OpenCV笔记 1
| Structure Contains | Represents |
| CvPoint int x, y | Point in image |
| CvPoint2D32f float x, y | Points in R 2 |
| CvPoint3D32f float x, y, z | Points in R 3 |
| CvSize int width, height | Size of image |
| CvRect int x, y, width, height | Portion of image |
| CvScalar double val[4] | RGBA value |
cvScalar() , takes one, two, three, or four arguments and assigns those arguments to the corresponding elements of val[] . set四个值
cvRealScalar() ; it takes one argument, which it assigns to val[0] while setting the other entries to 0. set第一个值,其余为0
cvScalarAll() , which takes a single argument but sets all four elements of val[] to that same argument. 全set成同一个值
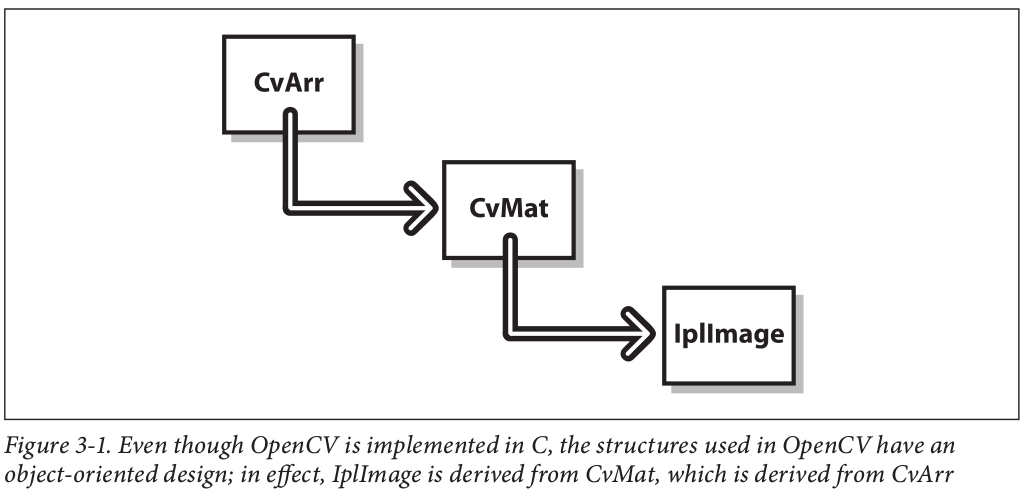
For all intents andpurposes, an IplImage can be thought of as being derived from CvMat . Therefore, it is best to understand the (would-be) base class before attempting to understand the added complexities of the derived class. A third class, called CvArr , can be thought of as an abstract base class from which CvMat is itself derived. You will oft en see CvArr (or, more accurately, CvArr* ) in function prototypes. When it appears, it is acceptable to pass CvMat* or IplImage* to the routine.
32-bit floats ( CV_32FC1 ),
unsigned integer 8-bit triplets ( CV_8UC3 )
typedef struct CvMat {
int type;
int step;
int* refcount;
// for internal use only
union {
uchar* ptr;
short* s;
int* i;
float* fl;
double* db;
} data;
union {
int rows;
int height;
};
union {
int cols;
int width;
};
} CvMat;
cvCreateMatHeader() creates the CvMat structure without allocating memory for the data.
cvCreateData() handles the data allocation.
cvCreateMat() = cvCreateMatHeader() + cvCreateData() .
cvCloneMat(CvMat*) creates a new matrix from an existing one.*
cvReleaseMat(CvMat**) release.
* cvCloneMat() and other OpenCV functions containing the word “clone” not only create a new header that
is identical to the input header, they also allocate a separate data area and copy the data from the source to
the new object.

* For the regular two-dimensional matrices discussed here, dimension zero (0) is always the “width” and dimension one (1) is always the height.
二维矩阵中,维度0通常是宽,维度1通常是高。
矩阵某个位置的元素:the location of any given point is given by the formula:
δ = ( row ) ⋅ N cols ⋅ N channels + ( col ) ⋅ N channels + ( channel) 通道
IplImage header structure
typedef struct _IplImage {
int nSize;
int ID;
int nChannels;
int alphaChannel;
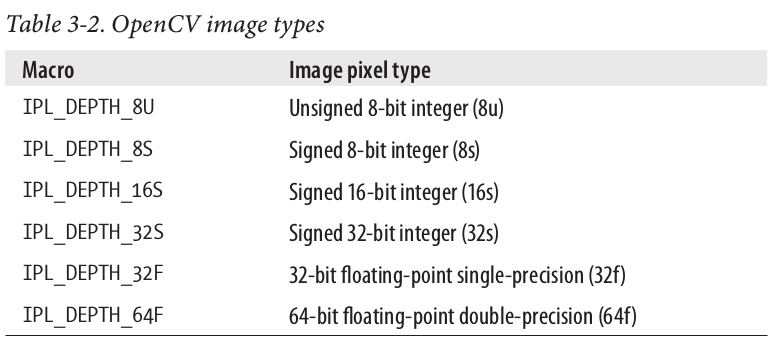
int depth;
char colorModel[];
char channelSeq[];
int dataOrder;
int origin;
int align;
int width;
int height;
struct _IplROI* roi;
struct _IplImage* maskROI;
void* imageId;
struct _IplTileInfo* tileInfo;
int imageSize;
char* imageData;
int widthStep;
int BorderMode[];
int BorderConst[];
char* imageDataOrigin;
} IplImage;
Th e possible values for nChannels are 1, 2, 3, or 4.
origin : IPL_ORIGIN_TL or IPL_ORIGIN_BL (the origin of coordinates being located in either the upper-left or lower-left corners of the image, respectively.)
dataOrder: IPL_DATA_ORDER_PIXEL or IPL_DATA_ORDER_PLANE .(whether the data should be packed with multiple channels one aft er the other for each pixel (interleaved, the usual case), or rather all of the channels clustered into image planes with the planes placed one aft er another.)
ROI:感兴趣的区域
COI:感兴趣的通道 channel of interest


矩阵和图像操作的方法
cvAbs 计算数组中所有元素的绝对值
cvAbsDiff 计算两个数组差值的绝对值

cvXXX 对两个数组作XXX操作
cvXXXS 对数组和一个固定值作XXX操作
cvXXXRS 对固定值和数组作XXX操作(和cvXXXS相反)
void cvCvtColor(
const CvArr* src,
CvArr* dst,
int code
);
code转换方式




RGB555
RGB565
RGB24
RGB32
HSV(Hue, Saturation, Value)是根据颜色的直观特性由A. R. Smith在1978年创建的一种颜色空间, 也称六角锥体模型(Hexcone Model)。








OpenCV笔记 1的更多相关文章
- OpenCV笔记大集锦(转载)
整理了我所了解的有关OpenCV的学习笔记.原理分析.使用例程等相关的博文.排序不分先后,随机整理的.如果有好的资源,也欢迎介绍和分享. 1:OpenCV学习笔记 作者:CSDN数量:55篇博文网址: ...
- opencv笔记6:角点检测
time:2015年10月09日 星期五 23时11分58秒 # opencv笔记6:角点检测 update:从角点检测,学习图像的特征,这是后续图像跟踪.图像匹配的基础. 角点检测是什么鬼?前面一篇 ...
- opencv笔记5:频域和空域的一点理解
time:2015年10月06日 星期二 12时14分51秒 # opencv笔记5:频域和空域的一点理解 空间域和频率域 傅立叶变换是f(t)乘以正弦项的展开,正弦项的频率由u(其实是miu)的值决 ...
- opencv笔记4:模板运算和常见滤波操作
time:2015年10月04日 星期日 00时00分27秒 # opencv笔记4:模板运算和常见滤波操作 这一篇主要是学习模板运算,了解各种模板运算的运算过程和分类,理论方面主要参考<图像工 ...
- opencv笔记3:trackbar简单使用
time:2015年 10月 03日 星期六 13:54:17 CST # opencv笔记3:trackbar简单使用 当需要测试某变量的一系列取值取值会产生什么结果时,适合用trackbar.看起 ...
- opencv笔记2:图像ROI
time:2015年 10月 03日 星期六 12:03:45 CST # opencv笔记2:图像ROI ROI ROI意思是Region Of Interests,感兴趣区域,是一个图中的一个子区 ...
- opencv笔记1:opencv的基本模块,以及环境搭建
opencv笔记1:opencv的基本模块,以及环境搭建 安装系统 使用fedora22-workstation-x86_64 安装opencv sudo dnf install opencv-dev ...
- OpenCV基本架构[OpenCV 笔记0]
最近正在系统学习OpenCV,将不定期发布笔记,主要按照毛星云的<OpenCV3编程入门>的顺序学习,会参考官方教程和文档.学习工具是Xcode+CMake,会对书中一部分内容更正,并加入 ...
- 查找并绘制轮廓[OpenCV 笔记XX]
好久没有更新了,原谅自己放了个假最近又在赶进度,所以...更新的内容是很靠后的第八章,因为最近工作要用就先跳了,后面会更新笔记编号...加油加油! 在二值图像中寻找轮廓 void cv::findCo ...
- 访问图像中的像素[OpenCV 笔记16]
再更一发好久没更过的OpenCV,不过其实写到这个部分对计算机视觉算法有所了解的应该可以做到用什么查什么了,所以后面可能会更的慢一点吧,既然开了新坑,还是机器学习更有研究价值吧... 图像在内存中的存 ...
随机推荐
- servlet cannot be resolved to a type解决办法
工程里的路径权限高,eclipse并到classpath里寻找jar位置. 项目名-->右键 Property-->选择 Build Path-->选择 Configure Buil ...
- 配置SSH密码登录
在客户端生成公钥: ssh-keygen –t rsa 生成的公钥默认位置在~/.ssh/目录 把公钥上传到服务器端: scp id_rsa.pub root@ip地址:文件保存路径 cat id_r ...
- java JDBC与MySQL 关于日间与日期
//MySQL Date类型 -> java.sql.Date java.sql.Date d = new java.sql.Date(Calendar.getInstance().getTim ...
- Eclipse中Maven的本地仓库引导配置
简单整理一下,方便理解操作. 1.本地拷贝maven文件后,打开maven中的.setting 文件: 2.配置文件: <?xml version="1.0" encodin ...
- [转载]Java开发在线打开编辑保存Word文件
Java调用logo是“P”图标的第三方插件,实现在线编辑保存Word文件(以jsp调用为例,支持SSM.SSH.SpringMVC等流行框架) 工具/原料 Eclipse或MyEclipse等j ...
- 用css方法 可以实现多行 超出宽度 出点点点号
overflow: hidden; -webkit-line-clamp: 2; display: -webkit-box; -webkit-box-orient: vertical;
- mysql 逻辑查询语句执行顺序
一 SELECT语句关键字的定义顺序 SELECT DISTINCT <select_list> FROM <left_table> <join_type> JOI ...
- 分布式_理论_04_ 3PC
一.前言 五.参考资料 1.分布式理论(四)—— 一致性协议之 3PC 2.分布式理论(四) - 3PC协议 3.
- C++结构体成员列表初始化
C++关于struct和class的区别,可以看上一篇文章:c ++ class和struct[转] 结构体成员列表初始化,来个例子: #include <iostream> #inclu ...
- 织梦dedecms如何批量替换文章内容和缩略图
文章来自:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_475ea1130101co6w.html 第一种方法: 进入后台,点左侧的采集,点选批量维护的数据库内容替换. 1.替换标题内 ...
