Sentiment analysis in nlp
Sentiment analysis in nlp
The goal of the program is to analysis the article title is Sarcasm or not, i use tensorflow 2.5 to solve this problem.
Dataset download url: https://www.kaggle.com/rmisra/news-headlines-dataset-for-sarcasm-detection/home
a sample of the dataset:
{
"article_link": "https://www.huffingtonpost.com/entry/versace-black-code_us_5861fbefe4b0de3a08f600d5",
"headline": "former versace store clerk sues over secret 'black code' for minority shoppers",
"is_sarcastic": 0
}
we want to depend on headline to predict the is_sarcastic, 1 means True,0 means False.
preprocessing
use pandas to read json file.
import pandas as pd
# lines = True means headle the json for each line
df = pd.read_json("Sarcasm_Headlines_Dataset_v2.json" ,lines="True")
df
'''
is_sarcastic headline article_link
0 1 thirtysomething sci... https://www.theonion.co...
1 0 dem rep. totally ... https://www.huffingtonpos..
'''build list for each column
labels = []
sentences = []
urls = []
# a tips for convert series to list
'''
type(df['is_sarcastic'])
# Series
type(df['is_sarcastic'].values)
# ndarray
type(df['is_sarcastic'].values.tolist())
# list
'''
labels = df['is_sarcastic'].values.tolist()
sentences = df['headline'].values.tolist()
urls = df['article_link'].values.tolist()
len(labels) # 28619
len(sentences) # 28619split dataset into train set and test set
# train size is the 2/3 of the all dataset.
train_size = int(len(labels) / 3 * 2)
train_sentences = sentences[0: train_size]
test_sentences = sentences[train_size:]
train_y = labels[0:train_size]
test_y = labels[train_size:]init some parameter
# some parameter
vocab_size = 10000
# input layer to embedding
embedding_dim = 16
# each input sentence length
max_length = 100
# padding method
trunc_type='post'
padding_type='post'
# token the unfamiliar word
oov_tok = "<OOV>"preprocessing on train set and test set
# processing on train set and test set
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
tokenizer = Tokenizer(oov_token = oov_tok)
tokenizer.fit_on_texts(train_sentences)
train_X = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(train_sentences)
# padding the data
train_X = pad_sequences(train_X,
maxlen = max_length,
truncating = trunc_type,
padding = padding_type)
train_X[:2]
# convery the list to nparray
train_y = np.array(train_y)
# same operator to test set
test_X = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(test_sentences)
test_X = pad_sequences(test_X ,
maxlen = max_length,
truncating = trunc_type,
padding = padding_type)
test_y = np.array(test_y)
build the model
some important functions and args:
tf.keras.layers.Dense # Dense
implements the operation:output = activation(dot(input, kernel) + bias) , a NN layeractivation # Activation function to use. If you don't specify anything, no activation is applied (ie. "linear" activation:
a(x) = x).use_bias # Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias vector.
tf.keras.Sequential # contain a linear stack of layer into a
tf.keras.Model.tf.keras.Model # to train and predict
config the model with losses and metrics with
model.compile(args)optimizer
some args
AdamRMSpropSGDAdagrad
loss # The loss value that will be minimized by the model will then be the sum of all individual losses.
metrices # List of metrics to be evaluated by the model during training and testing.
train the model with
model.fit(x=None,y=None)batch_size # Number of samples per gradient update. If unspecified,
batch_sizewill default to 32.epochs # Number of epochs to train the model
verbose # Verbosity mode. 0 = silent, 1 = progress bar, 2 = one line per epoch,verbose=2 is recommended when not running interactively
validation_data #( valid_X, valid_y )
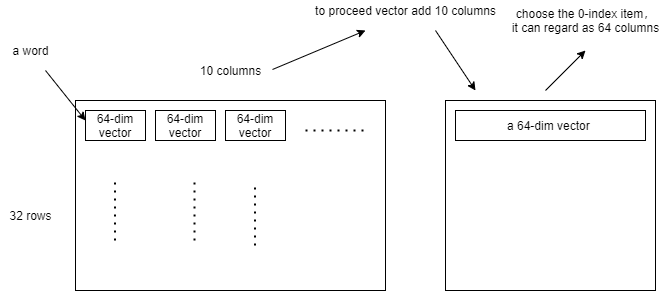
tf.keras.layers.Embedding # Turns positive integers (indexes) into dense vectors of fixed size. as shown in following figure
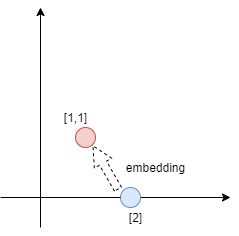
the purpose of the embedding is making the 1-dim integer proceed the muti-dim vectors add. can find the hide feature and connect to predict the labels. in this program ,every word's emotion direction can be trained many times.
tf.keras.layer.GlobalAveragePooling1D # add all muti-dim vectors ,if the output layer shape is (32, 10, 64), after the pooling, the shape will be changed as (32,64), as shown in following figure
-
code is more simple then theory
# build the model
model = tf.keras.Sequential(
[
# make a word became a 64-dim vector
tf.keras.layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim, input_length = max_length),
# add all word vector
tf.keras.layers.GlobalAveragePooling1D(),
# NN
tf.keras.layers.Dense(24, activation = 'relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, activation = 'sigmoid')
]
)
model.compile(loss = 'binary_crossentropy', optimizer = 'adam' , metrics = ['accuracy'])
train the model
num_epochs = 30
history = model.fit(train_X, train_y, epochs = num_epochs,
validation_data = (test_X, test_y),
verbose = 2)
after the 30 epochs
Epoch 30/30
597/597 - 8s - loss: 1.8816e-04 - accuracy: 1.0000 - val_loss: 1.2858 - val_accuracy: 0.8216
predict our sentence
mytest_sentence = ["you are so cute", "you are so cute but looks like stupid"]
mytest_X = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(mytest_sentence)
mytest_X = pad_sequences(mytest_X ,
maxlen = max_length,
truncating = trunc_type,
padding = padding_type)
mytest_y = model.predict(mytest_X)
# if result is bigger then 0.5 ,it means the title is Sarcasm
print(mytest_y > 0.5)
'''
[[False]
[ True]]
'''
reference:
tensorflow API: https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/Sequential
colab: bit.ly/tfw-sarcembed
Sentiment analysis in nlp的更多相关文章
- Sentiment Analysis resources
Wikipedia: Sentiment analysis (also known as opinion mining) refers to the use of natural language p ...
- NAACL 2013 Paper Mining User Relations from Online Discussions using Sentiment Analysis and PMF
中文简单介绍:本文对怎样基于情感分析和概率矩阵分解从网络论坛讨论中挖掘用户关系进行了深入研究. 论文出处:NAACL'13. 英文摘要: Advances in sentiment analysis ...
- 【Deep Learning Nanodegree Foundation笔记】第 10 课:Sentiment Analysis with Andrew Trask
In this lesson, Andrew Trask, the author of Grokking Deep Learning, will walk you through using neur ...
- 论文阅读:Multi-task Learning for Multi-modal Emotion Recognition and Sentiment Analysis
论文标题:Multi-task Learning for Multi-modal Emotion Recognition and Sentiment Analysis 论文链接:http://arxi ...
- 使用RNN进行imdb影评情感识别--use RNN to sentiment analysis
原创帖子,转载请说明出处 一.RNN神经网络结构 RNN隐藏层神经元的连接方式和普通神经网路的连接方式有一个非常明显的区别,就是同一层的神经元的输出也成为了这一层神经元的输入.当然同一时刻的输出是不可 ...
- Deep Learning for NLP 文章列举
Deep Learning for NLP 文章列举 原文链接:http://www.xperseverance.net/blogs/2013/07/2124/ 大部分文章来自: http://w ...
- 转 Deep Learning for NLP 文章列举
原文链接:http://www.xperseverance.net/blogs/2013/07/2124/ 大部分文章来自: http://www.socher.org/ http://deepl ...
- Standford CoreNLP--Sentiment Analysis初探
Stanford CoreNLP功能之一是Sentiment Analysis(情感分析),可以标识出语句的正面或者负面情绪,包括:Positive,Neutral,Negative三个值. 运行有两 ...
- Java自然语言处理NLP工具包
1. Java自然语言处理 LingPipe LingPipe是一个自然语言处理的Java开源工具包.LingPipe目前已有很丰富的功能,包括主题分类(Top Classification).命名实 ...
随机推荐
- NodeJS学习日报day4——模块化
// console.log(module); // 执行顺序不同,结果也不同 // module.exports = { // name : 'Cra2iTeT', // hi() { // con ...
- Ajax错误处理
控制台报的错误是: Access to XMLHttpRequest at 'http://localhost:3000/error' from origin 'null' has been bloc ...
- 重磅!业界首个云原生批量计算项目Volcano正式晋级为CNCF孵化项目
摘要:4月7日,云原生计算基金会(CNCF)宣布,由华为云捐献的业界首个云原生批量计算项目Volcano正式晋级为CNCF孵化项目. 4月7日,云原生计算基金会(CNCF)宣布,由华为云捐献的业界首个 ...
- C3P0反序列化链学习
C3P0 c3p0第一次听闻是用于fastjson的回显上,大佬们总结三种方法,后面两种主要就是用于fastjson和jackjson的回显利用(注入内存马) http base jndi hex序列 ...
- 6.1 SHELL脚本
6.1 SHELL脚本元素 第一行的脚本声明(#!)用来告诉系统使用哪种Shell解释器来执行该脚本: 第二行的注释信息(#)是对脚本功能和某些命令的介绍信息,使得自己或他人在日后看到这个脚本内容时, ...
- [笔记] 2-sat
定义 简单的说就是给出 \(n\) 个集合,每个集合有两个元素,已知形如选 \(a\) 则必须选 \(b\) 的若干个条件, 问是否存在从每个集合选择一个元素满足条件的方案,通常可以题目只要求任意一种 ...
- Linux 设置开机自启动脚本(ES、MySQL、Nacos、Nginx)
/etc/rc.d/init.d 中文件会在 Linux 系统各项服务都启动完毕之后再被运行 cd /etc/rc.d/init.d:新建xxx.sh文件. chmod +x xxx.sh,赋予可执行 ...
- zabbix的web界面访问失败问题排查
现象:用curl访问显示拒绝链接,查看zabbix-server日志也无异常 1.检查防火墙,SElinux是否关闭 2.检查zabbix-server服务是否启动 3.检查80端口是否被占用,比方是 ...
- 8┃音视频直播系统之 WebRTC 信令系统实现以及通讯核心并实现视频通话
一.信令系统 信令系统主要用来进行信令的交换 在通信双方彼此连接.传输媒体数据之前,它们要通过信令服务器交换一些信息,如规范协商 若 A 与 B 要进行音视频通信,那么 A 要知道 B 已经上线了,同 ...
- 【多线程】观测线程状态 getState()
观测线程状态 getState() Thread.State(查看JDK帮助文档) 线程状态.线程可以处于以下状态之一: [NEW] 尚未启动的线程处于此状态. [RUNNABLE] 在Java虚拟机 ...