Kubernetes容器生命周期 —— 钩子函数详解(postStart、preStop)
1、概述
容器生命周期钩子(Container Lifecycle Hooks)监听容器生命周期的特定事件,并在事件发生时执行已注册的回调函数。
钩子函数能够感知自身生命周期中的事件,并在相应的时刻到来时运行用户指定的程序代码。
kubernetes在主容器的启动之后和停止之前提供了两个钩子函数:
- postStart:一种容器钩子。该钩子在容器被创建后立刻触发,通知容器它已经被创建。该钩子不需要向其所对应的Hook Handler传入任何参数。如果该钩子对应的Hook Handler执行失败,则该容器会终止运行,并根据该容器的重启策略决定是否要重启该容器。更多信息,请参见Container Lifecycle Hooks。
- preStop :一种容器钩子。该钩子在容器被删除前触发,其所对应的Hook Handler必须在删除该容器的请求发送给Docker Daemon之前完成。在该钩子对应的Hook Handler完成后不论执行的结果如何,Docker Daemon会发送一个SIGTERN信号给Docker Daemon来删除该容器。更多信息,请参见Container Lifecycle Hooks 以及《详解Kubernetes Pod优雅退出》这篇博文。
2、钩子函数定义方式
钩子的回调函数支持两种方式定义动作,下面以 postStart 为例讲解,preStop 定义方式与其一致:
2.1 exec模式
在容器中执行指定的命令。如果命令退出时返回码为0,判定为执行成功。
示例:
lifecycle:
postStart:
exec:
command:
- cat
- /var/lib/redis.conf
2.2 httpGet模式
对容器中的指定端点执行HTTP GET请求,如果响应的状态码大于等于200且小于400,判定为执行成功。
httpGet模式支持以下配置参数:
Host:HTTP请求主机地址,不设置时默认为Pod的IP地址。
Path:HTTP请求路径,默认值是/。
Port:HTTP请求端口号。
Scheme:协议类型,支持HTTP和HTTPS协议,默认是HTTP。
HttpHeaders:自定义HTTP请求头。
示例:访问 http://192.168.2.150:80/users
lifecycle:
postStart:
httpGet:
path: /users
port: 80
host: 192.168.2.150
scheme: HTTP # 或者HTTPS
3、源码讲解
3.1 PostStart
Kubernetes源码(1.21.5,已在源码中移除dockershim模块):
pkg/kubelet/kuberuntime/kuberuntime_container.go:
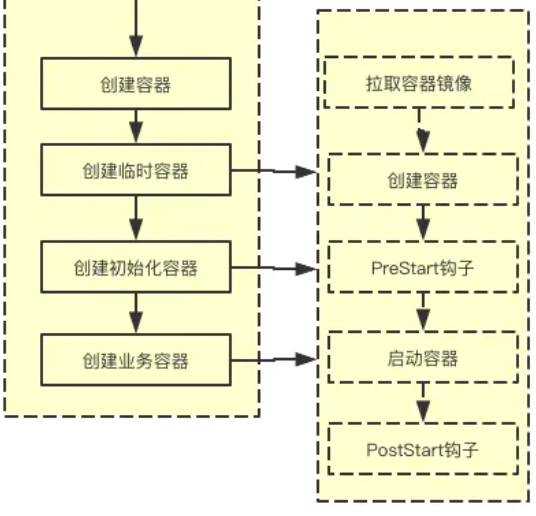
开始容器方法主要包括拉取镜像、创建容器、start容器、运行容器postStart钩子函数。
// startContainer starts a container and returns a message indicates why it is failed on error.
// It starts the container through the following steps:
// * pull the image
// * create the container
// * start the container
// * run the post start lifecycle hooks (if applicable)
func (m *kubeGenericRuntimeManager) startContainer(podSandboxID string, podSandboxConfig *runtimeapi.PodSandboxConfig, spec *startSpec, pod *v1.Pod, podStatus *kubecontainer.PodStatus, pullSecrets []v1.Secret, podIP string, podIPs []string) (string, error) {
container := spec.container // Step 1: pull the image.
imageRef, msg, err := m.imagePuller.EnsureImageExists(pod, container, pullSecrets, podSandboxConfig)
if err != nil {
s, _ := grpcstatus.FromError(err)
m.recordContainerEvent(pod, container, "", v1.EventTypeWarning, events.FailedToCreateContainer, "Error: %v", s.Message())
return msg, err
} // Step 2: create the container.
// For a new container, the RestartCount should be 0
restartCount := 0
containerStatus := podStatus.FindContainerStatusByName(container.Name)
if containerStatus != nil {
restartCount = containerStatus.RestartCount + 1
} target, err := spec.getTargetID(podStatus)
if err != nil {
s, _ := grpcstatus.FromError(err)
m.recordContainerEvent(pod, container, "", v1.EventTypeWarning, events.FailedToCreateContainer, "Error: %v", s.Message())
return s.Message(), ErrCreateContainerConfig
} containerConfig, cleanupAction, err := m.generateContainerConfig(container, pod, restartCount, podIP, imageRef, podIPs, target)
if cleanupAction != nil {
defer cleanupAction()
}
if err != nil {
s, _ := grpcstatus.FromError(err)
m.recordContainerEvent(pod, container, "", v1.EventTypeWarning, events.FailedToCreateContainer, "Error: %v", s.Message())
return s.Message(), ErrCreateContainerConfig
} err = m.internalLifecycle.PreCreateContainer(pod, container, containerConfig)
if err != nil {
s, _ := grpcstatus.FromError(err)
m.recordContainerEvent(pod, container, "", v1.EventTypeWarning, events.FailedToCreateContainer, "Internal PreCreateContainer hook failed: %v", s.Message())
return s.Message(), ErrPreCreateHook
} containerID, err := m.runtimeService.CreateContainer(podSandboxID, containerConfig, podSandboxConfig)
if err != nil {
s, _ := grpcstatus.FromError(err)
m.recordContainerEvent(pod, container, containerID, v1.EventTypeWarning, events.FailedToCreateContainer, "Error: %v", s.Message())
return s.Message(), ErrCreateContainer
}
err = m.internalLifecycle.PreStartContainer(pod, container, containerID)
if err != nil {
s, _ := grpcstatus.FromError(err)
m.recordContainerEvent(pod, container, containerID, v1.EventTypeWarning, events.FailedToStartContainer, "Internal PreStartContainer hook failed: %v", s.Message())
return s.Message(), ErrPreStartHook
}
m.recordContainerEvent(pod, container, containerID, v1.EventTypeNormal, events.CreatedContainer, fmt.Sprintf("Created container %s", container.Name)) // Step 3: start the container.
err = m.runtimeService.StartContainer(containerID)
if err != nil {
s, _ := grpcstatus.FromError(err)
m.recordContainerEvent(pod, container, containerID, v1.EventTypeWarning, events.FailedToStartContainer, "Error: %v", s.Message())
return s.Message(), kubecontainer.ErrRunContainer
}
m.recordContainerEvent(pod, container, containerID, v1.EventTypeNormal, events.StartedContainer, fmt.Sprintf("Started container %s", container.Name)) // Symlink container logs to the legacy container log location for cluster logging
// support.
// TODO(random-liu): Remove this after cluster logging supports CRI container log path.
containerMeta := containerConfig.GetMetadata()
sandboxMeta := podSandboxConfig.GetMetadata()
legacySymlink := legacyLogSymlink(containerID, containerMeta.Name, sandboxMeta.Name,
sandboxMeta.Namespace)
containerLog := filepath.Join(podSandboxConfig.LogDirectory, containerConfig.LogPath)
// only create legacy symlink if containerLog path exists (or the error is not IsNotExist).
// Because if containerLog path does not exist, only dangling legacySymlink is created.
// This dangling legacySymlink is later removed by container gc, so it does not make sense
// to create it in the first place. it happens when journald logging driver is used with docker.
if _, err := m.osInterface.Stat(containerLog); !os.IsNotExist(err) {
if err := m.osInterface.Symlink(containerLog, legacySymlink); err != nil {
klog.ErrorS(err, "Failed to create legacy symbolic link", "path", legacySymlink,
"containerID", containerID, "containerLogPath", containerLog)
}
} // Step 4: execute the post start hook.
if container.Lifecycle != nil && container.Lifecycle.PostStart != nil {
kubeContainerID := kubecontainer.ContainerID{
Type: m.runtimeName,
ID: containerID,
}
msg, handlerErr := m.runner.Run(kubeContainerID, pod, container, container.Lifecycle.PostStart)
if handlerErr != nil {
m.recordContainerEvent(pod, container, kubeContainerID.ID, v1.EventTypeWarning, events.FailedPostStartHook, msg)
if err := m.killContainer(pod, kubeContainerID, container.Name, "FailedPostStartHook", reasonFailedPostStartHook, nil); err != nil {
klog.ErrorS(fmt.Errorf("%s: %v", ErrPostStartHook, handlerErr), "Failed to kill container", "pod", klog.KObj(pod),
"podUID", pod.UID, "containerName", container.Name, "containerID", kubeContainerID.String())
}
return msg, fmt.Errorf("%s: %v", ErrPostStartHook, handlerErr)
}
} return "", nil
}
(1)关注下创建容器,kubelet调用docker csi,相当于执行 docker create 命令:
pkg/kubelet/cri/remote/remote_runtime.go:
// CreateContainer creates a new container in the specified PodSandbox.
func (r *remoteRuntimeService) CreateContainer(podSandBoxID string, config *runtimeapi.ContainerConfig, sandboxConfig *runtimeapi.PodSandboxConfig) (string, error) {
klog.V(10).InfoS("[RemoteRuntimeService] CreateContainer", "podSandboxID", podSandBoxID, "timeout", r.timeout)
ctx, cancel := getContextWithTimeout(r.timeout)
defer cancel() resp, err := r.runtimeClient.CreateContainer(ctx, &runtimeapi.CreateContainerRequest{
PodSandboxId: podSandBoxID,
Config: config,
SandboxConfig: sandboxConfig,
})
if err != nil {
klog.ErrorS(err, "CreateContainer in sandbox from runtime service failed", "podSandboxID", podSandBoxID)
return "", err
} klog.V(10).InfoS("[RemoteRuntimeService] CreateContainer", "podSandboxID", podSandBoxID, "containerID", resp.ContainerId)
if resp.ContainerId == "" {
errorMessage := fmt.Sprintf("ContainerId is not set for container %q", config.GetMetadata())
err := errors.New(errorMessage)
klog.ErrorS(err, "CreateContainer failed")
return "", err
} return resp.ContainerId, nil
}
(2)start容器,kubelet调用docker csi,相当于执行 docker start 命令:
pkg/kubelet/cri/remote/remote_runtime.go:
// StartContainer starts the container.
func (r *remoteRuntimeService) StartContainer(containerID string) error {
klog.V(10).InfoS("[RemoteRuntimeService] StartContainer", "containerID", containerID, "timeout", r.timeout)
ctx, cancel := getContextWithTimeout(r.timeout)
defer cancel() _, err := r.runtimeClient.StartContainer(ctx, &runtimeapi.StartContainerRequest{
ContainerId: containerID,
})
if err != nil {
klog.ErrorS(err, "StartContainer from runtime service failed", "containerID", containerID)
return err
}
klog.V(10).InfoS("[RemoteRuntimeService] StartContainer Response", "containerID", containerID) return nil
}
(3)运行容器postStart钩子函数(kubelet):
pkg/kubelet/lifecycle/handlers.go:
func (hr *handlerRunner) Run(containerID kubecontainer.ContainerID, pod *v1.Pod, container *v1.Container, handler *v1.Handler) (string, error) {
switch {
case handler.Exec != nil:
var msg string
// TODO(tallclair): Pass a proper timeout value.
output, err := hr.commandRunner.RunInContainer(containerID, handler.Exec.Command, 0)
if err != nil {
msg = fmt.Sprintf("Exec lifecycle hook (%v) for Container %q in Pod %q failed - error: %v, message: %q", handler.Exec.Command, container.Name, format.Pod(pod), err, string(output))
klog.V(1).ErrorS(err, "Exec lifecycle hook for Container in Pod failed", "execCommand", handler.Exec.Command, "containerName", container.Name, "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "message", string(output))
}
return msg, err
case handler.HTTPGet != nil:
msg, err := hr.runHTTPHandler(pod, container, handler)
if err != nil {
msg = fmt.Sprintf("HTTP lifecycle hook (%s) for Container %q in Pod %q failed - error: %v, message: %q", handler.HTTPGet.Path, container.Name, format.Pod(pod), err, msg)
klog.V(1).ErrorS(err, "HTTP lifecycle hook for Container in Pod failed", "path", handler.HTTPGet.Path, "containerName", container.Name, "pod", klog.KObj(pod))
}
return msg, err
default:
err := fmt.Errorf("invalid handler: %v", handler)
msg := fmt.Sprintf("Cannot run handler: %v", err)
klog.ErrorS(err, "Cannot run handler")
return msg, err
}
}
cri-dockerd源码:
(1)创建容器
core/container_create.go:
// CreateContainer creates a new container in the given PodSandbox
// Docker cannot store the log to an arbitrary location (yet), so we create an
// symlink at LogPath, linking to the actual path of the log.
func (ds *dockerService) CreateContainer(
_ context.Context,
r *v1.CreateContainerRequest,
) (*v1.CreateContainerResponse, error) {
podSandboxID := r.PodSandboxId
config := r.GetConfig()
sandboxConfig := r.GetSandboxConfig() if config == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("container config is nil")
}
if sandboxConfig == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("sandbox config is nil for container %q", config.Metadata.Name)
} labels := makeLabels(config.GetLabels(), config.GetAnnotations())
// Apply a the container type label.
labels[containerTypeLabelKey] = containerTypeLabelContainer
// Write the container log path in the labels.
labels[containerLogPathLabelKey] = filepath.Join(sandboxConfig.LogDirectory, config.LogPath)
// Write the sandbox ID in the labels.
labels[sandboxIDLabelKey] = podSandboxID apiVersion, err := ds.getDockerAPIVersion()
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("unable to get the docker API version: %v", err)
} image := ""
if iSpec := config.GetImage(); iSpec != nil {
image = iSpec.Image
}
containerName := makeContainerName(sandboxConfig, config)
mounts := config.GetMounts()
terminationMessagePath, _ := config.Annotations["io.kubernetes.container.terminationMessagePath"] sandboxInfo, err := ds.client.InspectContainer(r.GetPodSandboxId())
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("unable to get container's sandbox ID: %v", err)
}
createConfig := dockerbackend.ContainerCreateConfig{
Name: containerName,
Config: &container.Config{
Entrypoint: strslice.StrSlice(config.Command),
Cmd: strslice.StrSlice(config.Args),
Env: libdocker.GenerateEnvList(config.GetEnvs()),
Image: image,
WorkingDir: config.WorkingDir,
Labels: labels,
// Interactive containers:
OpenStdin: config.Stdin,
StdinOnce: config.StdinOnce,
Tty: config.Tty,
// Disable Docker's health check until we officially support it
// (https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/issues/25829).
Healthcheck: &container.HealthConfig{
Test: []string{"NONE"},
},
},
HostConfig: &container.HostConfig{
Mounts: libdocker.GenerateMountBindings(mounts, terminationMessagePath),
RestartPolicy: container.RestartPolicy{
Name: "no",
},
Runtime: sandboxInfo.HostConfig.Runtime,
},
} // Only request relabeling if the pod provides an SELinux context. If the pod
// does not provide an SELinux context relabeling will label the volume with
// the container's randomly allocated MCS label. This would restrict access
// to the volume to the container which mounts it first.
if selinuxOpts := config.GetLinux().GetSecurityContext().GetSelinuxOptions(); selinuxOpts != nil {
mountLabel, err := selinuxMountLabel(selinuxOpts)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("unable to generate SELinux mount label: %v", err)
}
if mountLabel != "" {
// Equates to "Z" in the old bind API
const shared = false
for _, m := range mounts {
if m.SelinuxRelabel {
if err := label.Relabel(m.HostPath, mountLabel, shared); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("unable to relabel %q with %q: %v", m.HostPath, mountLabel, err)
}
}
}
}
} hc := createConfig.HostConfig
err = ds.updateCreateConfig(
&createConfig,
config,
sandboxConfig,
podSandboxID,
securityOptSeparator,
apiVersion,
)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to update container create config: %v", err)
}
// Set devices for container.
devices := make([]container.DeviceMapping, len(config.Devices))
for i, device := range config.Devices {
devices[i] = container.DeviceMapping{
PathOnHost: device.HostPath,
PathInContainer: device.ContainerPath,
CgroupPermissions: device.Permissions,
}
}
hc.Resources.Devices = devices securityOpts, err := ds.getSecurityOpts(
config.GetLinux().GetSecurityContext().GetSeccomp(),
securityOptSeparator,
)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf(
"failed to generate security options for container %q: %v",
config.Metadata.Name,
err,
)
} hc.SecurityOpt = append(hc.SecurityOpt, securityOpts...) cleanupInfo, err := ds.applyPlatformSpecificDockerConfig(r, &createConfig)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
} createResp, createErr := ds.client.CreateContainer(createConfig)
if createErr != nil {
createResp, createErr = recoverFromCreationConflictIfNeeded(
ds.client,
createConfig,
createErr,
)
} if createResp != nil {
containerID := createResp.ID if cleanupInfo != nil {
// we don't perform the clean up just yet at that could destroy information
// needed for the container to start (e.g. Windows credentials stored in
// registry keys); instead, we'll clean up when the container gets removed
ds.setContainerCleanupInfo(containerID, cleanupInfo)
}
return &v1.CreateContainerResponse{ContainerId: containerID}, nil
} // the creation failed, let's clean up right away - we ignore any errors though,
// this is best effort
ds.performPlatformSpecificContainerCleanupAndLogErrors(containerName, cleanupInfo) return nil, createErr
}
调用CreateContainer方法(libdocker/kube_docker_client.go),然后作为 docker 客户端调用 docker 服务端 ContainerCreate 方法。
func (d *kubeDockerClient) CreateContainer(
opts dockerbackend.ContainerCreateConfig,
) (*dockercontainer.CreateResponse, error) {
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), d.timeout)
defer cancel()
// we provide an explicit default shm size as to not depend on docker daemon.
if opts.HostConfig != nil && opts.HostConfig.ShmSize <= 0 {
opts.HostConfig.ShmSize = defaultShmSize
}
createResp, err := d.client.ContainerCreate(
ctx,
opts.Config,
opts.HostConfig,
opts.NetworkingConfig,
nil,
opts.Name,
)
if ctxErr := contextError(ctx); ctxErr != nil {
return nil, ctxErr
}
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &createResp, nil
}
vendor/github.com/docker/docker/client/container_create.go:
// ContainerCreate creates a new container based on the given configuration.
// It can be associated with a name, but it's not mandatory.
func (cli *Client) ContainerCreate(ctx context.Context, config *container.Config, hostConfig *container.HostConfig, networkingConfig *network.NetworkingConfig, platform *ocispec.Platform, containerName string) (container.CreateResponse, error) {
var response container.CreateResponse // Make sure we negotiated (if the client is configured to do so),
// as code below contains API-version specific handling of options.
//
// Normally, version-negotiation (if enabled) would not happen until
// the API request is made.
if err := cli.checkVersion(ctx); err != nil {
return response, err
} if err := cli.NewVersionError(ctx, "1.25", "stop timeout"); config != nil && config.StopTimeout != nil && err != nil {
return response, err
}
if err := cli.NewVersionError(ctx, "1.41", "specify container image platform"); platform != nil && err != nil {
return response, err
}
if err := cli.NewVersionError(ctx, "1.44", "specify health-check start interval"); config != nil && config.Healthcheck != nil && config.Healthcheck.StartInterval != 0 && err != nil {
return response, err
}
if err := cli.NewVersionError(ctx, "1.44", "specify mac-address per network"); hasEndpointSpecificMacAddress(networkingConfig) && err != nil {
return response, err
} if hostConfig != nil {
if versions.LessThan(cli.ClientVersion(), "1.25") {
// When using API 1.24 and under, the client is responsible for removing the container
hostConfig.AutoRemove = false
}
if versions.GreaterThanOrEqualTo(cli.ClientVersion(), "1.42") || versions.LessThan(cli.ClientVersion(), "1.40") {
// KernelMemory was added in API 1.40, and deprecated in API 1.42
hostConfig.KernelMemory = 0
}
if platform != nil && platform.OS == "linux" && versions.LessThan(cli.ClientVersion(), "1.42") {
// When using API under 1.42, the Linux daemon doesn't respect the ConsoleSize
hostConfig.ConsoleSize = [2]uint{0, 0}
}
} // Since API 1.44, the container-wide MacAddress is deprecated and will trigger a WARNING if it's specified.
if versions.GreaterThanOrEqualTo(cli.ClientVersion(), "1.44") {
config.MacAddress = "" //nolint:staticcheck // ignore SA1019: field is deprecated, but still used on API < v1.44.
} query := url.Values{}
if p := formatPlatform(platform); p != "" {
query.Set("platform", p)
} if containerName != "" {
query.Set("name", containerName)
} body := configWrapper{
Config: config,
HostConfig: hostConfig,
NetworkingConfig: networkingConfig,
} serverResp, err := cli.post(ctx, "/containers/create", query, body, nil)
defer ensureReaderClosed(serverResp)
if err != nil {
return response, err
} err = json.NewDecoder(serverResp.body).Decode(&response)
return response, err
}
(2)start容器
core/container_start.go
// StartContainer starts the container.
func (ds *dockerService) StartContainer(
_ context.Context,
r *v1.StartContainerRequest,
) (*v1.StartContainerResponse, error) {
err := ds.client.StartContainer(r.ContainerId) // Create container log symlink for all containers (including failed ones).
if linkError := ds.createContainerLogSymlink(r.ContainerId); linkError != nil {
// Do not stop the container if we failed to create symlink because:
// 1. This is not a critical failure.
// 2. We don't have enough information to properly stop container here.
// Kubelet will surface this error to user via an event.
return nil, linkError
} if err != nil {
err = transformStartContainerError(err)
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to start container %q: %v", r.ContainerId, err)
} return &v1.StartContainerResponse{}, nil
}
libdocker/kube_docker_client.go
func (d *kubeDockerClient) StartContainer(id string) error {
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), d.timeout)
defer cancel()
err := d.client.ContainerStart(ctx, id, dockercontainer.StartOptions{})
if ctxErr := contextError(ctx); ctxErr != nil {
return ctxErr
}
return err
}
github.com/docker/docker/client/container_start.go
// ContainerStart sends a request to the docker daemon to start a container.
func (cli *Client) ContainerStart(ctx context.Context, containerID string, options container.StartOptions) error {
query := url.Values{}
if len(options.CheckpointID) != 0 {
query.Set("checkpoint", options.CheckpointID)
}
if len(options.CheckpointDir) != 0 {
query.Set("checkpoint-dir", options.CheckpointDir)
} resp, err := cli.post(ctx, "/containers/"+containerID+"/start", query, nil, nil)
ensureReaderClosed(resp)
return err
}
moby源码(docker改名为moby):
(1)创建容器
api/server/router/container/container.go:
router.NewPostRoute("/containers/create", r.postContainersCreate),
api/server/router/container/container_routes.go:
func (s *containerRouter) postContainersCreate(ctx context.Context, w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request, vars map[string]string) error {
if err := httputils.ParseForm(r); err != nil {
return err
}
if err := httputils.CheckForJSON(r); err != nil {
return err
}
name := r.Form.Get("name")
config, hostConfig, networkingConfig, err := s.decoder.DecodeConfig(r.Body)
if err != nil {
return err
}
version := httputils.VersionFromContext(ctx)
adjustCPUShares := versions.LessThan(version, "1.19")
// When using API 1.24 and under, the client is responsible for removing the container
if hostConfig != nil && versions.LessThan(version, "1.25") {
hostConfig.AutoRemove = false
}
if hostConfig != nil && versions.LessThan(version, "1.40") {
// Ignore BindOptions.NonRecursive because it was added in API 1.40.
for _, m := range hostConfig.Mounts {
if bo := m.BindOptions; bo != nil {
bo.NonRecursive = false
}
}
// Ignore KernelMemoryTCP because it was added in API 1.40.
hostConfig.KernelMemoryTCP = 0
// Older clients (API < 1.40) expects the default to be shareable, make them happy
if hostConfig.IpcMode.IsEmpty() {
hostConfig.IpcMode = container.IPCModeShareable
}
}
if hostConfig != nil && versions.LessThan(version, "1.41") && !s.cgroup2 {
// Older clients expect the default to be "host" on cgroup v1 hosts
if hostConfig.CgroupnsMode.IsEmpty() {
hostConfig.CgroupnsMode = container.CgroupnsModeHost
}
}
if hostConfig != nil && versions.LessThan(version, "1.42") {
for _, m := range hostConfig.Mounts {
// Ignore BindOptions.CreateMountpoint because it was added in API 1.42.
if bo := m.BindOptions; bo != nil {
bo.CreateMountpoint = false
}
// These combinations are invalid, but weren't validated in API < 1.42.
// We reset them here, so that validation doesn't produce an error.
if o := m.VolumeOptions; o != nil && m.Type != mount.TypeVolume {
m.VolumeOptions = nil
}
if o := m.TmpfsOptions; o != nil && m.Type != mount.TypeTmpfs {
m.TmpfsOptions = nil
}
if bo := m.BindOptions; bo != nil {
// Ignore BindOptions.CreateMountpoint because it was added in API 1.42.
bo.CreateMountpoint = false
}
}
}
if hostConfig != nil && versions.GreaterThanOrEqualTo(version, "1.42") {
// Ignore KernelMemory removed in API 1.42.
hostConfig.KernelMemory = 0
for _, m := range hostConfig.Mounts {
if o := m.VolumeOptions; o != nil && m.Type != mount.TypeVolume {
return errdefs.InvalidParameter(fmt.Errorf("VolumeOptions must not be specified on mount type %q", m.Type))
}
if o := m.BindOptions; o != nil && m.Type != mount.TypeBind {
return errdefs.InvalidParameter(fmt.Errorf("BindOptions must not be specified on mount type %q", m.Type))
}
if o := m.TmpfsOptions; o != nil && m.Type != mount.TypeTmpfs {
return errdefs.InvalidParameter(fmt.Errorf("TmpfsOptions must not be specified on mount type %q", m.Type))
}
}
}
if hostConfig != nil && runtime.GOOS == "linux" && versions.LessThan(version, "1.42") {
// ConsoleSize is not respected by Linux daemon before API 1.42
hostConfig.ConsoleSize = [2]uint{0, 0}
}
var platform *specs.Platform
if versions.GreaterThanOrEqualTo(version, "1.41") {
if v := r.Form.Get("platform"); v != "" {
p, err := platforms.Parse(v)
if err != nil {
return errdefs.InvalidParameter(err)
}
platform = &p
}
}
if hostConfig != nil && hostConfig.PidsLimit != nil && *hostConfig.PidsLimit <= 0 {
// Don't set a limit if either no limit was specified, or "unlimited" was
// explicitly set.
// Both `0` and `-1` are accepted as "unlimited", and historically any
// negative value was accepted, so treat those as "unlimited" as well.
hostConfig.PidsLimit = nil
}
ccr, err := s.backend.ContainerCreate(types.ContainerCreateConfig{
Name: name,
Config: config,
HostConfig: hostConfig,
NetworkingConfig: networkingConfig,
AdjustCPUShares: adjustCPUShares,
Platform: platform,
})
if err != nil {
return err
}
return httputils.WriteJSON(w, http.StatusCreated, ccr)
}
(2)start容器
api/server/router/container/container.go:
router.NewPostRoute("/containers/{name:.*}/start", r.postContainersStart),
daemon/start.go:
// containerStart prepares the container to run by setting up everything the
// container needs, such as storage and networking, as well as links
// between containers. The container is left waiting for a signal to
// begin running.
func (daemon *Daemon) containerStart(container *container.Container, checkpoint string, checkpointDir string, resetRestartManager bool) (err error) {
start := time.Now()
container.Lock()
defer container.Unlock() if resetRestartManager && container.Running { // skip this check if already in restarting step and resetRestartManager==false
return nil
} if container.RemovalInProgress || container.Dead {
return errdefs.Conflict(errors.New("container is marked for removal and cannot be started"))
} if checkpointDir != "" {
// TODO(mlaventure): how would we support that?
return errdefs.Forbidden(errors.New("custom checkpointdir is not supported"))
} // if we encounter an error during start we need to ensure that any other
// setup has been cleaned up properly
defer func() {
if err != nil {
container.SetError(err)
// if no one else has set it, make sure we don't leave it at zero
if container.ExitCode() == 0 {
container.SetExitCode(128)
}
if err := container.CheckpointTo(daemon.containersReplica); err != nil {
logrus.Errorf("%s: failed saving state on start failure: %v", container.ID, err)
}
container.Reset(false) daemon.Cleanup(container)
// if containers AutoRemove flag is set, remove it after clean up
if container.HostConfig.AutoRemove {
container.Unlock()
if err := daemon.ContainerRm(container.ID, &types.ContainerRmConfig{ForceRemove: true, RemoveVolume: true}); err != nil {
logrus.Errorf("can't remove container %s: %v", container.ID, err)
}
container.Lock()
}
}
}() if err := daemon.conditionalMountOnStart(container); err != nil {
return err
} if err := daemon.initializeNetworking(container); err != nil {
return err
} spec, err := daemon.createSpec(container)
if err != nil {
return errdefs.System(err)
} if resetRestartManager {
container.ResetRestartManager(true)
container.HasBeenManuallyStopped = false
} if err := daemon.saveAppArmorConfig(container); err != nil {
return err
} if checkpoint != "" {
checkpointDir, err = getCheckpointDir(checkpointDir, checkpoint, container.Name, container.ID, container.CheckpointDir(), false)
if err != nil {
return err
}
} shim, createOptions, err := daemon.getLibcontainerdCreateOptions(container)
if err != nil {
return err
} ctx := context.TODO() err = daemon.containerd.Create(ctx, container.ID, spec, shim, createOptions)
if err != nil {
if errdefs.IsConflict(err) {
logrus.WithError(err).WithField("container", container.ID).Error("Container not cleaned up from containerd from previous run")
// best effort to clean up old container object
daemon.containerd.DeleteTask(ctx, container.ID)
if err := daemon.containerd.Delete(ctx, container.ID); err != nil && !errdefs.IsNotFound(err) {
logrus.WithError(err).WithField("container", container.ID).Error("Error cleaning up stale containerd container object")
}
err = daemon.containerd.Create(ctx, container.ID, spec, shim, createOptions)
}
if err != nil {
return translateContainerdStartErr(container.Path, container.SetExitCode, err)
}
} // TODO(mlaventure): we need to specify checkpoint options here
pid, err := daemon.containerd.Start(context.Background(), container.ID, checkpointDir,
container.StreamConfig.Stdin() != nil || container.Config.Tty,
container.InitializeStdio)
if err != nil {
if err := daemon.containerd.Delete(context.Background(), container.ID); err != nil {
logrus.WithError(err).WithField("container", container.ID).
Error("failed to delete failed start container")
}
return translateContainerdStartErr(container.Path, container.SetExitCode, err)
} container.HasBeenManuallyRestarted = false
container.SetRunning(pid, true)
container.HasBeenStartedBefore = true
daemon.setStateCounter(container) daemon.initHealthMonitor(container) if err := container.CheckpointTo(daemon.containersReplica); err != nil {
logrus.WithError(err).WithField("container", container.ID).
Errorf("failed to store container")
} daemon.LogContainerEvent(container, "start")
containerActions.WithValues("start").UpdateSince(start) return nil
}
3.2 PreStop
源码分析见《详解Kubernetes Pod优雅退出》这篇博文,本文不再赘余。
4、postStart 异步执行
在第三章节讲述开始容器方法时,我们已经很清晰知道,开始容器方法先运行容器,再运行运行容器 postStart 钩子函数。
需要注意的事,docker start 命令在启动容器时,并不会等待 ENTRYPOINT 命令执行完毕后才返回。它只会等待容器的主进程启动并确认其正常运行,然后立即返回。换句话说,docker start 命令返回时,ENTRYPOINT 命令已经开始执行,但不一定已经执行完毕。
所以PostStart的执行相对于容器主进程的执行是异步的,它会在容器start后立刻触发,并不能保证PostStart钩子在容器ENTRYPOINT之前运行。
4.1 关于postStart异步执行测试
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: test-post-start
spec:
containers:
- name: test-post-start-container
image: busybox
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "sleep 5 && echo $(date) 'written by entrypoint' >> log.log && sleep 600"]
lifecycle:
postStart:
exec:
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "sleep 10 && echo $(date) 'written by post start' >> log.log"]
创建上面的pod,通过进入pod,查看log.log打印日志,证明:
- PostStart是否会挡住主进程的启动
- PostStart是否是异步执行
如果 PostStart 会阻挡 ENTRYPOINT 的启动,则日志文件内容应该是:
(时间点 T)written by post start
(时间点 T + 约 10 秒)written by entrypoint
否则内容应该是:
(时间点 T)written by entrypoint
(时间点 T + 约 5 秒)written by post start
```log
实验结果:
/ # cat log.log
Thu Jun 4 06:14:50 UTC 2020 written by entrypoint
Thu Jun 4 06:14:55 UTC 2020 written by post start
修改YAML文件:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: test-post-start
spec:
containers:
- name: test-post-start-container
image: busybox
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "sleep 15 && echo $(date) 'written by entrypoint' >> log.log && sleep 600"]
lifecycle:
postStart:
exec:
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "sleep 10 && echo $(date) 'written by post start' >> log.log"]
如果 PostStart 不是异步执行,则日志文件内容应该是:
(时间点 T)written by entrypoint
(时间点 T + 约 5 秒)written by post start
```log 否则内容应该是:
```log
(时间点 T)written by post start
(时间点 T + 约 5 秒)written by entrypoint
实验结果:
[root@master k8s]# kubectl exec -it test-post-start sh
/ # cat log.log
Thu Jun 4 06:17:54 UTC 2020 written by post start
Thu Jun 4 06:17:59 UTC 2020 written by entrypoint
/ #
4.2 结论
- PostStart不会挡住主进程的启动
- PostStart是异步执行
5、使用场景
5.1 postStart
- 数据库连接:在容器启动后,可以使用 postStart 钩子来建立数据库连接,并确保应用程序在启动时可以正常访问数据库;
- 文件下载:容器启动后,可以使用 postStart 钩子从外部下载文件,并将其放置在容器内部以供应用程序使用;
- 启动后台任务:在容器启动后,可以使用 postStart 钩子来启动或触发后台任务,例如数据同步、日志收集等。
5.2 preStop
- 优雅终止:在容器终止之前,可以使用 preStop 钩子发送信号或通知给应用程序,让应用程序优雅地处理未完成的请求或任务,并进行清理操作;
- 数据持久化:在容器终止之前,可以使用 preStop 钩子将容器中的数据持久化到外部存储,以确保数据不会丢失;
- 日志上传:在容器终止之前,可以使用 preStop 钩子将容器中的日志上传到中央日志系统,以便进一步分析和存档。
6、总结
容器生命周期钩子(PostStart和PreStop)提供在容器启动后和停止前执行自定义操作的能力,适用于数据库连接、文件下载、优雅终止等场景。postStart平时用的场景不是很多,重点关注preStop。
Kubernetes容器生命周期 —— 钩子函数详解(postStart、preStop)的更多相关文章
- vue生命周期钩子函数详解
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明. 本文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35585701/article/ ...
- 关于 vue 生命周期 钩子函数 事件
vue实例有一个完整的生命周期,也就是从开始创建.初始化数据.编译模板.挂载Dom.渲染->更新->渲染.卸载等一系列过程,我们称这是vue的生命周期. 通俗的将就是vue实例从创建到销毁 ...
- Vue生命周期 钩子函数和组件传值
Vue生命周期 钩子函数 每个 Vue 实例在被创建时都要经过一系列的初始化过程——例如,需要设置数据监听.编译模板.将实例挂载到 DOM 并在数据变化时更新 DOM 等. 同时在这个过程中也会运行一 ...
- java多线程并发(二)--线程的生命周期及方法详解
上篇随笔介绍了线程的相关基础知识以及新启线程的几种方法,本片将继续介绍线程的生命周期及方法详解. 一.线程的生命周期 在Thread代码中,线程的状态被分为6种 public enum State { ...
- Android四大组件之——Activity的生命周期(图文详解)
转载请在文章开头处注明本博客网址:http://www.cnblogs.com/JohnTsai 联系方式:JohnTsai.Work@gmail.com [Andro ...
- vue之生命周期钩子函数之运用
一.什么是生命周期钩子函数: 每个 Vue 实例在被创建时都要经过一系列的初始化过程——例如,需要设置数据监听.编译模板.将实例挂载到 DOM 并在数据变化时更新 DOM 等.同时在这个过程中也会运行 ...
- react中自定义函数、生命周期钩子函数、修改状态、组件、组件传值
1.回顾 2.自定义函数 事件的首字母大小 onclick ==> onClick onchange ==> onChange 普通的点击事件 ---- 调用事件不加(),加了立即执行 i ...
- day68:Vue:类值操作/style样式操作&v-for&filer/computed/watch&生命周期钩子函数&axios
目录 1.类值操作 :class 2.style操作样式 :style 3:示例:选项卡 @click+:class 4.v-for示例:循环商品显示 5.过滤器:filter 6.计算属性:comp ...
- vue2.0项目实战(4)生命周期和钩子函数详解
最近的项目都使用vue2.0来开发,不得不说,vue真的非常好用,大大减少了项目的开发周期.在踩坑的过程中,因为对vue的生命周期不是特别了解,所以有时候会在几个钩子函数里做一些事情,什么时候做,在哪 ...
- 对vue生命周期/钩子函数的理解
对于实现页面逻辑交互等效果,我们必须知晓vue的生命周期,才能愉快的玩耍,知道我们写的东西应该挂载到哪里,vue官方给出的api讲解的那叫一个简单啊,如下: 所有的生命周期钩子自动绑定this上下文到 ...
随机推荐
- 高性能消息中间件-Nats使用
一.Nats简介 官网:https://nats.io/ 官网下载:https://nats.io/download/ github:https://github.com/nats-io/nats-s ...
- 2024-05-04:用go语言,给定一个起始索引为0的字符串s和一个整数k。 要进行分割操作,直到字符串s为空: 选择s的最长前缀,该前缀最多包含k个不同字符; 删除该前缀,递增分割计数。如果有剩余
2024-05-04:用go语言,给定一个起始索引为0的字符串s和一个整数k. 要进行分割操作,直到字符串s为空: 选择s的最长前缀,该前缀最多包含k个不同字符: 删除该前缀,递增分割计数.如果有剩余 ...
- 程序员天天 CURD,怎么才能成长,职业发展的思考(2)
接着上一篇:程序员天天 CURD,怎么才能成长,职业发展思考 上一篇写到了用年限来谈程序员的发展,在 4 - 6 年这个时间段需要做的一些事情,接着写这个时间段的. 第 4.5 年时候,你可能会做一些 ...
- 如何在Ubuntu 20.04上安装Pyenv 管理多版本Python
目录 ubuntu安装pyenv 管理多版本Python 参考文档: 安装pyenv: pyenv 命令列表 pycharm配置 ubuntu安装pyenv 管理多版本Python 参考文档: htt ...
- Laravel 实现自定义资源路由
Laravel 如何实现自定义资源路由 最近在开发过程中,发现总有一些路由需要重复定义,比如切换状态,导出,回收站啊之类的.如果使用 Laravel 自带的资源路由方法,还不足以满足重复劳动得过程.所 ...
- webapi动态创建后台任务(使用排队的后台任务)
很多时候我们都会使用后台定时任务,但有些任务不需要定时执行,只需要请求到来时执行一次,比如请求服务器到某个地方同步数据,但请求不需要等数据同步完成再响应.这时候就可以使用排队的后台任务. 基本原理是用 ...
- PasteSpider之接口的授权实现为什么不采用JWT方式
PasteTemplate序列的接口权限控制使用的都是一套逻辑 包括不限于PasteSpider,PasteTimer,PasteTicker等 大致逻辑一致,具体的细节可能会根据项目做一些调整! 实 ...
- CSS——引入方式
1.行内式 <div style="color: white;background-color: #369;text-align: center">行内设置</d ...
- .net core 5,6,7【多线程笔记】取消令牌(CancellationToken) CancellationTokenSource
介绍 在使用C#异步的场景,多多少少会接触到CancellationTokenSource.它和取消异步任务相关的,CancellationToken就是它生产出来的. 演示 任务取消执行回调 var ...
- Java并发编程(一)JUC同步类
JUC 是学习 Java 并发编程的小伙伴不可避免的一个 pkg,JUC提供了对并发编程的底层支持,比如我们熟悉的线程池.MQ.线程同步... 都有JUC的影子,下面我们一起来看看JUC下比较重要的几 ...
