并将内容居中, 20 代指总长度; * 代指空白填充
- name = 'hkey'
- v3 = name.center(20,'#')
- print(v3)
- # 执行结果:
- ########hkey########
(4) count()
在字符串中寻找子序列出现的个数
- name = 'hkeyxiaoxiao'
- v = name.count('x')
- print(v)
- # 执行结果:
- 2
- # 可设置起始位置和结束位置
- name = 'hkeyxiaoxiao'
- v1 = name.count('x', 0, 8)
- print(v1)
- # 直接结果:
- 1
(5) startswith() endswith()
startswith():已什么序列开头,结果为布尔值
endswith(): 以什么序列结尾,结果为布尔值
- name = 'hkey'
- v = name.startswith('h')
- print(v)
- # 执行结果:
- True
- v1 = name.endswith('y')
- print(v1)
- # 执行结果:
- True
(6) find() rfind()
从开始往后找,找到第一个,获取其索引, 结果为: -1 表示没找到
- name = 'hkeykey'
- # 从开始找第一个匹配的序列,并打印序列起始的索引位置
- v1 = name.find('key')
- print(v1)
- # 执行结果:
- 1
- # (sub, start=None, end=None) start:起始位置 end: 结束位置
- v2 = name.find('key', 0, 3)
- print(v2)
- # 执行结果:
- -1
- name = 'khkeykey'
- # 从右到左查找字符索引位置
- print(name.rfind('y'))
- # 执行结果:
- # 7
(7) format() format_map()
format() 格式化,将一个字符串中指定的占位符替换为值,占位符用 {} 表示format_map() 格式化,通过字典的形式将值传给对应 key 的占位符
- # 格式化,将一个字符串中指定的占位符替换为值
- test = 'i am {name}, age {a}'
- print(test)
- # 执行结果:
- i am {name}, age {a}
- v = test.format(name='hkey', a=20)
- print(v)
- # 执行结果:
- i am hkey, age
- # 可使用索引直接指定占位符
- test = 'i am {0}, age {1}'
- print(test)
- # 执行结果:
- i am {0}, age {1}
- v = test.format('hkey', 20)
- print(v)
- # 执行结果:
- i am hkey, age 20
- # format_map 通过字典的形式将值传给对应 key 的占位符
- test = 'i am {name}, age {a}'
- v1 = test.format_map({'name': 'hkey', 'a': 20})
- print(v1)
- # 执行结果:
- # i am hkey, age 20
(8) index()
从开始往后找,找到第一个,获取其索引, 如果没有就报错。
- name = 'hkey'
- v = name.index('y')
- print(v)
- # 执行结果:
- # 3
- v1 = name.index('z')
- print(v1)
- # 执行结果:
- # Traceback (most recent call last):
- # File "E:/learn_python/day11/s2.py", line 119, in <module>
- # v1 = name.index('z')
- # ValueError: substring not found
(9) isalnum
字符串中是否只包含 字母和数字
- test = 'abcd+_'
- v = test.isalnum()
- print(v)
- # 执行结果:
- # False
- test = 'abcd'
- v = test.isalnum()
- print(v)
- # 执行结果:
- # True
(10) expandtabs
如果字符串中含有制表符 ' \t ' ,则作为制表符来分割字符串。
- s = 'username\temail\tpassword\nhkey\thkey@qq.com\thkeyy'
- v = s.expandtabs(20)
- print(v)
- # 执行结果:
- # username email password
- # hkey hkey@qq.com hkeyy
(11) isalpha()
判断字符串是否包含数字,包含数字为 False,不包含数字为: True
- s = 'superman'
- v = s.isalpha()
- print(v)
- # 执行结果:
- # True
(12) isdecimal() isdigit() isnumeric()
判断字符串是否为数字
isdigit() 能识别特殊符号的数字写法
isnumeric() 能够判断中文的数字写法 ‘二’
- test = '②'
- v1 = test.isdecimal()
- v2 = test.isdigit()
- print(v1, v2)
- # 执行结果:
- # False True
- test1 = '二'
- v1 = test1.isdecimal()
- v2 = test1.isdigit()
- # 能够判断中文数字的写法
- v3 = test1.isnumeric()
- print(v1, v2, v3)
- # 执行结果:
- # False False True
(13) islower()
判断字符串小写。
- test='hkey'
- v=test.islower()
- print(v)
- #执行结果:
- #True
(14) isprintable()
判断字符串中是否含有不可显示的字符,如 \t \n 等
- test = 'abcdefg\t'
- v = test.isprintable()
- print(v)
- # 执行结果:
- # False
(15) isspace()
判断变量是否全部为空格
- test = ' '
- v = test.isspace()
- print(v)
- # 执行结果:
- # True
(16) istitle() title()
istitle() 判断是否为首字母都是大写的字符串
title() 将字符串转换为首字母大写的标题
- test = 'my heart will go on'
- v = test.istitle()
- v1 = test.title()
- print(v)
- print(v1)
- # 执行结果:
- # False
- # My Heart Will Go On
(17) join()
将字符串中的每个元素按照指定的分隔符进行拼接
- test = '看不见你的笑我怎么睡得着'
- v = '#'.join(test)
- print(v)
- # 执行结果:
- # 看#不#见#你#的#笑#我#怎#么#睡#得#着
(18) ljust() rjust()
设置宽度:
ljust() 字符串放置左边
rjust() 字符串放置右边
- name = 'hkey'
- v1 = name.ljust(20,'*')
- v2 = name.rjust(20, '*')
- print(v1)
- print(v2)
- # 执行结果:
- # hkey****************
- # ****************hkey
(19) zfill()
不能指定字符,只是 0 填充到左边
- name = 'hkey'
- v1 = name.zfill(20)
- print(v1)
- # 执行结果:
- # 0000000000000000hkey
(20) isupper() upper()
upper() 将小写字符串转换为大写
isupper() 判断字符串是否为大写
- test = 'my heart will go on'
- v1 = test.isupper()
- v2 = test.upper()
- print(v1)
- print(v2)
- # 执行结果:
- # False
- # MY HEART WILL GO ON
(21) lstrip() rstrip() strip()
lstrip() 去除字符串首部特殊符号及空格
rstrip() 去除字符串尾部特殊符号及空格
strip() 去除字符串首尾及空格
- name = '\nhkey\n'
- v1 = name.lstrip()
- v2 = name.rstrip()
- v3 = name.strip()
- print(v1)
- print(v2)
- print(v3)
- # 执行结果:
- # v1:
- # hkey
- #
- # v2:
- #
- # hkey
- # v3:
- # hkey
(22) maketrans()
translate() maketrans() 将两个一一对应的字符串进行替换
translate() 替换maketrans中两个字符串
- test1 = 'abcdefg'
- test2 = '1234567'
- v = 'adfasdfzcvdrfhkljwerto'
- m = str.maketrans(test1, test2)
- new_m = v.translate(m)
- print(new_m)
- # 执行结果:
- # 1461s46z3v4r6hkljw5rto
(23) partition() rpartition() split() rsplit()
partition() 将字符串分割为三分,并将分隔符作为独立的元素进行分割
rpartition() 从右边开始,将字符串分割为三分,并将分隔符作为独立的元素进行分割
split() 用指定的字符分割字符串,分割后的列表中不包含分割的字符,可执行分割次数
rsplit() 从右边开始,用指定的字符分割字符串,分割后的列表中不包含分割的字符,可执行分割次数
- test = 'asdfadfsdfxzscv'
- # 将字符串分割为三分,并将分隔符作为独立的元素进行分割
- v = test.partition('s')
- print(v)
- # 从右边开始,将字符串分割为三分,并将分隔符作为独立的元素进行分割
- v1 = test.rpartition('s')
- print(v1)
- # 用指定的字符分割字符串,分割后的列表中不包含分割的字符,可执行分割次数
- v2 = test.split('s', 1)
- print(v2)
- # 从右边开始,用指定的字符分割字符串,分割后的列表中不包含分割的字符,可执行分割次数
- v3 = test.rsplit('s', 1)
- print(v3)
- # 执行结果:
- #
- # v:
- # ('a', 's', 'dfadfsdfxzscv')
- # v1:
- # ('asdfadfsdfxz', 's', 'cv')
- # v2:
- # ['asdfadfsdfxz', 'cv']
- # v3:
- # ['a', 'dfadfsdfxzscv']
- # v4:
- # ['asdfadfsdfxz', 'cv']
(24) splitlines()
分割,只能根据:True、False 是否保留换行
- test = 'adfaf\nadfadf\nadfaf\n'
- v = test.splitlines(True)
- v1 = test.splitlines(False)
- print(v)
- print(v1)
- # 执行结果:
- # v:
- # ['adfaf\n', 'adfadf\n', 'adfaf\n']
- # v1:
- # ['adfaf', 'adfadf', 'adfaf']
(25) startswith() endswith()
startswith: 以什么开头
endswith: 以什么结尾
- test = 'hkey'
- # 以什么开头
- v1 = test.startswith('h')
- # 以什么结尾
- v2 = test.endswith('e')
- print(v1)
- print(v2)
- # 执行结果:
- # True
- # False
(26) swapcase()
大小写转换
- name = 'HkEy'
- v = name.swapcase()
- print(v)
- # 执行结果:
- # hKeY
(27) isidentifier()
检测字符串是否是字母开头
- test = '1a1dsf123'
- print(test.isidentifier())
- # 执行结果;
- # False
(28) replace()
替换字符串
- name = 'hkeykey'
- # 将字符串中的 'k' 替换为 'f' 最多替换1次
- print(name.replace('k', 'f', 1))
- # 执行结果:
- # hfeykey
总结:
字符串中几个常用的属性:
join() 、 split() 、 find() 、 strip() 、 upper() 、 lower() 、lower()
4. 常用的字符串操作
(1) 通过索引获取字符
- name = 'hkey'
- print(name[2])
- # 执行结果:
- # e
(2) 切片
通过索引的起始值、结束值、步长 来切分字符串
- name = 'hkey'
- v1 = name[0:2]
- v2 = name[0:4:2]
- print(v1)
- print(v2)
- # 执行结果:
- # v1:
- # hk
- # v2:
- # he
(3) 获取字符串的长度
- name = 'hkey'
- print(len(name))
- # 执行结果:
- # 4
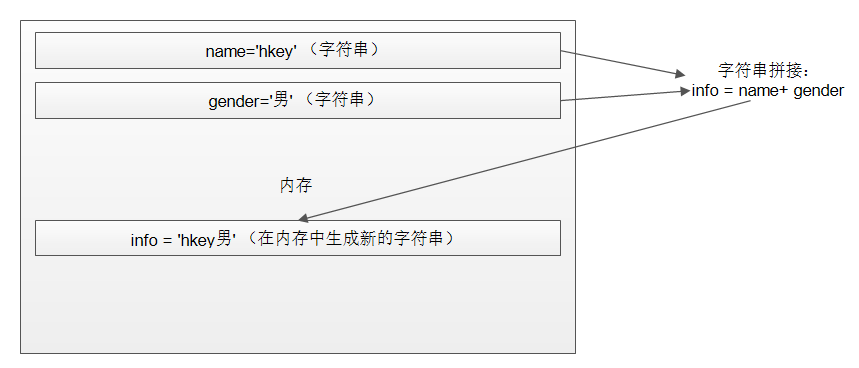
5. 操作字符串解析
字符串在内存中一旦创建就无法被修改,如果对字符串进行修改或者拼接,必然会生成一个新的字符串
[ Python ] 基本数据类型及属性(上篇)的更多相关文章
- [ Python ] 基本数据类型及属性(下篇)
1. 基本数据类型 (1) list 列表 (2) tuple 元组 (3) dict 字典 (4) set 集合 2. list 列表方法 Python 内置的一种数据类型, ...
- Python基础数据类型-列表(list)和元组(tuple)和集合(set)
Python基础数据类型-列表(list)和元组(tuple)和集合(set) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 本篇博客使用的是Python3.6版本,以及以后分享的 ...
- 23.python中的类属性和实例属性
在上篇的时候,我们知道了:属性就是属于一个对象的数据或者函数,我们可以通过句点(.)来访问属性,同时 python 还支持在运作中添加和修改属性. 而数据变量,类似于: name = 'scolia' ...
- Python基本数据类型之字符串、数字、布尔
一.数据类型种类 Python中基本数据类型主要有以下几类: Number(数字) String(字符串) Bool (布尔) List(列表) Tuple(元组) Sets(集合) Diction ...
- Python之路番外:PYTHON基本数据类型和小知识点
Python之路番外:PYTHON基本数据类型和小知识点 一.基础小知识点 1.如果一行代码过长,可以用续行符 \换行书写 例子 if (signal == "red") and ...
- [python学习手册-笔记]002.python核心数据类型
python核心数据类型 ❝ 本系列文章是我个人学习<python学习手册(第五版)>的学习笔记,其中大部分内容为该书的总结和个人理解,小部分内容为相关知识点的扩展. 非商业用途转载请注明 ...
- 跟我学Python图像处理丨获取图像属性、兴趣ROI区域及通道处理
摘要:本篇文章主要讲解Python调用OpenCV获取图像属性,截取感兴趣ROI区域,处理图像通道. 本文分享自华为云社区<[Python图像处理] 三.获取图像属性.兴趣ROI区域及通道处理 ...
- python 基本数据类型分析
在python中,一切都是对象!对象由类创建而来,对象所拥有的功能都来自于类.在本节中,我们了解一下python基本数据类型对象具有哪些功能,我们平常是怎么使用的. 对于python,一切事物都是对象 ...
- python常用数据类型内置方法介绍
熟练掌握python常用数据类型内置方法是每个初学者必须具备的内功. 下面介绍了python常用的集中数据类型及其方法,点开源代码,其中对主要方法都进行了中文注释. 一.整型 a = 100 a.xx ...
随机推荐
- 【题解】HNOI2014世界树
脑子不清醒的时候千万别写题.写题写不下去了千万别死扛,重构才是你唯一的出路QAQ 昨天很想快点写道题,思路没有很清晰的时候就写了,结果……今天一怒之下决定重整思路重构代码,其实不过是半个小时的事情…… ...
- [洛谷P4999]烦人的数学作业
题目大意:定义$f(x)$表示$x$每一个数位(十进制)的数之和,求$\sum\limits_{i=l}^rf(i)$,多组询问. 题解:数位$DP$,可以求出每个数字的出现个数,再乘上每个数字的大小 ...
- POJ1228:Grandpa's Estate——题解
http://poj.org/problem?id=1228 题目大意:给一个凸包,问是否为稳定凸包. ———————————————————————— 稳定凸包的概念为:我任意添加一个点都不能使这个 ...
- HDU3652:B-number——题解
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3652 题目大意:给一个数n,求1-n所有满足下列条件的数的个数: 1.包含一个子串为“13” 2.能被13整除. ...
- BZOJ3156: 防御准备 【斜率优化dp】
3156: 防御准备 Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 512 MB Submit: 2207 Solved: 933 [Submit][Status][Discu ...
- 添加网站标题logo
如何在标题栏title前添加网站logo? 第一种方法:据说在网站根目录下放着我们的ico型logo,命名为favicon.ico,浏览器会自动去找到并显示.试了试,在firefox23和ie8下都没 ...
- Linux环境下用Weblogic发布项目【三】 -- 启动、登陆、停止WebLogic
一.启动WebLogic: 1.启动前,修改访问端口.IP地址方法: 在config.xml中修改,具体路径如下: /root/Oracle/Middleware/user_projects/doma ...
- HDU 5656
CA Loves GCD Time Limit: 6000/3000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 262144/262144 K (Java/Others)To ...
- nginx 负载均衡实现
https://www.cnblogs.com/wang-meng/p/5861174.html
- Java——Iterate through a HashMap
遍历Map import java.util.*; public class IterateHashMap { public static void main(String[] args) { Map ...
