C++程序设计实验考试准备资料(2019级秋学期)
程序设计实验考试准备资料
——傲珂
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
C++常用函数:
<math.h>头文件
floor()
函数原型:double floor(double x);
作用:用于输出浮点类型中小于此数的最大整数
注:floor(n+0.5)可用于进行四舍五入的处理
ceil()
函数原型:double ceil(double x);
作用:用于输出浮点类型中大于此数的最大整数
atan()
作用:用来求π的值:atan(1)=π/4 π=4.0*atan(1)
int abs ( int x) 求整数x的绝对值 绝对值
double
fabs(double x) 求实数x的绝对值 绝对值
long
labs (long x) 求长整型数的绝对值
绝对值
double acos(double x) 计算arcos(x)的值 计算结果
double asin(double x) 计算arsin(x)的值 计算结果
double atan(double x) 计算arctan(x)的值 计算结果
double cos(double x) 计算cos(x)的值 计算结果
double cosh(double x) 计算x的双曲余弦cosh(x)的值 计算结果
double exp(double x) 求的值 计算结果
double fmod(double x, double y) 求x/y的余数 余数的双精度数
double
log(double x) 计算In(x)的值 计算结果
double log10(double x) 计算的值 计算结果
double modf(double x, double *y) 取x的整数部分送到y所指向的单元格中 x的小数部分
double sin(double x) 计算sin(x)的值 计算结果
double tan(double x) 计算tan(x)的值 计算结果
double
sqrt(double x) 求的值 计算结果
头文件#include <stdlib.h>
double atof(const char *s)
将s所指向的字符串转换成实数 实数值
int atoi(const char *s) 将s所指向的字符串转换成整数 整数值
long
atol(const char *s) 将s所指的字符串转换成长整数 长整数值
max(a, b) 求两个数中的大数 大数 参数为任意类型
min(a,b) 求两个数中的小数 小数 参数为任意类型
int rand(void) 产生一个随机整数 随机整数
void srand(unsigned int) 初始化随机数产生器
★C++标准库提供了兼容C语言的字符串处理函数
#include <string.h>
1. 字符串复制函数 (string copy)
△strcpy
strcpy(str1,str2);
//复制str2到str1
△strncpy
strncpy(str1,str2,n); //复制str2中不超过n个字符的字符串复制到str1
2.
字符串连接函数
(string catenate)
△strcat
strcat(str1,str2); //将str2连接到str1,包括空字符,并且str2无变化
△sstrncat
strncat(str1,str2,n); //将str2中不超过n个字符的字符串连接到str1上
3.
字符串比较函数(string compare)
△strcmp
strcmp(str1,str2); //自左向右比较str1和str2里面的字符的ASCII数值,直到出现不同字符或者空字符为止
4.
计算字符串长度函数(string length)
△strlen
L=strlen(str1); l=sizeof str1; //字面意思(但是不包括空字符)(注意:sizeof计算的是字符数组的长度)
5. 字符串转化为数值函数;
△atof
//双精度浮点型
△atoi //整形
6.
数据写入字符串的格式化输出函数sprintf
sprintf(str,“%d*%d=%d",1,2,2)
; //输出结果不显示,存储在str中(“1*2=2”)
7.
从字符串读入数据的格式化输入函数sscanf
sscanf(“12 34”,“%d%d",&a,&b);
8.
返回一个指针,指向字符串s1中字符ch的第一次出现的位置;strchr(s1,ch);
9.
返回一个指针,指向字符串s1中字符串s2的第一次出现的位置;strstr(s1,s2);
```cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
char str1[] = "Hello";
char str2[] = "World";
char str3[];
int len ;
// 复制 str1 到 str3
strcpy( str3, str1);
cout << "strcpy( str3, str1) : " << str3 << endl;
// 连接 str1 和 str2
strcat( str1, str2);
cout << "strcat( str1, str2): " << str1 << endl;
// 连接后,str1 的总长度
len = strlen(str1);
cout << "strlen(str1) : " << len << endl;
return ;
}
```
★C++中的字符串类(动态内存管理(不必担心存储空间是否足够))(面向对象)
#include <string>
输入 getline(cin,str);(输入一行,回车结束)
11. 复制(=)
str1 =“java”;
2. 将string转换为c风格字符串,返回char指针
str1.c_str();
3. 把str1中从pos开始的n个字符复制到s1字符组
str1.copy(s1,n,pos);
4. 将C风格字符串S1开始的n个字符赋值给str1
str1.assign(S1,n);
5. string对象允许使用加号(+)和复合赋值(+=)运算符来实现两 个字符串连接操作。
str1="12" , str2="AB" , str3="CD";
str1 = str2 + str3; //str1结果为ABCD
str1 = str1 + "PHP"; //str1结果为12PHP
str1 += str3; //str1结果为12CD
6. string对象可以使用关系运算符来对字符串进行比较
str1="ABC" , str1="XYZ";
str1 > str2; //结果为假
str1 == str2;//结果为假
7. string对象可以调用其成员函数来实现字符串处理,这里列举一些 重要的操作,更详细的内容可以查阅C++标准库手册。
str1="ABCDEFGHIJK"; //获取字符串的长度
n = str1.size(); //n为11
n = str1.length(); //n为11
b = str1.empty(); //b为假 //检查字符串是否为空字符串
//得到子字符串 str2 =
str1.substr(2,4); //从下标2开始的4个字符,str2为CDEF
//查找子字符串 n = str1.find("DEF",pos);
//从pos开始查找字符串"DEF"在str1中的位置,n为 3
//删除字符 str1.erase(3,5);
//从下标3开始往后删5个字符,str1变为ABCIJK
//增加字符
str1.append("12345",1,3); //在str1末尾增加"12345"下标从1开始的3个字符, 即"234"
//字符串替换和插入操作
str1.replace(p0,n0,S1,n); //删除从p0开始的n0个字符,然后在p0处插入字符串 S1前n个字符
str1.replace(p0,n0,str2,pos,n); //删除从p0开始的n0个字符,然后在p0处插
入字符串str2中pos开始的前n个字符
str1.insert(p0,S1,n); //在p0位置插入字符串S1前n个字符
str1.insert(p0,str2,pos,n); //在p0位置插入字符串str2中pos开始的
前n个字符
字符串对象数组 可以定义字符串对象数组,即数组元素是字符串对象,定义形式与
数组类似,
例如: string SY[5]={"Jiang","Cao","Zou","Liu","Wei"};
//定义字符串对象数组且初始化
string
SY[5]={"123","12","1234","1","12345"};
//长度 3,2,4,1,5
char
SA[5][20]={"123","12","1234","1","12345"};
//长度均是20
```cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
string str1 = "Hello";
string str2 = "World";
string str3;
int len ;
// 复制 str1 到 str3
str3 = str1;
cout << "str3 : " << str3 << endl;
// 连接 str1 和 str2
str3 = str1 + str2;
cout << "str1 + str2 : " << str3 << endl;
// 连接后,str3 的总长度
len = str3.size();
cout << "str3.size() : " << len << endl;
return ;
}
```
1. append() -- 在字符串的末尾添加字符
2.
find() -- 在字符串中查找字符串
4.
insert() -- 插入字符
5.
length() -- 返回字符串的长度
6.
replace() -- 替换字符串
7.
substr() -- 返回某个子字符串
```cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//定义一个string类对象
string http = "onlinetutor";
//打印字符串长度
cout<<http.length()<<endl;
//拼接
http.append("/C++");
cout<<http<<endl; //打印结果为:onlinetutor/C++
//删除
int pos = http.find("/C++"); //查找"C++"在字符串中的位置
cout<<pos<<endl;
http.replace(pos, , ""); //从位置pos开始,之后的4个字符替换为空,即删除
cout<<http<<endl;
//找子串runoob
int first = http.find_first_of("."); //从头开始寻找字符'.'的位置
int last = http.find_last_of("."); //从尾开始寻找字符'.'的位置
cout<<http.substr(first+, last-first-)<<endl; //提取"runoob"子串并打印
return ;
}
```
```cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define N 100
int main()
{
char X[N];
cin.getline(X,N); //以cin.getline形式输入
int a=,b=;
for(int i=;i<N;i++)
{
if(X[i]=='#') //为#为结束标志
break;
if(X[i]>=''&&X[i]<='')
a++; //统计数字个数
if((X[i]>='a'&&X[i]<='z')||(X[i]>='A'&&X[i]<='Z'))
b++; //统计英文字母个数
}
cout<<a<<endl<<b<<endl;
return ;
}
```
将一个数字逆序:
Int nixu(int n){
int t,k=;
for(t=n;t>;t=t/){
k=*k+t%;
}
return k;
}
该年的第几天:(输入日期YYYY-MM-DD)
int count(int Y, int M, int D){
const short MD[]={,,,,,,,,,,,,};
int s,i;
s=D;
for (i=;i<M;i++) s+=MD[i];
if (((Y%==)&&(Y%!=)||(Y%==)) && (M>)) s++;
return s;
}
main(){
int y,m,d;
scanf("%4d%*c%2d%*c%2d",&y,&m,&d);//注意这个输入方式(*的位置可以输入-等符号)
cout<<count(y,m,d)<<endl;
return ;
}
判断一个数是否是素数:
Int judge_prime(int n){
If(n<) return ;
If(n==) return ;
For(int i=;i<=sqrt(n);i++){
If(n%i==) return ;
}
Return ;
}
二分法求根:
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
double f(double x){
return *x*x*x-*x*x+*x-;}
int main(){
double a,b,x;
cin>>a>>b;
while(abs(a-b)>0.001){ //abs()取绝对值函数
x=(a+b)/;
if(f(x)*f(a)<) b=x;
else a=x;
}
cout<<fixed<<setprecision()<<x<<endl;
}
平方根的迭代公式:
double sqrt(double a,double x0)
{
double x1,y;
x1=(x0+a/x0)/;
if(fabs(x1-x0)>1e-)
y=sqrt(a,x1);
else
y=x1;
return y;
}
你会存钱吗?
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i8,i5,i3,i2,i1,n8,n5,n3,n2,n1;
double m=,term;
for(i8=;i8<;i8++)
for(i5=;i5<=(-*i8)/;i5++)
for(i3=;i3<=(-*i8-*i5)/;i3++)
for(i2=;i2<=(-*i8-*i5-*i3)/;i2++)
{
i1=-*i8-*i5-*i3-*i2;
term=2000.0*pow((double)(+0.0063*),
(double)i1)*pow((double)(+*0.0063*),
(double)i2)*pow((double)(+*0.0069*),
(double)i3)*pow((double)(+*0.0075*),
(double)i5)*pow((double)(+*0.0084*),
(double)i8);
if(term>m){ m=term; n1=i1; n2=i2; n3=i3; n5=i5; n8=i8; };
};
cout<<n8<<" "<<n5<<" "<<n3<<" "<<n2<<" "<<n1<<endl;
cout<<fixed<<setprecision()<<m<<endl;
return ;
}
找零:(最少张数人民币)
void change(double m,double c){
double a[]={0.01,0.02,0.05,0.1,0.2,0.5,,,,,,};
double s1,s2;
s1=c-m;
int i,b[],d;
for(b[]=;b[]<;b[]++){
for(b[]=;b[]<;b[]++){
for(b[]=;b[]<;b[]++){
for(b[]=;b[]<;b[]++){
for(b[]=;b[]<;b[]++){
for(b[]=;b[]<;b[]++){
for(b[]=;b[]<;b[]++){
for(b[]=;b[]<;b[]++){
for(b[]=;b[]<;b[]++){
for(b[]=;b[]<;b[]++){
for(b[]=;b[]<;b[]++){
for(b[]=;b[]<;b[]++){
s2=a[]*b[]+a[]*b[]+a[]*b[]+a[]*b[]+a[]*b[]+a[]*b[]+a[]*b[]+a[]*b[]+a[]*b[]+a[]*b[]+a[]*b[]+a[]*b[];
if(s1==s2) {
for(i=;i<;i++){
cout<<a[i]<<"\t"<<b[i]<<endl;
}
for(i=,d=;i<;i++){
d=d+b[i];
}
cout<<d<<endl;
return ;
1的传奇:(by 马哥)
#include<stdio.h>
//#include<math.h>
int mypower(int baseNum,int repeatNum)
{
if (repeatNum == )
return ;
int i;
int result=;
for (i = ; i < repeatNum; i++)
result *= baseNum;
return result;
}
/*
使用算法进行计算
输入参数:
N:要计算的数
trace: 代表是否进行跟踪输出,0:不输出;1:输出
输出参数:计算结果
*/
int calculate(int N,int trace)
{
int i;
int result=,j=;
int totalNum = ;
int prevModNum = ;
while(N>)
{ i=N%;
N=N/;
if (i>)
{
result=mypower(,j)+i*(mypower(,j-)*j);
totalNum += result;
}
else if (i == )
{
if (trace==)
printf("ignore 0\n");
}
else
{
result = (prevModNum+)+i*(mypower(,j-)*j);
if (trace==)
printf("result=%d------(%d+1)=%d-----i*pow(10,j-1)*j=%d\n",result,prevModNum,(prevModNum+),(i*mypower(,j-)*j));
totalNum += result;
}
if (trace==)
printf("跟踪输出:j=%d,i=%d,N=%d,prevModNum=%d,result=%d,totalSum=%d\n",j,i,N,prevModNum,result,totalNum);
prevModNum = prevModNum+i*mypower(,j);
j=j+;
//printf("pow(10,%d)=%d,prevModNum=%d\n",j,pow(10,j),prevModNum);
}
//result+=1;
if (trace == )
printf("%d\n",totalNum);
return totalNum;
}
int main()
{
int willTrace = ;
int inputNumber;
scanf("%d",&inputNumber);
int totalNum = ;
//int totalNum1 = 0;
totalNum = calculate(inputNumber,willTrace);
printf("%d",totalNum);
return ;
}
排序(升序):
void paixu(int a[],int n)
{
for(int i=;i<n;i++){
for(int j=;j<n;j++){
if(a[j]>a[j+]){
int t=a[j];
a[j]=a[j+];
a[j+]=t;
}
}
}
}
1:2:3:
int main(){
int n,i,s,A[];
for(n=;n<;n++){
for(i=,s=n;i<;i++){
A[i]=s%;
s=s/;
}
for(i=,s=*n;i<;i++){
A[i]=s%;
s=s/;
}
for(i=,s=*n;i<;i++){
A[i]=s%;
s=s/;
}
paixu(A,);
if(judge(A,)) cout<<n<<" "<<*n<<" "<<*n<<endl;
}
return ;
}
合数世纪://这个世纪中没有一个数是素数
int main()
{
int n,i,j,m,k,cnt=;
cin>>n;
for(i=;;i++){
for(j=*i,k=;j<*(i+);j++){
if(judge_primer(j)) break;
k++;
if(k==){
cnt++;
if(cnt==n){
cout<<*i<<ends<<*i+;
}
}
}
}
}
危险的组合:(dp)对于输入的n,n<=30,求有多少个不超过n位2进制的数,有连续的3个1 / n个盒子摆放成一排,当有3个以上U摆放在一起的时候,就会有危险,求总共有多少种危险的情况。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 40
int n,dp[N][N];
long long ans;
inline void DP()
{
memset(dp,,sizeof(dp));
dp[][]=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=;j<=;j++)dp[i][]+=dp[i-][j];
for(int j=;j<=;j++)dp[i][j]+=dp[i-][j-];
}
ans=;
for(int i=;i<=;i++)ans+=dp[n][i];
printf("%lld\n",(<<n)-ans);
}
//大同小异每放置一个新的盒子,都对应2种情况:设dp[n]=当盒子数目为n的情况下,符合要求(出现连续三个U)的放置方法的情况个数。
1. 前面n-1个盒子已经能符合要求,则第n个盒子无论是U还是L,都满足情况。情况有(2*dp[n-1])种。
2. 前面n-1个盒子不能符合要求,即只有最后4个满足情况LUUU并且前面并没有连续的三个U的情况才能满足情况。有((1<<(n-4))-dp[n-4])种情况。
(1<<(n-4))为n-4个盒子放置的总情况数,dp[n-4]为n-4个盒子放置出现危险(有连续三个U出现)的情况数。最后四个盒子仅一种摆法,可忽略。
状态转移方程:
dp[n]=2*dp[n-1]+(1<<(n-4))-dp[n-4]
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
long long dp[];
int n,ans;
int main()
{
memset(dp,,sizeof(dp));
dp[]=;
dp[]=;
for(int i=;i<=;i++)//记录排列i个盒子方式
{
dp[i]=*dp[i-]+(<<(i-))-dp[i-];
}
while(scanf("%d",&n)&&n)
printf("%lld\n",dp[n]);
return ;
}
最大乘积:(输入n个元素组成的序列s,找出一个乘积最大的连续子序列)
int main()
{
int a[],n,s,t,ans=;
cin>>n;
for(int i=;i<n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
}
for(int i=;i<n;i++){
t=a[i];s=a[i];
for(int j=i+;j<n;j++){
s=s*a[j];
if(t<s) t=s;
}
if(t>ans) ans=t;
}
if(ans>) cout<<ans;
else cout<<-;
return ;
}
判断一个数中是否有数字7:
int f2(int i)
{
int t=i;
while(t>){
if(t%==) return ;
t/=;
}
return ;
}
函数模板(判断xyz的大小):
template <typename T> void sort (T x,T y,T z){
if(x<y){
if(y<z){
cout<<x<<" "<<y<<" "<<z<<endl;
}
else {
if(x<z) cout<<x<<" "<<z<<" "<<y<<endl;
else cout<<z<<" "<<x<<" "<<y<<endl;
}
}
else
{
if(x<z)
cout<<y<<" "<<x<<" "<<z<<endl;
else
{
if(y<z) cout<<y<<" "<<z<<" "<<x<<endl;
else cout<<z<<" "<<y<<" "<<x<<endl;
}
}
}
循环移位:
int move(int value,int n)
{
if(n==) return value;
else if(n<)
{
n=-n;
value=(value<<n)|(value>>(-n));
}
else value=(value>>n)|(value<<(-n));
return value;
}
十进制数转换为2进制数:
void zhuaner(int n,int a[]){
int i;
for(i=;n>;i++){
a[i]=n%;
n=n/;
}
for(i=i-;i>=;i--)
if(i!=) break;
for(;i>=;i--)
cout<<a[i];
}
亲和数(两个数的真约数之和交叉等于这俩个数):
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int zys(int n){
int i,s=;
for(i=;i<n;i++){
if(n%i==) s=s+i;
}
return s;
}
int main()
{
int A,B;
cin>>A>>B;
if(A==zys(B)) cout<<"YES"<<endl;
else cout<<"NO"<<endl;
return ;
}
阶乘:
int factorial(int n)
{
int i=,s=;
while(i<=n){
s=s*i;i++;
}
return s;
}
组合数公式:
int combinatorial_number(int m,int n)
{
if(m==) return ;
return factorial(n)/factorial(m)/factorial(n-m);
}
冒泡排序(无标志位):
void BubbleSort(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int i = ; i < n - ; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < n - i - ; j++)
{
if (arr[j] > arr[j + ])
{
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + ];
arr[j + ] = temp;
}
}
}
}
改进冒泡排序(有标志位):
void OptimBubbleSort(int arr[], int n)
{
Bool flag = false;//设置一个标志位
for (int i = ; i < n - ; i++)
{
Flag = true;
for (int j = ; j < n - i - ; j++)
{
if (arr[j] > arr[j + ])
{
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + ];
arr[j + ] = temp;
flag=false;
}
}
}
}
二分查找:
int binary_find(int n,int arr[],int m)
{
int a=,b=n-,i=(a+b)/;
while(arr[i]!=m){
if(m<arr[i]){
b=i;
i=(a+b)/;
}
else {
a=i;
i=(a+b)/;
}
}
return i;
}
选择排序(正版):
void selectSort(int a[], int len)
{
int minindex, temp;
for(int i = ; i<len-;i++)
{
minindex = i;
for(int j = i+; j<len; j++)
{
if(a[j]<a[minindex])
minindex = j;
}
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[minindex];
a[minindex] = temp;
}
}
选择排序(noj版:从数组A第s个元素起始,连续m个元素升序排序。)
int SectionSort(int A[],int s,int m){
int i,j,t,k;
for(i=s;i<s+m;i++){
k=i;
for(j=i+;j<s+m;j++)
if(A[j]>A[k]) k=j;
if(i!=k){
t=A[i];
A[i]=A[k];
A[k]=t;
}
}
}
两两交换之最少次数排序:
int paixu(int a[],int m){
int i,j,k,t,s=;
for(i=;i<m;i++){
k=a[i];
for(j=i-;j>=&&k<a[j];j--){
s++;
a[j+]=a[j];
}
a[j+]=k;
}
return s; //函数的返回值是最少的交换次数
}
恐怖水母:(改进冒泡排序,最优化)
void OptimBubbleSort(int arr[], int n)
{
bool flag = false;//设置一个标志位
for (int i = ; i < n - ; i++)
{
flag = true;
for (int j = ; j < n - i - ; j++)
{
if (arr[j] > arr[j + ])
{
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + ];
arr[j + ] = temp;
flag=false;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int a[],b[],n,m,ans=;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
cin>>a[i];
for(int i=;i<m;i++)
cin>>b[i];
OptimBubbleSort(a,n);
OptimBubbleSort(b,m);
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=;j<m;j++)
{
if(b[j]>=a[i])
{
ans=ans+b[j];
b[j]=;
break;
}
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return ;
}
右下角(左上角):
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
int i,ii,A[][];
for(i=;i<n;i++){
for(ii=;ii<n;ii++){
cin>>A[i][ii];
}
}
for(i=;i<n;i++){
for(ii=;ii<n;ii++){
if(ii<=n--i) cout<<" ";
else cout<<A[i][ii]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
return ;
}
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
int i,ii,A[][];
for(i=;i<n;i++){
for(ii=;ii<n;ii++){
cin>>A[i][ii];
}
}
for(i=;i<n;i++){
for(ii=;ii<n;ii++){
if(ii<=n--i) cout<<A[i][ii]<<" ";
else cout<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
return ;
}
-----
矩阵边芯与内芯之差:
int main(){
int n,m,s1=,s2=;
cin>>n>>m;
int i,ii,A[][];
for(i=;i<n;i++){
for(ii=;ii<m;ii++){
cin>>A[i][ii];
}
}
for(i=;i<n;i++){
for(ii=;ii<m;ii++){
if((i==)|(i==n-)) s1=s1+A[i][ii];
if(i<n-&&i>){
if((ii==)|(ii==m-)) s1=s1+A[i][ii];
else s2=s2+A[i][ii];
}
}
}
cout<<s1-s2<<endl;
return ;
}
字符串复制:(nojAC C++版的不给AC,先弄上来吧……)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
char A[];
int i=,j,a;
while((A[i]=getchar())!='\n')i++;
scanf("%d",&a);
for(j=a;j<i;j++)
printf("%c",A[j]);
return ;
}
字符串比较:(从第一个开始,返回值是第一个不同字母ASCII码的差值)
int stringcompare(char s1[],char s2[]){
int i,s=,a,b;
for(i=;s1[i]!='\0'&&s2[i]!='\0';i++){
a=s1[i];
b=s2[i];
if(s1[i]!=s2[i]) {s=a-b;break;}
}
return s;
}
字符串替换:(you are what you do you替换为we we are what
we do)
#include <stdio.h> //noj AC版
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char s[],b[];
int i,n,h=;
gets(s);
n=strlen(s);
for(i=;i<n;i++){
if(s[i]==&&s[i+]==&&s[i+]==){
b[h]=;b[h+]=;h=h+;i=i+;
}
else {
b[h]=s[i];h++;
};
}
for(i=;i<h;i++) printf("%c",b[i]);
return ;
}
#include<iostream> //理论上可行版
using namespace std;
#include<cstring>
int main()
{
string str1;
getline(cin,str1);
int pos=str1.find("you");
while(pos!=-){
str1.replace(pos,,"we");
pos=str1.find("you");
}
cout<<str1;
return ;
}
分离单词:(编写程序以字符串为单位,以空格或标点符号(字符串中仅含英文逗号,或小数点.作为标点符号)作为分隔符对字符串中的所有单词进行倒排,然后把已经处理的字符串打印出来)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char s[],b[][];
int i,n,j,h=,m;
gets(s);
n=strlen(s);
for(i=;i<n;i++){
if((s[i]>&&s[i]<)||(s[i]>&&s[i]<)){
m=;
for(j=i;;j++) {if((s[j]>&&s[j]<)||(s[j]>&&s[j]<)) {
b[h][m]=s[j];m++;i++;
}
else {
b[h][m]=' ';
h++;
break;
}
}
h++;
}
}
for(i=h-;i>=;i--)
printf("%s",b[i]);
return ;
}
字符串排序:(输入十个等长的字符串(每个字符串最多10个字符,对他们进行排序,并打印)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char s[][],b[][];
int i,k,j;
for(i=;i<;i++) scanf("%s",s[i]);
for(i=;i<;i++){
k=;
for(j=;j<;j++)
if (strcmp(s[i],s[j])>) k++;
strcpy(b[k],s[i]);}
for(i=;i<;i++) printf("%s ",b[i]);
return ;
}
子字符串替换:(将一个长字符串str中凡是与str1相同的字符替换成str2)
#include<iostream> //理论上可行版1
using namespace std;
#include<cstring>
int main()
{
string str,str1,str2;
getline(cin,str);
getline(cin,str1);
getline(cin,str2);
int pos=str.find(str1);
while(pos!=-){
str.replace(pos,str1.length(),str2);
pos=str.find(str1);
}
cout<<str;
return ;
}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>//理论上可行版2(且noj AC)
using namespace std;
int main(){
string str,str1,str2;
getline(cin,str);
cin>>str1>>str2;
int a,b;
a=str1.length();
b=str.length();
int pos,i=;
while(str.find(str1)!=string::npos){
pos=str.find(str1);
str.replace(pos,a,str2);
}
cout<<str;
return ;
}
分数加减法:
#include<iostream> //noj AC……就这样吧
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a,b,c,d,e,f,n,h=;
char s;
scanf("%d/%d%c%d/%d",&a,&b,&s,&c,&d);
if(s=='+'){
e=a*d+b*c;
f=b*d;
n=f;
if(e==) {printf("");
return ;}
if(e<) e=-e,h=;
if(f%e==){
f=f/e;
e=e/(f/n);
}
if(h==) printf("%d/%d",e,f);
else printf("-%d/%d",e,f);
}
if(s=='-'){
e=a*d-b*c;
f=b*d;
n=f;
if(e==) {printf("");
return ;}
if(e<) e=-e,h=;
if(f%e==){
f=f/e;
e=e/(f/n);
}
if(h==) printf("%d/%d",e,f);
else printf("-%d/%d",e,f);
}
return ;
}
重组字符串:(将参数s所指的字符串中除了下标为奇数,同时ASCII码也为奇数的字符之外,其余字符都删除,并将重组后的字符串打印出来)
#include <iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int b;
void fun(char *s,char *t){
int i=,a;
for(;s[i]!='\0';i++)
for(a=,b=;a<i+;a++){
if(a%!=&&s[i]%!=) {t[b]=s[a];b++;}
}
}
int main(){
char s[],t[];
gets(s);
fun(s,t);
for(int i=;i<=b;i++) cout<<t[i];
return ;
}
文件比较:(已有两个文本文件(DATA5613.TXT和DATA5613.CPP),请编写程序从这两个文件中读取相应行和列上的字符,如果遇到互不相同的字符,输出他是第几行第几列的字符)
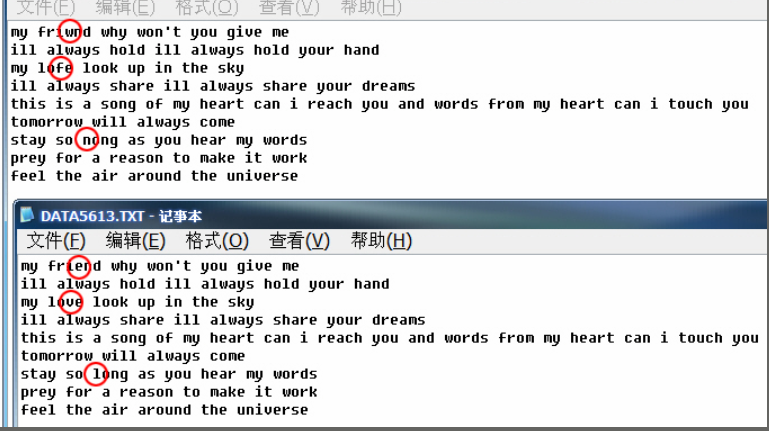
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char a[][],b[][];
FILE *p1,*p2;
int i=,j=,n;
p1=fopen("DATA5613.TXT","r");
p2=fopen("DATA5613.CPP","rb");
while(!feof(p1)){
if(fgets(a[i],,p1)==NULL)continue;
i++;
}
i=;
while(!feof(p2)){
if(fgets(b[i],,p2)==NULL)continue;
i++;
}
n=i;
for(i=;i<n;i++)
for(j=;j<strlen(a[i])-;j++) if(a[i][j]!=b[i][j]) {printf("%d %d\n",i+,j+);
break;};
return ;
}
单词频次:
#include<iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
int main()
{
char s[][];
FILE *p;
int i,j=,k=,h=,q=,e;
p=fopen("DATA5610.TXT","r");
while(!feof(p)){
if(fgets(s[q],,p)==NULL) continue;
q++;
}
e=q;
for(q=;q<e;q++)
for(i=;i<;i++){
if(s[q][i]=='i'&&s[q][i+]=='f') h++;
if(s[q][i]=='w'&&s[q][i+]=='h'&&s[q][i+]=='i'&&s[q][i+]=='l'&&s[q][i+]=='e')
j++;
if(s[q][i]=='f'&&s[q][i+]=='o'&&s[q][i+]=='r') k++;
}
printf("%d %d %d",h,j,k);
return ;
}
检查文件格式:

#include<iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
FILE *fp = fopen("DATA5609.DAT", "rb");
if (fp==NULL)return -;
char buf[] = "";
fread(buf, sizeof(buf),,fp);
if (strncmp("JFIF",buf+,strlen("JFIF"))==){
printf("JPEG");
}
else if (strncmp("GIF89a",buf,strlen("GIF89a"))==){
printf("GIF");
}
else if (strncmp("PNG",buf+,strlen("PNG"))==){
printf("PNG");
}
else{
printf("UNKNOW");
}
return ;
}
检测位图长宽:

#include<iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
int main()
{
FILE *p;
long biWidth,biHeight;
p=fopen("DATA5611.BMP","rb");
if(p!=NULL)
{
fseek(p,,SEEK_SET);
fread(&biWidth,sizeof(long),,p);
fread(&biHeight,sizeof(long),,p);
printf("%ld %ld",biWidth,biHeight);
fclose(p);
}
return ;
}
symmetric sort:
描述在东大管理公司(DongDa Management Inc.,没错,它是由一群小丑运营的)工作时,你刚写完一个程序,它的输出是一个按长度排序的名字列表(因此每个名字至少与前一个名字一样长)。但是,您的老板不喜欢输出的方式,而是希望输出看起来更对称,更短的字符串在顶部和底部,更长的字符串在中间。他的规则是,每对名字都在列表的两端,而第一个名字总是在列表的顶部。在下面的例子中,Bo和Pat是第一对,lean和Kevin是第二对,等等。输入输入由一组字符串组成,每组从一行开始,其中包含一个整数n, n是该集合中的字符串数,后面跟着n个未排序的字符串。没有字符串包含空格。每组至少有一个不超过15个字符串。每个字符串最长不超过25个字符。输出对于每个输入集,输出集如示例输出所示。,若两个字符串长度相等,则按原顺序排列。
#include<iostream> //二维字符数组的应用
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char s[][],a[];
int i,j,n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=;i<n;i++) scanf("%s",s[i]);
for(i=;i<n-;i++)
for(j=;j<n--i;j++)
if(strlen(s[i])>strlen(s[i+])) strcpy(a,s[i]),strcpy(s[i],s[i+]),strcpy(s[i+],a);
if(n%==){
for(i=;i<n-;i=i+) printf("%s ",s[i]);
printf("%s ",s[n-]);
for(i=i-;i>;i=i-) printf("%s ",s[i]);
}
else{
for(i=;i<n-;i=i+) printf("%s ",s[i]);
printf("%s ",s[n-]);
for(i=i-;i>;i=i-) printf("%s ",s[i]);
}
return ;
}
大数:
大数除法:
#include<iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
#define maxx 1025
void chu(char *str1, char *str2, char *str3)
{
int i1, i2, i, j, jj, tag, carry, cf, c[maxx];
int len1 = strlen(str1), len2 = strlen(str2), lend;
char d[maxx];
memset(c, , sizeof(c));
memcpy(d, str1, len2);
lend = len2; j = ;
for( i1=len2-; i1 < len1; ++i1 )
{
if( lend < len2 )
{
d[lend] = str1[i1+]; c[j] = ;
++j; ++lend;
}
else
if( lend == len2 )
{
jj = ;
for( i=; i < lend; ++i )
{
if( d[i] > str2[i] ) break;
else if( d[i] < str2[i] )
{
jj = ; break;
}
}
if( jj == )
{
d[lend] = str1[i1+]; c[j] = ;
++j; ++lend;
continue;
}
}
if( jj== || lend > len2 )
{
cf = jj=;
while( d[jj] <= '' && jj < lend ) ++jj;
if( lend-jj > len2 ) cf = ;
else
if( lend-jj < len2 ) cf = ;
else
{
i2 = ; cf = ;
for( i=jj; i < lend; ++i )
{
if( d[i] < str2[i2] )
{
cf = ; break;
}
else if( d[i] > str2[i2] )
{
break;
}
++i2;
}
}
while( cf )
{
i2 = len2-; cf = ;
for( i=lend-; i >= lend-len2; --i )
{
d[i] = d[i]-str2[i2]+'';
if( d[i] < '' )
{
d[i] = d[i]+; carry = ;
--d[i-];
}
else carry = ;
--i2;
}
++c[j]; jj=;
while( d[jj] <= '' && jj < lend ) ++jj;
if( lend-jj > len2 ) cf = ;
else
if( lend-jj < len2 ) cf = ;
else
{
i2 = ; cf = ;
for( i=jj; i < lend; ++i )
{
if( d[i] < str2[i2] )
{
cf = ; break;
}
else if( d[i] > str2[i2] )
{
break;
}
++i2;
}
}
}
jj = ;
while( d[jj] <= '' && jj < lend ) ++jj;
for( i=;i < lend-jj; ++i ) d[i] = d[i+jj];
d[i] = str1[i1+]; lend = i+;
++j;
}
}
i = tag = ;
while( c[i] == ) ++i;
for( ; i < j; ++i, ++tag ) str3[tag] = c[i]+'';
str3[tag] = '\0';
}
int main()
{
char a[], b[], c[];
gets(a);gets(b);
if(a[]=='-'&&b[]!='-') printf("-");
if(b[]=='-'&&a[]!='-') printf("-");
chu( a, b, c );
printf( "%s\n", c );
return ;
}
大数减法:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void jian(int st1[],int st2[],int len);
int st1[]={},st2[]={},st3[]={};
int a,b,c=,i,j,k;
int main(){
string str1,str2,str3;
getline(cin,str1);
getline(cin,str2);
a=str1.length();
b=str2.length();
for(i=a-,j=;i>=;i--){
st1[j]=str1[i]-'';j++;
}
for(i=b-,j=;i>=;i--){
st2[j]=str2[i]-'';j++;
}
if(a>b){
jian(st1,st2,a);
}
if(b>a){
cout<<"-";
jian(st2,st1,b);
}
if(a==b){
for(i=a-;i>=;i--){
if(st1[i]==st2[i]) continue;
if(st1[i]>st2[i]) {
jian(st1,st2,a);break;
}
if(st2[i]>st1[i]){
cout<<"-";
jian(st2,st1,a);break;
}
}
}
}
void jian(int st1[],int st2[],int a){
for(i=;i<a;i++){
if(st1[i]>=st2[i]) st3[i]=st1[i]-st2[i];
else{
st3[i]=st1[i]+-st2[i];
st1[i+]--;
}
}
for(i=a-;i>=;i--){
if(st3[i]!=) break;
}
for(;i>=;i--){
cout<<st3[i];
}
}
大数加法:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int max(int a,int b);
int main(){
string str1,str2,str3;
getline(cin,str1);
getline(cin,str2);
int a,b,c=,i,j,k;
a=str1.length();
b=str2.length();
int st1[]={},st2[]={},st3[]={};
for(i=a-,j=;i>=;i--){
st1[j]=str1[i]-'';j++;
}
for(i=b-,j=;i>=;i--){
st2[j]=str2[i]-'';j++;
}
for(i=;i<max(a,b);i++){
st3[i]=st2[i]+st1[i]+c;
c=;
if(st3[i]>){
c=st3[i]/;
st3[i]%=;
}
}
for(i=(max(a,b)-);i>=;i--){
cout<<st3[i];
}
return ;
}
int max(int a,int b){
int m;
m= a>b? a:b;
return m;
}
大数乘法:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void cheng(char a[],char b[])
{
int i,j,ca,cb,*s;
ca=strlen(a);
cb=strlen(b);
s=(int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*(ca+cb));
for (i=;i<ca+cb;i++) s[i]=;
for (i=;i<ca;i++)
for (j=;j<cb;j++)
s[i+j+]+=(a[i]-'')*(b[j]-'');
for (i=ca+cb-;i>=;i--)
if (s[i]>=)
{
s[i-]+=s[i]/;
s[i]%=;
}
i=;
while(s[i]==) i++;
for (;i<ca+cb;i++) printf("%d",s[i]);
printf("\n");
free(s);
}
int main()
{
char a[],b[];
gets(a),gets(b);
if(a[]=='-'&&b[]!='-')
{
printf("-");
cheng(&a[],b);
}
else if(a[]=='-'&&b[]=='-')
{
cheng(&a[],&b[]);
}
else if(a[]!='-'&&b[]=='-')
{
printf("-");
cheng(a,&b[]);
}
else
cheng(a,b);
return ;
}
大数乘幂:
#include<iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char a[];
int n,b=,c[]={},i,j,x,flag=;
c[]=;
cin>>a>>n;
for(i=;a[i]!='\0';i++)
{
if(a[i]=='.')
{
x=i;
flag=;
continue;
}
b=b*+a[i]-'';
}
x=i-x-;
for(i=;i<n+;i++)
{
for(j=;j<;j++)
c[j]*=b;
for(j=;j>=;j--)
if(c[j]>=)
{
c[j-]+=c[j]/;
c[j]%=;
}
}
if(flag==)
{
for(i=;c[i]==;i++);
for(;i<;i++)
cout<<c[i];
}
else if(a[]=='')
{
flag=;
cout<<"";
for(j=i;j<;j++)
if(c[j]!=)
{
flag=;
break;
}
if(flag==)
{
cout<<".";
for(j=;c[j]==&&j>=i;j--);
for(i=-n*x;i<=j;i++)
cout<<c[i];
}
}
else
{
flag=;
for(i=;c[i]==;i++);
for(;i<-n*x;i++)
cout<<c[i];
for(j=i;j<;j++)
if(c[j]!=)
{
flag=;
break;
}
if(flag==)
{
cout<<".";
for(j=;c[j]==&&j>=i;j--);
for(;i<=j;i++)
cout<<c[i];
} }
return ;
}
C++程序设计实验考试准备资料(2019级秋学期)的更多相关文章
- 2019年春季学期《C语言程序设计II》助教注意事项
本学期<C语言程序设计II>课程安排 理论课时24(1-12周),实验课时8(13周),课程设计课时16(14-15周) 理论课教学内容 附:教学进度表 本学期实验课和课程设计参考教材 & ...
- Python全国二级等级考试(2019)
一.前言 2018年9月随着全国计算机等级考试科目中加入“二级Python”,也确立了Python在国内的地位,猪哥相信Python语言势必会像PS那般普及.不久的将来,谁会Python谁就能获得女神 ...
- C语言程序设计实验报告三
C程序设计实验报告 姓 名:张美盛 实验地点:家 实验时间:2020年3月29日 实验项目:4.3.1 If语句的应用 4.3.2 switch-case的应用 4.3.3 switch-case嵌套 ...
- 160809208沈昊辰c语言程序设计实验选择结构设计
<C语言程序设计>实验报告 学 号 160809208 姓 名 沈昊辰 专业.班 计科16-2班 学 期 2016-2017 第1学期 指导教师 黄俊莲 吴喆 实验地点 C区二层机房 ...
- 160809209_李梦鑫_C语言程序设计实验3 循环结构程序设计
<C语言程序设计>实验报告 学 号 160809209 姓 名 李梦鑫 专业.班 计科16-2班 学 期 2016-2017 第1学期 指导教师 黄俊莲 吉吉老师 实验地点 C05 ...
- 20145213《Java程序设计》实验二Java面向对象程序设计实验报告
20145213<Java程序设计>实验二Java面向对象程序设计实验报告 实验内容 初步掌握单元测试和TDD 理解并掌握面向对象三要素:封装,继承,多态 初步掌握UML建模 熟悉S.O. ...
- 20145206《Java程序设计》实验二Java面向对象程序设计实验报告
20145206<Java程序设计>实验二Java面向对象程序设计实验报告 实验内容 初步掌握单元测试和TDD 理解并掌握面向对象三要素:封装.继承.多态 初步掌握UML建模 熟悉S.O. ...
- 20145308刘昊阳 《Java程序设计》实验二 Java面向对象程序设计 实验报告
20145308刘昊阳 <Java程序设计>实验二 Java面向对象程序设计 实验报告 实验名称 Java面向对象程序设计 实验内容 初步掌握单元测试和TDD 理解并掌握面相对象三要素:封 ...
- Java程序设计 实验二 Java面向对象程序设计
北京电子科技学院(BESTI) 实 验 报 告 课程:Java程序设计 班级:1353 姓名:李海空 学号:20135329 成绩: 指导教师:娄嘉鹏 ...
随机推荐
- 题解 P3954 【成绩】
题目评级: ★ (水题) 内容及算法: 无,简单模拟计算即可 代码: /** *@author little_frog */ #include <bits/stdc++.h> using ...
- python的Requests库的使用
Requests模块: Requests 是用Python语言编写,基于 urllib,采用 Apache2 Licensed 开源协议的 HTTP 库.它比 urllib 更加方便,可以节约我们大量 ...
- java path
static{ String path = new Object(){ public String getPath() { return this.getClass().getResource(&qu ...
- vue 结合 Echarts 实现半开环形图
Echarts 实现半开环形图 1.先看看实现的图 2.HTML部分 创建id 是 chart 的div标签. <div class="content-item"> & ...
- centos7更新php5.4到php5.6/php7
centos7系统yum安装的php版本为5.4. 因业务需求,开发可能需要php5.6环境. 本文应需而生,介绍从php5.4升级到php5.6. 如需更新到php7环境,步骤一样. 如果是线上应用 ...
- 网络OSI七层模型以及数据传输过程
网络OSI七层模型 模型图 国际标准化组织(ISO)制定了osi七层模型,iso规定了各种各样的协议,并且分了7层 每一层的详细信息 具体7层 数据格式 功能与连接方式 典型设备 应用层 Applic ...
- shell特殊符号及cut、sort_wc_uniq、tee_tr_split命令 使用介绍
第6周第2次课(4月24日) 课程内容: 8.10 shell特殊符号cut命令8.11 sort_wc_uniq命令8.12 tee_tr_split命令8.13 shell特殊符号下 扩展1. s ...
- Python小数据保存,有多少中分类?不妨看看他们的类比与推荐方案...
小数据存储 我们在编写代码的时候,经常会涉及到数据存储的情况,如果是爬虫得到的大数据,我们会选择使用数据库,或者excel存储.但如果只是一些小数据,或者说关联性较强且存在存储后复用的数据,我们该如何 ...
- RestTemplate常用的get和post带参数请求
在RestTemplate提供的方法中,有一个参数就是目标URL,参数是跟在后面的一个数量可变参数,但是在这里就有个问题,这个方法怎么知道我传的参数值是对应在目标接口的哪个参数的呢: public & ...
- 从“职场小白”进阶为“行业大牛”,四个"锦囊"教你破局
在早期软件行业,会存在一个普遍的现象,有些大学的本科,或者研究生毕业,他们去面试工作的时候会发现,面试下来代码能力可能不是太好,这种情况下公司会问你愿不愿意去做测试? 如果说早期软件测试行业还是一个风 ...
