HDU1890 Robotic Sort[splay 序列]
Robotic Sort
Time Limit: 6000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 3913 Accepted Submission(s): 1717
In this task, you are to write software for a robot that handles samples in such a laboratory. Imagine there are material samples lined up on a running belt. The samples have different heights, which may cause troubles to the next processing unit. To eliminate such troubles, we need to sort the samples by their height into the ascending order.
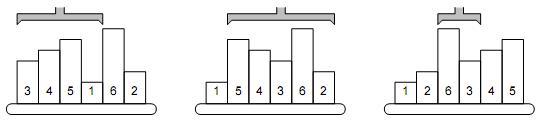
Reordering is done by a mechanical robot arm, which is able to pick up any number of consecutive samples and turn them round, such that their mutual order is reversed. In other words, one robot operation can reverse the order of samples on positions between A and B.
A possible way to sort the samples is to find the position of the smallest one (P1) and reverse the order between positions 1 and P1, which causes the smallest sample to become first. Then we find the second one on position P and reverse the order between 2 and P2. Then the third sample is located etc.
The picture shows a simple example of 6 samples. The smallest one is on the 4th position, therefore, the robot arm reverses the first 4 samples. The second smallest sample is the last one, so the next robot operation will reverse the order of five samples on positions 2–6. The third step will be to reverse the samples 3–4, etc.
Your task is to find the correct sequence of reversal operations that will sort the samples using the above algorithm. If there are more samples with the same height, their mutual order must be preserved: the one that was given first in the initial order must be placed before the others in the final order too.
The last scenario is followed by a line containing zero.
Each Pi must be an integer (1 ≤ Pi ≤ N ) giving the position of the i-th sample just before the i-th reversal operation.
Note that if a sample is already on its correct position Pi , you should output the number Pi anyway, indicating that the “interval between Pi and Pi ” (a single sample) should be reversed.
3 4 5 1 6 2
4
3 3 2 1
0
4 2 4 4
//
// main.cpp
// hdu1890
//
// Created by Candy on 30/11/2016.
// Copyright © 2016 Candy. All rights reserved.
//
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
#define pa t[x].fa
#define lc t[x].ch[0]
#define rc t[x].ch[1]
const int N=1e5+;
inline int read(){
char c=getchar();int x=,f=;
while(c<''||c>''){if(c=='-')f=-;c=getchar();}
while(c>=''&&c<=''){x=x*+c-'';c=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
struct node{
int fa,ch[],w,size,flp;
}t[N];
int root;
inline void update(int x){t[x].size=t[lc].size+t[rc].size+t[x].w;}
inline int wh(int x){return t[pa].ch[]==x;}
inline void pushDown(int x){
if(t[x].flp){
swap(lc,rc);
t[lc].flp^=;t[rc].flp^=;
t[x].flp=;
}
}
inline void rotate(int x){
int f=t[x].fa,g=t[f].fa,c=wh(x);
if(g) t[g].ch[wh(f)]=x;t[x].fa=g;
t[f].ch[c]=t[x].ch[c^];t[t[f].ch[c]].fa=f;
t[x].ch[c^]=f;t[f].fa=x;
update(f);update(x);
}
inline void splay(int x,int tar){
for(;t[x].fa!=tar;rotate(x))
if(t[pa].fa!=tar) rotate(wh(pa)==wh(x)?pa:x);
if(tar==) root=x;
}
int ne[N];
void spl(int x,int tar){
int _=x;
while(x!=tar) ne[pa]=x,x=pa;
x=_;
for(int i=tar;i!=x;i=ne[i]) pushDown(i);
pushDown(x);
splay(x,tar);
}
int build(int l,int r){
if(l>r) return ;
int x=(l+r)>>;
lc=build(l,x-);rc=build(x+,r);
t[lc].fa=t[rc].fa=x;
t[x].w=;t[x].flp=;
update(x);
//printf("build %d %d %d\n",x,lc,rc);
return x;
}
int kth(int k){
int x=root,ls=;
while(x!=){
pushDown(x);
int _=ls+t[lc].size;
if(_<k&&k<=_+t[x].w) return x;
if(k<=_) x=lc;
else ls=_+t[x].w,x=rc;
}
return -;
}
void rever(int l,int r){//printf("rev %d %d ",l,r);
splay(kth(l),);
int x=kth(r+);//printf("x %d\n",x);
splay(x,root);
t[lc].flp^=;
}
int n;
struct data{
int id,v;
bool operator <(const data &a)const{
if(v==a.v) return id<a.id;
return v<a.v;
}
}a[N];
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]){
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF&&n){
memset(t,,sizeof(t));
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) a[i].v=read(),a[i].id=i+;
sort(a+,a++n);
root=build(,n+);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
int x=a[i].id;//printf("hi %d %d\n",i,x);
spl(x,);
printf("%d%c",t[lc].size,i<n?' ':'\n');
rever(i,t[lc].size);
}
}
return ;
}
HDU1890 Robotic Sort[splay 序列]的更多相关文章
- hdu1890 Robotic Sort (splay+区间翻转单点更新)
Problem Description Somewhere deep in the Czech Technical University buildings, there are laboratori ...
- HDU1890 Robotic Sort Splay tree反转,删除
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1890 题目中涉及数的反转和删除操作,需要用Splay tree来实现.首先对数列排序,得到每个数在数列 ...
- HDU 1890 Robotic Sort | Splay
Robotic Sort Time Limit: 6000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) [Pr ...
- BZOJ 1552: [Cerc2007]robotic sort( splay )
kpm大神说可以用块状链表写...但是我不会...写了个splay.... 先离散化 , 然后splay结点加个min维护最小值 , 就可以了... ( ps BZOJ 3506 题意一样 , 双倍经 ...
- hdu 1890 Robotic Sort(splay 区间反转+删点)
题目链接:hdu 1890 Robotic Sort 题意: 给你n个数,每次找到第i小的数的位置,然后输出这个位置,然后将这个位置前面的数翻转一下,然后删除这个数,这样执行n次. 题解: 典型的sp ...
- 【BZOJ1552】[Cerc2007]robotic sort Splay
[BZOJ1552][Cerc2007]robotic sort Description Input 输入共两行,第一行为一个整数N,N表示物品的个数,1<=N<=100000.第二行为N ...
- 【bzoj1552/3506】[Cerc2007]robotic sort splay翻转,区间最值
[bzoj1552/3506][Cerc2007]robotic sort Description Input 输入共两行,第一行为一个整数N,N表示物品的个数,1<=N<=100000. ...
- [BZOJ1552] [Cerc2007] robotic sort (splay)
Description Input 输入共两行,第一行为一个整数N,N表示物品的个数,1<=N<=100000.第二行为N个用空格隔开的正整数,表示N个物品最初排列的编号. Output ...
- HDU 1890 - Robotic Sort - [splay][区间反转+删除根节点]
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1890 Time Limit: 6000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Li ...
随机推荐
- ReSharper.8.0.14.856注册码
ReSharper.8.0.14.856注册码 用户名:ronle 注册码:ZoJzmeVBoAv9Sskw76emgksMMFiLn4NM 网络转载
- ibatis 和 mybatis
ibatis 在daoImpl 层 继承 SqlMapClientDaoSupport 实现 dao 层的接口. this.getSqlMapClientTemplate().queryForObj ...
- Spring容器深入(li)
spring中最常用的控制反转和面向切面编程. 一.IOC IoC(Inversion of Control,控制倒转).对于spring框架来说,就是由spring来负责控制对象的生命周期和对象间的 ...
- No.006:ZigZag Conversion
问题: The string "PAYPALISHIRING" is written in a zigzag pattern on a given number of rows l ...
- 最短路径之Floyd算法
Floyd算法又称弗洛伊德算法,也叫做Floyd's algorithm,Roy–Warshall algorithm,Roy–Floyd algorithm, WFI algorithm. Floy ...
- Linux Cmd Tool 系列之—history & search command history
History cmd is for list Bash's log of the historical cmd you typed 1. List last n commands history n ...
- TouchPoint.js – 可视化展示 HTML 原型点击效果
TouchPoint.js 是一个用于 HTML 原型展示的 JavaScript 库(作为UX过程的一部分),通过视觉表现用户在屏幕上的点击.TouchPoint 是高度可定制,非常适合屏幕录制,用 ...
- Bootstrap之样式风格与下拉菜单
背景颜色 bg-primary 字体颜色 text-primary 文字居中 text-center 按钮 btn btn-primary btn-default默认 btn-link链接 按钮大小 ...
- 纯HTML5+CSS3制作生日蛋糕
以一个前端开发的身份绘制一个简单的蛋糕庆祝一下今天这个好日子吧,程序员庆生的乐趣与哀愁啊.写的比较简陋,感兴趣的看一下吧. 先发个效果图吧 蛋糕分为三个部分,底部蛋糕,顶层蛋糕和蜡烛部分.HTML的布 ...
- 如何通过ArcMap Add-in机制实现十字叉线地理配准工具
下图为自定义的ArcMap Add-in实现的十字叉线位图地理配准功能演示.