Python 常用方法和模块的使用(time & datetime & os &random &sys &shutil)-(六)
1 比较常用的一些方法
1.eval()方法:执行字符串表达式,并返回到字符串。
2.序列化:变量从内存中变成可存储或传输到文件或变量的过程,可以保存当时对象的状态,实现其生命周期的延长,并且需要时可以再次将这个对象读取出来.
涉及到2个方法:变量:dumps()、loads()和文件:dump()、load()
3.静态方法、类方法、属性方法
2 比较常用的一些模块
对应模块下如何查看对应的变量和方法:
模块名.__all__
help(模块名.变量/方法)
#查看对应模块下有哪些方法和变量
>>> random.__all__
['Random', 'seed', 'random', 'uniform', 'randint', 'choice', 'sample', 'randrange', 'shuffle', 'normalvariate', 'lognormvariate', 'expovariate', 'vonmisesvariate', 'gammavariate', 'triangular', 'gauss', 'betavariate', 'paretovariate', 'weibullvariate', 'getstate', 'setstate', 'getrandbits', 'choices', 'SystemRandom'] #查看对应模块的内容
>>> help(random.seed)
Help on method seed in module random: seed(a=None, version=2) method of random.Random instance
Initialize internal state from hashable object. None or no argument seeds from current time or from an operating
system specific randomness source if available. If *a* is an int, all bits are used. For version 2 (the default), all of the bits are used if *a* is a str,
bytes, or bytearray. For version 1 (provided for reproducing random
sequences from older versions of Python), the algorithm for str and
bytes generates a narrower range of seeds.
1.time 、datetime模块
通常有这三种方式来表示时间:时间戳、元组(struct_time)、格式化的时间字符串:
(1)时间戳(timestamp) :通常来说,时间戳表示的是从1970年1月1日00:00:00开始按秒计算的偏移量。我们运行“type(time.time())”,返回的是float类型。
(2)格式化的时间字符串(Format String):'2019-11-13',返回的是字符串类型。
(3)元组(struct_time) :struct_time元组共有9个元素共九个元素:(年,月,日,时,分,秒,一年中第几周,一年中第几天等),返回的是元组。
| 索引(Index) | 属性(Attribute) | 值(Values) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | tm_year(年) | 比如2011 |
| 1 | tm_mon(月) | 1 - 12 |
| 2 | tm_mday(日) | 1 - 31 |
| 3 | tm_hour(时) | 0 - 23 |
| 4 | tm_min(分) | 0 - 59 |
| 5 | tm_sec(秒) | 0 - 60 |
| 6 | tm_wday(weekday) | 0 - 6(0表示周一) |
| 7 | tm_yday(一年中的第几天) | 1 - 366 |
| 8 | tm_isdst(是否是夏令时) | 默认为0 |
主要关系如下:
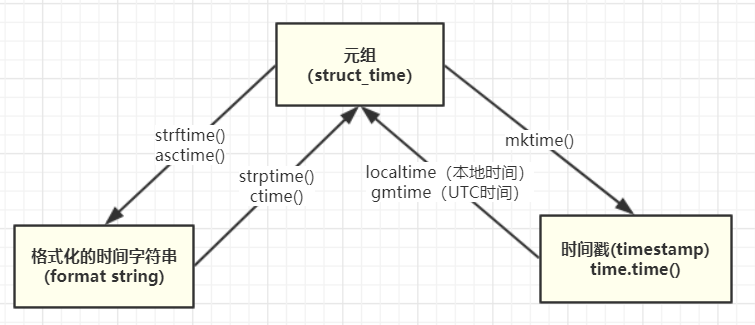
举例:
import time
t=time.time #获得时间戳
a=time.localtime(t) #获得当地时间的时间元组
b=time.gmtime(t)#获得格林威治时间的时间元组,有8个小时的时差
time.asctime(a) #获得时间的字符串
time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',a) #获得指定格式的本地时间
time.strptime(时间字符串,字符串对应格式) #获得时间元组
ex:
#获取时间戳
>>> time.time()
1573629408.9401257 #时间戳--->元组时间
>>> time.gmtime(time.time())
time.struct_time(tm_year=2019, tm_mon=11, tm_mday=13, tm_hour=7, tm_min=17, tm_sec=35, tm_wday=2, tm_yday=317, tm_isdst=0) >>> time.localtime(time.time())
time.struct_time(tm_year=2019, tm_mon=11, tm_mday=13, tm_hour=15, tm_min=17, tm_sec=8, tm_wday=2, tm_yday=317, tm_isdst=0) #元组时间--->时间戳
>>> time.mktime(time.localtime(time.time()))
1573628709.0 #元组时间 --->格式化时间
>>> time.asctime(time.localtime(time.time()))
'Wed Nov 13 15:19:04 2019' >>> time.ctime()
'Wed Nov 13 15:24:26 2019' >>> time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d',time.localtime(time.time()))
'2019-11-13' #格式化时间---> 元组时间
#time.strptime(时间字符串,字符串对应格式)
>>> time.strptime('2019-11-13','%Y-%m-%d')
time.struct_time(tm_year=2019, tm_mon=11, tm_mday=13, tm_hour=0, tm_min=0, tm_sec=0, tm_wday=2, tm_yday=317, tm_isdst=-1) >>> time.ctime()
'Wed Nov 13 15:24:26 2019'
参考如下:
https://www.runoob.com/python3/python3-date-time.html
https://docs.python.org/3/library/time.html
2.random
#random()方法返回随机生成的一个实数,在[0,1)范围内
>>> import random
>>> random.random()
0.9769965303661935 #uniform()随机生成0-20之间的浮点数
>>> random.uniform(0,20)
1.3427421915969069
>>> random.uniform(0,20)
1.302763489201494 #randint()方法随机生成1-3之间的整数
>>> random.randint(1,3)
2 #randrange()方法随机生成0-100之间的偶数,步长为2
>>> random.randrange(0,100,2)
14 #对序列随机选择一个元素
>>> random.choice('改变世界')
'界'
>>> random.choice('改变世界')
'改' >>> random.choice(['sumshine','is','lower']) #对列表选择一个元素
'sumshine'
>>> random.choice(['sumshine','is','lower'])
'is' >>> random.choice(('sumshine','is','lower')) #对元组选择一个元素
'is' #对列表元素随机排序
>>> list=[1,2,3]
>>> random.shuffle(list)
>>> list
[1, 3, 2]
3.os
>>> os.__all__
['altsep', 'curdir', 'pardir', 'sep', 'pathsep', 'linesep', 'defpath', 'name', 'path', 'devnull', 'SEEK_SET', 'SEEK_CUR', 'SEEK_END', 'fsencode', 'fsdecode', 'get_exec_path', 'fdopen', 'popen', 'extsep', '_exit', 'DirEntry', 'F_OK', 'O_APPEND', 'O_BINARY', 'O_CREAT', 'O_EXCL', 'O_NOINHERIT', 'O_RANDOM', 'O_RDONLY', 'O_RDWR', 'O_SEQUENTIAL', 'O_SHORT_LIVED', 'O_TEMPORARY', 'O_TEXT', 'O_TRUNC', 'O_WRONLY', 'P_DETACH', 'P_NOWAIT', 'P_NOWAITO', 'P_OVERLAY', 'P_WAIT', 'R_OK', 'TMP_MAX', 'W_OK', 'X_OK', 'abort', 'access', 'chdir', 'chmod', 'close', 'closerange', 'cpu_count', 'device_encoding', 'dup', 'dup2', 'environ', 'error', 'execv', 'execve', 'fspath', 'fstat', 'fsync', 'ftruncate', 'get_handle_inheritable', 'get_inheritable', 'get_terminal_size', 'getcwd', 'getcwdb', 'getlogin', 'getpid', 'getppid', 'isatty', 'kill', 'link', 'listdir', 'lseek', 'lstat', 'mkdir', 'open', 'pipe', 'putenv', 'read', 'readlink', 'remove', 'rename', 'replace', 'rmdir', 'scandir', 'set_handle_inheritable', 'set_inheritable', 'spawnv', 'spawnve', 'startfile', 'stat', 'stat_result', 'statvfs_result', 'strerror', 'symlink', 'system', 'terminal_size', 'times', 'times_result', 'truncate', 'umask', 'uname_result', 'unlink', 'urandom', 'utime', 'waitpid', 'write', 'makedirs', 'removedirs', 'renames', 'walk', 'execl', 'execle', 'execlp', 'execlpe', 'execvp', 'execvpe', 'getenv', 'supports_bytes_environ', 'spawnl', 'spawnle'
4.sys & shutil
shutil主要作用与拷贝文件用的.
shutil.copyfileobj(文件1,文件2):将文件1的数据覆盖copy给文件2。
shutil.copyfile(文件1,文件2):不用打开文件,直接用文件名进行覆盖copy。
shutil.copymode(文件1,文件2):之拷贝权限,内容组,用户,均不变。
shutil.copystat(文件1,文件):只拷贝了权限。
参考博文:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiangsikai/p/7787101.html
5.shelve
shelve模块 也可以序列化Python所有数据类型,而且可以多次序列化;shelve模块通过key-value方式持久化
参考博文:https://www.cnblogs.com/bert227/p/9324591.html
6.xml处理
参考博文:https://www.cnblogs.com/ginvip/p/6891534.html
https://www.runoob.com/python/python-xml.html
7.configparser
参考博文:https://www.cnblogs.com/ming5218/p/7965973.html
3、python常用注意点
3.1 python在不同层级目录import模块的方法:一般有2种方式,通过sys.path.append("路径")和在目录中添加__init__.py文件。
参考文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/kex1n/p/5971590.html
3.2 python 接口测试-使用requests模块发送GET请求:有参数、无参数、带header参数
参考文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/feiyueNotes/p/7857784.html
Python 常用方法和模块的使用(time & datetime & os &random &sys &shutil)-(六)的更多相关文章
- Python 第五篇(上):算法、自定义模块、系统标准模块(time 、datetime 、random 、OS 、sys 、hashlib 、json和pickle)
一:算法回顾: 冒泡算法,也叫冒泡排序,其特点如下: 1.比较相邻的元素.如果第一个比第二个大,就交换他们两个. 2.对每一对相邻元素作同样的工作,从开始第一对到结尾的最后一对.在这一点,最后的元素应 ...
- python常用模块collections os random sys
Python 模块(Module),是一个 Python 文件,以 .py 结尾,包含了 Python 对象定义和Python语句. 模块让你能够有逻辑地组织你的 Python 代码段. 把相关的代码 ...
- 包及常用模块(time、datetime、random、sys)
什么是包?‘ #官网解释 Packages are a way of structuring Python’s module namespace by using “dotted module nam ...
- day16——自定义模块、time、datetime、random
day16 自定义模块 自定义一个模块 import :导入(拿工具箱) # import test # test.func() 导入发生的事情 在当前的名称空间中开辟一个新的空间 将模块中所有的代码 ...
- Python包,json&pickle,time&datetime,random模块
补充内容: 解决模块循环导入的两种方法:(不得已而为之,表示程序结构不够严谨) 将导入模块语句放在文件最下方 保证语句导入之前函数内代码能够被执行 将导入语句放进函数体内 使其不影响整个函数的运行 包 ...
- Python模块:time、datetime、random、os、sys、optparse
time模块的方法: 时间戳表示的是从1970年1月1日00:00:00开始按秒计算的偏移量. struct_time时间元组,共有九个元素组.如下图: time.localtime([secs]): ...
- 包与time,datetime,random,sys,shutil 模块
一.包 包是什么? 包是一种通过使用‘.模块名’来组织python模块名称空间的方式. 注意: 1. 在python3中,即使包下没有__init__.py文件,import 包仍然不会报错,而在py ...
- Python之常用模块(re,时间,random,os,sys,序列化模块)(Day20)
一.时间模块 #常用方法 1.time.sleep(secs) (线程)推迟指定的时间运行.单位为秒. 2.time.time() 获取当前时间戳 在Python中表示时间的三种方式:时间戳,元组(s ...
- Python3基础(5)常用模块:time、datetime、random、os、sys、shutil、shelve、xml处理、ConfigParser、hashlib、re
---------------个人学习笔记--------------- ----------------本文作者吴疆-------------- ------点击此处链接至博客园原文------ 1 ...
随机推荐
- php 获取时间相差的月份和天数
function getMonthAndDay($date1,$date2){ $datestart= date('Y-m-d',strtotime($date1)); if(strtotime($d ...
- git 分支合并到master
[参考:] https://segmentfault.com/q/1010000000181403 我们一般这样:远程创建一个主分支,本地每人创建功能分支,日常工作流程如下: # 去自己的工作分支 ...
- ubuntu12.04 安装lamp <1>
安装:lamp: sudo apt-get install apache2 libapache2-mod-php5 php5-mysql mysql-server 删除mysql sudo apt-g ...
- 强迫自己学习Jquery三
元素定位问题 offset 和 position必须要好好看一下,
- 关于“Failed to configure a DataSource: 'url' attribute is not specified and no embedded datasource could be configured.”
Consider the following: If you want an embedded database (H2, HSQL or Derby), please put it on the c ...
- 信号-linux
https://www.linuxjournal.com/article/3985 每个信号在 signal.h 头文件中通过宏进行定义,实际是在 signal.h 中定义,对于编号以及信号名的映射关 ...
- Spring Boot优雅地处理404异常
背景 在使用SpringBoot的过程中,你肯定遇到过404错误.比如下面的代码: @RestController @RequestMapping(value = "/hello" ...
- C# 简易的串口监视上位机实现
实现上位机和下位机之间的通信,通常使用的是串口通信,接下来实现一个通过上位机和串口调试助手来完成串口通信测试. 首先创建一个WInfrom窗体应用工程文件,创建过程可参考https://www.cnb ...
- 网站实现微信扫码登录 php
微信开放平台账号一个,必须是商户,不然你也开不了 1.在开放平台创建应用,并设置回调地址(域名即可) 2.生成二维码,前端代码,用户扫码后会给你的回调地址发送code <span id=&quo ...
- kali 系列学习04 - 漏洞扫描
一.比较三类漏洞扫描工具 1.Rapid7 Nexpose 适合较大网络 2.Nessus 更经济,可以申请个人版,搞之后硬盘占用达到20G 以上2个是商业软件,使用容易上手,输入IP地址就能完成所有 ...
