AVL Tree (1) - Definition, find and Rotation
1. 定义
- (15-1) [AVL tree]:
- 一棵空二叉树是 AVL tree;
- 若 T 是一棵非空二叉树, 则 T 满足以下两个条件时, T 是一棵 AVL tree:
- T_LeftSubtree 和 T_RightSubtree 是 AVL tree.
- \(| h_{Left} - h_{Right}| \leq 1\).
- [AVL search tree]: AVL tree + binary search tree.
- AVL tree 的高度 \(h=O(\log{n})\)
- [balance foctor] 平衡因子可能取值为
-1,0,1;
对于 nodex, \(bf(x)\) 定义为: \(h_{x\_LeftSubtree} - h_{x\_RightSubtree}\).
AVL Tree 的宗旨在于使 BST 保持平衡, 进而避免 BST 过度倾斜 (极端情况下 BST 有可能成为链表) .
2. btNode 和 AVLTree 的定义
<utility> 头文件提供了 std::pair 的定义, 便于使用融合 key 类型和 value 类型的复合类型.
<iostream> 头文件提供的输出方法由 private method preOrder 使用, 以测试代码正确性.
Click to show the codes
// AVL Tree
#include <utility>
#include <iostream>
/**
* @brief Binary tree node.
* @tparam T Should be std::pair<Key_Type, Element_Type> in binary search tree.
*/
template<class T>
struct btNode
{
T data;
btNode<T>* left, * right;
// Constructor for btNode.
btNode(T d = {}, btNode<T>* l = nullptr, btNode<T>* r = nullptr) :
data(d), left(l), right(r) {}
};
template<class K, class E>
class AVLTree
{
public:
// Constructor for AVLTree.
AVLTree() :root(nullptr) {}
// @brief PreOrder ouput.
void preOrder() { preOrder(this->root); }
public:
// @brief Find the node with key {tKey} and return its address.
btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* find(const K& theKey) const;
// @brief [Iteration] Create a node with {tPair} and insert it to the tree.
void insert_I(const std::pair<K, E>& tPair);
// @brief [Recursion] Create a node with {tPair} and invoke method {m_insert_R}.
void insert_R(const std::pair<K, E>& tPair);
// @brief [Iteration] Erase the node with key {tKey}.
void erase_I(const K& tKey);
// @brief [Recursion] Erase the node with key {tKey}.
void erase_R(const K& tKey);
private: // Rotate methods.
// @brief Right rotate subtree whose root is {tRoot}, return {tRoot->left} as new root.
// e.g. To rotate {parentTarget->left} : parentTarget->left = rightRotate(parentTarget->left)
inline btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* rightRotate(btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* tRoot);
// @brief Left rotate subtree whose root is {tRoot}, return {tRoot->right} as new root.
// e.g. To rotate {parentTarget->left} : parentTarget->left = leftRotate(parentTarget->left);
inline btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* leftRotate(btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* tRoot);
// @brief For LL case, right rotate subtree {tRoot}, return {tRoot->left} as new root.
// e.g. To rotate {parentTarget->left} : parentTarget->left = llRotation(parentTarget->left);
inline btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* llRotation(btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* tRoot);
// @brief For RR case, left rotate subtree {tRoot}, return {tRoot->left} as new root.
// e.g. To rotate {parentTarget->left} : parentTarget->left = rrRotation(parentTarget->left);
inline btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* rrRotation(btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* tRoot);
// @brief For LR case, left rotate {tRoot->left}, right rotate {tRoot}, return {tRoot->left->right}.
// e.g. To rotate {parentTarget->left} : parentTarget->left = lrRotation(parentTarget->left);
inline btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* lrRotation(btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* tRoot);
// @brief For RL case, right rotate {tRoot->right}, left rotate {tRoot}, return {tRoot->right->left}.
// e.g. To rotate {parentTarget->left} : parentTarget->left = rlRotation(parentTarget->left);
inline btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* rlRoattion(btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* tRoot);
private:
// @brief Private recurse method to insert.
btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* m_insert_R(btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* tRoot, btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* tNode);
// @brief Private recurse method to erase.
btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* m_erase_R(btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* tRoot, const K& tKey);
// @brief Private recurse method for preorder output.
void preOrder(btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* tRoot);
private:
btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* root;
};
template<class K, class E>
void AVLTree<K, E>::preOrder(btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* tRoot)
{
if (!tRoot) return;
std::cout << tRoot->data.second;
preOrder(tRoot->left);
preOrder(tRoot->right);
}
3. Find
解释可以参照 BST 的 find 方法.
Click to show the codes
// @brief Find the node with key {tKey} and return its address.
template<class K, class E>
btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* AVLTree<K, E>::find(const K& theKey) const
{
// {keyNode} traverse the tree, searching for matched node.
btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* keyNode = root;
// Iteration ends if {keyNode} is nullptr.
while (keyNode) {
if (theKey < keyNode->data.first) {
keyNode = keyNode->left;
} else if (theKey > keyNode->element.first) {
keyNode = keyNode->right;
}
// ELSE: {keyNode->data.first} equals {tKey}.
else {
return keyNode;
}
}
// No matching pair.
return nullptr;
}
4. Left Rotate & Right Rotate
在探讨何时要旋转以及如何旋转之前, 我们不妨先实现两个单纯的左右旋转方法.
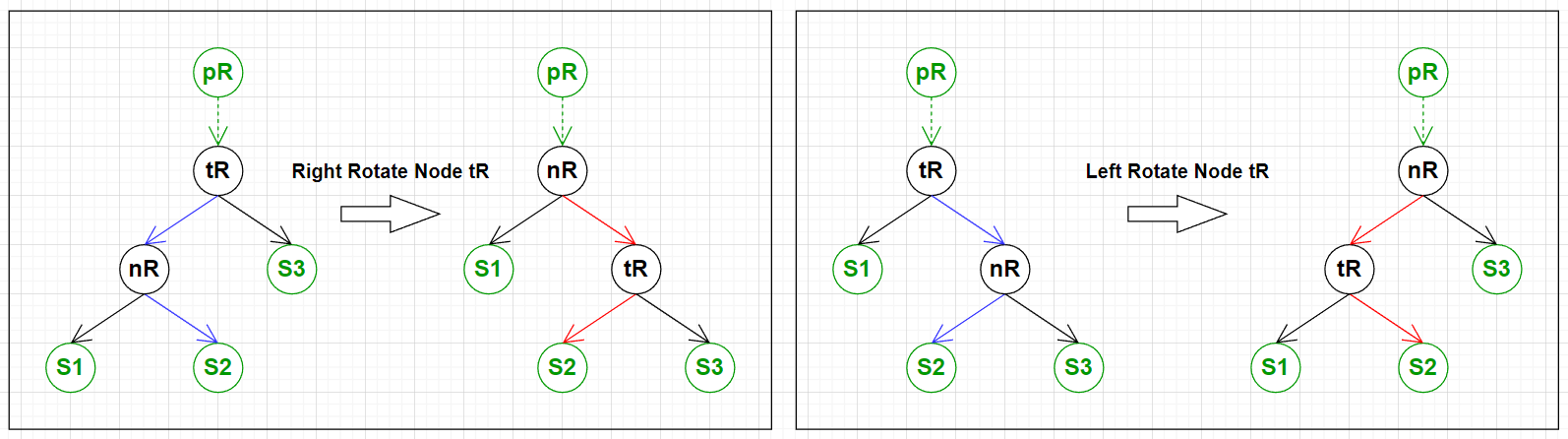
上图中左边是向右旋转 rightRotate , 右边是向左旋转 leftRotate .
很直观, 也没什么好多说的, 上代码.
Click to show the codes
// @brief Right rotate subtree whose root is {tRoot}, return {tRoot->left} as new root.
// e.g. To rotate {parentTarget->left} : parentTarget->left = rightRotate(parentTarget->left)
template<class K, class E>
inline btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* AVLTree<K, E>::rightRotate(btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* tRoot)
{
btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* new_tRoot = tRoot->left;
tRoot->left = new_tRoot->right;
new_tRoot->right = tRoot;
return new_tRoot;
}
// @brief Left rotate subtree whose root is {tRoot}, return {tRoot->right} as new root.
// e.g. To rotate {parentTarget->left} : parentTarget->left = leftRotate(parentTarget->left)
template<class K, class E>
inline btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* AVLTree<K, E>::leftRotate(btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* tRoot)
{
btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* new_tRoot = tRoot->right;
tRoot->right = new_tRoot->left;
new_tRoot->left = tRoot;
return new_tRoot;
}
5. 4 Cases for Rotation
AVL Tree 保持平衡的方法是计算 balance factor 后进行旋转.
下面四张图展示了需要旋转的 4 种情况以及旋转的方式.
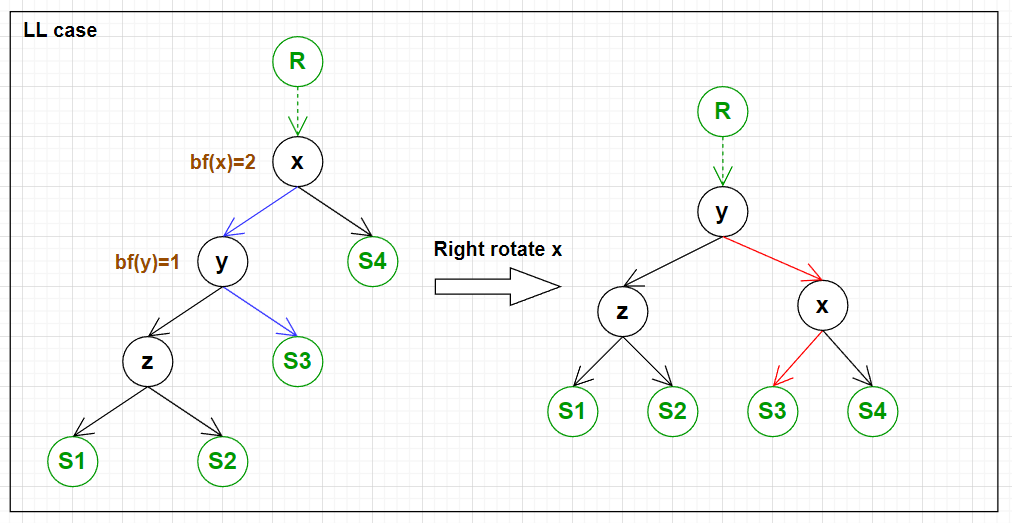
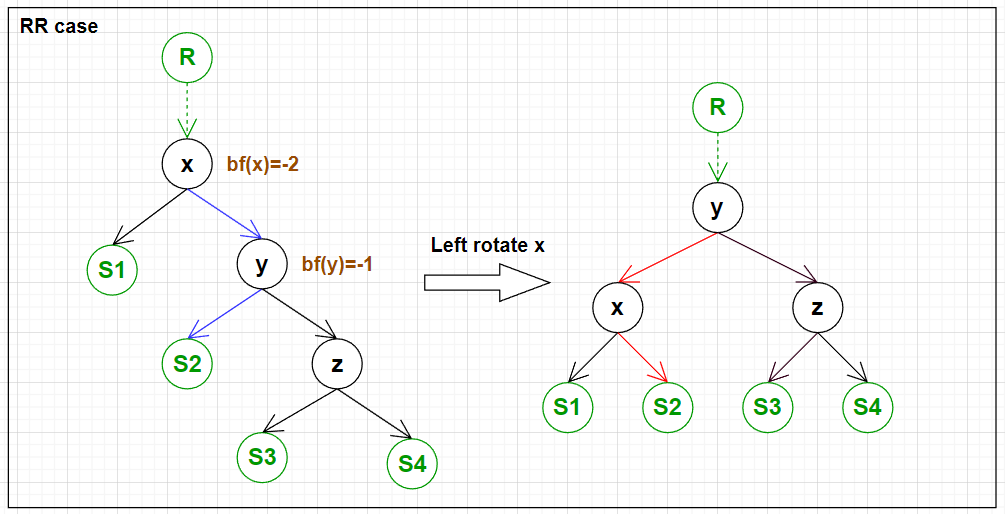
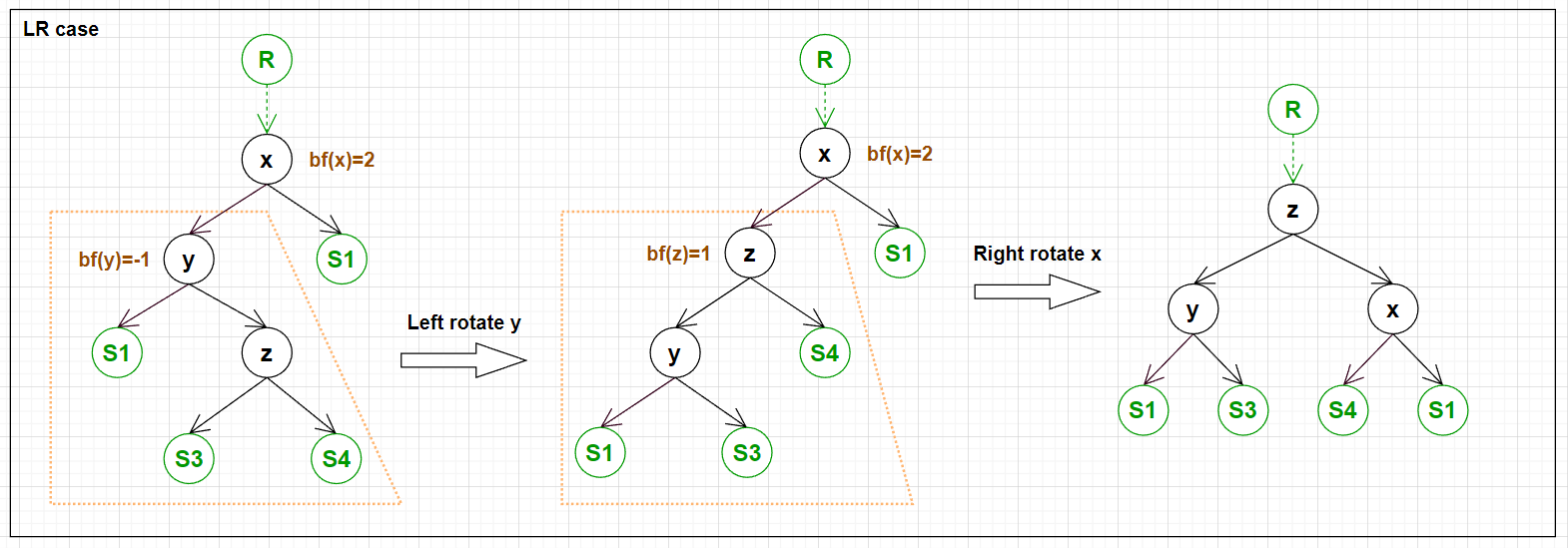
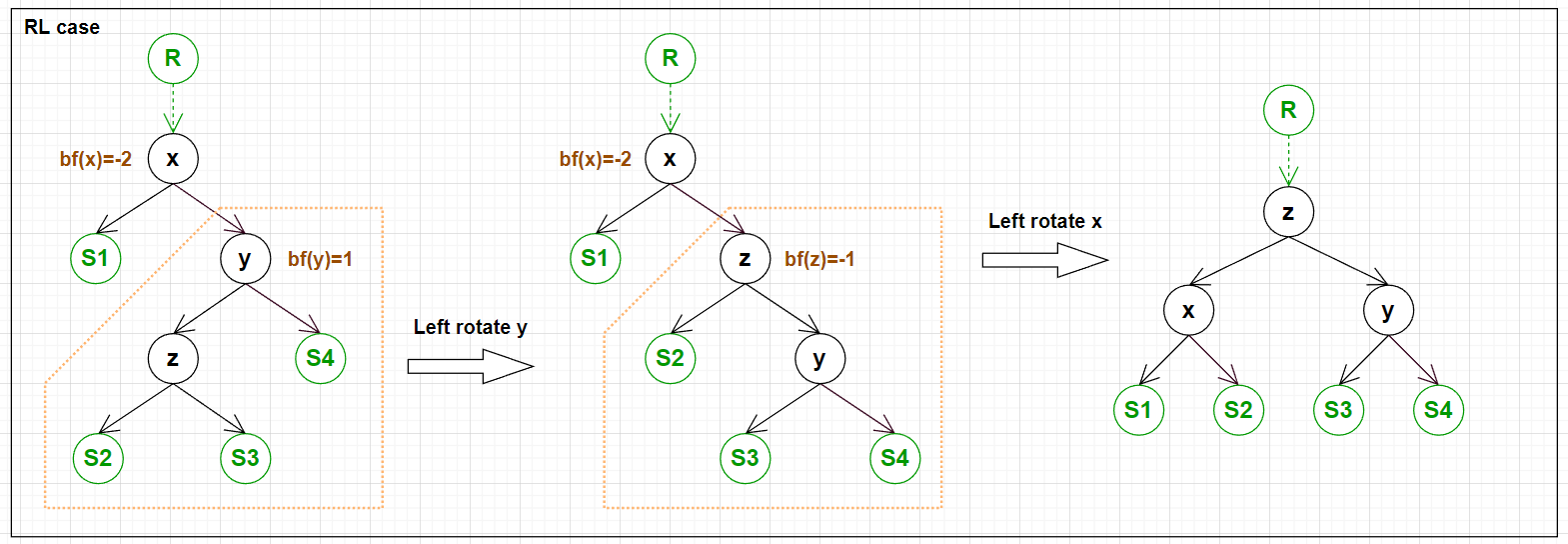
实现四种情况的旋转的代码:
Click to show the codes
// @brief For LL case, right rotate subtree {tRoot}, return {tRoot->left} as new root.
// e.g. To rotate {parentTarget->left} : parentTarget->left = llRotation(parentTarget->left);
template<class K, class E>
inline btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* AVLTree<K, E>::llRotation(btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* tRoot)
{
return rightRotate(tRoot);
}
// @brief For LL case, left rotate subtree {tRoot}, return {tRoot->left} as new root.
// e.g. To rotate {parentTarget->left} : parentTarget->left = rrRotation(parentTarget->left);
template<class K, class E>
inline btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* AVLTree<K, E>::rrRotation(btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* tRoot)
{
return leftRotate(tRoot);
}
// @brief For LR case, left rotate {tRoot->left}, right rotate {tRoot}, return {tRoot->left->right}.
// e.g. To rotate {parentTarget->left} : parentTarget->left = lrRotation(parentTarget->left);
template<class K, class E>
inline btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* AVLTree<K, E>::lrRotation(btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* tRoot)
{
tRoot->left = leftRotate(tRoot->left);
return rightRotate(tRoot);
}
// @brief For RL case, right rotate {tRoot->right}, left rotate {tRoot}, return {tRoot->right->left}.
// e.g. To rotate {parentTarget->left} : parentTarget->left = rlRotation(parentTarget->left);
template<class K,class E>
inline btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* AVLTree<K, E>::rlRoattion(btNode<std::pair<K, E>>* tRoot)
{
tRoot->right = rightRotate(tRoot->right);
return leftRotate(tRoot);
}
Reference |
(1) Data Structures, Algoritms, and Applications in C++, Sartaj Sahni
(2) AVL Tree | Set 1 (Insertion), princiraj1992, rathbhupendra, Akanksha_Rai, sohamshinde04, nocturnalstoryteller, rdtank, kaiwenzheng644, hardikkoriintern
AVL Tree (1) - Definition, find and Rotation的更多相关文章
- AVL Tree Insertion
Overview AVL tree is a special binary search tree, by definition, any node, its left tree height and ...
- 04-树5 Root of AVL Tree
平衡二叉树 LL RR LR RL 注意画图理解法 An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the he ...
- 1066. Root of AVL Tree (25)
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child sub ...
- 1066. Root of AVL Tree
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child su ...
- 树的平衡 AVL Tree
本篇随笔主要从以下三个方面介绍树的平衡: 1):BST不平衡问题 2):BST 旋转 3):AVL Tree 一:BST不平衡问题的解析 之前有提过普通BST的一些一些缺点,例如BST的高度是介于lg ...
- 1123. Is It a Complete AVL Tree (30)
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child sub ...
- A1123. Is It a Complete AVL Tree
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child sub ...
- A1066. Root of AVL Tree
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child sub ...
- PAT A1123 Is It a Complete AVL Tree (30 分)——AVL平衡二叉树,完全二叉树
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child sub ...
随机推荐
- 更强的 JsonPath 兼容性及性能测试之2022版(Snack3,Fastjson2,jayway.jsonpath)
2022年了,重新做了一份json path的兼容性与性能测试.三个市面上流行框架比较性测试. 免责声明:可能测试得方式不对而造成不科学的结果(另外,机器不同结果会有不同),可以留言指出来.以下测试数 ...
- Tapdata Cloud 版本上新!率先支持数据校验、类型映射等6大新功能
Tapdata Cloud cloud.tapdata.net Tapdata Cloud 是国内首家异构数据库实时同步云平台,目前支持 Oracle.MySQL.PG.SQL Server.Mong ...
- 循环控制-break语句和continue语句
break关键字的用法有常见的两种: 1.可以用switch语句当中,一旦执行,整个switch语句立刻结束 2.还可以用在循环语句当中,一定执行,整个循环语句立刻结束,打断循环 关于循环的选择,有一 ...
- Jenkins安装推荐插件前,更换插件源
网上找了很多都解决不了问题,直到看到jenkins-update-center,还有一个问题,就是尽量在实体机上装,感觉docker坑太多.... 安装jenkins,以Debian系为例 安装包在这 ...
- RESTAPI 版本控制策略【eolink 翻译】
微服务,是现阶段开发建设云原生应用程序的流行趋向.API 版本控制有益于在辨别出所需要的调节时加速迭代更新的速度. 根据微服务架构的关键构件其一,是 API 的设计和规范.针对 API,版本控制是不可 ...
- CF605A Sorting Railway Cars 题解
To CF 这道题依题意可得最终答案为序列长度-最长子序列长度. 数据范围至 \(100000\) 用 \(O(n^2)\) 的复杂度肯定会炸. 用 \(O(nlogn)\) 的复杂度却在第 \(21 ...
- DFS序和7种模型
DFS序就是将树的节点按照先根的顺序遍历得到的节点顺序 性质:一个子树全在一个连续的区间内,可以与线段树和树状数组搭配使用 很好写,只需在dfs中加几行代码即可. 代码: void dfs(ll u, ...
- 高通cDSP简单编程例子(实现查询高通cDSP使用率、签名),RK3588 npu使用率查询
PS:要转载请注明出处,本人版权所有. PS: 这个只是基于<我自己>的理解, 如果和你的原则及想法相冲突,请谅解,勿喷. 前置说明 本文作为本人csdn blog的主站的备份.(Bl ...
- 如何有效地开发 Jmix 扩展组件
扩展组件的概念在使用 Jmix 框架开发中扮演着非常重要的角色.我们将在本文探索什么是扩展组件以及 Jmix Studio 在扩展组件开发和应用程序模块化方面能给开发者带来什么帮助. Jmix 中的扩 ...
- docker容器技术基础入门
目录 docker容器技术基础入门 容器(Container) 传统虚拟化与容器的区别 Linux容器技术 Linux Namespaces CGroups LXC docker基本概念 docker ...
