遗传算法 Genetic Algorithms
遗传算法 Genetic Algorithms
遗传算法是一种“adaptive heuristic search algorithm”(自适应启发式搜索算法),虽不明、但觉厉。其实遗传算法的思路很朴素,实现起来也并不复杂(用到一点点生物学科普级别的知识,学科交叉还挺有趣的)。
遗传算法模拟的是自然界中,一个种群内生物基因的传递模式。可以预料到在大自然“优胜劣汰”的筛选机制下,那些能适应环境的强者往往更容易与配偶结合将自己的基因保留到下一代;而体弱多病的弱者会面临死亡,基因无法保存的下场。对于一个种群而言,这种淘汰机制可以让更多的优质基因得以留存,有利于种群的延续。
思路
现在我们假设:
- 问题的一个解,对应于一个“个体”(这是一种只有一个染色体的简单物种)
- 一个解应该由一个字符串来表示,其中一个字符对应于“基因”
- 存在一个判断机制来充当“优胜劣汰”机制,帮助我们判断哪些解更有价值
- 并让这些解“交配”,期望在下一代解中优质解变得更多

上图中有大、中、小三个红框:最小的代表一个解是由一个字符串,或者数字字符排列组合而成的;中间的指一个完整的解;而最大的红框则是指全体解集合(这里有优质解也有劣质解,需要我们甄别)
适应度函数
每一个解都有有一个,用来定量判断这个基因“竞争能力”的值,适应度函数。“竞争能力”更强的个体有更高的概率活到下一代,或者与配偶繁衍子代;但是由于种群内个体的数量是固定的,那些“竞争能力”弱的个体会死掉,被其它“竞争能力”更强的个体取代。
这样、下一代群体中个体的适应度函数的平均值会高于上一代(也就是这些解是问题更佳的解)。当父代与子代群体中的个体之间没有明显差异了,代表进化收敛了,这个算法也就找到了最优质的解。
变异
自然界中,决定后代基因的不仅仅是爹娘双方染色体的融合,还包括变异。引入变异可以提高种群个体的多样性,有利于提高种群的平均适应度函数,进而找到最优解。
算法流程
在原始种群被生成后(通常是随机出来的),遗传算法会采取以下措施来产生下一代:
- 选择环节
对于适应度函数高的个体,给予更大的优先级来让它们保存与繁衍
- 交配环节
对于从“选择环节”中调出的两个个体,让它们随机地结合,产生后代(就像两个染色体整合形成新的染色休那样!)。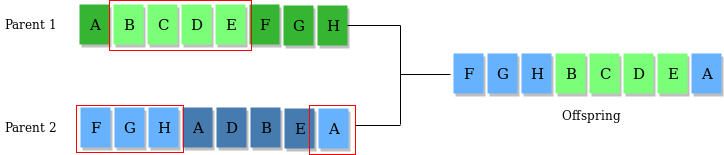
- 变异环节
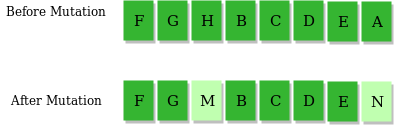
以相对较小的概率任意改变子代的若干基因,提高种群差异性,防止种群进化的进程过早地收敛。
用遗传算法完成一次光荣的进化!
用遗传算法打印,“welcome to ticmis's blog”
C++
// C++ program to create target string, starting from
// random string using Genetic Algorithm
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Number of individuals in each generation
#define POPULATION_SIZE 100
// Valid Genes
const string GENES = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOP"\
"QRSTUVWXYZ 1234567890,'.-;:_!\"#%&/()=?@${[]}";
// Target string to be generated
const string TARGET = "Welcome to ticmis's blog";
// Function to generate random numbers in given range
int random_num(int start, int end)
{
int range = (end-start)+1;
int random_int = start+(rand()%range);
return random_int;
}
// Create random genes for mutation
char mutated_genes()
{
int len = GENES.size();
int r = random_num(0, len-1);
return GENES[r];
}
// create chromosome or string of genes
string create_gnome()
{
int len = TARGET.size();
string gnome = "";
for(int i = 0;i<len;i++)
gnome += mutated_genes();
return gnome;
}
// Class representing individual in population
class Individual
{
public:
string chromosome;
int fitness;
Individual(string chromosome);
Individual mate(Individual parent2);
int cal_fitness();
};
Individual::Individual(string chromosome)
{
this->chromosome = chromosome;
fitness = cal_fitness();
};
// Perform mating and produce new offspring
Individual Individual::mate(Individual par2)
{
// chromosome for offspring
string child_chromosome = "";
int len = chromosome.size();
for(int i = 0;i<len;i++)
{
// random probability
float p = random_num(0, 100)/100;
// if prob is less than 0.45, insert gene
// from parent 1
if(p < 0.45)
child_chromosome += chromosome[i];
// if prob is between 0.45 and 0.90, insert
// gene from parent 2
else if(p < 0.90)
child_chromosome += par2.chromosome[i];
// otherwise insert random gene(mutate),
// for maintaining diversity
else
child_chromosome += mutated_genes();
}
// create new Individual(offspring) using
// generated chromosome for offspring
return Individual(child_chromosome);
};
// Calculate fitness score, it is the number of
// characters in string which differ from target
// string.
int Individual::cal_fitness()
{
int len = TARGET.size();
int fitness = 0;
for(int i = 0;i<len;i++)
{
if(chromosome[i] != TARGET[i])
fitness++;
}
return fitness;
};
// Overloading < operator
bool operator<(const Individual &ind1, const Individual &ind2)
{
return ind1.fitness < ind2.fitness;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
srand((unsigned)(time(0)));
// current generation
int generation = 0;
vector<Individual> population;
bool found = false;
// create initial population
for(int i = 0;i<POPULATION_SIZE;i++)
{
string gnome = create_gnome();
population.push_back(Individual(gnome));
}
while(! found)
{
// sort the population in increasing order of fitness score
sort(population.begin(), population.end());
// if the individual having lowest fitness score ie.
// 0 then we know that we have reached to the target
// and break the loop
if(population[0].fitness <= 0)
{
found = true;
break;
}
// Otherwise generate new offsprings for new generation
vector<Individual> new_generation;
// Perform Elitism, that mean 10% of fittest population
// goes to the next generation
int s = (10*POPULATION_SIZE)/100;
for(int i = 0;i<s;i++)
new_generation.push_back(population[i]);
// From 50% of fittest population, Individuals
// will mate to produce offspring
s = (90*POPULATION_SIZE)/100;
for(int i = 0;i<s;i++)
{
int len = population.size();
int r = random_num(0, 50);
Individual parent1 = population[r];
r = random_num(0, 50);
Individual parent2 = population[r];
Individual offspring = parent1.mate(parent2);
new_generation.push_back(offspring);
}
population = new_generation;
cout<< "Generation: " << generation << "\t";
cout<< "String: "<< population[0].chromosome <<"\t";
cout<< "Fitness: "<< population[0].fitness << "\n";
generation++;
}
cout<< "Generation: " << generation << "\t";
cout<< "String: "<< population[0].chromosome <<"\t";
cout<< "Fitness: "<< population[0].fitness << "\n";
}
Python3
# Python3 program to create target string, starting from
# random string using Genetic Algorithm
import random
# Number of individuals in each generation
POPULATION_SIZE = 100
# Valid genes
GENES = '''abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOP
QRSTUVWXYZ 1234567890,'.-;:_!"#%&/()=?@${[]}'''
# Target string to be generated
TARGET = "Welcome to ticmis's blog"
class Individual(object):
'''
Class representing individual in population
'''
def __init__(self, chromosome):
self.chromosome = chromosome
self.fitness = self.cal_fitness()
@classmethod
def mutated_genes(self):
'''
create random genes for mutation
'''
global GENES
gene = random.choice(GENES)
return gene
@classmethod
def create_gnome(self):
'''
create chromosome or string of genes
'''
global TARGET
gnome_len = len(TARGET)
return [self.mutated_genes() for _ in range(gnome_len)]
def mate(self, par2):
'''
Perform mating and produce new offspring
'''
# chromosome for offspring
child_chromosome = []
for gp1, gp2 in zip(self.chromosome, par2.chromosome):
# random probability
prob = random.random()
# if prob is less than 0.45, insert gene
# from parent 1
if prob < 0.45:
child_chromosome.append(gp1)
# if prob is between 0.45 and 0.90, insert
# gene from parent 2
elif prob < 0.90:
child_chromosome.append(gp2)
# otherwise insert random gene(mutate),
# for maintaining diversity
else:
child_chromosome.append(self.mutated_genes())
# create new Individual(offspring) using
# generated chromosome for offspring
return Individual(child_chromosome)
def cal_fitness(self):
'''
Calculate fitness score, it is the number of
characters in string which differ from target
string.
'''
global TARGET
fitness = 0
for gs, gt in zip(self.chromosome, TARGET):
if gs != gt: fitness+= 1
return fitness
# Driver code
def main():
global POPULATION_SIZE
#current generation
generation = 1
found = False
population = []
# create initial population
for _ in range(POPULATION_SIZE):
gnome = Individual.create_gnome()
population.append(Individual(gnome))
while not found:
# sort the population in increasing order of fitness score
population = sorted(population, key = lambda x:x.fitness)
# if the individual having lowest fitness score ie.
# 0 then we know that we have reached to the target
# and break the loop
if population[0].fitness <= 0:
found = True
break
# Otherwise generate new offsprings for new generation
new_generation = []
# Perform Elitism, that mean 10% of fittest population
# goes to the next generation
s = int((10*POPULATION_SIZE)/100)
new_generation.extend(population[:s])
# From 50% of fittest population, Individuals
# will mate to produce offspring
s = int((90*POPULATION_SIZE)/100)
for _ in range(s):
parent1 = random.choice(population[:50])
parent2 = random.choice(population[:50])
child = parent1.mate(parent2)
new_generation.append(child)
population = new_generation
print("Generation: {}\tString: {}\tFitness: {}".\
format(generation,
"".join(population[0].chromosome),
population[0].fitness))
generation += 1
print("Generation: {}\tString: {}\tFitness: {}".\
format(generation,
"".join(population[0].chromosome),
population[0].fitness))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Output:
Generation: 0 String: BLQx{m?"d}#tz#zXQ"#xw1Pv Fitness: 22
Generation: 1 String: WokJyv' a.oH{4Ch6u.EyK$_ Fitness: 22
Generation: 2 String: r&s4Sd7f![MAm?_R9#5 f3wg Fitness: 22
Generation: 3 String: r&s4Sd7f![MAm?_R9#5 f3wg Fitness: 22
Generation: 4 String: r&s4Sd7f![MAm?_R9#5 f3Zg Fitness: 22
Generation: 5 String: BLQx{m?"d}#tz#zXQ"#xw1Pv Fitness: 22
Generation: 6 String: r&s4Sd7f![MAm?_R9#5 f3wg Fitness: 22
Generation: 7 String: [&s4Sd7f![MAm?_R9#5 f3Zg Fitness: 22
.
.
.
Generation: 858 String: Welcome to t'cmis's blog Fitness: 1
Generation: 859 String: Welcome to tTcmis's blog Fitness: 1
Generation: 860 String: Welcome to tCcmis's blog Fitness: 1
Generation: 861 String: Welcome to tCcmis's blog Fitness: 1
Generation: 862 String: Welcome to ticmis's blog Fitness: 0
遗传算法 Genetic Algorithms的更多相关文章
- 基于遗传算法(Genetic Algorithm)的TSP问题求解(C)
基于遗传算法的TSP问题求解(C) TSP问题: TSP(Travelling salesman problem): 译作“旅行商问题”, 一个商人由于业务的需要,要到n个城市,每个城市之间都有一条路 ...
- 遗传算法Genetic Algorithm
遗传算法Genetic Algorithm 好家伙,回回都是这个点,再这样下去人估计没了,换个bgm<夜泊秦淮>,要是经典咏流传能投票选诗词,投票选歌,俺一定选这个 开始瞎叨叨 遗传算法的 ...
- 遗传算法 Genetic Algorithm
2017-12-17 19:12:10 一.Evolutionary Algorithm 进化算法,也被成为是演化算法(evolutionary algorithms,简称EAs),它不是一个具体的算 ...
- 超详细的遗传算法(Genetic Algorithm)解析
https://blog.csdn.net/u010451580/article/details/51178225 https://www.jianshu.com/p/c82f09adee8f 00 ...
- 【智能算法】超详细的遗传算法(Genetic Algorithm)解析和TSP求解代码详解
喜欢的话可以扫码关注我们的公众号哦,更多精彩尽在微信公众号[程序猿声] 文章声明 此文章部分资料和代码整合自网上,来源太多已经无法查明出处,如侵犯您的权利,请联系我删除. 00 目录 遗传算法定义 生 ...
- MIP启发式算法:遗传算法 (Genetic algorithm)
*本文主要记录和分享学习到的知识,算不上原创 *参考文献见链接 本文主要讲述启发式算法中的遗传算法.遗传算法也是以local search为核心框架,但在表现形式上和hill climbing, ta ...
- 遗传算法(Genetic Algorithm)——基于Java实现
一.遗传算法原理介绍 遗传算法(Genetic Algorithm)是模拟达尔文生物进化论的自然选择和遗传学机理的生物进化过程的计算模型,是一种通过模拟自然进化过程搜索最优解的方法.遗传算法是从代表问 ...
- 遗传算法中几种不同选择算子及Python实现
前言 本文对遗传算法中的几种选择策略进行了总结, 其中包括: Proportionate Roulette Wheel Selection Linear Ranking Selection Expon ...
- 【遗传编程/基因规划】Genetic Programming
目录 背景介绍 程序表示 初始化 (Initialization) Depth定义 Grow方法 Full方法 Ramped half-and-half方法 适应度(Fitness)与选择(Selec ...
随机推荐
- 常用RE对照表——敬请期待!!!
.* #任意长度任意字符
- jmeter中获取token和cookie
## 登录获取token 1.添加请求 1.1 输入接口中需要携带的参数的值 2.正则表达式提取器提取出值 3.输入token数据 "token":"(.+?)" ...
- iOS App 上架App Store及提交审核详细教程
上架App Store审核分7步进行: 1.安装iOS上架辅助软件Appuploader 2.申请iOS发布证书(p12) 3.申请iOS发布描述文件(mobileprovision) 4.打包ipa ...
- Qt--无边框窗口完美(FrameLess)实现,包含缩放和移动功能重写。
前言 Qt原本的窗口虽然可以通过QSS样式进行美化,但是只是对客户区有用,对于客户区是无效的.所以想做出一个比较好看的程序,还得自己重写实现无边框窗口. Qt实现无边框其实一句代码就可以,但是窗口自带 ...
- K8S节点配置资源驱逐
#参考文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangrui153169/p/15726165.html 当节点内存到达多少时.对节点的pod进行驱逐 [root@lecode-tes ...
- 第一章 计算机和C++简介
1.1 简介 C++是一种强大的计算机面向对象编程的程序设计语言,它是制造软件的一种编程语言,适合程序员和刚接触编程的技术人员.当今智能手机销量爆炸式增长给移动应用程序的开发带来了很多机会,而C++就 ...
- centos8换可用公网yum源
这个咋说呢,总之就是非常简单 百度上找一个公网源替换进去就好 但是就是麻烦,在此做个笔记,也当给大家一个现成的范例 以下为https://vault.centos.org官网源的一个简单的替换脚本,一 ...
- C++两种方法改变输出颜色
方法一: 使用 SetConsoleTextAttribute 需要引入 #include "windows.h" SetConsoleTextAttribute(Ge ...
- MQ系列8:数据存储,消息队列的高可用保障
MQ系列1:消息中间件执行原理 MQ系列2:消息中间件的技术选型 MQ系列3:RocketMQ 架构分析 MQ系列4:NameServer 原理解析 MQ系列5:RocketMQ消息的发送模式 MQ系 ...
- 【每日一题】【list转int数组】【Lambda的简化-方法引用】2022年1月15日-NC45 实现二叉树先序,中序和后序遍历
描述 给定一棵二叉树,分别按照二叉树先序,中序和后序打印所有的节点. 数据范围:0 \le n \le 10000≤n≤1000,树上每个节点的val值满足 0 \le val \le 1000≤ ...
