corosync基本使用
相关rpm:
corosync-2.4.0-4.el6.x86_64.rpm The Corosync Cluster Engine and Application Programming Interfaces。
corosynclib-2.4.0-4.el6.x86_64.rpm The Corosync Cluster Engine Libraries
crmsh-2.2.0-7.1.x86_64.rpm
crmsh-scripts-2.2.0-7.1.x86_64.rpm
dlm-4.0.6-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
dlm-lib-4.0.6-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
libqb-1.0-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
perl-TimeDate-1.16-13.el6.noarch.rpm
python-dateutil-1.4.1-7.el6.noarch.rpm
python-parallax-1.0.1-28.1.noarch.rpm
resource-agents-3.9.5-46.el6.x86_64.rpm
pacemaker-1.1.15-11.x86_64.rpm
pacemaker-cli-1.1.15-11.x86_64.rpm
pacemaker-cluster-libs-1.1.15-11.x86_64.rpm
pacemaker-cts-1.1.15-11.x86_64.rpm
pacemaker-libs-1.1.15-11.x86_64.rpm
pacemaker-remote-1.1.15-11.x86_64.rpm
python-lxml-2.2.3-1.1.el6.x86_64.rpm
python-six-1.9.0-2.el6.noarch.rpm
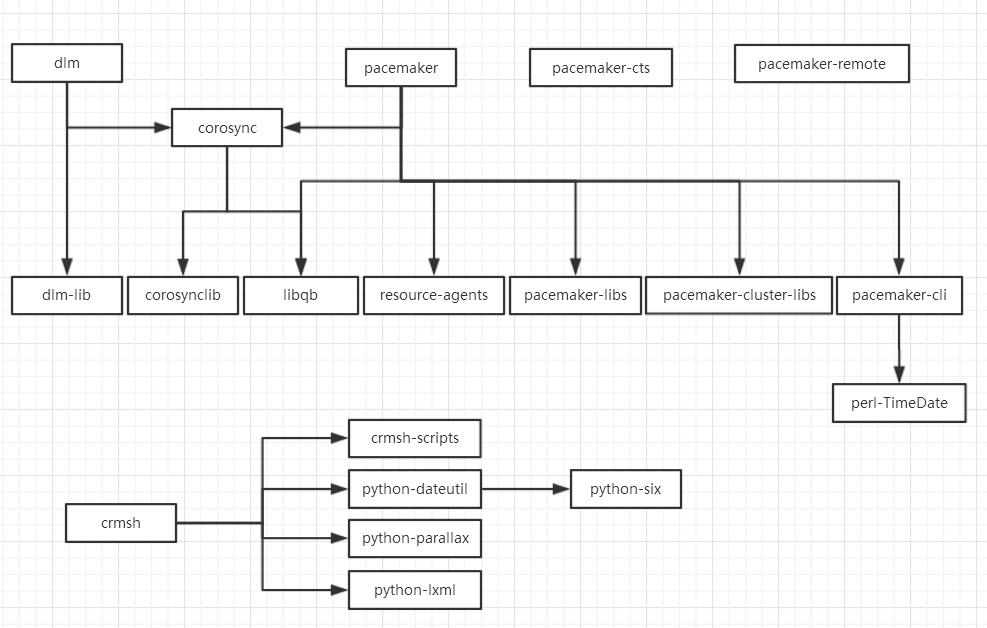
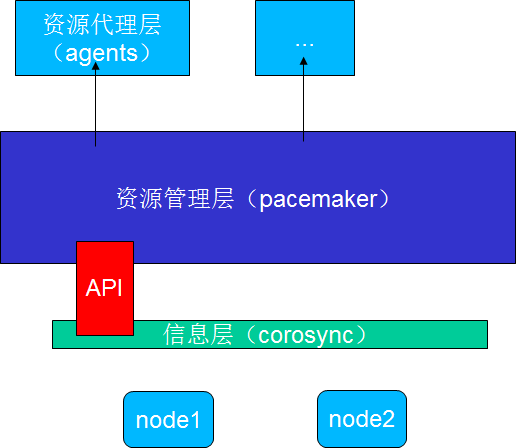
集群的组成机构
HA Cluster:
Messaging and Infrastructure Layer|Heartbeat Layer 集群信息事务层
Membership Layer 集群成员关系层
CCM 投票系统
Resource Allocation Layer 资源分配层
CRM,
DC:LRM,PE,TE,CIB
Other:LRM,CIB
Resource Layer 资源代理
RA
dlm
Distributed Lock Manager
The kernel dlm requires a user daemon to control membership.
dlm位于内核,集群架构(corosync和group management)在用户空间。位于内核的dlm需要调整或恢复一定的集群事件。dlm负责接收这些事件和,如果需要重新配置内核dlm。
dlm_controld 通过sysfs 和 configfs 文件控制配置dlm。sysfs 和configfs 文件作为 dlm-internal的接口。
cman 初始化脚本通常启动 dlm_controld 守护进程。
DLM启动前必须已经启动syslog、network、corosync
/etc/init.d/dlm中的启动参数DLM_CONTROLD_OPTS是从/etc/sysconfig/dlm中读取,包含的是dlm_controld的启动参数。dlm_members存放于/sys/kernel/config/dlm/cluster/spaces/下,每一次打开dlm时总是先到此读取,如果不存在则自己创建;
开启dlm_controld时,需要读取集群的配置,集群的名字、集群的通信模式等消息,从集群通信的ring_id中获得通信成员的信息node_id和通信IP等消息(rrp模式记录两个通信IP)。
主机Join时,首先检查是否在memb中,如果在则检查主机是否有fence,和是否被fence(fence操作时必须达到with quorum,否则不能继续往下执行),如果被fence的话需要重启之后才能重新Join;
开启dlm_controld时,需要读取集群的配置,集群的名字、集群的通信模式等消息,从集群通信的ring_id中获得通信成员的信息node_id和通信IP等消息(rrp模式记录两个通信IP)。
服务:
/etc/rc.d/init.d/dlm_controld 根据集群事件配置dlm的守护进程。
服务启动时,初始化corosync。
命令:
1. /usr/sbin/dlm_controld
命令行选项重载在 cluster.conf 中的设置。/etc/cluster/cluster.conf, 不直接被读写,其他集群部件加载内容到内存,这些值通过libccs库被访问。
dlm 和 dlm_controld 的配置项被加载到 cluster.conf 的<dlm />部分,顶部为 <cluster> 部分。.
服务启动时,会初始化 corosync配置。
2. /usr/sbin/dlm_stonith
3. /usr/sbin/dlm_tool
[root@vClass-QIVXM init.d]# dlm_tool -h
Usage: dlm_tool [command] [options] [name] Commands:
ls, status, dump, dump_config, fence_ack
log_plock, plocks
join, leave, lockdebug Options:
-n Show all node information in ls
-e | Exclusive create off/on in join, default
-f | FS (filesystem) flag off/on in join, default
-m <mode> Permission mode for lockspace device (octal), default
-s Summary following lockdebug output (experimental)
-v Verbose lockdebug output
-w Wide lockdebug output
-h Print help, then exit
-V Print program version information, then exit
4. 相关命令
/sbin/restorecon 用来恢复SELinux文件属性即恢复文件的安全上下文
policycoreutils-2.0.83-19.1.el6.x86_64.rpm SELinux policy core utilities
配置:
/etc/sysconfig/dlm
日志:
/var/log/messages
dlm_controld[108162]: 163350 corosync cfg init error
pacemaker
Pacemaker,即Cluster Resource Manager(CRM),管理整个HA,客户端通过pacemaker管理监控整个集群。
Pacemaker工作在资源分配层,提供资源管理器的功能,并以crmsh这个资源配置的命令接口来配置资源。
CRM支持ocf和lsb两种资源类型:
ocf格式的启动脚本在/usr/lib/ocf/resource.d/下面。
lsb的脚本一般在/etc/rc.d/init.d/下面。
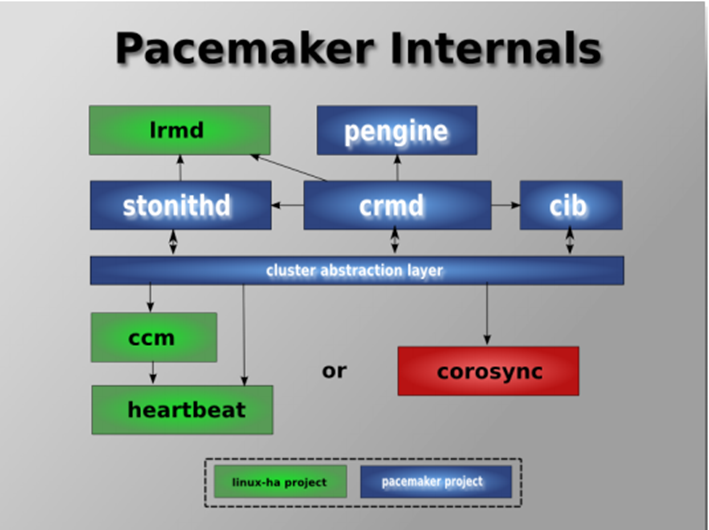
stonithd: 心跳系统
lrmd: 本地资源管理守护进程,提供了一个通用的接口支持的资源类型。直接调用资源代理(脚本)。
CIB: 集群信息库。包含所有集群选项,节点,资源,他们彼此之间的关系和现状的定义。同步更新到所有集群节点。
CRMD: 集群资源管理守护进行。主要是消息代理的 PEngine和LRM,还选举一个领导者(DC)统筹活动(包括启动/停止资源)的集群
pengine: 政策引擎。根据当前状态和配置集群计算的下一个状态。产生一个过度图,包含行动和依赖关系的列表
CCM: 共识集群成员,心跳成员层。
attrd
CIB使用XML表示集群中所有资源的配置和当前状态。CIB的内容会被自动的在整个集群中同步,使用PEngine计算集群的理想状态,生成指令列表,然后输送到DC(指定协调员)。Pacemaker集群中所有节点选举的DC节点作为主决策节点。如果当选DC节点宕机,它会在所有的节点上,迅速建立一个新的DC。DC将PEngine生成的策略,传递给其他节点上的LRMD(本地资源管理守护进程)或CRMD通过集群消息传递基础结构。当集群中有节点宕机,PEngine重新计算理想策略。在某些情况下,可能有必要关闭节点,以保护共享数据或完整的资源回收。为此,Pacemaker配备了stonithd设备。 stonith可以将其他节点“爆头”,通常是实现与电源开关。Pacemaker会将STONITH设备,配置为资源保存在CIB中,使他们可以更容易地检测资源失败或宕机。
默认的表决规则建议集群中的节点个数为奇数且不低于3。当集群只有2个节点,其中1个节点崩坏,由于不符合默认的表决规则,集群资源不发生转移,集群整体仍不可用。no-quorum-policy="ignore"可以解决此双节点的问题,但不要用于生产环境。换句话说,生产环境还是至少要3节点。
pacemaker根据信息层传递的健康信息来决定节点服务的启动或者停止
- primitive 也称之为local类型,同一时刻只能运行在一个节点
- group 组资源,组资源运行在一个节点上
- clone 需要在每个Node上运行的资源
- Master-Slave 只能运行在两个节点,一主一从
资源约束表示了资源间的相互关系:
- 位置约束(Location):定义了某个资源留在哪个节点的倾向性,如三节点N1,N2,N3,设N1挂了,资源更倾向于哪个节点转移?
- 顺序约束(Order):定义了资源的启动顺序。
- 排列约束(Collocation):定义了资源间的排列关系。比如:IP资源与httpd资源能不能运行在一起,还是必须在一起。
定义约束时,还需要指定分数。各种分数是集群工作方式的重要组成部分。从迁移资源到决定在已降级集群中停止哪些资源的整个过程是通过以某种方式修改分数来实现的。分数按每个资源来计算,资源分数为负的任何节点都无法运行该资源。分数较高的约束先应用,分数较低的约束后应用。通过使用不同的分数为既定资源创建更多位置约束,可以指定资源要故障转移至的目标节点的顺序
服务
/etc/rc.d/init.d/pacemaker
命令
/usr/sbin/cibadmin 直接访问集群配置
/usr/sbin/crm_diff
/usr/sbin/crm_error
/usr/sbin/crm_failcount 管理记录每个资源的故障计数的计数器。
/usr/sbin/crm_mon 显示集群状态概要
/usr/sbin/crm_report
/usr/sbin/crm_resource
/usr/sbin/crm_shadow
/usr/sbin/crm_simulate
/usr/sbin/crm_standby
/usr/sbin/crm_ticket
/usr/sbin/crm_verify
/usr/sbin/crmadmin
/usr/sbin/iso8601
/usr/sbin/attrd_updater
/usr/sbin/crm_attribute 允许查询、修改和删除节点属性和群集选项
/usr/sbin/crm_master
/usr/sbin/crm_node
/usr/sbin/fence_legacy
/usr/sbin/fence_pcmk
/usr/sbin/pacemakerd
/usr/sbin/stonith_admin
cibadmin
Provides direct access to the cluster configuration.
crm_mon
实时监测显示集群节点状态。 需要pacemaker服务正常,否者一直等待。
Stack: corosync
Current DC: vClass-CPLjR (version 1.1.15-11-e174ec8) - partition with quorum
Last updated: Mon Jul 24 16:52:50 2017 Last change: Mon Jul 24 16:48:53 2017 by hacluster via crmd on vClass-2lgAr
2 nodes and 0 resources configured
Online: [ vClass-2lgAr vClass-CPLjR ]
No active resources
如果状态不好,会出现“脑裂”现象。即在所有节点上分别运行crm_mon,看到的Current DC不是统一的,而是各自本身。出现此问题其中一种可能的原因是开启了防火墙。
crm_failcount 管理记录每个资源的故障计数的计数器。
可查询指定节点上每个资源的故障计数。此工具还可用于重设置故障计数,并允许资源在它多次失败的节点上再次运行。
当资源在当前节点上趋向失败时强制将该资源故障转移到其他节点。资源携带了一个 resource-stickiness 属性以确定它希望在某个节点上运行的自愿程度。它还具有 migration-threshold 属性,可用于确定资源应故障转移到其他节点的阈值。
可将 failcount 属性添加到资源,它的值将根据资源监视到的故障而递增。将 failcount的值与 migration-threshold 的值相乘,可确定该资源的故障转移分数。如果此数字超过该资源的自选设置,则该资源将被移到其他节点并且不会在原始节点上再次运行,直到重设置故障计数。
crm_failcount - A convenience wrapper for crm_attribute Set, update or remove the failcount for the specified resource on the named node Usage: crm_failcount -r resource_name command [options]
Options:
--help This text
--version Version information
-V, --verbose Increase debug output
-q, --quiet Print only the value on stdout -r, --resource-id=value The resource to update. Commands:
-G, --query Query the current value of the attribute/option
-v, --update=value Update the value of the attribute/option
-D, --delete Delete the attribute/option Additional Options:
-N, --node=value Set an attribute for the named node (instead of the current one).
-l, --lifetime=value Until when should the setting take affect.
Valid values: reboot, forever
-i, --id=value (Advanced) The ID used to identify the attribute
[root@vClass-CPLjR ~]# crm_failcount -r myvip
scope=status name=fail-count-myvip value=0
[root@vClass-CPLjR ~]# crm_failcount -r myvip -G -Q
0
重设置节点 node1 上资源 myrsc 的故障计数:
#crm_failcount -D -U node1 -r my_rsc
查询节点 node1 上资源 myrsc 的当前故障计数:
#crm_failcount -G -U node1 -r my_rsc
crm_attribute 允许查询、修改和删除节点属性和群集选项
在 CIB 的主机 myhost 的 nodes 部分中查询 location 属性的值:
crm_attribute -G -t nodes -U myhost -n location
在 CIB 的 crm_config 部分中查询 cluster-delay 属性的值:
crm_attribute -G -t crm_config -n cluster-delay
在 CIB 的 crm_config 部分中查询 cluster-delay 属性的值。只打印值:
crm_attribute -G -Q -t crm_config -n cluster-delay
从 CIB 的 nodes 部分删除主机 myhost 的 location 属性:
crm_attribute -D -t nodes -U myhost -n location
将值为 office 的名为 location 的新属性添加到 CIB 中 nodes 部分的set子部分(设置将应用到主机 myhost):
crm_attribute -t nodes -U myhost -s set -n location -v office
更改 myhost 主机的 nodes 部分中的 location 属性:
crm_attribute -t nodes -U myhost -n location -v backoffice
配置
/etc/sysconfig/pacemaker
日志
corosync
作为通信层并提供关系管理服务. 提供集群的信息层(messaging layer)的功能,传递心跳信息和集群事务信息,包括: cfg、cmap、CPG(closed process group)、quorum算法、sam、totem协议、Extended Virtual Synchrony 算法。
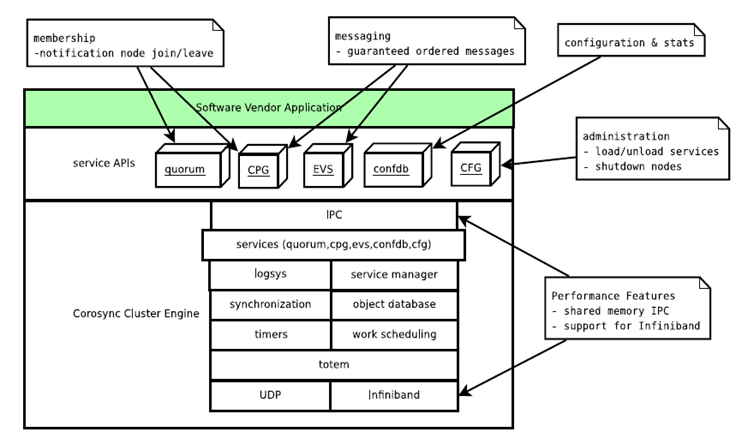
服务
/etc/rc.d/init.d/corosync 命令: corosync 端口:5404(udp) 5405(udp) 配置: /etc/sysconfig/corosync /etc/corosync/corosync.conf 日志: /var/log/messages /var/log/cluster/cluster.log
/etc/rc.d/init.d/corosync-notifyd Corosync Dbus and snmp notifier 命令: corosync-notifyd 端口: 配置: /etc/sysconfig/corosync-notifyd 日志
命令
/usr/bin/corosync-blackbox
/usr/bin/corosync-xmlproc
/usr/bin/cpg_test_agent
/usr/bin/sam_test_agent
/usr/bin/votequorum_test_agent
/usr/sbin/corosync
/usr/sbin/corosync-cfgtool
/usr/sbin/corosync-cmapctl
/usr/sbin/corosync-cpgtool
/usr/sbin/corosync-keygen 为corosync生成authkey的命令,此命令是根据内核的熵池来生成认证文件的,如果熵池的随机性不足,则会运行此命令后一直卡着,此时用户只有不断的敲击键盘使产生足够的随机数后才能生成authkdy文件
/usr/sbin/corosync-notifyd
/usr/sbin/corosync-quorumtool
corosync-cmapctl 查看corosync的服务状态
[root@vClass-2lgAr ~]# corosync-cmapctl -h
usage: corosync-cmapctl [-b] [-dghsTtp] [params...]
-b show binary values
Set key:
corosync-cmapctl -s key_name type value
where type is one of ([i|u][|||] | flt | dbl | str | bin)
for bin, value is file name (or - for stdin)
Load settings from a file:
corosync-cmapctl -p filename
the format of the file is:
[^[^]]<key_name>[ <type> <value>]
Keys prefixed with single caret ('^') are deleted (see -d).
Keys (actually prefixes) prefixed with double caret ('^^') are deleted by prefix (see -D).
<type> and <value> are optional (not checked) in above cases.
Other keys are set (see -s) so both <type> and <value> are required.
Delete key:
corosync-cmapctl -d key_name...
Delete multiple keys with prefix:
corosync-cmapctl -D key_prefix...
Get key:
corosync-cmapctl [-b] -g key_name...
Display all keys:
corosync-cmapctl [-b]
Display keys with prefix key_name:
corosync-cmapctl [-b] key_name...
Track changes on keys with key_name:
corosync-cmapctl [-b] -t key_name
Track changes on keys with key prefix:
corosync-cmapctl [-b] -T key_prefix
[root@vClass-2lgAr ~]# corosync-cmapctl
aisexec.group (str) = root
aisexec.user (str) = root
config.totemconfig_reload_in_progress (u8) =
internal_configuration.service..name (str) = corosync_cmap
internal_configuration.service..ver (u32) =
internal_configuration.service..name (str) = corosync_cfg
internal_configuration.service..ver (u32) =
internal_configuration.service..name (str) = corosync_cpg
internal_configuration.service..ver (u32) =
internal_configuration.service..name (str) = corosync_quorum
internal_configuration.service..ver (u32) =
internal_configuration.service..name (str) = corosync_pload
internal_configuration.service..ver (u32) =
internal_configuration.service..name (str) = corosync_votequorum
internal_configuration.service..ver (u32) =
logging.debug (str) = off
logging.fileline (str) = off
logging.logfile (str) = /var/log/cluster/corosync.log
logging.logger_subsys.QUORUM.debug (str) = off
logging.logger_subsys.QUORUM.subsys (str) = QUORUM
logging.timestamp (str) = on
logging.to_logfile (str) = yes
logging.to_stderr (str) = no
logging.to_syslog (str) = no
quorum.expected_votes (u32) =
quorum.last_man_standing (u8) =
quorum.last_man_standing_window (u32) =
quorum.provider (str) = corosync_votequorum
quorum.wait_for_all (u8) =
runtime.blackbox.dump_flight_data (str) = no
runtime.blackbox.dump_state (str) = no
runtime.config.totem.consensus (u32) =
runtime.config.totem.downcheck (u32) =
runtime.config.totem.fail_recv_const (u32) =
runtime.config.totem.heartbeat_failures_allowed (u32) =
runtime.config.totem.hold (u32) =
runtime.config.totem.join (u32) =
runtime.config.totem.max_messages (u32) =
runtime.config.totem.max_network_delay (u32) =
runtime.config.totem.merge (u32) =
runtime.config.totem.miss_count_const (u32) =
runtime.config.totem.rrp_autorecovery_check_timeout (u32) =
runtime.config.totem.rrp_problem_count_mcast_threshold (u32) =
runtime.config.totem.rrp_problem_count_threshold (u32) =
runtime.config.totem.rrp_problem_count_timeout (u32) =
runtime.config.totem.rrp_token_expired_timeout (u32) =
runtime.config.totem.send_join (u32) =
runtime.config.totem.seqno_unchanged_const (u32) =
runtime.config.totem.token (u32) =
runtime.config.totem.token_retransmit (u32) =
runtime.config.totem.token_retransmits_before_loss_const (u32) =
runtime.config.totem.window_size (u32) =
runtime.connections.active (u64) =
runtime.connections.attrd::0x55fb1ec2ac70.client_pid (u32) =
runtime.connections.attrd::0x55fb1ec2ac70.dispatched (u64) =
runtime.connections.attrd::0x55fb1ec2ac70.flow_control (u32) =
runtime.connections.attrd::0x55fb1ec2ac70.flow_control_count (u64) =
runtime.connections.attrd::0x55fb1ec2ac70.invalid_request (u64) =
runtime.connections.attrd::0x55fb1ec2ac70.name (str) = attrd
runtime.connections.attrd::0x55fb1ec2ac70.overload (u64) =
runtime.connections.attrd::0x55fb1ec2ac70.queue_size (u32) =
runtime.connections.attrd::0x55fb1ec2ac70.recv_retries (u64) =
runtime.connections.attrd::0x55fb1ec2ac70.requests (u64) =
runtime.connections.attrd::0x55fb1ec2ac70.responses (u64) =
runtime.connections.attrd::0x55fb1ec2ac70.send_retries (u64) =
runtime.connections.attrd::0x55fb1ec2ac70.service_id (u32) =
runtime.connections.cib::0x55fb1ee2fce0.client_pid (u32) =
runtime.connections.cib::0x55fb1ee2fce0.dispatched (u64) =
runtime.connections.cib::0x55fb1ee2fce0.flow_control (u32) =
runtime.connections.cib::0x55fb1ee2fce0.flow_control_count (u64) =
runtime.connections.cib::0x55fb1ee2fce0.invalid_request (u64) =
runtime.connections.cib::0x55fb1ee2fce0.name (str) = cib
runtime.connections.cib::0x55fb1ee2fce0.overload (u64) =
runtime.connections.cib::0x55fb1ee2fce0.queue_size (u32) =
runtime.connections.cib::0x55fb1ee2fce0.recv_retries (u64) =
runtime.connections.cib::0x55fb1ee2fce0.requests (u64) =
runtime.connections.cib::0x55fb1ee2fce0.responses (u64) =
runtime.connections.cib::0x55fb1ee2fce0.send_retries (u64) =
runtime.connections.cib::0x55fb1ee2fce0.service_id (u32) =
runtime.connections.closed (u64) =
runtime.connections.corosync-cmapct::0x55fb1ee3ff60.client_pid (u32) =
runtime.connections.corosync-cmapct::0x55fb1ee3ff60.dispatched (u64) =
runtime.connections.corosync-cmapct::0x55fb1ee3ff60.flow_control (u32) =
runtime.connections.corosync-cmapct::0x55fb1ee3ff60.flow_control_count (u64) =
runtime.connections.corosync-cmapct::0x55fb1ee3ff60.invalid_request (u64) =
runtime.connections.corosync-cmapct::0x55fb1ee3ff60.name (str) = corosync-cmapct
runtime.connections.corosync-cmapct::0x55fb1ee3ff60.overload (u64) =
runtime.connections.corosync-cmapct::0x55fb1ee3ff60.queue_size (u32) =
runtime.connections.corosync-cmapct::0x55fb1ee3ff60.recv_retries (u64) =
runtime.connections.corosync-cmapct::0x55fb1ee3ff60.requests (u64) =
runtime.connections.corosync-cmapct::0x55fb1ee3ff60.responses (u64) =
runtime.connections.corosync-cmapct::0x55fb1ee3ff60.send_retries (u64) =
runtime.connections.corosync-cmapct::0x55fb1ee3ff60.service_id (u32) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35410.client_pid (u32) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35410.dispatched (u64) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35410.flow_control (u32) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35410.flow_control_count (u64) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35410.invalid_request (u64) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35410.name (str) = crmd
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35410.overload (u64) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35410.queue_size (u32) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35410.recv_retries (u64) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35410.requests (u64) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35410.responses (u64) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35410.send_retries (u64) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35410.service_id (u32) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35ab0.client_pid (u32) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35ab0.dispatched (u64) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35ab0.flow_control (u32) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35ab0.flow_control_count (u64) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35ab0.invalid_request (u64) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35ab0.name (str) = crmd
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35ab0.overload (u64) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35ab0.queue_size (u32) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35ab0.recv_retries (u64) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35ab0.requests (u64) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35ab0.responses (u64) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35ab0.send_retries (u64) =
runtime.connections.crmd::0x55fb1ee35ab0.service_id (u32) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec27530.client_pid (u32) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec27530.dispatched (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec27530.flow_control (u32) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec27530.flow_control_count (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec27530.invalid_request (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec27530.name (str) = pacemakerd
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec27530.overload (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec27530.queue_size (u32) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec27530.recv_retries (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec27530.requests (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec27530.responses (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec27530.send_retries (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec27530.service_id (u32) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2b7d0.client_pid (u32) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2b7d0.dispatched (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2b7d0.flow_control (u32) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2b7d0.flow_control_count (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2b7d0.invalid_request (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2b7d0.name (str) = pacemakerd
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2b7d0.overload (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2b7d0.queue_size (u32) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2b7d0.recv_retries (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2b7d0.requests (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2b7d0.responses (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2b7d0.send_retries (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2b7d0.service_id (u32) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2c070.client_pid (u32) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2c070.dispatched (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2c070.flow_control (u32) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2c070.flow_control_count (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2c070.invalid_request (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2c070.name (str) = pacemakerd
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2c070.overload (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2c070.queue_size (u32) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2c070.recv_retries (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2c070.requests (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2c070.responses (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2c070.send_retries (u64) =
runtime.connections.pacemakerd::0x55fb1ec2c070.service_id (u32) =
runtime.connections.stonithd::0x55fb1ec29000.client_pid (u32) =
runtime.connections.stonithd::0x55fb1ec29000.dispatched (u64) =
runtime.connections.stonithd::0x55fb1ec29000.flow_control (u32) =
runtime.connections.stonithd::0x55fb1ec29000.flow_control_count (u64) =
runtime.connections.stonithd::0x55fb1ec29000.invalid_request (u64) =
runtime.connections.stonithd::0x55fb1ec29000.name (str) = stonithd
runtime.connections.stonithd::0x55fb1ec29000.overload (u64) =
runtime.connections.stonithd::0x55fb1ec29000.queue_size (u32) =
runtime.connections.stonithd::0x55fb1ec29000.recv_retries (u64) =
runtime.connections.stonithd::0x55fb1ec29000.requests (u64) =
runtime.connections.stonithd::0x55fb1ec29000.responses (u64) =
runtime.connections.stonithd::0x55fb1ec29000.send_retries (u64) =
runtime.connections.stonithd::0x55fb1ec29000.service_id (u32) =
runtime.services.cfg..rx (u64) =
runtime.services.cfg..tx (u64) =
runtime.services.cfg..rx (u64) =
runtime.services.cfg..tx (u64) =
runtime.services.cfg..rx (u64) =
runtime.services.cfg..tx (u64) =
runtime.services.cfg..rx (u64) =
runtime.services.cfg..tx (u64) =
runtime.services.cfg.service_id (u16) =
runtime.services.cmap..rx (u64) =
runtime.services.cmap..tx (u64) =
runtime.services.cmap.service_id (u16) =
runtime.services.cpg..rx (u64) =
runtime.services.cpg..tx (u64) =
runtime.services.cpg..rx (u64) =
runtime.services.cpg..tx (u64) =
runtime.services.cpg..rx (u64) =
runtime.services.cpg..tx (u64) =
runtime.services.cpg..rx (u64) =
runtime.services.cpg..tx (u64) =
runtime.services.cpg..rx (u64) =
runtime.services.cpg..tx (u64) =
runtime.services.cpg..rx (u64) =
runtime.services.cpg..tx (u64) =
runtime.services.cpg..rx (u64) =
runtime.services.cpg..tx (u64) =
runtime.services.cpg.service_id (u16) =
runtime.services.pload..rx (u64) =
runtime.services.pload..tx (u64) =
runtime.services.pload..rx (u64) =
runtime.services.pload..tx (u64) =
runtime.services.pload.service_id (u16) =
runtime.services.quorum.service_id (u16) =
runtime.services.votequorum..rx (u64) =
runtime.services.votequorum..tx (u64) =
runtime.services.votequorum..rx (u64) =
runtime.services.votequorum..tx (u64) =
runtime.services.votequorum..rx (u64) =
runtime.services.votequorum..tx (u64) =
runtime.services.votequorum..rx (u64) =
runtime.services.votequorum..tx (u64) =
runtime.services.votequorum.service_id (u16) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.rrp..faulty (u8) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.avg_backlog_calc (u32) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.avg_token_workload (u32) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.commit_entered (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.commit_token_lost (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.consensus_timeouts (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.continuous_gather (u32) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.continuous_sendmsg_failures (u32) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.firewall_enabled_or_nic_failure (u8) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.gather_entered (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.gather_token_lost (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.mcast_retx (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.mcast_rx (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.mcast_tx (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.memb_commit_token_rx (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.memb_commit_token_tx (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.memb_join_rx (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.memb_join_tx (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.memb_merge_detect_rx (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.memb_merge_detect_tx (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.members..config_version (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.members..ip (str) = r() ip(10.17.55.253)
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.members..join_count (u32) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.members..status (str) = joined
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.members..config_version (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.members..ip (str) = r() ip(10.17.55.254)
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.members..join_count (u32) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.members..status (str) = joined
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.mtt_rx_token (u32) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.operational_entered (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.operational_token_lost (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.orf_token_rx (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.orf_token_tx (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.recovery_entered (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.recovery_token_lost (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.rx_msg_dropped (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.token_hold_cancel_rx (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.token_hold_cancel_tx (u64) =
runtime.totem.pg.msg_queue_avail (u32) =
runtime.totem.pg.msg_reserved (u32) =
runtime.votequorum.ev_barrier (u32) =
runtime.votequorum.this_node_id (u32) =
runtime.votequorum.two_node (u8) =
runtime.votequorum.wait_for_all_status (u8) =
service.name (str) = pacemaker
service.ver (str) =
totem.cluster_name (str) = fMOQ0nGciUIFxoRq
totem.config_version (u64) =
totem.crypto_cipher (str) = none
totem.crypto_hash (str) = none
totem.interface..bindnetaddr (str) = 10.17.55.0
totem.interface..mcastaddr (str) = 239.255.1.1
totem.interface..mcastport (u16) =
totem.interface..ttl (u8) =
totem.send_join (u32) =
totem.token (u32) =
totem.version (u32) =
totem.window_size (u32) =
uidgid.gid. (u8) =
配置
/etc/corosync/corosync.conf.example 主配置文件模板, corosync可执行文件的配置文件
/etc/corosync/corosync.conf.example.udpu
/etc/corosync/corosync.xml.example
/etc/corosync/uidgid.d
/etc/logrotate.d/corosync
/etc/sysconfig/corosync
/etc/sysconfig/corosync-notifyd
通过 主配置文件模板:/etc/corosync/corosync.conf.example 复制生成配置文件 /etc/corosync/corosync.conf, 修改如下:
# Please read the corosync.conf.5 manual page
compatibility:whitetank # 表示兼容 whitetank版本,其实是corosync0.8之前的版本,即 openais-0.80.z。 缺省是 whiteank。
totem { # top level 定义集群环境下各corosync间通讯机制,totem 协议。 7个配置项,一个必选项,5个可选项,1个是ip6使用的
version: 2 # corosync 配置文件的版本号,固定为:2
# secauth:Enable mutual node authentication.If you choose to
# enable this(on),then do remember to create ashared
# secret with corosync-keygen.
# secauth:off
secauth: on # 表示基于authkey的方式来验证各节点, 启动加密, 缺省值是on。##安全认证,当使用aisexec时,会非常消耗CPU
threads: 0 # 启动的线程数,0表示不启动线程机制,默认即可。 根据CPU个数和核心数确定 token: 10000 # token的时效,单位: 毫秒, 缺省值1000
token_retransmits_before_loss_const: 10 # 缺省值: 4
vsftype: none # 缺省值: ykd。 虚拟同步过滤器类型。 支持:YKD dynamic linear voting
rrp_mode: active # 指定冗余换的模式。支持:active,passive,none。 如果只有一个interface,自动设置为none。
# 网络通讯接口,如果定义多个,需要设置 rrp_mode
# interface: define at least one interface to communicate
# over. If you define more than one interface stanza, you must
# also set rrp_mode.
interface { # 定义哪个接口来传递心跳信息和集群事务信息
# Rings must be consecutively numbered, starting at 0.
ringnumber: 0 # 表示心跳信息发出后能够在网络中转几圈,保持默认值即可。 必须是以0开始的数字。 ##冗余环号,节点有多个网卡是可定义对应网卡在一个环内
# This is normally the *network* address of the
# interface to bind to. This ensures that you can use
# identical instances of this configuration file
# across all your cluster nodes, without having to
# modify this option.
bindnetaddr: 192.168.0.0 # 绑定的网络地址,##绑定心跳网段
# However, if you have multiple physical network
# interfaces configured for the same subnet, then the
# network address alone is not sufficient to identify
# the interface Corosync should bind to. In that case,
# configure the *host* address of the interface
# instead:
#bindnetaddr: 192.168.1.1
# When selecting a multicast address, consider RFC
# (which, among other things, specifies that
# 239.255.x.x addresses are left to the discretion of
# the network administrator). Do not reuse multicast
# addresses across multiple Corosync clusters sharing
# the same network.
mcastaddr: 239.255.21.111 # 监听的多播地址,不要使用默认,##心跳组播地址
# Corosync uses the port you specify here for UDP
# messaging, and also the immediately preceding
# port. Thus if you set this to 5405, Corosync sends
# messages over UDP ports 5405 and 5404.
mcastport: 5405 # corosync 间传递信息使用的端口,默认即可。 ##心跳组播使用端口
# Time-to-live for cluster communication packets. The
# number of hops(routers) that this ring will allow
# itself to pass. Note that multicast routing must be
# specifically enabled on most network routers.
ttl: 1 # 包的生存周期,保持默认1即可。 如果网络是经过route的网络,可以设置大一些。范围 1-255. 仅仅在 multicast 类型下有效。 # broadcast: yes # 广播方式,不要使用mcastaddr参数。 如果设置了 broadcast 为yes, mcastaddr不能设置。
# transport: udp # 控制传输的方法, 如果要完全消除多播,指定udpu单播传输参数。这需要用nodelist指定成员列表。transport默认是udp,也可以设置成updu或iba。
} #interface {
# ringnumber: 1
# bindnetaddr: 10.0.42.0
# mcastaddr: 239.255.42.2
# mcastport: 5405
#}
}
logging { # top level, 定义日志选项
# Log the source file and line where messages are being
# generated. When in doubt, leave off. Potentially useful for
# debugging.
fileline: off ##指定要打印的行
# Log to standard error. When in doubt, set to no. Useful when
# running in the foreground(when invoking corosync -f)
to_stderr: no ##是否发送到标准错误输出
# Log to a log file. When set to no, the log file option
# must not be set.
to_logfile: yes ##记录到文件
logfile: /var/log/cluster/corosync.log
# Log to the system log daemon. When in doubt, set to yes.
to_syslog: no # 关闭日志发往 syslog ##记录到syslog
# Log debug messages(very verbose). When in doubt, leave off.
debug: off
# Log messages with time stamps. When in doubt, set to on
# (unless you are only logging to syslog, where double
# time stamps can be annoying).
timestamp: on # 打印日志时是否记录时间戳,会消耗较多的cpu资源
logger_subsys {
subsys: AMF
debug: off
}
} event { # top level, 事件服务配置 } amf {
mode: disabled
} quorum {
provider: corosync_votequorum # 启动了votequorum
expected_votes: 7 # 7表示,7个节点,quorum为4。如果设置了nodelist参数,expected_votes无效
wait_for_all: 1 # 值为1表示,当集群启动,集群quorum被挂起,直到所有节点在线并加入集群,这个参数是Corosync 2.0新增的。
last_man_standing: 1 # 为1表示,启用LMS特性。默认这个特性是关闭的,即值为0。
# 这个参数开启后,当集群的处于表决边缘(如expected_votes=7,而当前online nodes=4),处于表决边缘状态超过last_man_standing_window参数指定的时间,
# 则重新计算quorum,直到online nodes=2。如果想让online nodes能够等于1,必须启用auto_tie_breaker选项,生产环境不推荐。
last_man_standing_window: 10000 # 单位为毫秒。在一个或多个主机从集群中丢失后,重新计算quorum
} # 新增加以下内容
service {
ver: 0 # ver: 1表示corosync不自动启动pacemaker。如果要corosync自动启动pacemaker,设置ver为0。
name: pacemaker # 表示以插件化方式启用 pacemaker, ##定义corosync启动时同时启动pacemaker
# use_mgmtd: yes
}
aisexec { # 运行openaix时所使用的用户及组,默认时也是采用root,可以不定义
user:root
group:root
} nodelist { # 每个节点,必须至少有一个ring0_addr字段,其它可能的选项有ring{X}_addr和nodeid,{X}是ring的序号,ring{X}_addr指定节点IP,nodeid是需要同时使用IPv4和IPv6时才指定。
node {
ring0_addr: 192.168.42.1
ring1_addr: 10.0.42.1
nodeid: 1 # ip4 可选项,ip6必选项。 32 bits value bound with ring 0。 0值是保留的,不能使用
}
node {
ring0_addr: 192.168.42.2
ring1_addr: 10.0.42.2
nodeid: 2
}
}
1、token和token_retransmits_before_loss_const相乘的结果决定了集群的故障转移时间。token的单位是毫秒。如果某个节点超过$(token*token_retransmits_before_loss_const)未响应,则被认为节点死亡。
2、如果启用了secauth选项,则节点间的通讯使用128位密钥加密,密钥存储在/etc/corosync/authkey,可以使用corosync-keygen生成。
3、Corosync配置需要冗余网络(用到不只一个网络接口),必须采用RRR模式,注意下述推荐的接口配置:
3.1、每个接口的配置必须有一个唯一的ringnumber,且起始数值为0。
3.2、bindnetaddr是你想要绑定的IP地址网段,
3.3、多组播地址mcastaddr不能在跨越集群的边界重用,即从来没有两个独立的集群使用了相同的多播组地址。多播组的地址必须遵循RFC 2365, “Administratively Scoped IP Multicast”
3.4、防火墙配置方面,Corosync仅需要UDP通信,使用mcastport(接收)和mcastport - 1(发送)。
4、pacemaker服务可以在corosync.conf中声明,也可以在/etc/corosync/service.d/pacemaker中声明。
注意:如果是在Ubuntu 14.04下的Corosync(version 2),需要注释服务stanza中启动pacemaker的命令。此外,要需要注意Corosync和Pacemaker的启动顺序,需要手动指定:
# update-rc.d pacemaker start 20 2 3 4 5 . stop 00 0 1 6 .
/etc/corosync/uidgid.d/pacemaker必须增加:
uidgid {
uid: hacluster
gid: haclient
}
5、注意所有节点上的corosync.conf和authkey都要保持同步。
6、service节点中,ver: 1表示corosync不自动启动pacemaker。如果要corosync自动启动pacemaker,设置ver为0。由于centos7没有/etc/rc.d/init.d/pacemaker脚本(pacemaker服务在centos7中可以用systemctl命令设置),故我的配置中没有这个小节。可手动创建/etc/rc.d/init.d/pacemaker,与下一篇关于haproxy的文章中创建/etc/rc.d/init.d/haproxy脚本的方法相同。
votequorum方式配置
votequorum库是Corosync项目中的一部分。采用votequorum是为了避免脑裂发生,以及:
1、查询quorum状态;
2、获得quorum服务所知道的节点列表;
3、接收quorum状态改变的通知;
4、改变votes的数量,并分配域一个节点(Change the number of votes assigned to a node)
5、Change the number of expected votes for a cluster to be quorate
6、Connect an additional quorum device to allow small clusters remain quorate during node outages
votequorum库被创建于用来替换和取代qdisk(表决盘)。
日志
/var/log/cluster/
/var/log/messages
Can't read file /etc/corosync/corosync.conf reason = (No such file or directory)
注意:
1.启动时,必须有 corosync 配置文件 corosync.conf
2.
crmsh
配置管理群集 High Availability cluster command-line interface
The crm shell is a command-line interface for High-Availability
cluster management on GNU/Linux systems. It simplifies the
configuration, management and troubleshooting of Pacemaker-based
clusters, by providing a powerful and intuitive set of features.
1.3 CRM中的几个基本概念
1.3.1 资源粘性:
资源粘性表示资源是否倾向于留在当前节点,如果为正整数,表示倾向,负数则会离开,-inf表示正无穷,inf表示正无穷。
1.3.2 资源类型:
- primitive(native):基本资源,原始资源
- group:资源组
- clone:克隆资源(可同时运行在多个节点上),要先定义为primitive后才能进行clone。主要包含STONITH和集群文件系统(cluster filesystem)
- master/slave:主从资源,如drdb(下文详细讲解)
1.3.3 RA类型:
- Lsb:linux表中库,一般位于/etc/rc.d/init.d/目录下的支持start|stop|status等参数的服务脚本都是lsb
- ocf:Open cluster Framework,开放集群架构
- heartbeat:heartbaet V1版本
- stonith:专为配置stonith设备而用
3.2 法定票数问题:
在双节点集群中,由于票数是偶数,当心跳出现问题(脑裂)时,两个节点都将达不到法定票数,默认quorum策略会关闭集群服务,为了避免这种情况,可以增加票数为奇数(如前文的增加ping节点),或者调整默认quorum策略为【ignore】。
crm(live)configure# property no-quorum-policy=ignore
3.3 防止资源在节点恢复后移动
故障发生时,资源会迁移到正常节点上,但当故障节点恢复后,资源可能再次回到原来节点,这在有些情况下并非是最好的策略,因为资源的迁移是有停机时间的,特别是一些复杂的应用,如oracle数据库,这个时间会更长。为了避免这种情况,可以根据需要,使用本文1.3.1介绍的资源粘性策略。
crm(live)configure# rsc_defaults resource-stickiness= ##设置资源粘性为100
3.4.3 资源约束
- 由此可见,即便集群拥有所有必需资源,但它可能还无法进行正确处理。资源约束则用以指定在哪些群集节点上运行资源,以何种顺序装载资源,以及特定资源依赖于哪些其它资源。pacemaker共给我们提供了三种资源约束方法:
1)Resource Location(资源位置):定义资源可以、不可以或尽可能在哪些节点上运行;
2)Resource Collocation(资源排列):排列约束用以定义集群资源可以或不可以在某个节点上同时运行;
3)Resource Order(资源顺序):顺序约束定义集群资源在节点上启动的顺序; - 定义约束时,还需要指定分数。各种分数是集群工作方式的重要组成部分。其实,从迁移资源到决定在已降级集群中停止哪些资源的整个过程是通过以某种方式修改分数来实现的。分数按每个资源来计算,资源分数为负的任何节点都无法运行该资源。在计算出资源分数后,集群选择分数最高的节点。INFINITY(无穷大)目前定义为 1,000,000。加减无穷大遵循以下3个基本规则:
1)任何值 + 无穷大 = 无穷大
2)任何值 - 无穷大 = -无穷大
3)无穷大 - 无穷大 = -无穷大
定义资源约束时,也可以指定每个约束的分数。分数表示指派给此资源约束的值。分数较高的约束先应用,分数较低的约束后应用。通过使用不同的分数为既定资源创建更多位置约束,可以指定资源要故障转移至的目标节点的顺序。
服务
无
命令
/etc/bash_completion.d/crm.sh
/usr/sbin/crm
Help overview for crmsh
Available topics:
Overview Help overview for crmsh
Topics Available topics
Description Program description
CommandLine Command line options
Introduction Introduction
Interface User interface
Completion Tab completion
Shorthand Shorthand syntax
Features Features
Shadows Shadow CIB usage
Checks Configuration semantic checks
Templates Configuration templates
Testing Resource testing
Security Access Control Lists (ACL)
Resourcesets Syntax: Resource sets
AttributeListReferences Syntax: Attribute list references
AttributeReferences Syntax: Attribute references
RuleExpressions Syntax: Rule expressions
Reference Command reference
Available commands:
cd Navigate the level structure
help Show help (help topics for list of topics)
ls List levels and commands
quit Exit the interactive shell
report Create cluster status report
status Cluster status
up Go back to previous level
assist/ Configuration assistant
template Create template for primitives
weak-bond Create a weak bond between resources
cib/ CIB shadow management # CIB管理模块
cibstatus CIB status management and editing
commit Copy a shadow CIB to the cluster
delete Delete a shadow CIB
diff Diff between the shadow CIB and the live CIB
import Import a CIB or PE input file to a shadow
list List all shadow CIBs
new Create a new shadow CIB
reset Copy live cib to a shadow CIB
use Change working CIB
cibstatus/ CIB status management and editing
load Load the CIB status section
node Change node status
op Edit outcome of a resource operation
origin Display origin of the CIB status section
quorum Set the quorum
run Run policy engine
save Save the CIB status section
show Show CIB status section
simulate Simulate cluster transition
ticket Manage tickets
cluster/ Cluster setup and management
add Add a new node to the cluster
copy Copy file to other cluster nodes
diff Diff file across cluster
health Cluster health check
init Initializes a new HA cluster
remove Remove a node from the cluster
run Execute an arbitrary command on all nodes
start Start cluster services
status Cluster status check
stop Stop cluster services
wait_for_startup Wait for cluster to start
configure/ CIB configuration ##CRM配置,包含资源粘性、资源类型、资源约束等。逻辑上被分为四部分:nodes, resources, constraints, and (cluster) properties and attributes.
acl_target Define target access rights ACL
cib CIB shadow management
cibstatus CIB status management and editing
clone Define a clone resource
colocation Colocate resources constraints
commit Commit the changes to the CIB ##提交配置
default-timeouts Set timeouts for operations to minimums from the meta-data
delete Delete CIB objects
edit Edit CIB objects
erase Erase the CIB
fencing_topology Node fencing order define fencing order (stonith resource priorities)
filter Filter CIB objects
graph Generate a directed graph
group Define a group resources
load Import the CIB from a file
location A location preference contraints
modgroup Modify group
monitor Add monitor operation to a primitive resources
ms Define a master-slave resource resources
node Define a cluster node
op_defaults Set resource operations defaults attribute
order Order resources contraints
primitive Define a resource 定义一个资源 resources
property Set a cluster property attributes
ptest Show cluster actions if changes were committed
refresh Refresh from CIB
rename Rename a CIB object
role Define role access rights ACL access control lists
rsc_defaults Set resource defaults attributes
rsc_template Define a resource template 为了简化大量配置,定义一个模板,原生资源继承在模板中的所有属性。
rsc_ticket Resources ticket dependency
rsctest Test resources as currently configured
save Save the CIB to a file
schema Set or display current CIB RNG schema
set Set an attribute value
show Display CIB objects 显示CIB对象
show_property Show property value 显示属性值
tag Define resource tags
template Edit and import a configuration from a template
upgrade Upgrade the CIB
user Define user access rights ACL access control lists
validate-all Help for command validate-all
validate_all Call agent validate-all for resource
verify Verify the CIB with crm_verify ##检查当前配置语法
xml Raw xml corosync/ Corosync management
add-node Add a corosync node
del-node Remove a corosync node
diff Diffs the corosync configuration
edit Edit the corosync configuration
get Get a corosync configuration value
log Show the corosync log file
pull Pulls the corosync configuration
push Push the corosync configuration
reload Reload the corosync configuration
set Set a corosync configuration value
show Display the corosync configuration
status Display the corosync status history/ Cluster history
detail Set the level of detail shown
diff Cluster states/transitions difference
events Show events in log
exclude Exclude log messages
graph Generate a directed graph from the PE file
info Cluster information summary
latest Show latest news from the cluster
limit Limit timeframe to be examined
log Log content
node Node events
peinputs List or get PE input files
refresh Refresh live report
resource Resource events
session Manage history sessions
setnodes Set the list of cluster nodes
show Show status or configuration of the PE input file
source Set source to be examined
transition Show transition
wdiff Cluster states/transitions difference maintenance/ Maintenance mode commands # 保持模式控制, 控制整个集群或一个资源代理是否有 maintenance 模式
action Invoke a resource action
off Disable maintenance mode
on Enable maintenance mode node/ Node management ##节点管理
attribute Manage attributes 设置、显示、删除节点的属性值
clearstate Clear node state 使节点处于 maintenance 状态
delete Delete node 删除一个节点,此节点一定不能出去active状态。(offline状态不是 非active状态),通过停止corosync服务,可以置node为非active状态。
fence Fence node 关闭一个节点。依赖stonith资源,如果没有stonith,此命令无效
maintenance Put node into maintenance mode 使节点处于maintenance状态,上面运行的资源,将脱离crm的管理。通过readby可以恢复。
online Set node online 节点上线,不加指定node参数,将操作本地。
ready Put node into ready mode 使节点从 maintenace 状态变为ready状态。上面运行的资源,收crm的管理。
show Show node 显示节点: 节点名、id、状态
standby Put node into standby 节点下线,不加指定node参数,将操作本地。
status Show nodes' status as XML xml方式显示节点信息
status-attr Manage status attributes
utilization Manage utilization attributes options/ User preferences
add-quotes Add quotes around parameters containing spaces
check-frequency When to perform semantic check
check-mode How to treat semantic errors
colorscheme Set colors for output
editor Set preferred editor program
manage-children How to handle children resource attributes
output Set output type
pager Set preferred pager program
reset Reset user preferences to factory defaults
save Save the user preferences to the rc file
set Set the value of a given option
show Show current user preference
skill-level Set skill level
sort-elements Sort CIB elements
user Set the cluster user
wait Synchronous operation ra/ Resource Agents (RA) lists and documentation 资源代理 class:provider:agent
classes List classes and providers 显示资源代理的分类和提供者: lsb ocf service stonith
info Show meta data for a RA 获取资源代理的元数据及参数信息。 输入info 按下 tab键,显示系统所有可能的RA
list List RA for a class (and provider) 根据class(和provider)列表显示系统的RA, 输入 list,按下 tab 键,显示系统支持的class
providers Show providers for a RA and a class 获取资源代理的提供者,如: heartbeat pacemaker rabbitmq,位置: /usr/lib/ocf/resource.d
validate Validate parameters for RA resource/ Resource management ##资源管理模块
ban Ban a resource from a node
cleanup Cleanup resource status
constraints Show constraints affecting a resource
demote Demote a master-slave resource
failcount Manage failcounts ## 设置、显示、删除 资源的失败数(在节点上)。
maintenance Enable/disable per-resource maintenance mode
manage Put a resource into managed mode
meta Manage a meta attribute
migrate Migrate a resource to another node ## 迁移一个资源到另一个节点
operations Show active resource operations
param Manage a parameter of a resource
promote Promote a master-slave resource
refresh Refresh CIB from the LRM status
reprobe Probe for resources not started by the CRM
restart Restart resources
scores Display resource scores
secret Manage sensitive parameters
start Start resources ## 启动资源
status Show status of resources ## 显示资源状态: started、
stop Stop resources ## 停止资源
trace Start RA tracing
unmanage Put a resource into unmanaged mode
unmigrate Unmigrate a resource to another node
untrace Stop RA tracing
utilization Manage a utilization attribute script/ Cluster script management
json JSON API for cluster scripts
list List available scripts
run Run the script
show Describe the script
verify Verify the script site/ GEO clustering site support
ticket Manage site tickets template/ Edit and import a configuration from a template
apply Process and apply the current configuration to the current CIB
delete Delete a configuration
edit Edit a configuration
list List configurations/templates
load Load a configuration
new Create a new configuration from templates
show Show the processed configuration
configure CIB 配置项
primitive 定义原始资源, 原始资源是最基本的资源类型。
Usage:
primitive <rsc> {[<class>:[<provider>:]]<type>|@<template>}
[description=<description>]
[[params] attr_list]
[meta attr_list]
[utilization attr_list]
[operations id_spec]
[op op_type [<attribute>=<value>...] ...]
attr_list :: [$id=<id>] [<score>:] [rule...]
<attr>=<val> [<attr>=<val>...]] | $id-ref=<id>
id_spec :: $id=<id> | $id-ref=<id>
op_type :: start | stop | monitor
元属性 meta
元属性是可以为资源添加的选项。它们告诉 CRM 如何处理特定资源。 可以为添加的每个资源定义选项。群集使用这些选项来决定资源的行为方式,它们会告知 CRM 如何对待特定的资源。可使用 crm_resource --meta 命令或 GUI 来设置资源选项,请参见。
原始资源选项:
|
选项 |
描述 |
|---|---|
|
priority |
如果不允许所有的资源都处于活动状态,群集会停止优先级较低的资源以便保持较高优先级资源处于活动状态。 |
|
target-role |
群集应试图将此资源保持在何种状态?允许的值:Stopped 和 Started。 |
|
is-managed |
是否允许群集启动和停止资源?允许的值:true 和 false。 |
|
resource-stickiness |
资源留在所处位置的自愿程度如何?默认为 default- resource-stickiness的值。 |
|
migration-threshold |
节点上的此资源应发生多少故障后才能确定该节点没有资格主管此资源?默认值:none。 |
|
multiple-active |
如果发现资源在多个节点上活动,群集该如何操作?允许的值:block(将资源标记为未受管)、stop_only 和 stop_start。 |
|
failure-timeout |
在恢复为如同未发生故障一样正常工作(并允许资源返回它发生故障的节点)之前,需要等待几秒钟?默认值:never。 |
实例属性
实例属性是特定资源类的参数,用于确定资源类的行为方式及其控制的服务实例。有关更多信息,请参考部分 17.5, 实例属性。
clone 定义一个克隆资源。 克隆是可以在多个主机上处于活动状态的资源。如果各个资源代理支持,则任何资源均可克隆。
crm(live)configure# help clone
Define a clone The clone command creates a resource clone. It may contain a clone命令创建一个资源clone。它可能包含一个单独的原生资源或一组资源。
single primitive resource or one group of resources. Usage: clone <name> <rsc>
[description=<description>]
[meta <attr_list>]
[params <attr_list>] attr_list :: [$id=<id>] <attr>=<val> [<attr>=<val>...] | $id-ref=<id> Example: clone cl_fence apc_1 \
meta clone-node-max= globally-unique=false
group 组资源。 组包含一系列需要放置在一起、按顺序启动和以反序停止的资源
ms 主资源。 主资源是一种特殊的克隆资源,主资源可以具有多种模式。主资源必须只能包含一个组或一个常规资源。
show_property 显示集群属性。不带属性时,显示集群所有属性。
crm(live)configure# show_property
stop-orphan-resources election-timeout dc-deadtime node-health-green placement-strategy
node-action-limit symmetric-cluster stonith-timeout maintenance-mode enable-acl
default-action-timeout batch-limit node-health-yellow pe-warn-series-max start-failure-is-fatal
enable-startup-probes shutdown-escalation stop-orphan-actions stop-all-resources default-resource-stickiness
no-quorum-policy cluster-recheck-interval dc-version cluster-infrastructure startup-fencing
concurrent-fencing crmd-integration-timeout stonith-enabled stonith-watchdog-timeout pe-input-series-max
crmd-finalization-timeout stonith-action have-watchdog pe-error-series-max migration-limit
is-managed-default load-threshold node-health-red node-health-strategy remove-after-stop
cluster-delay crmd-transition-delay
crm(live)configure# show_property enable-acl
false
pe-warn-series-max、pe-input-series-max、pe-error-series-max 代表日志深度。
cluster-recheck-interval是节点重新检查的频率。
no-quorum-policy="ignore"可以解决此双节点的问题, 缺省是“stop”。在双节点一下,需要忽略法定仲裁,集群才正常。即设置属性值为ignore。
stonith-enabled:stonith是一种能够接受指令断电的物理设备,测试环境无此设备,如果不关闭该选项,执行crm命令总是含其报错信息。stonith翻译为爆头,就是fence。
migration-threshold: 属性,可用于确定资源因故障转移到其他节点的阈值。
maintenance-mode:保持模式下,所有的资源处理 unmanaged状态。在crm_mon 命令下显示: *** Resource management is DISABLED ***。 资源的start、stop命令无效。通过资源的 maintenance命令可以控制具体的资源。

定义HAProxy和VIP必须在同一节点上运行:
#crm configure colocation haproxy-with-vip INFINITY: haproxy myvip
定义先接管VIP之后才启动HAProxy:
# crm configure order haproxy-after-vip mandatory: myvip haproxy
由于需要将集群资源绑定到VIP,需要修改各节点的内核参数:
# echo 'net.ipv4.ip_nonlocal_bind = 1'>>/etc/sysctl.conf
# sysctl -p
cluster
init
crm(live)cluster# help init
Initializes a new HA cluster Installs and configures a basic HA cluster on a set of nodes. Usage: init node1 node2 node3
init --dry-run node1 node2 node3
crm(live)cluster# init ddd
INFO: Initialize a new cluster
INFO: Nodes: ddd
ERROR: [ddd]: Start: Exited with error code , Error output: command-line: line : Bad configuration option: ControlPersist
ERROR: [ddd]: Clean: Exited with error code , Error output: command-line: line : Bad configuration option: ControlPersist
ERROR: cluster.init: Failed to connect to one or more of these hosts via SSH: ddd
增加配置属性:
crm(live)configure# show
node : vClass-2lgAr
property cib-bootstrap-options: \
have-watchdog=false \
dc-version=1.1.--e174ec8 \
cluster-infrastructure=corosync \
cluster-name=fMOQ0nGciUIFxoRq
crm(live)configure# property stonith-enabled=true
crm(live)configure# show
node : vClass-2lgAr
property cib-bootstrap-options: \
have-watchdog=false \
dc-version=1.1.--e174ec8 \
cluster-infrastructure=corosync \
cluster-name=fMOQ0nGciUIFxoRq \
stonith-enabled=true
crm(live)configure#
crm(live)configure# property stonith-action=reboot
crm(live)configure# property stonith-timeout=120s
crm(live)configure# property no-quorum-policy=stop
crm(live)configure# rsc_defaults resource-stickiness=
crm(live)configure# property symmetric-cluster=false
crm(live)configure# property crmd-transition-delay=5s
crm(live)configure# property start-failure-is-fatal="FALSE"
crm(live)configure# rsc_defaults migration-threshold=
crm(live)configure# show
node : vClass-2lgAr
property cib-bootstrap-options: \
have-watchdog=false \
dc-version=1.1.--e174ec8 \
cluster-infrastructure=corosync \
cluster-name=fMOQ0nGciUIFxoRq \
stonith-enabled=true \
stonith-action=reboot \
stonith-timeout=120s \
no-quorum-policy=stop \
symmetric-cluster=false \
crmd-transition-delay=5s \
start-failure-is-fatal=FALSE
rsc_defaults rsc-options: \
resource-stickiness= \
migration-threshold=
ra
info
crm(live)ra# help info
Show meta data for a RA Show the meta-data of a resource agent type. This is where users
can find information on how to use a resource agent. It is also
possible to get information from some programs: pengine,
crmd, cib, and stonithd. Just specify the program name
instead of an RA. Usage: info [<class>:[<provider>:]]<type>
info <type> <class> [<provider>] (obsolete) Example: info apache
info ocf:pacemaker:Dummy
info stonith:ipmilan
info pengine crm(live)ra# info lsb:netconsole
lsb:netconsole netconsole Operations' defaults (advisory minimum): start timeout=
stop timeout=
status timeout=
restart timeout=
force-reload timeout=
monitor timeout= interval=
resource
failcount
Manage failcounts Show/edit/delete the failcount of a resource. Usage: failcount <rsc> set <node> <value>
failcount <rsc> delete <node>
failcount <rsc> show <node> Example: failcount fs_0 delete node2
ban / unban 阻止一个资源到一个节点上
crm(live)resource# help ban ## 当ban 的node为资源正在运行的节点,将触发迁移
Ban a resource from a node 创建一个 rsc_location constraint(约束), 通过 crm_resource --clear 可以清除此约束。 通过资源的contraints命令,可以查看资源的位置约束条件 Ban a resource from running on a certain node. If no node is given
as argument, the resource is banned from the current location. See migrate for details on other arguments. Usage: ban <rsc> [<node>] [<lifetime>] [force]
crm(live)resource# help unban 通 unmigrade/unmove. 清除 migrate/ban/move 生成的 约束条件。
Unmigrate a resource to another node
(Redirected from unban to unmigrate) Remove the constraint generated by the previous migrate command. Usage: unmigrate <rsc>
manage/unmange 使资源是否在管理状态。
Put a resource into unmanaged mode 是资源不受管理。 可以对资源进行 启动(start)、停止(stop)。不支持: 迁移(migrate、move),所在节点停止后,资源处于stop状态, Unmanage a resource using the is-managed attribute. If there
are multiple meta attributes sets, the attribute is set in all of
them. If the resource is a clone, all is-managed attributes are
removed from the children resources. For details on group management see options manage-children. Usage: unmanage <rsc>
maintenance 是资源是否处于保持状态。
crm(live)resource# help maintenace 处于保持状态的资源,不受crm的管理,不支持对资源的 启动(start)、停止(stop)、前置(migrate、move)。设置后,在资源中有一个属性对应: maintenance=false/true
Enable/disable per-resource maintenance mode Enables or disables the per-resource maintenance mode. When this mode
is enabled, no monitor operations will be triggered for the resource. Usage: maintenance <resource> [on|off|true|false] Example: maintenance rsc1
maintenance rsc2 off
contraints 显示资源的约束条件(location、colocation)
crm(live)resource# help contraints
Show constraints affecting a resource Display the location and colocation constraints affecting the
resource. Usage: constraints <rsc>
migrate(move)/unmigrate (unmove)
crm(live)resource# help migrate ## 迁移一个资源到另一个节点。 生一个 contraints (可以带时效的)。通过资源的contraints可以查看。
Migrate a resource to another node Migrate a resource to a different node. If node is left out, the
resource is migrated by creating a constraint which prevents it from
running on the current node. Additionally, you may specify a
lifetime for the constraint---once it expires, the location
constraint will no longer be active. Usage: migrate <rsc> [<node>] [<lifetime>] [force]
crm(live)resource# help unmigrate ## 取消 migrate 产生的 location 约束
Unmigrate a resource to another node Remove the constraint generated by the previous migrate command. Usage: unmigrate <rsc>
scores 显示所有资源分配分数
crm(live)resource# help scores
Display resource scores Display the allocation scores for all resources. Usage: scores
operations 显示有效的资源操作
crm(live)resource# help operations
Show active resource operations Show active operations, optionally filtered by resource and node. Usage: operations [<rsc>] [<node>]
meta 设置、显示、删除资源的元数据属性
crm(live)resource# help meta ## 通过 ra 的 info 可以查看资源的参数和支持操作
Manage a meta attribute Show/edit/delete a meta attribute of a resource. Currently, all
meta attributes of a resource may be managed with other commands
such as resource stop. Usage: meta <rsc> set <attr> <value>
meta <rsc> delete <attr>
meta <rsc> show <attr> Example: meta ip_0 set target-role stopped
param 设置、删除、显示资源的属性
crm(live)resource# help param
Manage a parameter of a resource Show/edit/delete a parameter of a resource. Usage: param <rsc> set <param> <value>
param <rsc> delete <param>
param <rsc> show <param> Example: param ip_0 show ip
配置
/etc/crm/crm.conf
日志
注:
crmsh 从2014年10月份的版本中2.2.0开始使用systemd服务,即 systemctl命令行管理 corosync、pacemaker服务。
other
PCS(Pacemaker/Corosync configuration system)命令
fence-agents
一、建立群集:
创建集群
启动集群
设置资源默认粘性(防止资源回切)
设置资源超时时间
二个节点时,忽略节点quorum功能
没有 Fencing设备时,禁用STONITH 组件功能
在 stonith-enabled="false" 的情况下,分布式锁管理器 (DLM) 等资源以及依赖DLM 的所有服务(例如 cLVM2、GFS2 和 OCFS2)都将无法启动。
验证群集配置信息
二、建立群集资源
1、查看可用资源
2、配置虚拟IP
三、调整群集资源
1、配置资源约束
[shell]# pcs resource group add WebSrvs ClusterIP ## 配置资源组,组中资源会在同一节点运行
[shell]# pcs resource group remove WebSrvs ClusterIP ## 移除组中的指定资源
[shell]# pcs resource master WebDataClone WebData ## 配置具有多个状态的资源,如 DRBD master/slave状态
[shell]# pcs constraint colocation add WebServer ClusterIP INFINITY ## 配置资源捆绑关系
[shell]# pcs constraint colocation remove WebServer ## 移除资源捆绑关系约束中资源
[shell]# pcs constraint order ClusterIP then WebServer ## 配置资源启动顺序
[shell]# pcs constraint order remove ClusterIP ## 移除资源启动顺序约束中资源
[shell]# pcs constraint ## 查看资源约束关系, pcs constraint --full
2、配置资源位置
[shell]# pcs constraint location WebServer prefers node11 ## 指定资源默认某个节点,node=50 指定增加的 score
[shell]# pcs constraint location WebServer avoids node11 ## 指定资源避开某个节点,node=50 指定减少的 score
[shell]# pcs constraint location remove location-WebServer ## 移除资源节点位置约束中资源ID,可用pcs config获取
[shell]# pcs constraint location WebServer prefers node11=INFINITY ## 手工移动资源节点,指定节点资源的 score of INFINITY
[shell]# crm_simulate -sL ## 验证节点资源 score 值
3、修改资源配置
[shell]# pcs resource update WebFS ## 更新资源配置
[shell]# pcs resource delete WebFS ## 删除指定资源
4、管理群集资源
[shell]# pcs resource disable ClusterIP ## 禁用资源
[shell]# pcs resource enable ClusterIP ## 启用资源
[shell]# pcs resource failcount show ClusterIP ## 显示指定资源的错误计数
[shell]# pcs resource failcount reset ClusterIP ## 清除指定资源的错误计数
[shell]# pcs resource cleanup ClusterIP ## 清除指定资源的状态与错误计数
包括:创建资源、配置约束、指定故障转移节点和故障回复节点、配置资源监视、启动或删除资源、配置资源组或克隆资源,以及手动迁移资源。
创建VIP资源:
corosync和pacemaker状态无误,就能创建VIP资源了。我的VIP是“10.0.0.10”:
# crm configure primitive myvip ocf:heartbeat:IPaddr2 params ip="10.0.0.10" cidr_netmask="24" op monitor interval="30s"
常见的HA开源方案:
heartbeat v1 + haresources
heartbeat v2 + crm
heartbeat v3 + cluster-glue + pacemaker
corosync + cluster-glue + pacemaker
cman + rgmanager
keepalived + script
OCF 返回代码
根据 OCF 规范,有一些关于操作必须返回的退出代码的严格定义。群集会始终检查返回代码与预期结果是否相符。如果结果与预期值不匹配,则将操作视为失败,并将启动恢复操作。有三种类型的故障恢复:
|
恢复类型 |
描述 |
群集执行的操作 |
|---|---|---|
|
软 |
发生临时错误。 |
重启动资源或将它移到新位置。 |
|
硬 |
发生非临时错误。该错误可能特定于当前节点。 |
将资源移到别处,避免在当前节点上重试该资源。 |
|
致命 |
发生所有群集节点共有的非临时错误。这意味着指定了错误的配置。 |
停止资源,避免在任何群集节点上启动该资源。 |
假定将某个操作视为已失败,下表概括了不同的 OCF 返回代码以及收到相应的错误代码时群集将启动的恢复类型。
|
OCF 返回代码 |
OCF 别名 |
描述 |
恢复类型 |
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
OCF_SUCCESS |
成功。命令成功完成。这是所有启动、停止、升级和降级命令的所需结果。 |
软 |
|
1 |
OCF_ERR_GENERIC |
通用 |
软 |
|
2 |
OCF_ERR_ARGS |
此计算机上的资源配置无效(例如,它引用了节点上找不到的某个位置/工具)。 |
硬 |
|
3 |
OCF_ERR_UNIMPLEMENTED |
请求的操作未实现。 |
硬 |
|
4 |
OCF_ERR_PERM |
资源代理不具备完成该任务的足够特权。 |
硬 |
|
5 |
OCF_ERR_INSTALLED |
资源所需的工具未安装在此计算机上。 |
硬 |
|
6 |
OCF_ERR_CONFIGURED |
资源的配置无效(例如,缺少必需的参数)。 |
致命 |
|
7 |
OCF_NOT_RUNNING |
资源未运行。群集将不会尝试停止为任何操作返回此代码的资源。 此 OCF 返回代码可能需要或不需要资源恢复,这取决于所需的资源状态。如果出现意外,则执行软恢复。 |
不适用 |
|
8 |
OCF_RUNNING_MASTER |
资源正在主节点中运行。 |
软 |
|
9 |
OCF_FAILED_MASTER |
资源在主节点中,但已失败。资源将再次被降级、停止再重启动(然后也可能升级)。 |
软 |
|
其他 |
不适用 |
自定义错误代码。 |
软 |
专有名词:
STONITH : ("Shoot The Other Node In The Head" or "Shoot The Offending Node In The Head")。 关闭其他节点。 STONITH 设备是一个电源开关,用于群集重设置被认为出现故障的节点。重设置没有检测信号的节点是确保存在但出现故障的节点未执行数据破坏的唯一可靠方法。
Resource Agent: 用来控制服务启停、监控服务状态的脚本集合,这些脚本将被LRM调用从而实现各种资源启动、停止、监控等等。
FAQ:
1. 启动corosync-notifyd服务失败,在/var/log/messages出现如下信息
err daemon vClass-6WUNV notifyd[]: [error] Not compiled with DBus support enabled, exiting.
2. 各节点之间ssh互信
[root@node1 ~]# ssh-keygen -t rsa -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa -P ''
[root@node1 ~]# ssh-copy-id -i .ssh/id_rsa.pub root@node2.test.com
建立互信后,通过shell访问时,依然需要输入密码。需要修改配置文件 /etc/ssh/sshd_config 中 StrictModes 为 no。 缺省为yes
#LoginGraceTime 2m
#PermitRootLogin yes
StrictModes no
#MaxAuthTries
#MaxSessions
修改完毕配置文件,需要重启 sshd服务
service sshd restart
3. ssh过低导致出现如下问题
crm(live)cluster# health
INFO: Check the health of the cluster
INFO: Nodes: vClass-CPLjR, vClass-2lgAr
ERROR: [vClass-CPLjR]: Start: Exited with error code , Error output: command-line: line : Bad configuration option: ControlPersist
ERROR: [vClass-CPLjR]: Clean: Exited with error code , Error output: command-line: line : Bad configuration option: ControlPersist
ERROR: cluster.health: Failed to connect to one or more of these hosts via SSH: vClass-CPLjR
4. 遇到第一个问题,如果有多个网卡用来做心跳怎么办?
心跳IP的配置在corosync.conf中totem配置项下的interface子项。多个心跳网卡配置多个interface,并把ringnumber加1(第一个是0),但是要注意totem配置中添加rrp_mode:active或者passive不然启动orosync时会报错。acitve对应延迟较低,但是性能较差,passive表示没看到英文解释。。。默认情况下单个心跳rrp_mode是none的。
TIPs:rrp即路由冗余协议,我们接触到比较多的是keepalived里面的vrrp。
5. 资源默认不起动问题
configure下直接edite,在资源配置下方的meta后添加
meta target-role="Started"
链接:
corosync 官网: http://corosync.github.io/corosync/
pacemaker 官网: http://clusterlabs.org/
crmsh 官网: https://github.com/ClusterLabs/crmsh/tree/master
http://flymanhi.blog.51cto.com/1011558/1435851/
https://linux.die.net/man/8/dlm_controld
PCS命令配置corosync&pacemaker群集操作步骤 https://wenku.baidu.com/view/b2a3199bc281e53a5902ff7c.html
corosync+pacemaker安装配置实验 https://wenku.baidu.com/view/e69f537904a1b0717fd5ddff.html?re=view
corosync+pacemaker+crmsh实现高可用 http://www.2cto.com/net/201507/425844.html
STONITH https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/STONITH
corosync基本使用的更多相关文章
- 基于corosync+pacemaker+drbd+LNMP做web服务器的高可用集群
实验系统:CentOS 6.6_x86_64 实验前提: 1)提前准备好编译环境,防火墙和selinux都关闭: 2)本配置共有两个测试节点,分别coro1和coro2,对应的IP地址分别为192.1 ...
- 手动配置三台虚拟机pacemaker+corosync并添加httpd服务
创建三台虚拟机,实验环境:centos7.1,选择基础设施服务安装. 每台虚拟机两块网卡,第一块为pxe,第二块连通外网,手动为两块网卡配置IP.网关,使它们都能ping通外网并可以互相通过hostn ...
- pacemaker+corosync/heartbeat对比及资源代理RA脚本
一.Pacemaker概念 (1)Pacemaker(心脏起搏器),是一个高可用的群集资源管理器.它实现最大可用性资源管理的节点和资源级故障检测和恢复,通过使用首选集群基础设施(Corosync或He ...
- ZABBIX冗余架构构筑(Centos6.4+pacemaker+corosync+drbd)
基本构成: 用pacemaker+corosync控制心跳和资源迁移 用drbd同步zabbix配置文件和mysql数据库 所有软件都用yum安装至默认路径 主机的drbd领域挂载至/drbd,备机不 ...
- coroSync packmarker
CoroSync+Pacemaker实现web高可用 2015-04-12 23:38:19 标签:CoroSync pacemaker 原创作品,允许转载,转载时请务必以超链接形式标明文章 原始出处 ...
- corosync+pacemaker实现高可用(HA)集群
corosync+pacemaker实现高可用(HA)集群(一) 重要概念 在准备部署HA集群前,需要对其涉及的大量的概念有一个初步的了解,这样在实际部署配置时,才不至于不知所云 资源.服务与 ...
- Corosync+Pacemaker+DRBD+MySQL 实现高可用(HA)的MySQL集群
大纲一.前言二.环境准备三.Corosync 安装与配置四.Pacemaker 安装与配置五.DRBD 安装与配置六.MySQL 安装与配置七.crmsh 资源管理 推荐阅读: Linux 高可用(H ...
- corosync+pacemaker and drbd实现mysql高可用集群
DRBD:Distributed Replicated Block Device 分布式复制块设备,原理图如下 DRBD 有主双架构和双主架构的,当处于主从架构时,这个设备一定只有一个节点是可以读写的 ...
- 【原】ubuntu下Mysql的HA(corosync+pacemaker+drbd)
一.前提准备: 1.OS:ubuntu 12.04 2.cat /etc/hosts: 127.0.0.1 localhost 192.168.153.154 ha1 192.168.153.155 ...
- LINUX HA:Pacemaker + Corosync初配成功
参考很多文档: http://zhumeng8337797.blog.163.com/blog/static/100768914201218115650522/ 下一步,想想这个PC组和与HAPROX ...
随机推荐
- 15.3,redis持久化RDB与AOF
redis持久化 Redis是一种内存型数据库,一旦服务器进程退出,数据库的数据就会丢失,为了解决这个问题,Redis提供了两种持久化的方案,将内存中的数据保存到磁盘中,避免数据的丢失. RDB持久化 ...
- 内部类inner class
1.什么是内部类,为什么要用内部类? 可以将一个类定义在另一个类的定义内部,这就是内部类. 当描述事物时,事物的内部还有事物,该事物用内部类来描述,因为内部事物在使用外部事物的内容. 如: class ...
- Maven学习 (五) Elipse中发布一个Maven项目到Tomcat
对于maven初学者的我,经常遇到一个问题就是,maven项目创建成功后,本来已经添加了jar的依赖,但是发布到Tomcat中就是没有jar包存在, 启动Tomcat总是报没有找到jar包,可项目结构 ...
- convlstm学习资料
https://guanfuchen.github.io/post/markdown_blog_ws/markdown_blog_2017_11/convolutional_lstm_network_ ...
- hasOne
public boolean hasOne(int n) { int lastdigit=0; while( n >0 ){ lastdigit=(n % 10); if(lastdigit== ...
- NOIP2018 集训(一)
A题 Simple 时间限制:1000ms | 空间限制:256MB 问题描述 对于给定正整数\(n,m\),我们称正整数\(c\)为好的,当且仅当存在非负整数\(x,y\)使得\(n×x+m×y=c ...
- packstack测试环境安装heat
虚机all in one环境测试安装heat [root@armstrong ~]# tmux at -t mysql MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE hea ...
- PHP7 深入理解
读 PHP7的内核剖析 php7-internal 记录 3 PHP的相关组成 3.1 SAPI php常见的四种运行模式 SAPI:Server Application Programming In ...
- (总结)Nginx与Apache、Tomcat、Resin动静分离核心配置
PS:近来有几个刚使用nginx的新童鞋老问我,nginx+fastcgi不够稳定,偶尔出现502错误,怎么解决?本人使用nginx也有3年多了,也认为php-fpm模块不够稳定,在访问量不大的时候没 ...
- PHP面向对象 封装与继承
知识点: PHP封装三个关键词: 一.public 公有的,被public修饰的属性和方法,对象可以任意访问和调用 二.private 私有的,被private修饰的属性和方法,只能在类内部的方法可以 ...
