曹工说Spring Boot源码(30)-- ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 实在太硬核了,为了了解它,我可能debug了快一天
写在前面的话
相关背景及资源:
曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享
曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,咱们对着接口,逐个方法讲解
曹工说Spring Boot源码(3)-- 手动注册Bean Definition不比游戏好玩吗,我们来试一下
曹工说Spring Boot源码(4)-- 我是怎么自定义ApplicationContext,从json文件读取bean definition的?
曹工说Spring Boot源码(5)-- 怎么从properties文件读取bean
曹工说Spring Boot源码(6)-- Spring怎么从xml文件里解析bean的
曹工说Spring Boot源码(7)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(上)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(8)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(util命名空间)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(9)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(context命名空间上)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(10)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(context:annotation-config 解析)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(11)-- context:component-scan,你真的会用吗(这次来说说它的奇技淫巧)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(12)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(context:component-scan完整解析)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(13)-- AspectJ的运行时织入(Load-Time-Weaving),基本内容是讲清楚了(附源码)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(14)-- AspectJ的Load-Time-Weaving的两种实现方式细细讲解,以及怎么和Spring Instrumentation集成
曹工说Spring Boot源码(15)-- Spring从xml文件里到底得到了什么(context:load-time-weaver 完整解析)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(16)-- Spring从xml文件里到底得到了什么(aop:config完整解析【上】)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(17)-- Spring从xml文件里到底得到了什么(aop:config完整解析【中】)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(18)-- Spring AOP源码分析三部曲,终于快讲完了 (aop:config完整解析【下】)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(19)-- Spring 带给我们的工具利器,创建代理不用愁(ProxyFactory)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(20)-- 码网恢恢,疏而不漏,如何记录Spring RedisTemplate每次操作日志
曹工说Spring Boot源码(21)-- 为了让大家理解Spring Aop利器ProxyFactory,我已经拼了
曹工说Spring Boot源码(22)-- 你说我Spring Aop依赖AspectJ,我依赖它什么了
曹工说Spring Boot源码(23)-- ASM又立功了,Spring原来是这么递归获取注解的元注解的
曹工说Spring Boot源码(24)-- Spring注解扫描的瑞士军刀,asm技术实战(上)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(25)-- Spring注解扫描的瑞士军刀,ASM + Java Instrumentation,顺便提提Jar包破解
曹工说Spring Boot源码(26)-- 学习字节码也太难了,实在不能忍受了,写了个小小的字节码执行引擎
曹工说Spring Boot源码(27)-- Spring的component-scan,光是include-filter属性的各种配置方式,就够玩半天了
曹工说Spring Boot源码(28)-- Spring的component-scan机制,让你自己来进行简单实现,怎么办
曹工说Spring Boot源码(29)-- Spring 解决循环依赖为什么使用三级缓存,而不是二级缓存
工程结构图:

本篇前言
本篇是单独基于spring-boot 2.1.7.RELEASE的版本写的,本来没有这篇文章的,本来正在写遇到的一个eureka client的问题,然后有一个eureka的自动配置类,我当时准备讲解一下:
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties
@ConditionalOnClass(EurekaClientConfig.class)
@Import(DiscoveryClientOptionalArgsConfiguration.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration.Marker.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "eureka.client.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
@ConditionalOnDiscoveryEnabled
@AutoConfigureBefore({ NoopDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration.class,
CommonsClientAutoConfiguration.class, ServiceRegistryAutoConfiguration.class })
@AutoConfigureAfter(name = {
"org.springframework.cloud.autoconfigure.RefreshAutoConfiguration"})
public class EurekaClientAutoConfiguration {
结果,我发现,对于这一坨注解的执行顺序,我并不是很了解,本来以为是spring.factories里配置了这个类,因此最早的入口是在那里,结果,实际debug起来,发现好像并不是,而是由另外一个eureka的自动配置类触发的。
因此,纠结半天,干脆好好好好学研究下spring boot/cloud下configuration类的处理过程。
测试代码
就是一个普通的spring boot下的eureka client程序,pom大致如下
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.7.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>demo</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>Greenwich.SR5</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web </artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
一个误会
一点点常识,大家可能都知道ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,这个类,负责处理各种@configuration注解配置的类(full模式),也包括轻量模式下的配置类(没有@configuration配置,但是有@bean方法等)。
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor实现了如下接口:
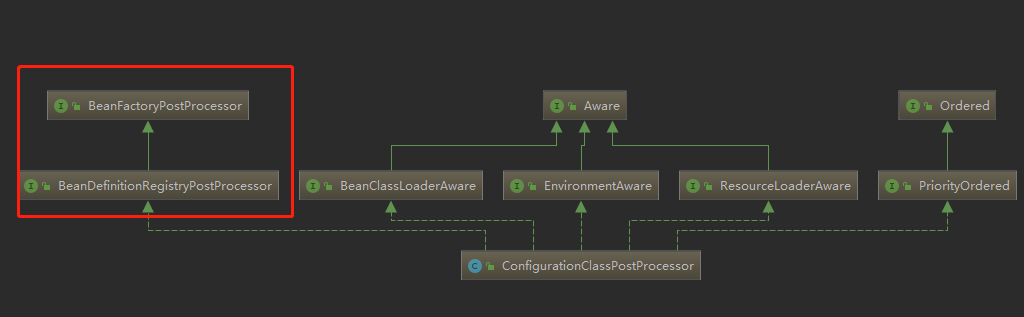
实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,总体来说,是对beanDefinition进行各种后置处理,比如增删改beanDefinition。
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean definition registry after its
* standard initialization. All regular bean definitions will have been loaded,
* but no beans will have been instantiated yet. This allows for adding further
* bean definitions before the next post-processing phase kicks in.
* @param registry the bean definition registry used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException;
}
这个方法,就是对beanFactory进行后置处理,而后置处理主要干啥呢,就是增加beanDefinition,比如我们一个类A上,注解@configuration,同时注解@Import,导入了其他类。
那么,就在这个方法中,就会去扫描configuration配置的类,比如扫描到类A,然后去获取类A上的注解,然后递归获取类A上的注解的元注解,最终检查其中:是否有PropertySource、是否有ComponentScan、是否有Import、是否有@bean方法等等,去获取更多的beanDefinition回来,并注册到beanFactory。
因此,入口基本就是在 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor#postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry。
因此,我把断点打在 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry,准备把这个各种注解的处理顺序搞清楚。
结果,我跟了大半天,还了解了:
在spring cloud下,是有两个applicationContext(如果有feign调用,会有更多,这里暂不考虑)。
其中一个,就是bootStrap applicationContext;另外一个,才是应用程序本身的applicationContext。
而且,bootStrap applicationContext 是应用本身的applicationContext的parent。

我一开始没注意到有两个,因为我以为只有配置了bootStrap.yml才会有;结果跟了很久,都没到我的应用的类,才意识到这个问题。
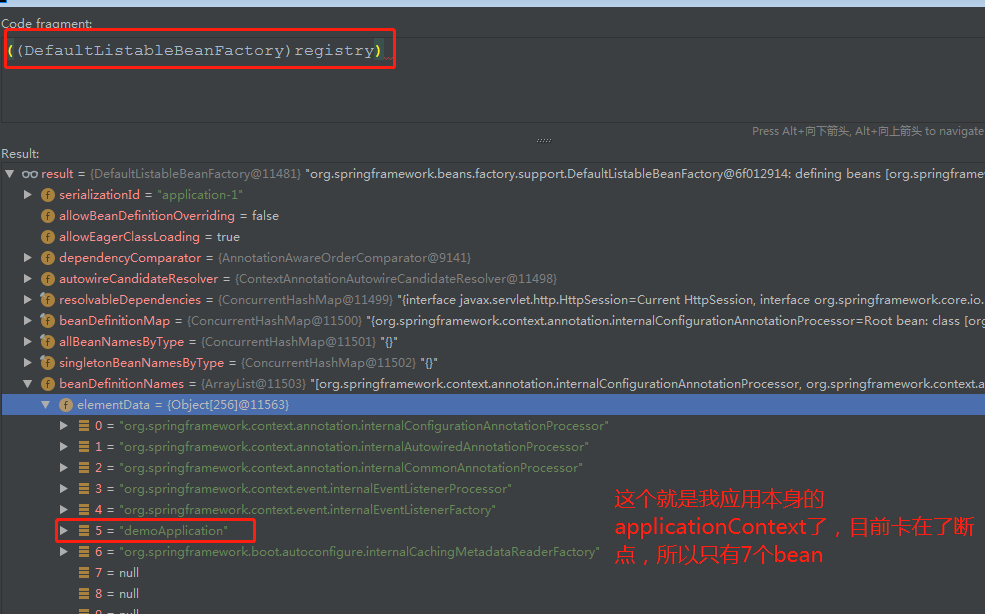
所以呢,跟了半天多的东西,其实是bootStrap applicationContext的东西,不过代码逻辑都是一样的;而且,学习bootStrap applicationContext也很有必要。
let‘s start
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry
/**
* Derive further bean definitions from the configuration classes in the registry.
*/
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
int registryId = System.identityHashCode(registry);
...
this.registriesPostProcessed.add(registryId);
processConfigBeanDefinitions(registry);
}
这里没多少东西,主要就是最后一行开始:
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#processConfigBeanDefinitions
该方法比较长,其实是ConfigurationClassPostProcessor太核心了,几乎是spring boot的基石,所以只能分为多个部分来顺序讲解。
获取候选bean集合
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<>();
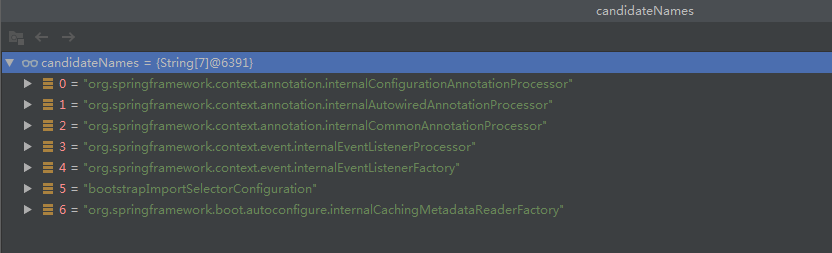
String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
断点显示,这里获取到了,如下candidate:
过滤出configuration注解的类
for (String beanName : candidateNames) {
BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef) ||
ConfigurationClassUtils.isLiteConfigurationClass(beanDef)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef);
}
}
else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName));
}
}
上面的几个候选类,经过这里筛选后,只剩下一个满足条件的bean。
bootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration
生成configuration类解析器
ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser(
this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,
this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
这个类,没有继承任何类,也没有实现任何接口
public ConfigurationClassParser(MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory,
ProblemReporter problemReporter, Environment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader,BeanNameGenerator componentScanBeanNameGenerator, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
this.metadataReaderFactory = metadataReaderFactory;
this.problemReporter = problemReporter;
this.environment = environment;
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
this.registry = registry;
// 1
this.componentScanParser = new ComponentScanAnnotationParser(
environment, resourceLoader, componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
// 2
this.conditionEvaluator = new ConditionEvaluator(registry, environment, resourceLoader);
}
这里1处,new了一个bean扫描解析器。
public ComponentScanAnnotationParser(Environment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader,
BeanNameGenerator beanNameGenerator, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
this.environment = environment;
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
this.beanNameGenerator = beanNameGenerator;
this.registry = registry;
}
2处,创建了一个condition计算器,负责各种@condition的解析计算。
public ConditionEvaluator(@Nullable BeanDefinitionRegistry registry,
@Nullable Environment environment, @Nullable ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.context = new ConditionContextImpl(registry, environment, resourceLoader);
}
使用ConfigurationClassParser循环解析
do {
// 1
parser.parse(candidates);
parser.validate();
Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>(parser.getConfigurationClasses());
configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed);
// Read the model and create bean definitions based on its content
if (this.reader == null) {
this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader(
registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment,
this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);
alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses);
candidates.clear();
if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) {
String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
Set<String> oldCandidateNames = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames));
Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<>();
for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) {
alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
}
for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) {
if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) {
BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this.metadataReaderFactory) &&
!alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) {
candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd, candidateName));
}
}
}
candidateNames = newCandidateNames;
}
}
while (!candidates.isEmpty());
接下来,先进入1处。
ConfigurationClassParser#parse
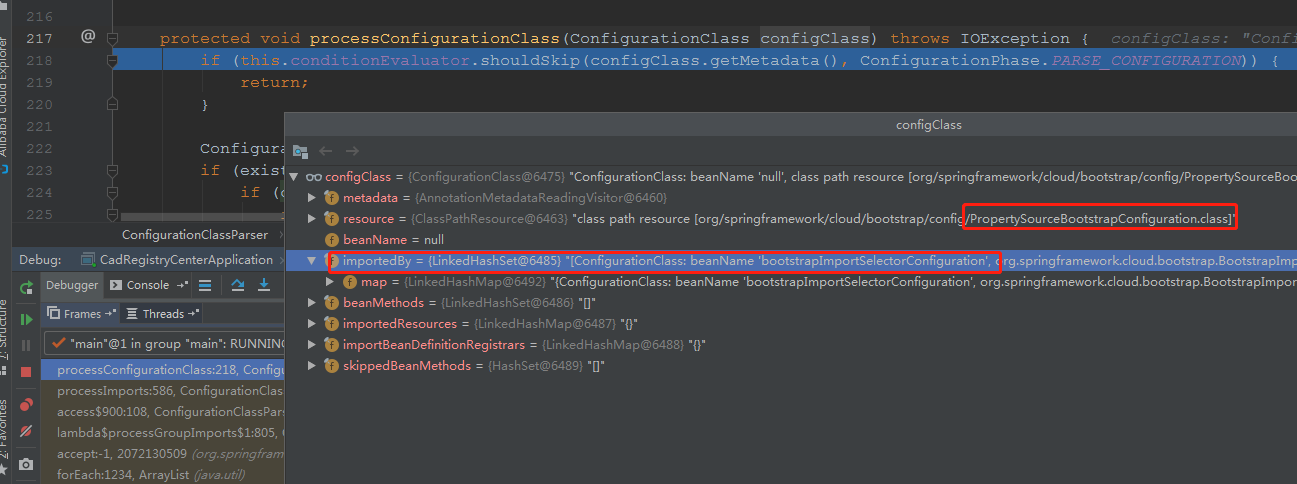
注意,进入此处时,参数configCandidates的值为:
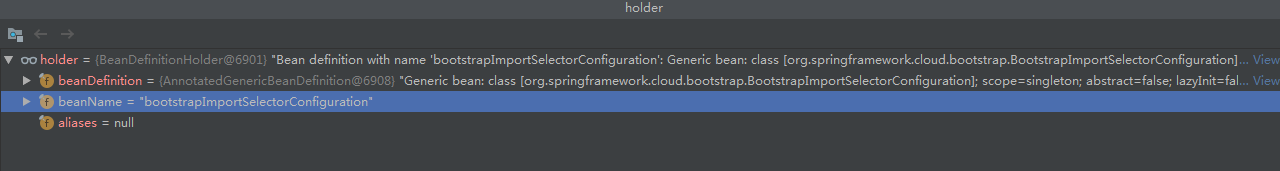
该holder中,就包含beanName和beanDefinition,其中bean对应的class类型为:
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration
public void parse(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates) {
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : configCandidates) {
BeanDefinition bd = holder.getBeanDefinition();
try {
if (bd instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
// 1
parse(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) bd).getMetadata(), holder.getBeanName());
}
else if (bd instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).hasBeanClass()) {
parse(((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).getBeanClass(), holder.getBeanName());
}
else {
parse(bd.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
}
this.deferredImportSelectorHandler.process();
}
这里会进入1处。
在进入该方法前,获取了beanDefinition中的MetaData。
(AnnotatedBeanDefinition) bd).getMetadata()
protected final void parse(AnnotationMetadata metadata, String beanName) {
processConfigurationClass(new ConfigurationClass(metadata, beanName));
}
这里先去new了一个ConfigurationClass。
public ConfigurationClass(AnnotationMetadata metadata, String beanName) {
Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null");
this.metadata = metadata;
this.resource = new DescriptiveResource(metadata.getClassName());
this.beanName = beanName;
}
这个类,主要是对于@configuration注解标注的类的封装。
/**
* Represents a user-defined {@link Configuration @Configuration} class.
* Includes a set of {@link Bean} methods, including all such methods
* defined in the ancestry of the class, in a 'flattened-out' manner.
*
*/
final class ConfigurationClass {
开始解析
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser#processConfigurationClass
protected void processConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass) {
// 1
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION)) {
return;
}
1处,使用condition计算器,进行判断,看看该bean是否满足
public boolean shouldSkip(@Nullable AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata, @Nullable ConfigurationPhase phase) {
if (metadata == null || !metadata.isAnnotated(Conditional.class.getName())) {
return false;
}
因为org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration类上,并没有condition注解,所以是默认生效的。
接下来进入下面的地方:
protected void processConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass){
// 0
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION)) {
return;
}
// 1
ConfigurationClass existingClass = this.configurationClasses.get(configClass);
if (existingClass != null) {
if (configClass.isImported()) {
if (existingClass.isImported()) {
existingClass.mergeImportedBy(configClass);
}
return;
}
else {
this.configurationClasses.remove(configClass);
this.knownSuperclasses.values().removeIf(configClass::equals);
}
}
// 2
SourceClass sourceClass = asSourceClass(configClass);
do {
// 3
sourceClass = doProcessConfigurationClass(configClass, sourceClass);
}
while (sourceClass != null);
this.configurationClasses.put(configClass, configClass);
}
0,就是前面说的判断condition是否满足
1,此时不满足条件,直接跳过
2,这里根据注解信息,获取sourceClass,不用细究
private SourceClass asSourceClass(ConfigurationClass configurationClass){
AnnotationMetadata metadata = configurationClass.getMetadata();
if (metadata instanceof StandardAnnotationMetadata) {
return asSourceClass(((StandardAnnotationMetadata) metadata).getIntrospectedClass());
}
return asSourceClass(metadata.getClassName());
}
3处,继续解析。
这个类较长,我们下面细讲。
doProcessConfigurationClass
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass){
// 3.1
if (configClass.getMetadata().isAnnotated(Component.class.getName())) {
//3.2 Recursively process any member (nested) classes first
processMemberClasses(configClass, sourceClass);
}
这里实际上,会进入3.1处。因为这个类上,加了@configuration注解的。
@Configuration
@Import(BootstrapImportSelector.class)
public class BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration {
}
处理member类
然后3.2处,member类处理,这里暂时不太清楚member类是什么,不过我们这个BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration也没有获取到任何的member class,所以先跳过。
处理PropertySource
接下来,开始解析bean的class上,是否注解了PropertySource.
// Process any @PropertySource annotations
for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(PropertySource.class)) {
if (this.environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
processPropertySource(propertySource);
}
}
这里,我们并没有注解PropertySource,所以也会跳过。
处理componnet-scan
这里也没有,跳过。
处理@imort
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), true);
在processImports之前,这里第三个参数,先去调用了getImports。
getImports
/**
* Returns {@code @Import} class, considering all meta-annotations.
*/
private Set<SourceClass> getImports(SourceClass sourceClass) throws IOException {
Set<SourceClass> imports = new LinkedHashSet<>();
Set<SourceClass> visited = new LinkedHashSet<>();
collectImports(sourceClass, imports, visited);
return imports;
}
private void collectImports(SourceClass sourceClass, Set<SourceClass> imports, Set<SourceClass> visited)
throws IOException {
if (visited.add(sourceClass)) {
for (SourceClass annotation : sourceClass.getAnnotations()) {
String annName = annotation.getMetadata().getClassName();
if (!annName.equals(Import.class.getName())) {
// 1
collectImports(annotation, imports, visited);
}
}
// 2
imports.addAll(sourceClass.getAnnotationAttributes(Import.class.getName(), "value"));
}
}
1,递归调用自己,获取@Import注解
2,将@import注解中value的值取出来,放到imports中。
这里处理完成后,我们获取到的东西如下:
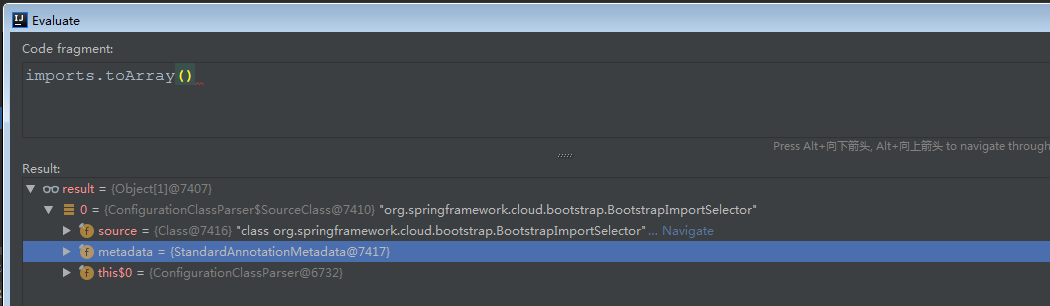
即:
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapImportSelector
processImport
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), true);
private void processImports(ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass currentSourceClass, Collection<SourceClass> importCandidates, boolean checkForCircularImports) {
if (importCandidates.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
this.importStack.push(configClass);
try {
// 0
for (SourceClass candidate : importCandidates) {
// 1
if (candidate.isAssignable(ImportSelector.class)) {
// Candidate class is an ImportSelector -> delegate to it to determine imports
Class<?> candidateClass = candidate.loadClass();
ImportSelector selector = BeanUtils.instantiateClass(candidateClass, ImportSelector.class);
ParserStrategyUtils.invokeAwareMethods(
selector, this.environment, this.resourceLoader, this.registry);
if (selector instanceof DeferredImportSelector) {
this.deferredImportSelectorHandler.handle(configClass, (DeferredImportSelector) selector);
}
else {
String[] importClassNames = selector.selectImports(currentSourceClass.getMetadata());
Collection<SourceClass> importSourceClasses = asSourceClasses(importClassNames);
processImports(configClass, currentSourceClass, importSourceClasses, false);
}
}
// 2
else if (candidate.isAssignable(ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class)) {
// Candidate class is an ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar ->
// delegate to it to register additional bean definitions
Class<?> candidateClass = candidate.loadClass();
ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar registrar =
BeanUtils.instantiateClass(candidateClass, ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class);
ParserStrategyUtils.invokeAwareMethods(
registrar, this.environment, this.resourceLoader, this.registry);
configClass.addImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar(registrar, currentSourceClass.getMetadata());
}
else {
// 3
// Candidate class not an ImportSelector or ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar ->
// process it as an @Configuration class
this.importStack.registerImport(
currentSourceClass.getMetadata(), candidate.getMetadata().getClassName());
processConfigurationClass(candidate.asConfigClass(configClass));
}
}
}
}
- 1处,当要import的是ImportSelector接口时
- 2处,当要import的bean class是:ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar
- 3处,当要import的是普通的configuration class时。
我们这里这个类,是实现了DeferredImportSelector,间接实现了ImportSelector:
public class BootstrapImportSelector implements EnvironmentAware, DeferredImportSelector
所以要进入下面这一坨逻辑:
for (SourceClass candidate : importCandidates) {
// 1
if (candidate.isAssignable(ImportSelector.class)) {
//2 Candidate class is an ImportSelector -> delegate to it to determine imports
Class<?> candidateClass = candidate.loadClass();
// 3
ImportSelector selector = BeanUtils.instantiateClass(candidateClass, ImportSelector.class);
// 4
ParserStrategyUtils.invokeAwareMethods(
selector, this.environment, this.resourceLoader, this.registry);
// 5
if (selector instanceof DeferredImportSelector) {
// 6
this.deferredImportSelectorHandler.handle(configClass, (DeferredImportSelector) selector);
}
else {
String[] importClassNames = selector.selectImports(currentSourceClass.getMetadata());
Collection<SourceClass> importSourceClasses = asSourceClasses(importClassNames);
processImports(configClass, currentSourceClass, importSourceClasses, false);
}
}
- 1, 判断如果是实现了ImportSelector
- 2,加载对应的bean class
- 3,通过反射实例化该bean
- 4,调用aware方法,注入environment等
- 5,判断是否为DeferredImportSelector,该类型需要被延迟import
- 6,处理该DeferredImportSelector
6处,使用专门的handler,来处理DeferredImportSelector类型的bean。
public void handle(ConfigurationClass configClass, DeferredImportSelector importSelector) {
// 1
DeferredImportSelectorHolder holder = new DeferredImportSelectorHolder(
configClass, importSelector);
if (this.deferredImportSelectors == null) {
DeferredImportSelectorGroupingHandler handler = new DeferredImportSelectorGroupingHandler();
handler.register(holder);
handler.processGroupImports();
}
else {
// 2
this.deferredImportSelectors.add(holder);
}
}
1,将configClass,和importSelector放进一个holder中。
public DeferredImportSelectorHolder(ConfigurationClass configClass, DeferredImportSelector selector) {
this.configurationClass = configClass;
this.importSelector = selector;
}
2,往如下的list中,添加一个holder实例。
@Nullable
private List<DeferredImportSelectorHolder> deferredImportSelectors = new ArrayList<>();
到这里,基本@import就处理完了,因为前面这个importSelector是deferred类型,是需要延期处理的,所以,加入该list后,处理结束。
处理@bean方法
这里没有bean方法,跳过。
处理接口中的默认方法
这个暂时不涉及,跳过。
处理deferredImportSelector
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser#parse
public void parse(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates) {
// 0
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : configCandidates) {
BeanDefinition bd = holder.getBeanDefinition();
try {
if (bd instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
// 1
parse(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) bd).getMetadata(), holder.getBeanName());
}
else if (bd instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).hasBeanClass()) {
parse(((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).getBeanClass(), holder.getBeanName());
}
else {
parse(bd.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
}
// 2
this.deferredImportSelectorHandler.process();
}
接下来,我们回到之前的代码,1处的parse方法终于处理结束了,本来应该进入0处的下一轮循环,但是这里因为集合中只有那么一个元素:bootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration。所以这步就算处理完了。
进入到2处。
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser.DeferredImportSelectorHandler#process
public void process() {
List<DeferredImportSelectorHolder> deferredImports = this.deferredImportSelectors;
this.deferredImportSelectors = null;
try {
if (deferredImports != null) {
//1
DeferredImportSelectorGroupingHandler handler = new DeferredImportSelectorGroupingHandler();
// 2
deferredImports.forEach(handler::register);
// 3
handler.processGroupImports();
}
}
finally {
this.deferredImportSelectors = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
- 1,new了一个handler,专门处理这种延迟导入的bean selector
- 2,对需要延迟导入的bean selector,进行遍历,然后调用handler的register
- 3,调用handler的批量import方法。
我们对2处和3处重点讲解。
handler::registered
public void register(DeferredImportSelectorHolder deferredImport) {
// 0
Class<? extends Group> group = deferredImport.getImportSelector()
.getImportGroup();
// 1
DeferredImportSelectorGrouping grouping = this.groupings.computeIfAbsent(
(group != null ? group : deferredImport),
key -> new DeferredImportSelectorGrouping(createGroup(group)));
// 2
grouping.add(deferredImport);
this.configurationClasses.put(deferredImport.getConfigurationClass().getMetadata(),
deferredImport.getConfigurationClass());
}
0,从holder二元组中,获取importSelector,然后获取其importGroup。
这里的group为null。
public interface DeferredImportSelector extends ImportSelector { /**
* Return a specific import group.
* <p>The default implementations return {@code null} for no grouping required.
* @return the import group class, or {@code null} if none
* @since 5.0
*/
@Nullable
default Class<? extends Group> getImportGroup() {
return null;
}
1处,比较复杂。
这里有个field:
private final Map<Object, DeferredImportSelectorGrouping> groupings = new LinkedHashMap<>();
1处我们可以看出,是在往上面这个map,放东西。
key:
(group != null ? group : deferredImport)因为我们这里group为null,所以这里的key为:
DeferredImportSelectorHolder deferredImport,也就是那个二元组。value是啥呢?
key -> new DeferredImportSelectorGrouping(createGroup(group))
我们先看看createGroup吧:
private Group createGroup(@Nullable Class<? extends Group> type) {
// 1
Class<? extends Group> effectiveType = (type != null ? type
: DefaultDeferredImportSelectorGroup.class);
Group group = BeanUtils.instantiateClass(effectiveType);
ParserStrategyUtils.invokeAwareMethods(group,
ConfigurationClassParser.this.environment,
ConfigurationClassParser.this.resourceLoader,
ConfigurationClassParser.this.registry);
return group;
}
1处,因为我们传入的参数:type为null,所以这里场景了一个DefaultDeferredImportSelectorGroup的实例,填充Aware字段后,返回。
然后,我们利用createGroup返回的实例,传给了:
key -> new DeferredImportSelectorGrouping(createGroup(group))
然后看看这个类呢:
private static class DeferredImportSelectorGrouping { private final DeferredImportSelector.Group group; private final List<DeferredImportSelectorHolder> deferredImports = new ArrayList<>();
// 1
DeferredImportSelectorGrouping(Group group) {
this.group = group;
}
2,我们上面一步,往map里放了个key、value。
private final Map<Object, DeferredImportSelectorGrouping> groupings = new LinkedHashMap<>();
3,现在需要往value(类型为DeferredImportSelectorGrouping),加入一个延迟importSelector的holder
public void register(DeferredImportSelectorHolder deferredImport) {
Class<? extends Group> group = deferredImport.getImportSelector()
.getImportGroup();
DeferredImportSelectorGrouping grouping = this.groupings.computeIfAbsent(
(group != null ? group : deferredImport),
key -> new DeferredImportSelectorGrouping(createGroup(group)));
//
grouping.add(deferredImport);
this.configurationClasses.put(deferredImport.getConfigurationClass().getMetadata(),
deferredImport.getConfigurationClass());
}
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser.DeferredImportSelectorGrouping#add
public void add(DeferredImportSelectorHolder deferredImport) {
this.deferredImports.add(deferredImport);
}
注册
public void register(DeferredImportSelectorHolder deferredImport) {
Class<? extends Group> group = deferredImport.getImportSelector()
.getImportGroup();
DeferredImportSelectorGrouping grouping = this.groupings.computeIfAbsent(
(group != null ? group : deferredImport),
key -> new DeferredImportSelectorGrouping(createGroup(group)));
grouping.add(deferredImport);
// 4
this.configurationClasses.put(deferredImport.getConfigurationClass().getMetadata(),
deferredImport.getConfigurationClass());
}
然后进入到上面的4处,这里把这个延迟importSelector的metadata作为key,configurationClass作为value,放进map。
private class DeferredImportSelectorGroupingHandler { private final Map<Object, DeferredImportSelectorGrouping> groupings = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// 1
private final Map<AnnotationMetadata, ConfigurationClass> configurationClasses = new HashMap<>();
即上面1处这个map。
进行group import
public void process() {
List<DeferredImportSelectorHolder> deferredImports = this.deferredImportSelectors;
this.deferredImportSelectors = null;
try {
if (deferredImports != null) {
DeferredImportSelectorGroupingHandler handler = new DeferredImportSelectorGroupingHandler();
deferredImports.sort(DEFERRED_IMPORT_COMPARATOR);
// 0
deferredImports.forEach(handler::register);
// 1
handler.processGroupImports();
}
}
finally {
this.deferredImportSelectors = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
前面已经把0处,讲解完毕;这里进入1处。
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser.DeferredImportSelectorGroupingHandler#processGroupImports
private Map<Object, DeferredImportSelectorGrouping> groupings = new LinkedHashMap<>();
public void processGroupImports() {
// 1
for (DeferredImportSelectorGrouping grouping : this.groupings.values()) {
// 2
grouping.getImports().forEach(entry -> {
ConfigurationClass configurationClass = this.configurationClasses.get(
entry.getMetadata());
try {
processImports(configurationClass, asSourceClass(configurationClass),
asSourceClasses(entry.getImportClassName()), false);
}
});
}
}
1处,我们这里遍历groupings这个map的value集合
2,获取这个grouping中的要import的集合
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser.DeferredImportSelectorGrouping#getImports private final List<DeferredImportSelectorHolder> deferredImports = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* Return the imports defined by the group.
* @return each import with its associated configuration class
*/
public Iterable<Group.Entry> getImports() {
// 1
for (DeferredImportSelectorHolder deferredImport : this.deferredImports) {
// 2
this.group.process(deferredImport.getConfigurationClass().getMetadata(),
deferredImport.getImportSelector());
}
return this.group.selectImports();
}
- 1,遍历全部的holder
- 2,获取holder中的,这个importSelector的类的元数据,和importSelector本身,传给this.group.process方法。
我们看看这里的process方法
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser.DefaultDeferredImportSelectorGroup private static class DefaultDeferredImportSelectorGroup implements Group { private final List<Entry> imports = new ArrayList<>(); @Override
public void process(AnnotationMetadata metadata, DeferredImportSelector selector) {
// 1
for (String importClassName : selector.selectImports(metadata)) {
this.imports.add(new Entry(metadata, importClassName));
}
} @Override
public Iterable<Entry> selectImports() {
return this.imports;
}
}
这里的1处,即调用了selector接口的方法了
public interface ImportSelector { /**
* Select and return the names of which class(es) should be imported based on
* the {@link AnnotationMetadata} of the importing @{@link Configuration} class.
*/
String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata); }
1处的selector.selectImports,我们可以看到,传进去了一个metadata,这个metaData都有啥数据呢?
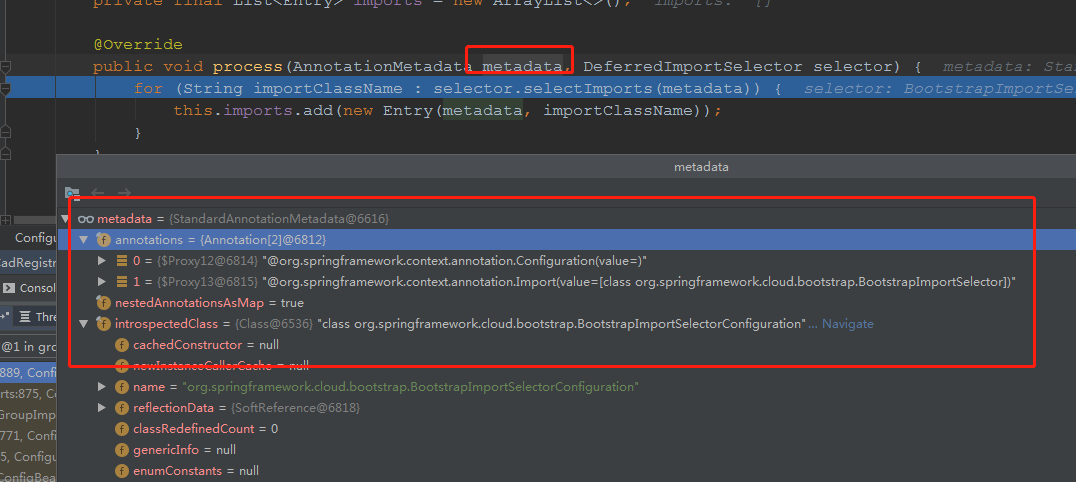
我们再看一眼下面这个类:
@Configuration
@Import(BootstrapImportSelector.class)
public class BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration { }
所以,传入的metaData就是这个被@Import注解,注解了的类的信息。
相当于说,你在类A上加上@Import注解,那么最终类A的信息,会被当做参数,传给ImportSelector的selectImports方法。
BootstrapImportSelector
前面说到了这个selector实现了DeferredImportSelector,我们看看怎么实现的吧:
public class BootstrapImportSelector implements EnvironmentAware, DeferredImportSelector {
private Environment environment;
private MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory = new CachingMetadataReaderFactory();
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = environment;
}
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
// 1
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>(SpringFactoriesLoader
.loadFactoryNames(BootstrapConfiguration.class, classLoader));
// 2
names.addAll(Arrays.asList(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(
this.environment.getProperty("spring.cloud.bootstrap.sources", ""))));
// 3
List<OrderedAnnotatedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
for (String name : names) {
try {
elements.add(
// 4
new OrderedAnnotatedElement(this.metadataReaderFactory, name));
}
catch (IOException e) {
continue;
}
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(elements);
String[] classNames = elements.stream().map(e -> e.name).toArray(String[]::new);
// 5
return classNames;
}
1,从spring.factories中,查找以
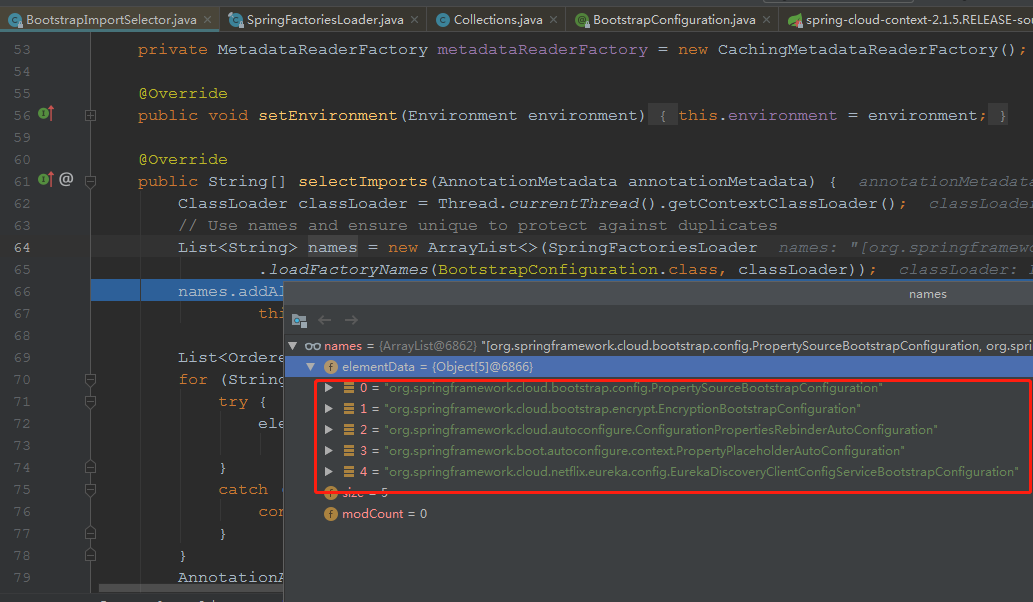
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration为key的property。我们目前这个代码中,在如下文件,找到了一处:
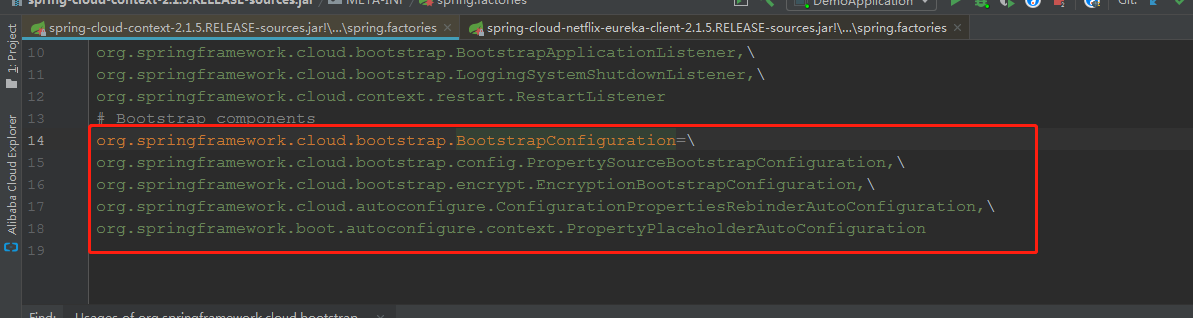
然后在eureka的jar包,找到一个:
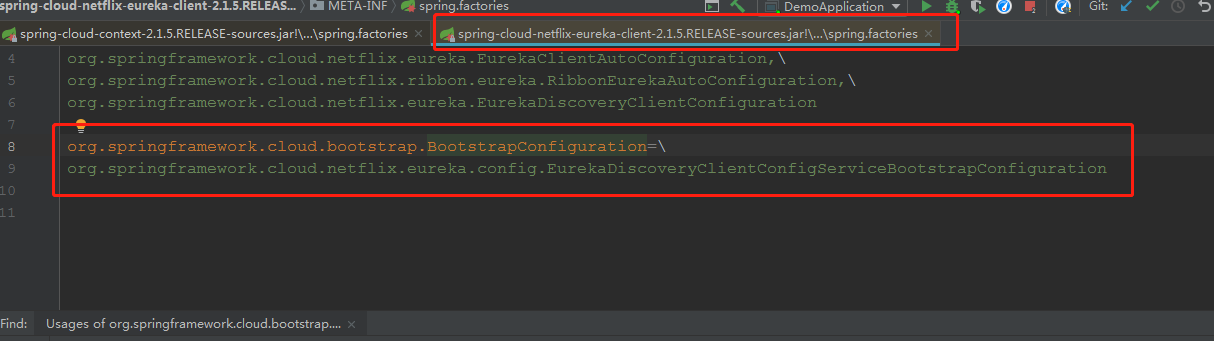
所以,我们拿到了5个值。
2处,从spring.cloud.bootstrap.sources属性中获取
3处,遍历所有这些要import的类名
4处,将类名转换为OrderedAnnotatedElement,这个会获取对应的类的元数据,然后获取其上注解的@order来获取顺序
OrderedAnnotatedElement(MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory, String name)
throws IOException {
MetadataReader metadataReader = metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(name);
AnnotationMetadata metadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata();
Map<String, Object> attributes = metadata
.getAnnotationAttributes(Order.class.getName());
this.name = name;
if (attributes != null && attributes.containsKey("value")) {
this.value = (Integer) attributes.get("value");
this.order = new Order() {
@Override
public Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType() {
return Order.class;
} @Override
public int value() {
return OrderedAnnotatedElement.this.value;
}
};
}
}
5处返回排序后的,要import的class的类名。
将要import的类名,存放起来
private static class DefaultDeferredImportSelectorGroup implements Group {
private final List<Entry> imports = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
public void process(AnnotationMetadata metadata, DeferredImportSelector selector) {
// 1
for (String importClassName : selector.selectImports(metadata)) {
// 2
this.imports.add(new Entry(metadata, importClassName));
}
}
@Override
public Iterable<Entry> selectImports() {
return this.imports;
}
}
前面讲完了1处,现在看看2处。
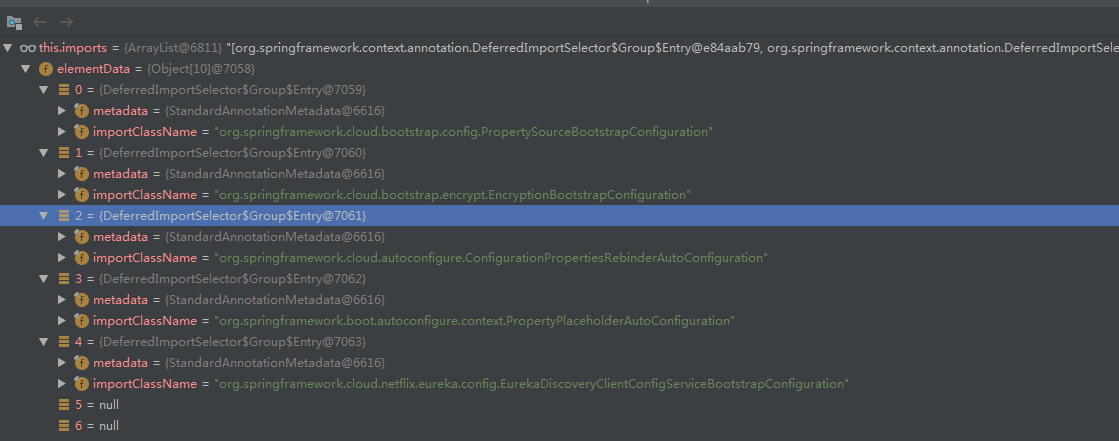
2处就是将前面拿到的5个要import的类,加入到这里的imports 集合中。
此时,imports集合如下:
递归处理下一个configuration class
上面我们获取到了5个要import的class。
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser.DeferredImportSelectorGroupingHandler#processGroupImports
public void processGroupImports() {
for (DeferredImportSelectorGrouping grouping : this.groupings.values()) {
// 1
grouping.getImports().forEach(entry -> {
ConfigurationClass configurationClass = this.configurationClasses.get(
entry.getMetadata());
try {
processImports(configurationClass, asSourceClass(configurationClass),
asSourceClasses(entry.getImportClassName()), false);
}
});
}
}
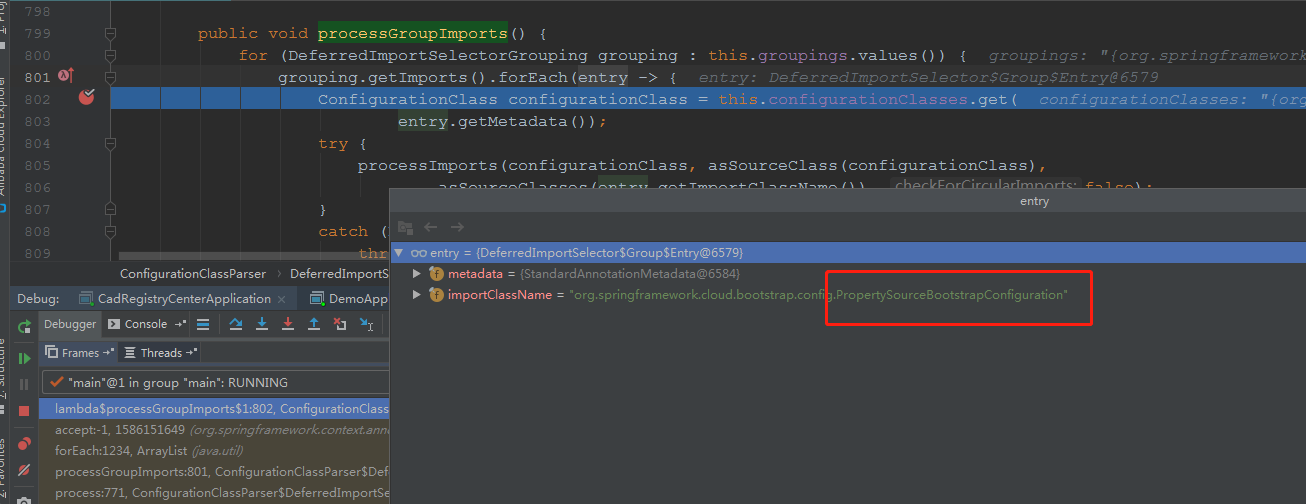
这里1处的grouping.getImports,就能拿到那5个元素。
这里又去开始循环处理,看下图。
处理PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration
我们看看这个类
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(PropertySourceBootstrapProperties.class)
public class PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration implements
ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>, Ordered {
private void processImports(ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass currentSourceClass,
Collection<SourceClass> importCandidates, boolean checkForCircularImports) {
if (importCandidates.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
this.importStack.push(configClass);
try {
for (SourceClass candidate : importCandidates) {
if (candidate.isAssignable(ImportSelector.class)) {
// 1
...
}
else if (candidate.isAssignable(ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class)) {
// 2
...
}
else {
// 3 process it as an @Configuration class
this.importStack.registerImport(
currentSourceClass.getMetadata(), candidate.getMetadata().getClassName());
// 4
processConfigurationClass(candidate.asConfigClass(configClass));
}
}
}
}
因为其没有实现ImportSelector等,所以进入3处,当做普通的Configuration类处理。
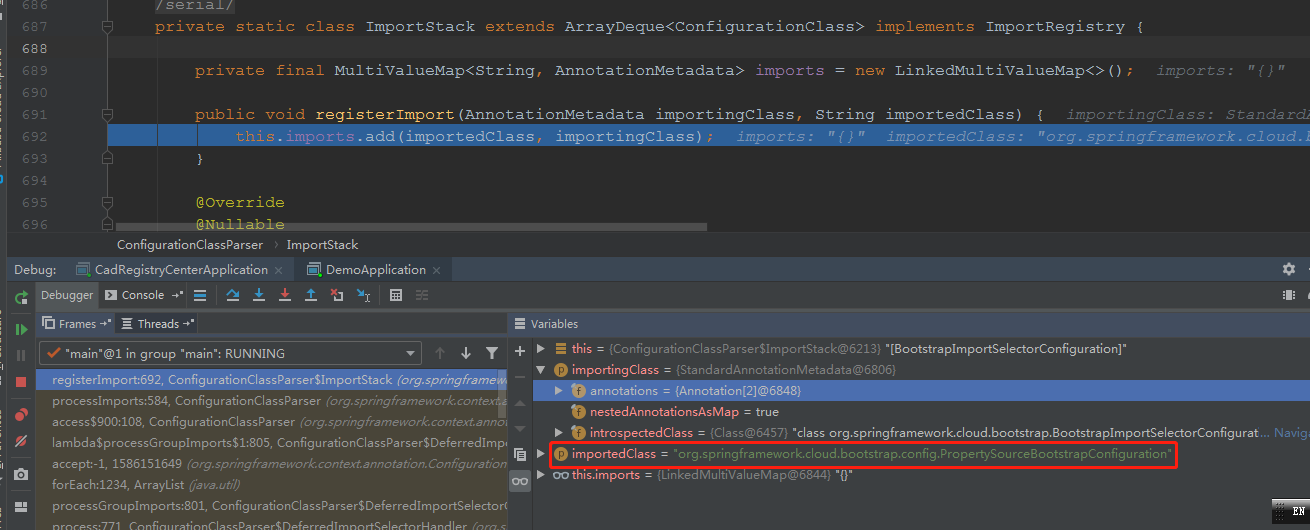
private static class ImportStack extends ArrayDeque<ConfigurationClass> implements ImportRegistry {
private final MultiValueMap<String, AnnotationMetadata> imports = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
//
public void registerImport(AnnotationMetadata importingClass, String importedClass) {
// 1
this.imports.add(importedClass, importingClass);
}
这里直接把其放到map中。
然后进入了前面的4处:
else {
// Candidate class not an ImportSelector or ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar ->
// process it as an @Configuration class
this.importStack.registerImport(
currentSourceClass.getMetadata(), candidate.getMetadata().getClassName());
// 4
processConfigurationClass(candidate.asConfigClass(configClass));
}
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser#processConfigurationClass
protected void processConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass) throws IOException {
// 1
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION)) {
return;
}
...
// Recursively process the configuration class and its superclass hierarchy.
SourceClass sourceClass = asSourceClass(configClass);
do {
// 2
sourceClass = doProcessConfigurationClass(configClass, sourceClass);
}
while (sourceClass != null);
this.configurationClasses.put(configClass, configClass);
}
和之前一样,这里,1处,判断是否满足condition注解,因为我们的PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration,并没有condition,所以是默认生效的。
处理member类
不涉及。
处理PropertySource注解
不涉及。
处理ComponentScan注解
不涉及
处理import注解
由于该类上,加了
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(PropertySourceBootstrapProperties.class)
public class PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration
而:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(EnableConfigurationPropertiesImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableConfigurationProperties {
所以,处理这里时:
// Process any @Import annotations
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), true);
在getImports调用,得到如下返回。
org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationPropertiesImportSelector
然后开始处理该import。
由于其实现了ImportSelector,会进入下面的地方。
private void processImports(ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass currentSourceClass, Collection<SourceClass> importCandidates, boolean checkForCircularImports) {
this.importStack.push(configClass);
try {
for (SourceClass candidate : importCandidates) {
if (candidate.isAssignable(ImportSelector.class)) {
//1 Candidate class is an ImportSelector -> delegate to it to determine imports
Class<?> candidateClass = candidate.loadClass();
ImportSelector selector = BeanUtils.instantiateClass(candidateClass, ImportSelector.class);
ParserStrategyUtils.invokeAwareMethods(
selector, this.environment, this.resourceLoader, this.registry);
if (selector instanceof DeferredImportSelector) {
this.deferredImportSelectorHandler.handle(configClass, (DeferredImportSelector) selector);
}
else {
// 2
String[] importClassNames = selector.selectImports(currentSourceClass.getMetadata());
Collection<SourceClass> importSourceClasses = asSourceClasses(importClassNames);
processImports(configClass, currentSourceClass, importSourceClasses, false);
}
}
1,反射创建该selector
2,调用该selector的selectImport方法,得到要import的类
class EnableConfigurationPropertiesImportSelector implements ImportSelector { private static final String[] IMPORTS = { ConfigurationPropertiesBeanRegistrar.class.getName(),
ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessorRegistrar.class.getName() }; @Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
return IMPORTS;
}
这里,我们就拿到了2个要import的类的类名。
接下来,又开始对这两个要import的类,进行处理。
for (SourceClass candidate : importCandidates) {
if (candidate.isAssignable(ImportSelector.class)) {
// Candidate class is an ImportSelector -> delegate to it to determine imports
Class<?> candidateClass = candidate.loadClass();
ImportSelector selector = BeanUtils.instantiateClass(candidateClass, ImportSelector.class);
ParserStrategyUtils.invokeAwareMethods(
selector, this.environment, this.resourceLoader, this.registry);
if (selector instanceof DeferredImportSelector) {
this.deferredImportSelectorHandler.handle(configClass, (DeferredImportSelector) selector);
}
else {
String[] importClassNames = selector.selectImports(currentSourceClass.getMetadata());
Collection<SourceClass> importSourceClasses = asSourceClasses(importClassNames);
// 1
processImports(configClass, currentSourceClass, importSourceClasses, false);
}
}
即上面的1这一处地方,进行递归处理,此时要import的两个类,是这样的:
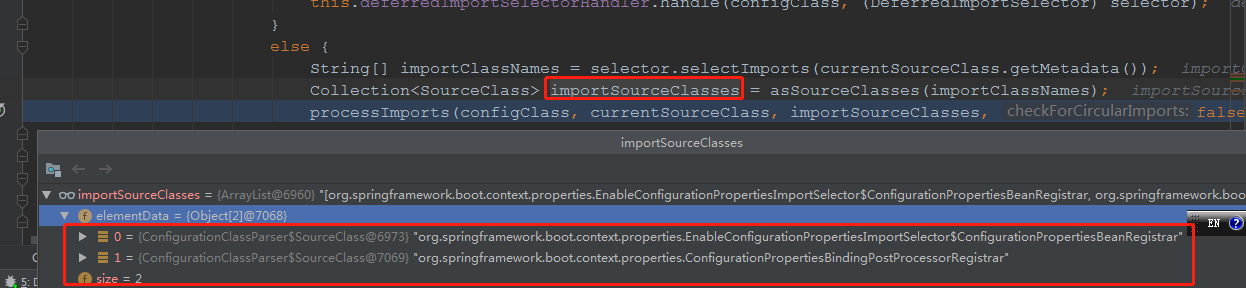
咱们这里不展开了,没完了。。
处理ImportResource注解
不涉及
处理bean方法
不涉及
处理EncryptionBootstrapConfiguration
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ TextEncryptor.class })
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ KeyProperties.class })
public class EncryptionBootstrapConfiguration {
这个类,大家看看就好。没有新东西,不会说再去import什么东西。
不过这个类上就有condition条件了。
在如下方法时,使用condition计算器,就会发现真的有一个condition要计算。
protected void processConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass) throws IOException {
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION)) {
return;
}
然后就又是同样流程,处理member、处理PropertySource、ComponentScan等等。
跳过后续的3个configuration类的处理
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration=\
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.config.PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.encrypt.EncryptionBootstrapConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.autoconfigure.ConfigurationPropertiesRebinderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration
这些都跳过,道理类似的。
parse完成后的后续处理
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<>();
String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
...
// Return immediately if no @Configuration classes were found
if (configCandidates.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// Parse each @Configuration class
ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser(
this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,
this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates);
Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet<>(configCandidates.size());
do {
// 1
parser.parse(candidates);
// 2
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);
alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses);
candidates.clear();
if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) {
String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
Set<String> oldCandidateNames = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames));
Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<>();
for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) {
alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
}
for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) {
if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) {
BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this.metadataReaderFactory) &&
!alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) {
candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd, candidateName));
}
}
}
candidateNames = newCandidateNames;
}
}
while (!candidates.isEmpty());
...
}
整个过程比较复杂,我们这里分析了那么多,主要是把1处的代码说的差不多了。
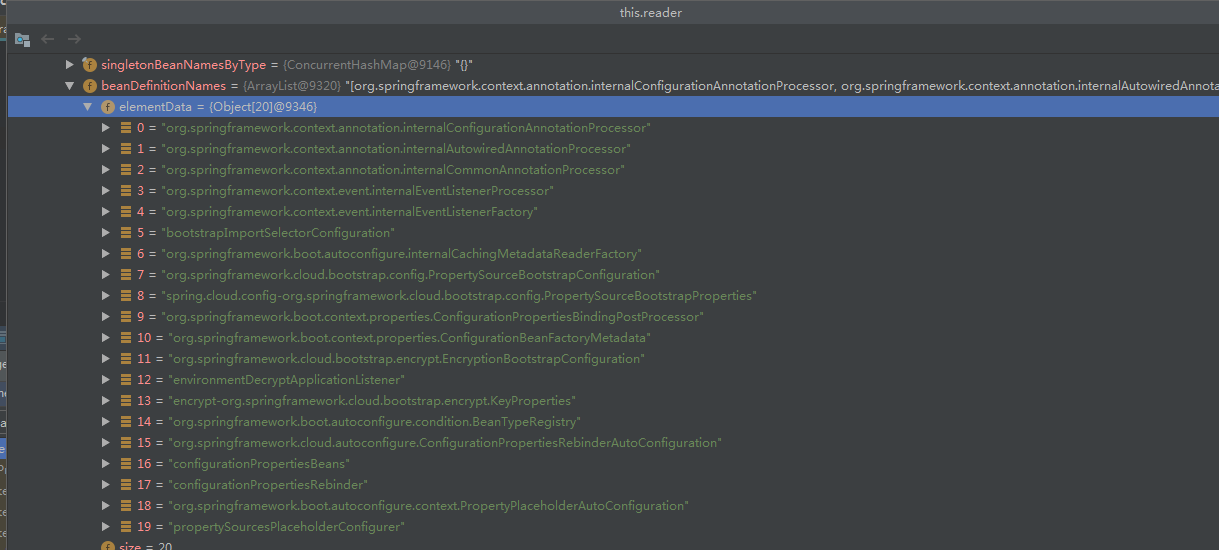
2处,加载beanDefinition。
经过这个步骤后,beanFactory中的bean如下:
总结
到此的话,几乎差不多吧,细节还是很多,有些地方肯定没讲到,后续再补上。
demo的源码本身很简单,如果大家需要,可以从这里获取:
https://gitee.com/ckl111/all-simple-demo-in-work-1/tree/master/eureka/
曹工说Spring Boot源码(30)-- ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 实在太硬核了,为了了解它,我可能debug了快一天的更多相关文章
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(19)-- Spring 带给我们的工具利器,创建代理不用愁(ProxyFactory)
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码系列开讲了(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享
写在前面的话&&About me 网上写spring的文章多如牛毛,为什么还要写呢,因为,很简单,那是人家写的:网上都鼓励你不要造轮子,为什么你还要造呢,因为,那不是你造的. 我不是要 ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,咱们对着接口,逐个方法讲解
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码系列开讲了(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 工程代码地址 思维导图地址 工程结构图: 正 ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(3)-- 手动注册Bean Definition不比游戏好玩吗,我们来试一下
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码系列开讲了(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 工程代码地址 思维导图地址 工程结构图: 大 ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(4)-- 我是怎么自定义ApplicationContext,从json文件读取bean definition的?
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码系列开讲了(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 工程代码地址 思维导图地址 工程结构图: 大 ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(5)-- 怎么从properties文件读取bean
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(6)-- Spring怎么从xml文件里解析bean的
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(7)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(上)
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(8)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(util命名空间)
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
随机推荐
- 入门大数据---SparkSQL外部数据源
一.简介 1.1 多数据源支持 Spark 支持以下六个核心数据源,同时 Spark 社区还提供了多达上百种数据源的读取方式,能够满足绝大部分使用场景. CSV JSON Parquet ORC JD ...
- 【部分】ASP.NET MVC的Controller接收输入详解
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/lxrj2008/article/details/79455360 ASP.NET mvc的Controller要正确的响应用户发出的请求就要获取到用 ...
- jQurey zTree API 3.5
https://jeesite.gitee.io/front/jquery-ztree/3.5/api/API_cn.html
- day08获取图片
wxml: <!--pages/publish/publish.wxml--> <text>pages/publish/publish.wxml</text> &l ...
- C++中string转换为char*类型返回后乱码问题
问题来源: 在写二叉树序列化与反序列化时发现序列化函数为char* Serialize1(TreeNode *root) 其函数返回类型为char*,但是我在实现的过程中为了更方便的操作添加字符串使 ...
- 解决for循环里获取到的索引是最后一个的问题
方法一 原理: 利用 setTimeout 函数的第三个参数,会作为回调函数的第一个参数传入 利用 bind 函数部分执行的特性 代码 1: for (var i = 0; i < 10; i+ ...
- msyql事务的四种隔离级别
一.事务的基本要素(ACID) 1.原子性(Atomicity):事务开始后所有操作,要么全部做完,要么全部不做,不可能停滞在中间环节.事务执行过程中出错,会回滚到事务开始前的状态,所有的操作就像没有 ...
- python数据处理(七)之数据探索和分析
1.探索数据 1.1 安装agate库 1.2 导入数据 1.3 探索表函数 a.排序 b.最值,均值 c.清除缺失值 d.过滤 e.百分比 1.4 连结多个数据集 a.捕捉异常 b.去重 c.缺失数 ...
- redis(三):Redis 命令(python)
import redis from redis import StrictRedis redis=StrictRedis(host='localhost',port=6379,db=0,passwor ...
- POJ 1057 File Mapping 最详细的解题报告
题目来源:POJ 1057 File Mapping 题目大意:像我的电脑那样显示文件夹和文件信息,其中在同一级目录内,文件夹排在文件的前面并且文件夹的顺序不变,同一级目录中文件按字母序排列.文件以‘ ...
