Why containers? Why should we care? 新旧容器的对比


https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/what-is-kubernetes/
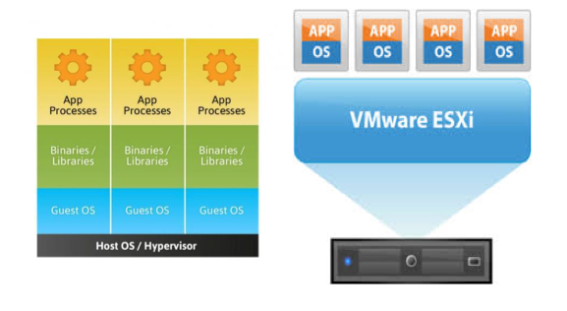
The Old Way to deploy applications was to install the applications on a host using the operating system package manager. This had the disadvantage of entangling the applications’ executables, configuration, libraries, and lifecycles with each other and with the host OS. One could build immutable virtual-machine images in order to achieve predictable rollouts and rollbacks, but VMs are heavyweight and non-portable.
The New Way is to deploy containers based on operating-system-level virtualization rather than hardware virtualization. These containers are isolated from each other and from the host: they have their own filesystems, they can’t see each others’ processes, and their computational resource usage can be bounded. They are easier to build than VMs, and because they are decoupled from the underlying infrastructure and from the host filesystem, they are portable across clouds and OS distributions.
Because containers are small and fast, one application can be packed in each container image. This one-to-one application-to-image relationship unlocks the full benefits of containers. With containers, immutable container images can be created at build/release time rather than deployment time, since each application doesn’t need to be composed with the rest of the application stack, nor married to the production infrastructure environment. Generating container images at build/release time enables a consistent environment to be carried from development into production. Similarly, containers are vastly more transparent than VMs, which facilitates monitoring and management. This is especially true when the containers’ process lifecycles are managed by the infrastructure rather than hidden by a process supervisor inside the container. Finally, with a single application per container, managing the containers becomes tantamount to managing deployment of the application.
Summary of container benefits:
- Agile application creation and deployment: Increased ease and efficiency of container image creation compared to VM image use.
- Continuous development, integration, and deployment: Provides for reliable and frequent container image build and deployment with quick and easy rollbacks (due to image immutability).
- Dev and Ops separation of concerns: Create application container images at build/release time rather than deployment time, thereby decoupling applications from infrastructure.
- Environmental consistency across development, testing, and production: Runs the same on a laptop as it does in the cloud.
- Cloud and OS distribution portability: Runs on Ubuntu, RHEL, CoreOS, on-prem, Google Container Engine, and anywhere else.
- Application-centric management: Raises the level of abstraction from running an OS on virtual hardware to run an application on an OS using logical resources.
- Loosely coupled, distributed, elastic, liberated micro-services: Applications are broken into smaller, independent pieces and can be deployed and managed dynamically – not a fat monolithic stack running on one big single-purpose machine.
- Resource isolation: Predictable application performance.
- Resource utilization: High efficiency and density.
https://aucouranton.com/2014/06/13/linux-containers-parallels-lxc-openvz-docker-and-more/
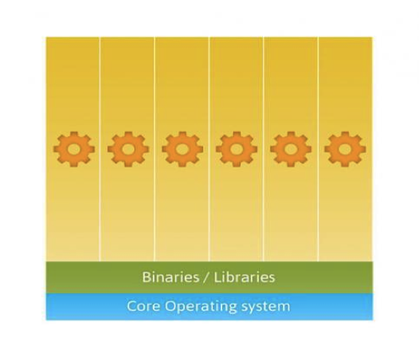
A container (Linux Container) at its core is an allocation, portioning, and assignment of host (compute) resources such as CPU Shares, Network I/O, Bandwidth, Block I/O, and Memory (RAM) so that kernel level constructs may jail-off, isolate or “contain” these protected resources so that specific running services (processes) and namespaces may solely utilize them without interfering with the rest of the system. These processes could be lightweight Linux hosts based on a Linux image, multiple web severs and applications, a single subsystem like a database backend, to a single process such as ‘echo “Hello”’ with little to no overhead.
Commonly known as “operating system-level virtualization” or “OS Virtual Environments” containers differ from hypervisor level virtualization. The main difference is that the container model eliminates the hypervisor layer, redundant OS kernels, binaries, and libraries needed to typically run workloads in a VM.
基于操作系统而非硬件 based on operating-system-level virtualization rather than hardware virtualization
独立文件系统filesystems,进程互补可见 processes
Why containers? Why should we care? 新旧容器的对比的更多相关文章
- Arcgis API For IOS扩展AGSDynamicLayer新旧版API对比
AGSDynamicLayer(ForSubclassEyesOnly) Category Reference Description This category organizes the meth ...
- Android新旧版本Notification
Android新旧版本Notification 在notification.setLatestEventInfo() 过时了 以前: NotificationManager mn = (Notific ...
- Matlab神经网络函数newff()新旧用法差异
摘要 在Matlab R2010a版中,如果要创建一个具有两个隐含层.且神经元数分别为5.3的前向BP网络,使用旧的语法可以这样写: net1 = newff(minmax(P), [5 3 1]); ...
- [ACM_数学] Taxi Fare [新旧出租车费差 水 分段函数]
Description Last September, Hangzhou raised the taxi fares. The original flag-down fare in Hangzhou ...
- Flex布局新旧混合写法详解(兼容微信)
原文链接:https://www.usblog.cc/blog/post/justzhl/Flex布局新旧混合写法详解(兼容微信) flex是个非常好用的属性,如果说有什么可以完全代替 float 和 ...
- 浅谈 angular新旧版本问题
一直在学习angularJs,之前用的版本比较老,前些天更新了一下angularJs的版本,然后发现了一些问题,希望和大家分享一下. 在老的版本里控制器直接用函数定义就可以 比如: 在angularJ ...
- css弹性盒子新旧兼容
前言:本篇随笔是对弹性盒子有了解的人来写的这篇文章,具体属性产生的效果这里不做说明,基础的东西去查文档.这里只是总结. 时至今日,css3的flex弹性盒子在移动端基本上都是支持的,但不排除有些些低版 ...
- spring加载配置新旧方式对比
老方式 1.首先要配置配置文件,如beans.xml,内容如下: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> &l ...
- Flex布局新旧混合写法详解
flex是个非常好用的属性,如果说有什么可以完全代替 float 和 position ,那么肯定是非它莫属了(虽然现在还有很多不支持 flex 的浏览器).然而国内很多浏览器对 Flex 的支持都不 ...
随机推荐
- BQ25890 charging ic evb 使用注意事項
Origin : 今天做了一個小實驗, 從 bq25890 spec 可以知道, enable bq25896 充電的功能,有二個條件, 1.CHG_CONFIG bit 需為1. 2.ce pin ...
- SQL注入原理及防范
1.1.2 正文 SQL Injection:就是通过把SQL命令插入到Web表单递交或输入域名或页面请求的查询字符串,最终达到欺骗服务器执行恶意的SQL命令. 具体来说,它是利用现有应用程序,将(恶 ...
- Glide加载图片问题记录
Glide加载图片相比于Picasso而言性能较好,又比Fresco轻巧,而且又支持加载gif动图,是Google 推荐.专注平滑的滚动.简单易用.可扩展的一款图片加载框架.但是使用时还是会遇到一些问 ...
- 微信小程序 使用HMACSHA1和md5为登陆注册报文添加指纹验证签名
对接口请求报文作指纹验证签名相信在开发中经常碰到, 这次在与java后端一起开发小程序时,就碰到需求对登陆注册请求报文添加指纹验证签名来防止信息被修改 先来看下我们与后端定制签名规则 2.4. 签名规 ...
- 微信小程序 本地缓存保持登录状态之wx.setStorageSync()使用技巧
微信小程序提供了一个如同浏览器cookie本地缓存方法,那就是今天要说的wx.setStorageSync() 注意,该方法是同步请求,还有个异步请求的方法是wx.setStorage(),参考官方文 ...
- MFC改变控件颜色
from http://www.cppblog.com/FandyM/archive/2010/07/21/120972.aspx MFC应用程序中,要改变控件的背景色可通过重载OnCtlColor( ...
- 唤醒你的大脑 --- javascript冒泡排序
var a; a = [1, 2, 3, 11, 55, 5, 0, 44]; (function bubbleSort() { for (var i = 0; i <= a.length - ...
- 纯CSS3美化radio和checkbox
如题,主要通过CSS3来实现将radio和checkbox美化的效果.可是兼容性并非非常好,PC端仅仅支持chrome浏览器(IE和Firefox測试不行,其它没有很多其它測试).然后微信端和QQ端訪 ...
- 计算广告、推荐系统论文以及DSP综述
http://www.huxmarket.com/detail/2966 DSP场景假定前提: 以CTR预估为例,向广告主以CPC(OCPC)方式收费,向ADX以CPM方式付费.投放计划受预算限制,在 ...
- Spring 让 LOB 数据操作变得简单易行,LOB 代表大对象数据,包括 BLOB 和 CLOB 两种类型
转自:https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-spring-lob/index.html 概述 LOB 代表大对象数据,包括 BLOB 和 CL ...
