Linux Thermal Framework分析及实施
关键词:Zone、Cooling、Governor、Step Wise、Fair Share、trip等等。
Linux Thermal的目的是控制系统运行过程中采样点温度,避免温度过高造成器件损坏,确保芯片长期稳定工作。
整个Thermal框架可以分为四部分:
- Thermal Driver负责将获取温度设备,注册成struct thermal_zone_device,比如Temp Sensor、NTC等。
- Thermal Governor则负责如何控制温度,注册成struct thermal_governor,比如Step Wise、Bang Bang等等。
- Thermal Cooling负责将控制温度设备,注册成struct thermal_cooling_device,比如风扇、CPU、DDR、GPU等。
- Thermal Core则是Thermal Driver、Thermal Governor、Thermal Governor的粘合剂,同时提供了用户空间sysfs节点等通用功能。
所以Thermal的工作流程是通过Thermal Driver获取温度,然后经过Thermal Governor决策,最后通过Thermal Cooling执行温度控制。
下面首先从总体详细分析Thermal框架以及数据结构、API(1. Thermal框架分析),然后分别分析Thermal Driver实例(2. Thermal Driver实例)、Thermal Governor(Step Wise和Fair Share)(3. Thermal Governor分析)、以及Thermal Cooling实例(4. Thermal Cooling实例)。
最后将这些内容串起来,分析Thermal是如何控制温度的。

1. Thermal框架分析
1.1 Thermal数据结构
struct thermal_zone_device是对获取温度设备的抽象,成员ops是对该Thermal Zone操作的抽象;governor是该Thermal Zone所使用的调温策略;thermal_instances是该Thermal Zone下的Cooling Device列表。
struct thermal_zone_device {
int id;
char type[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];
struct device device;
struct thermal_attr *trip_temp_attrs;
struct thermal_attr *trip_type_attrs;
struct thermal_attr *trip_hyst_attrs;
void *devdata;
int trips;---------------------------------------------------------thermal zone支持的trip数目。
unsigned long trips_disabled; /* bitmap for disabled trips */
int passive_delay;
int polling_delay;-------------------------------------------------轮询读取温度的建个,0表示采用中断形式。
int temperature;---------------------------------------------------当前温度。
int last_temperature;----------------------------------------------最近一次温度。
int emul_temperature;
int passive;
int prev_low_trip;
int prev_high_trip;
unsigned int forced_passive;
atomic_t need_update;
struct thermal_zone_device_ops *ops;------------------------------当前thermal zone操作函数集。
struct thermal_zone_params *tzp;----------------------------------当前thermal zone参数。
struct thermal_governor *governor;
void *governor_data;
struct list_head thermal_instances;-------------------------------当前thermal zone上thermal_instances列表。
struct idr idr;
struct mutex lock;
struct list_head node;
struct delayed_work poll_queue;
enum thermal_notify_event notify_event;
};
struct thermal_zone_device_ops {
int (*bind) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
struct thermal_cooling_device *);------------------------将cooling device绑定到thermal zone中,两者通过struct thermal_instances在thermal_zone_bind_cooling_device()中绑定。
int (*unbind) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
struct thermal_cooling_device *);
int (*get_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int *);
int (*set_trips) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int);
int (*get_mode) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
enum thermal_device_mode *);
int (*set_mode) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
enum thermal_device_mode);
int (*get_trip_type) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,
enum thermal_trip_type *);
int (*get_trip_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int *);
int (*set_trip_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int);
int (*get_trip_hyst) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int *);
int (*set_trip_hyst) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int);
int (*get_crit_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int *);
int (*set_emul_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int);
int (*get_trend) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,
enum thermal_trend *);
int (*notify) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,
enum thermal_trip_type);
};
struct thermal_bind_params {
struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev;
int weight;
int trip_mask;
unsigned long *binding_limits;
int (*match) (struct thermal_zone_device *tz,
struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev);
};
struct thermal_zone_params {
char governor_name[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];
bool no_hwmon;
int num_tbps; /* Number of tbp entries */
struct thermal_bind_params *tbp;
...
int slope;
int offset;
};
struct thermal_zone_of_device_ops {
int (*get_temp)(void *, int *);
int (*get_trend)(void *, int, enum thermal_trend *);
int (*set_trips)(void *, int, int);
int (*set_emul_temp)(void *, int);
int (*set_trip_temp)(void *, int, int);
};
struct thermal_cooling_device是对降温设备的抽象,对风扇设备就是不同的转速,对CPU、DDR、GPU就是不同的电压或者频率。
struct thermal_cooling_device_ops是Cooling Device操作函数集,其中set_cur_state()是对设备进行温度控制。
struct thermal_cooling_device {
int id;
char type[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];
struct device device;
struct device_node *np;
void *devdata;
const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops *ops;
bool updated; /* true if the cooling device does not need update */
struct mutex lock; /* protect thermal_instances list */
struct list_head thermal_instances;
struct list_head node;
};
struct thermal_cooling_device_ops {
int (*get_max_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long *);
int (*get_cur_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long *);
int (*set_cur_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long);
...
};
strcut thermal_governor是对温控策略的抽象,也就是根据Thermal Zone的trip来选择Thermal Cooling设备的行为。比如,温度越高风扇转速越快;温度越高CPU运行在更低电压和频率上。
struct thermal_governor {
char name[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];
int (*bind_to_tz)(struct thermal_zone_device *tz);---------------------将一个governor绑定到thermal zone得一个trip上。
void (*unbind_from_tz)(struct thermal_zone_device *tz);----------------将一个governor从thermal zone解绑。
int (*throttle)(struct thermal_zone_device *tz, int trip);-------------根据trip遍历当前thermal zone下所有的cooling device执行温控策略。
struct list_head governor_list;-------------------------------------thermal_governor_list上的一个列表元素。
};
所有的策略选择都是通过throttle()函数进行的,不同的Governor的区别也主要在这里。内核已经实现了Step Wise、User等等,并且还在演进中。
通过struct thermal_instances可以将thermal zone和thermal cooling设备绑定起来。
struct thermal_instance {
int id;
char name[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];
struct thermal_zone_device *tz;-------------------------------------------绑定的thermal zone。
struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev;--------------------------------------绑定的thermal cooling设备。
int trip;-----------------------------------------------------------------对应的thermal zone的trip。
bool initialized;
unsigned long upper; /* Highest cooling state for this trip point */---cooling设备的最高降温状态。
unsigned long lower; /* Lowest cooling state for this trip point */----cooling设备最低降温状态。
unsigned long target; /* expected cooling state */---------------------cooling设备的当前状态,也是thermal_cooling_device_ops->set_cur_state()设置后的值。
char attr_name[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];
struct device_attribute attr;
char weight_attr_name[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];
struct device_attribute weight_attr;
struct list_head tz_node; /* node in tz->thermal_instances */-------------thermal_zone_device->thermal_instances上的节点。
struct list_head cdev_node; /* node in cdev->thermal_instances */---------thermal_cooling_device->thermal_instances上的节点。
unsigned int weight; /* The weight of the cooling device */
};
thermal_device_mode表示当前的thermal zone是否使能。
thermal_trip_type表示thermal zone的当前trip类型,其中ACTIVE和PASSIVE属于non-critical类型,交由Governor进行处理;HOT和CRITICAL属于critical类型,其中CRITICAL会执行orderly_poweroff()。
thermal_trend表示thermal zone的温度趋势,是平缓、上升、下降还是跳跃式的,这就给Governor选择trip提供依据。
enum thermal_device_mode {
THERMAL_DEVICE_DISABLED = ,
THERMAL_DEVICE_ENABLED,
};
enum thermal_trip_type {
THERMAL_TRIP_ACTIVE = ,
THERMAL_TRIP_PASSIVE,
THERMAL_TRIP_HOT,
THERMAL_TRIP_CRITICAL,
};
enum thermal_trend {
THERMAL_TREND_STABLE, /* temperature is stable */-----------------------表示温度平稳。
THERMAL_TREND_RAISING, /* temperature is raising */---------------------表示当前温度趋势是升高的。
THERMAL_TREND_DROPPING, /* temperature is dropping */-------------------表示当前温度趋势是降低的。
THERMAL_TREND_RAISE_FULL, /* apply highest cooling action */------------直接应用upper对应的trip。
THERMAL_TREND_DROP_FULL, /* apply lowest cooling action */--------------直接应用lower对应的trip。
};
/* Thermal notification reason */
enum thermal_notify_event {
THERMAL_EVENT_UNSPECIFIED, /* Unspecified event */
THERMAL_EVENT_TEMP_SAMPLE, /* New Temperature sample */
THERMAL_TRIP_VIOLATED, /* TRIP Point violation */
THERMAL_TRIP_CHANGED, /* TRIP Point temperature changed */
THERMAL_DEVICE_DOWN, /* Thermal device is down */
THERMAL_DEVICE_UP, /* Thermal device is up after a down event */
THERMAL_DEVICE_POWER_CAPABILITY_CHANGED, /* power capability changed */
};
1.2 Thermal Core APIs
Thermal core是Thermal Zone、Thermal Cooling、ThermalGovernor的粘合剂。
通过Thermal core提供的API,将这三者相互关联起来;从Thermal Zone设备获取温度,选择对应的Thermal Governor,Thermal Governor设置Thermal Cooling的状态,进而达到控制温度的目的。
通过thermal_zone_device_register()注册thermal zone设备,创建一系列sysfs节点,并且和governor、cooling进行绑定。
struct thermal_zone_device *thermal_zone_device_register(const char *type,
int trips, int mask, void *devdata,
struct thermal_zone_device_ops *ops,
struct thermal_zone_params *tzp,
int passive_delay, int polling_delay)
{
struct thermal_zone_device *tz;
enum thermal_trip_type trip_type;
int trip_temp;
int result;
int count;
int passive = ;
struct thermal_governor *governor; if (type && strlen(type) >= THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH)
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL); if (trips > THERMAL_MAX_TRIPS || trips < || mask >> trips)
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL); if (!ops)
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL); if (trips > && (!ops->get_trip_type || !ops->get_trip_temp))
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL); tz = kzalloc(sizeof(struct thermal_zone_device), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!tz)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&tz->thermal_instances);------------------------------初始化thermal_instances链表,放置struct thermal_instances实例。通过thermal_instances可以关联thermal zone和thermal cooling。
idr_init(&tz->idr);
mutex_init(&tz->lock);
result = get_idr(&thermal_tz_idr, &thermal_idr_lock, &tz->id);
if (result) {
kfree(tz);
return ERR_PTR(result);
} strlcpy(tz->type, type ? : "", sizeof(tz->type));
tz->ops = ops;
tz->tzp = tzp;
tz->device.class = &thermal_class;------------------------------------创建的设备会在/sys/class/thermal下面有个链接。
tz->devdata = devdata;
tz->trips = trips;
tz->passive_delay = passive_delay;
tz->polling_delay = polling_delay;
/* A new thermal zone needs to be updated anyway. */
atomic_set(&tz->need_update, ); dev_set_name(&tz->device, "thermal_zone%d", tz->id);
result = device_register(&tz->device);--------------------------------创建/sys/devices/virtual/thermal/thermal_zone*设备。
if (result) {
release_idr(&thermal_tz_idr, &thermal_idr_lock, tz->id);
kfree(tz);
return ERR_PTR(result);
} /* sys I/F */---------------------------------------------------------分别创建type、temp、mode、trip等sysfs节点。
if (type) {
result = device_create_file(&tz->device, &dev_attr_type);
if (result)
goto unregister;
}
...
result = create_trip_attrs(tz, mask);-----------------------为每个trip创建trip_point_*_temp/hyst/type节点。
if (result)
goto unregister;
...
/* Update 'this' zone's governor information */
mutex_lock(&thermal_governor_lock); if (tz->tzp)-------------------------------------------------如果指定thermal zone的governor则通过__find_governor()选定;否则使用默认def_governor。
governor = __find_governor(tz->tzp->governor_name);
else
governor = def_governor; result =thermal_set_governor(tz, governor);-----------------将governor绑定到tz上,优先使用bind_to_tz()执行绑定;否则直接指定tz->governor为governor。
if (result) {
mutex_unlock(&thermal_governor_lock);
goto unregister;
} mutex_unlock(&thermal_governor_lock); if (!tz->tzp || !tz->tzp->no_hwmon) {
result = thermal_add_hwmon_sysfs(tz);
if (result)
goto unregister;
} mutex_lock(&thermal_list_lock);
list_add_tail(&tz->node, &thermal_tz_list);------------------------将当前thermal zone加入到thermal_tz_list列表上。
mutex_unlock(&thermal_list_lock); /* Bind cooling devices for this zone */bind_tz(tz);-------------------------------------------------------调用tz->ops->bind()将thermal_cdev_list上的cooling设备绑定到tz上。 INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&(tz->poll_queue), thermal_zone_device_check); thermal_zone_device_reset(tz);-------------------------------------对thermal zone的温度等复位。
/* Update the new thermal zone and mark it as already updated. */
if (atomic_cmpxchg(&tz->need_update, , ))
thermal_zone_device_update(tz, THERMAL_EVENT_UNSPECIFIED); return tz; unregister:
release_idr(&thermal_tz_idr, &thermal_idr_lock, tz->id);
device_unregister(&tz->device);
return ERR_PTR(result);
} static int thermal_set_governor(struct thermal_zone_device *tz,
struct thermal_governor *new_gov)
{
int ret = ; if (tz->governor && tz->governor->unbind_from_tz)
tz->governor->unbind_from_tz(tz);------------------------------先调用当前governor进行unbind()。 if (new_gov && new_gov->bind_to_tz) {
ret = new_gov->bind_to_tz(tz);---------------------------------使用当前governor进行bind()。
if (ret) {
bind_previous_governor(tz, new_gov->name); return ret;
}
} tz->governor = new_gov;--------------------------------------------更新tz->governor。 return ret;
} static void bind_tz(struct thermal_zone_device *tz)
{
int i, ret;
struct thermal_cooling_device *pos = NULL;
const struct thermal_zone_params *tzp = tz->tzp; if (!tzp && !tz->ops->bind)
return; mutex_lock(&thermal_list_lock); /* If there is ops->bind, try to use ops->bind */
if (tz->ops->bind) {
list_for_each_entry(pos, &thermal_cdev_list, node) {-----------遍历thermal_cdev_list的cooling设备,然后和当前thermal zone进行绑定。
ret = tz->ops->bind(tz, pos);
if (ret)
print_bind_err_msg(tz, pos, ret);
}
goto exit;
}
...
exit:
mutex_unlock(&thermal_list_lock);
} static void thermal_zone_device_check(struct work_struct *work)
{
struct thermal_zone_device *tz = container_of(work, struct
thermal_zone_device,
poll_queue.work);
thermal_zone_device_update(tz, THERMAL_EVENT_UNSPECIFIED);
}
thermal_zone_device_unregister()则执行相反的操作,将thermal zone从thermal_tz_list上摘除,并且和cooling设备去绑定,以及删除一系列sysfs节点。
void thermal_zone_device_unregister(struct thermal_zone_device *tz)
{
int i;
const struct thermal_zone_params *tzp;
struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev;
struct thermal_zone_device *pos = NULL; if (!tz)
return; tzp = tz->tzp; mutex_lock(&thermal_list_lock);
list_for_each_entry(pos, &thermal_tz_list, node)
if (pos == tz)
break;
if (pos != tz) {
/* thermal zone device not found */
mutex_unlock(&thermal_list_lock);
return;
}
list_del(&tz->node); /* Unbind all cdevs associated with 'this' thermal zone */
list_for_each_entry(cdev, &thermal_cdev_list, node) {
if (tz->ops->unbind) {
tz->ops->unbind(tz, cdev);
continue;
}
...
}
...
return;
}
thermal_cooling_device_register()创建cooling设备并放入thermal_cdev_list中,以及相关sysfs节点,并将cooling设备和thermal zone绑定。
thermal_cooling_device_unregister()则进行相反的操作。
struct thermal_cooling_device *
thermal_cooling_device_register(char *type, void *devdata,
const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops *ops)
{
return __thermal_cooling_device_register(NULL, type, devdata, ops);
} static struct thermal_cooling_device *
__thermal_cooling_device_register(struct device_node *np,
char *type, void *devdata,
const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops *ops)
{
struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev;
struct thermal_zone_device *pos = NULL;
int result; if (type && strlen(type) >= THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH)
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL); if (!ops || !ops->get_max_state || !ops->get_cur_state ||
!ops->set_cur_state)
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL); cdev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct thermal_cooling_device), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!cdev)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM); result = get_idr(&thermal_cdev_idr, &thermal_idr_lock, &cdev->id);
if (result) {
kfree(cdev);
return ERR_PTR(result);
} strlcpy(cdev->type, type ? : "", sizeof(cdev->type));
mutex_init(&cdev->lock);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&cdev->thermal_instances);
cdev->np = np;
cdev->ops = ops;
cdev->updated = false;
cdev->device.class = &thermal_class;---------------------------------cooling设备同样会在/sys/class/thermal下创建链接。
cdev->device.groups = cooling_device_attr_groups;--------------------创建cur_state、max_state、type三个sysfs节点。
cdev->devdata = devdata;
dev_set_name(&cdev->device, "cooling_device%d", cdev->id);
result = device_register(&cdev->device);-----------------------------创建/sys/devices/virtual/thermal/cooling_device*设备节点。
if (result) {
release_idr(&thermal_cdev_idr, &thermal_idr_lock, cdev->id);
kfree(cdev);
return ERR_PTR(result);
} /* Add 'this' new cdev to the global cdev list */
mutex_lock(&thermal_list_lock);
list_add(&cdev->node, &thermal_cdev_list);---------------------------将设备放入thermal_cdev_list设备链表。
mutex_unlock(&thermal_list_lock); /* Update binding information for 'this' new cdev */
bind_cdev(cdev);-----------------------------------------------------遍历thermal_tz_list,将cdev绑定到上面的thermal zone。 mutex_lock(&thermal_list_lock);
list_for_each_entry(pos, &thermal_tz_list, node)
if (atomic_cmpxchg(&pos->need_update, , ))
thermal_zone_device_update(pos,
THERMAL_EVENT_UNSPECIFIED);
mutex_unlock(&thermal_list_lock); return cdev;
} void thermal_cooling_device_unregister(struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev)
{
int i;
const struct thermal_zone_params *tzp;
struct thermal_zone_device *tz;
struct thermal_cooling_device *pos = NULL; if (!cdev)
return; mutex_lock(&thermal_list_lock);
list_for_each_entry(pos, &thermal_cdev_list, node)
if (pos == cdev)
break;
if (pos != cdev) {
/* thermal cooling device not found */
mutex_unlock(&thermal_list_lock);
return;
}
list_del(&cdev->node); /* Unbind all thermal zones associated with 'this' cdev */
list_for_each_entry(tz, &thermal_tz_list, node) {
if (tz->ops->unbind) {
tz->ops->unbind(tz, cdev);
continue;
} if (!tz->tzp || !tz->tzp->tbp)
continue; tzp = tz->tzp;
for (i = ; i < tzp->num_tbps; i++) {
if (tzp->tbp[i].cdev == cdev) {
__unbind(tz, tzp->tbp[i].trip_mask, cdev);
tzp->tbp[i].cdev = NULL;
}
}
} mutex_unlock(&thermal_list_lock); if (cdev->type[])
device_remove_file(&cdev->device, &dev_attr_cdev_type);
device_remove_file(&cdev->device, &dev_attr_max_state);
device_remove_file(&cdev->device, &dev_attr_cur_state); release_idr(&thermal_cdev_idr, &thermal_idr_lock, cdev->id);
device_unregister(&cdev->device);
return;
}
thermal_register_governor()首先判断thermal_governor_list上是否有同名governor,然后更新thermal_tz_list上未指定governor的thermal zone。
thermal_unregister_governor()则相反,将governor和thermal zone调用unbind_from_tz()并置空;最后从thermal_go上摘除。
int thermal_register_governor(struct thermal_governor *governor)
{
int err;
const char *name;
struct thermal_zone_device *pos; if (!governor)
return -EINVAL; mutex_lock(&thermal_governor_lock); err = -EBUSY;
if (__find_governor(governor->name) == NULL) {--------------------检查此governor是否已经在thermal_governor_list中,如果不在则加入thermal_governor_list。并且判断是否为def_governor。
err = ;
list_add(&governor->governor_list, &thermal_governor_list);
if (!def_governor && !strncmp(governor->name,
DEFAULT_THERMAL_GOVERNOR, THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH))
def_governor = governor;
} mutex_lock(&thermal_list_lock); list_for_each_entry(pos, &thermal_tz_list, node) {
if (pos->governor)--------------------------------------------如果thermal zone已经制定governor,则跳过。
continue;
name = pos->tzp->governor_name;
if (!strncasecmp(name, governor->name, THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH)) {
int ret; ret = thermal_set_governor(pos, governor);----------------给当前thermal zone制定governor。
if (ret)
dev_err(&pos->device,
"Failed to set governor %s for thermal zone %s: %d\n",
governor->name, pos->type, ret);
}
} mutex_unlock(&thermal_list_lock);
mutex_unlock(&thermal_governor_lock); return err;
} void thermal_unregister_governor(struct thermal_governor *governor)
{
struct thermal_zone_device *pos; if (!governor)
return; mutex_lock(&thermal_governor_lock); if (__find_governor(governor->name) == NULL)
goto exit; mutex_lock(&thermal_list_lock); list_for_each_entry(pos, &thermal_tz_list, node) {
if (!strncasecmp(pos->governor->name, governor->name,
THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH))
thermal_set_governor(pos, NULL);
} mutex_unlock(&thermal_list_lock);
list_del(&governor->governor_list);
exit:
mutex_unlock(&thermal_governor_lock);
return;
}
thermal_zone_bind_cooling_device()通过创建thermal_instances设备将Thermal Zone和Thermal Cooling绑定,这样Thermal Zone就可以根据温度处理Thermal Cooling设备。
thermal_zone_unbind_cooling_device() 则将关联Thermal Zone和Thermal Cooling的thermal_instances从两者的链表上摘除。
int thermal_zone_bind_cooling_device(struct thermal_zone_device *tz,
int trip,
struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev,
unsigned long upper, unsigned long lower,
unsigned int weight)
{
struct thermal_instance *dev;
struct thermal_instance *pos;
struct thermal_zone_device *pos1;
struct thermal_cooling_device *pos2;
unsigned long max_state;
int result, ret; if (trip >= tz->trips || (trip < && trip != THERMAL_TRIPS_NONE))
return -EINVAL; list_for_each_entry(pos1, &thermal_tz_list, node) {
if (pos1 == tz)
break;
}
list_for_each_entry(pos2, &thermal_cdev_list, node) {
if (pos2 == cdev)
break;
} if (tz != pos1 || cdev != pos2)
return -EINVAL; ret = cdev->ops->get_max_state(cdev, &max_state);----------------------从Cooling设备操作函数get_max_state()获取max_state,进而决定thermal_instances的lower和upper范围。
if (ret)
return ret; /* lower default 0, upper default max_state */
lower = lower == THERMAL_NO_LIMIT ? : lower;
upper = upper == THERMAL_NO_LIMIT ? max_state : upper; if (lower > upper || upper > max_state)
return -EINVAL; dev =
kzalloc(sizeof(struct thermal_instance), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!dev)
return -ENOMEM;
dev->tz = tz;
dev->cdev = cdev;
dev->trip = trip;
dev->upper = upper;
dev->lower = lower;
dev->target = THERMAL_NO_TARGET;
dev->weight = weight; result = get_idr(&tz->idr, &tz->lock, &dev->id);
if (result)
goto free_mem; sprintf(dev->name, "cdev%d", dev->id);
result =
sysfs_create_link(&tz->device.kobj, &cdev->device.kobj, dev->name);------cdevx连接到cooling_devicex。
if (result)
goto release_idr; sprintf(dev->attr_name, "cdev%d_trip_point", dev->id);-----------------------创建cdevx_trip_point和cdevx_weight节点。
sysfs_attr_init(&dev->attr.attr);
dev->attr.attr.name = dev->attr_name;
dev->attr.attr.mode = ;
dev->attr.show = thermal_cooling_device_trip_point_show;
result = device_create_file(&tz->device, &dev->attr);
if (result)
goto remove_symbol_link; sprintf(dev->weight_attr_name, "cdev%d_weight", dev->id);
sysfs_attr_init(&dev->weight_attr.attr);
dev->weight_attr.attr.name = dev->weight_attr_name;
dev->weight_attr.attr.mode = S_IWUSR | S_IRUGO;
dev->weight_attr.show = thermal_cooling_device_weight_show;
dev->weight_attr.store = thermal_cooling_device_weight_store;
result = device_create_file(&tz->device, &dev->weight_attr);
if (result)
goto remove_trip_file;...
} int thermal_zone_unbind_cooling_device(struct thermal_zone_device *tz,
int trip,
struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev)
{
struct thermal_instance *pos, *next; mutex_lock(&tz->lock);
mutex_lock(&cdev->lock);
list_for_each_entry_safe(pos, next, &tz->thermal_instances, tz_node) {
if (pos->tz == tz && pos->trip == trip && pos->cdev == cdev) {
list_del(&pos->tz_node);
list_del(&pos->cdev_node);
mutex_unlock(&cdev->lock);
mutex_unlock(&tz->lock);
goto unbind;
}
}
mutex_unlock(&cdev->lock);
mutex_unlock(&tz->lock); return -ENODEV; unbind:
device_remove_file(&tz->device, &pos->weight_attr);
device_remove_file(&tz->device, &pos->attr);
sysfs_remove_link(&tz->device.kobj, pos->name);
release_idr(&tz->idr, &tz->lock, pos->id);
kfree(pos);
return ;
}
thermal_zone_device_update()一般由Thermal驱动调用,有可能是polling或者中断触发。
然后更新当前Thermal Zone的温度,最后根据温度值通过handle_thermal_trip()进行处理。
monitor_thermal_zone()根据passive和polling的设置决定是否启动thermal_zone_device->pool_queue这个delayed_work。
整个polling流程由thermal_zone_device_update()触发,依次流程为:handle_thermal_trip()中启动monitor_thermal_zone(),monitor_thermal_zone()中调用mod_delayed_work()进行poll_queue延时值的更新。如果thermal zone有多个trip,poll_queue延时值可能被多次更新。poll_queue放入system_freezable_wq后,达到时间后调用thermal_zone_device_check(),进而调用thermal_zone_device_update()完成周期性循环。
void thermal_zone_device_update(struct thermal_zone_device *tz,
enum thermal_notify_event event)
{
int count; if (atomic_read(&in_suspend))
return; if (!tz->ops->get_temp)
return; update_temperature(tz); thermal_zone_set_trips(tz); tz->notify_event = event; for (count = ; count < tz->trips; count++)
handle_thermal_trip(tz, count);
} static void update_temperature(struct thermal_zone_device *tz)
{
int temp, ret; ret = thermal_zone_get_temp(tz, &temp);
if (ret) {
if (ret != -EAGAIN)
dev_warn(&tz->device,
"failed to read out thermal zone (%d)\n",
ret);
return;
} mutex_lock(&tz->lock);
tz->last_temperature = tz->temperature;
tz->temperature = temp;
mutex_unlock(&tz->lock); trace_thermal_temperature(tz);
if (tz->last_temperature == THERMAL_TEMP_INVALID)
dev_dbg(&tz->device, "last_temperature N/A, current_temperature=%d\n",
tz->temperature);
else
dev_dbg(&tz->device, "last_temperature=%d, current_temperature=%d\n",
tz->last_temperature, tz->temperature);
} void thermal_zone_set_trips(struct thermal_zone_device *tz)
{
int low = -INT_MAX;
int high = INT_MAX;
int trip_temp, hysteresis;
int i, ret; mutex_lock(&tz->lock); if (!tz->ops->set_trips || !tz->ops->get_trip_hyst)
goto exit; for (i = ; i < tz->trips; i++) {
int trip_low; tz->ops->get_trip_temp(tz, i, &trip_temp);
tz->ops->get_trip_hyst(tz, i, &hysteresis); trip_low = trip_temp - hysteresis; if (trip_low < tz->temperature && trip_low > low)
low = trip_low; if (trip_temp > tz->temperature && trip_temp < high)
high = trip_temp;
} /* No need to change trip points */
if (tz->prev_low_trip == low && tz->prev_high_trip == high)
goto exit; tz->prev_low_trip = low;
tz->prev_high_trip = high; dev_dbg(&tz->device,
"new temperature boundaries: %d < x < %d\n", low, high); ret = tz->ops->set_trips(tz, low, high);
if (ret)
dev_err(&tz->device, "Failed to set trips: %d\n", ret); exit:
mutex_unlock(&tz->lock);
} static void handle_thermal_trip(struct thermal_zone_device *tz, int trip)
{
enum thermal_trip_type type; /* Ignore disabled trip points */
if (test_bit(trip, &tz->trips_disabled))
return; tz->ops->get_trip_type(tz, trip, &type); if (type == THERMAL_TRIP_CRITICAL || type == THERMAL_TRIP_HOT)
handle_critical_trips(tz, trip, type);
elsehandle_non_critical_trips(tz, trip, type);
/*
* Alright, we handled this trip successfully.
* So, start monitoring again.
*/monitor_thermal_zone(tz);
} static void handle_critical_trips(struct thermal_zone_device *tz,
int trip, enum thermal_trip_type trip_type)
{
int trip_temp; tz->ops->get_trip_temp(tz, trip, &trip_temp); /* If we have not crossed the trip_temp, we do not care. */
if (trip_temp <= || tz->temperature < trip_temp)
return; trace_thermal_zone_trip(tz, trip, trip_type); if (tz->ops->notify)
tz->ops->notify(tz, trip, trip_type); if (trip_type == THERMAL_TRIP_CRITICAL) {
dev_emerg(&tz->device,
"critical temperature reached(%d C),shutting down\n",
tz->temperature / );
orderly_poweroff(true);
}
} static void handle_non_critical_trips(struct thermal_zone_device *tz,
int trip, enum thermal_trip_type trip_type)
{
tz->governor ? tz->governor->throttle(tz, trip) :
def_governor->throttle(tz, trip);
} static void monitor_thermal_zone(struct thermal_zone_device *tz)
{
mutex_lock(&tz->lock); if (tz->passive)-----------------------------------分别设置passive和polling两种延时工作。
thermal_zone_device_set_polling(tz, tz->passive_delay);
else if (tz->polling_delay)
thermal_zone_device_set_polling(tz, tz->polling_delay);
else
thermal_zone_device_set_polling(tz, ); mutex_unlock(&tz->lock);
} static void thermal_zone_device_set_polling(struct thermal_zone_device *tz,
int delay)
{
if (delay > )----------------------------------将poll_queue放入system_freezable_wq工作队列上,多次调用mod_delayed_work()在超时前只有最后一次生效。
mod_delayed_work(system_freezable_wq, &tz->poll_queue,
round_jiffies(msecs_to_jiffies(delay)));
else if (delay)
mod_delayed_work(system_freezable_wq, &tz->poll_queue,
msecs_to_jiffies(delay));
else
cancel_delayed_work(&tz->poll_queue);----------如果delay为0,则取消poll_queue延时工作。
}
thermal_cdev_update()是由Governor调用进行cooling device设置。
void thermal_cdev_update(struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev)
{
struct thermal_instance *instance;
unsigned long target = ; mutex_lock(&cdev->lock);
/* cooling device is updated*/
if (cdev->updated) {
mutex_unlock(&cdev->lock);
return;
} /* Make sure cdev enters the deepest cooling state */
list_for_each_entry(instance, &cdev->thermal_instances, cdev_node) {----------遍历当前cooling device上所有的thermal zone。
dev_dbg(&cdev->device, "zone%d->target=%lu\n",
instance->tz->id, instance->target);
if (instance->target == THERMAL_NO_TARGET)
continue;
if (instance->target > target)
target = instance->target;---------------------------------------------确保cooling设备选择最高cooling状态,然后调用cooling设备的set_cur_state()进行降温。
}
cdev->ops->set_cur_state(cdev, target);
cdev->updated = true;
mutex_unlock(&cdev->lock);
trace_cdev_update(cdev, target);
dev_dbg(&cdev->device, "set to state %lu\n", target);
}
1.3 Thermal初始化
thermal_init()在内核fs_initcall()阶段调用,进行governor、thermal_class、Generic Netlink注册等操作。
static int __init thermal_init(void)
{
int result; result = thermal_register_governors();---------------注册平台支持的所有governor。
if (result)
goto error; result = class_register(&thermal_class);-------------注册thermal_class。
if (result)
goto unregister_governors; result = genetlink_init();---------------------------注册Generic Netlink。
if (result)
goto unregister_class;...
return result;
} static void __exit thermal_exit(void)
{
unregister_pm_notifier(&thermal_pm_nb);
of_thermal_destroy_zones();
genetlink_exit();
class_unregister(&thermal_class);
thermal_unregister_governors();
...
} fs_initcall(thermal_init);
module_exit(thermal_exit);
2. Thermal Driver实例
下面首先简单看一下Temp Sensor的硬件,然后分析DTS,最后分析驱动的实现。
2.1 Temp Sensor硬件
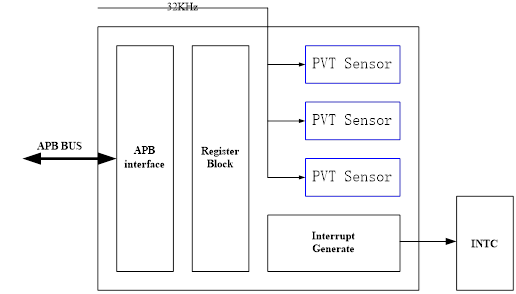
对Temp Sensor的配置可以通过APB BUS进行,包括两个Temp Sensor,每个Temp Sensor中包括3个Trip触发点设置,以及一个Alarm配置。
Trip达到后会触发中断,CPU的INTC收到中断后,进行中断处理;Alarm达到后直接导致CPU复位或者关闭PLL。
Temp Sensor默认使用32K时钟,每32768个时钟采样一次。还可以根据情况选择24M作为时钟输入。
一个重要工作就是根据实际情况,选定Trip温度以及Alarm温度。
另一个核心的工作就是确定如何根据Data寄存器的值计算出温度值。这就需要计算两个参数A和B。
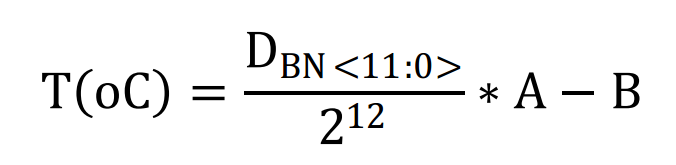
通过其他测量手段读出温度值,以及当前温度值下的DBN<11:0>。这获取一系列数据之后,通过直线数据拟合,得出A和B的值。
2.2 Temp Sensor DTS
DTS是对硬件的抽象,包括寄存器配置地址和范围、中断、3个trip温度、一个alarm温度。
sensor0: sensor0@0xfc20a000 {
compatible = "vsi,dp1000-thermal";
reg = <0xfc20a000 0x20>;
interrupts = <>;
vsi,temp0 = <>;
vsi,temp1 = <>;
vsi,temp2 = <>;
vsi,alarm_temp = <>;
vsi,alarm_en;
};
从DTS可以看出,通过配置不同trip和alarm的温度,中断触发后,CPU会读取温度进行相应处理。
2.3 Temp Sensor驱动
Temp Sensor的驱动首先解析DTS,并进行iomem映射;然后注册中断以及下半部workqueue处理;再进行硬件设置;最后注册thermal zone设备。
在设备正常工作中,根据配置的trip和alarm值触发中断,然后进行work处理;中间会用到struct thermal_zone_device_ops提供的成员函数获取温度、和cooling设备绑定等等操作。
2.3.1 Thermal Sensor注册
static int dp1000_thermal_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct dp1000_thermal_priv *priv;
struct resource *res;
int ret; priv = devm_kzalloc(&pdev->dev, sizeof(*priv), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!priv)
return -ENOMEM; res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, );
priv->reg_base = devm_ioremap_resource(&pdev->dev, res);
if (IS_ERR(priv->reg_base))
return PTR_ERR(priv->reg_base); if (device_property_read_u32(&pdev->dev, "vsi,temp0", &priv->temp0) < ) {
dev_dbg(&pdev->dev,
"\"temp0\" property is missing, using default value.\n");
priv->temp0 = ;
}
...
INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&priv->work, dp1000_thermal_work);---------------------创建delayed_work,对应的处理函数是dp1000_thermal_work()。 priv->irq = platform_get_irq(pdev, );
...
ret = devm_request_irq(&pdev->dev, priv->irq,
dp1000_thermal_interrupt, ,
dev_name(&pdev->dev), priv);-------------------------------irq注册,中断处理函数为dp1000_thermal_interrupt()。
...
dp1000_init_thermal(priv);------------------------------------------------硬件初始化。 priv->zone = thermal_zone_device_register("dp1000_thermal", DP1000_THERMAL_TRIPS, ,
priv, &dp1000_thermal_zone_ops, NULL, , );-------Thermal Zone注册。
#ifdef DP1000_THERMAL_STUB
if(priv->zone->id == )
thermal_zone_0 = priv->zone;
else if(priv->zone->id == )
thermal_zone_1 = priv->zone;
#endif
...
return ;
} static int dp1000_thermal_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct dp1000_thermal_priv *priv = dev_get_drvdata(&pdev->dev);
...
return ;
} static const struct of_device_id dp1000_thermal_id_table[] = {
{ .compatible = "vsi,dp1000-thermal" },-----------------------------------和dts匹配。
{ }
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, dp1000_thermal_id_table); static struct platform_driver dp1000_thermal_driver = {
.probe =dp1000_thermal_probe,
.remove =dp1000_thermal_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "dp1000_thermal",
.of_match_table = dp1000_thermal_id_table,
},
}; module_platform_driver(dp1000_thermal_driver);
dp1000_thermal_zone_ops函数集是Thermal Sensor的核心,对Thermal Zone的操作都是通过调用这些函数实现的。
static struct thermal_zone_device_ops dp1000_thermal_zone_ops = {
.bind = dp1000_thermal_bind,
.unbind = dp1000_thermal_unbind,
.get_trip_type = dp1000_thermal_get_trip_type,
.get_trip_hyst = dp1000_thermal_get_trip_hyst,
.get_temp = dp1000_thermal_get_temp,
.set_trip_temp = dp1000_thermal_set_trip_temp,
.get_trip_temp = dp1000_thermal_get_trip_temp,
.get_crit_temp = dp1000_thermal_get_crit_temp,
};
2.3.2 Thermal Driver中断能触发流程
当Thermal Sensor的温度达到trip值时,会触发中断。
然后进入dp1000_thermal_interrupt(),在延时300ms进行dp1000_thermal_work()处理。
static irqreturn_t dp1000_thermal_interrupt(int irq, void *id)
{
struct dp1000_thermal_priv *priv = (struct dp1000_thermal_priv *)id;
unsigned int status; if (status == )
return IRQ_NONE;
else {
schedule_delayed_work(&priv->work, msecs_to_jiffies());
} return IRQ_HANDLED;
} static void dp1000_thermal_work(struct work_struct *work)
{
struct dp1000_thermal_priv *priv; priv = container_of(work, struct dp1000_thermal_priv, work.work); thermal_zone_device_update(priv->zone, THERMAL_EVENT_UNSPECIFIED);
}
最终的工作交给thermal_zone_device_update()进行,读取温度,根据温度选择trip。
3. Thermal Governor分析
下面简单分析两个Governor:Step Wise和Fair Share。
3.1 Step Wise分析
首先看一下Step Wise的注册。
static struct thermal_governor thermal_gov_step_wise = {
.name = "step_wise",
.throttle =step_wise_throttle,
};
int thermal_gov_step_wise_register(void)
{
return thermal_register_governor(&thermal_gov_step_wise);
}
void thermal_gov_step_wise_unregister(void)
{
thermal_unregister_governor(&thermal_gov_step_wise);
}
在handle_non_critical_trips()中,首先选用当前thermal zone的throttle()进行处理。
对于Step Wise governor来说,对外的接口只有step_wise_throttle()。
static int step_wise_throttle(struct thermal_zone_device *tz, int trip)
{
struct thermal_instance *instance;
thermal_zone_trip_update(tz, trip);-----------------------------根据当前温度和上次温度对比,得到温度趋势;然后根据温度趋势得出Cooling设备对应的state。 if (tz->forced_passive)
thermal_zone_trip_update(tz, THERMAL_TRIPS_NONE); mutex_lock(&tz->lock); list_for_each_entry(instance, &tz->thermal_instances, tz_node)
thermal_cdev_update(instance->cdev);------------------------遍历cdev->thermal_instances选择最深的cooling状态。然后调用cdev->ops->set_cur_state()中。 mutex_unlock(&tz->lock); return ;
} static void thermal_zone_trip_update(struct thermal_zone_device *tz, int trip)
{
int trip_temp;
enum thermal_trip_type trip_type;
enum thermal_trend trend;
struct thermal_instance *instance;
bool throttle = false;
int old_target; if (trip == THERMAL_TRIPS_NONE) {
trip_temp = tz->forced_passive;
trip_type = THERMAL_TRIPS_NONE;
} else {
tz->ops->get_trip_temp(tz, trip, &trip_temp);
tz->ops->get_trip_type(tz, trip, &trip_type);
} trend = get_tz_trend(tz, trip);----------------------------------------根据当前温度tz->temperature和tz->last_temperature对比,判定tend是STABLE/RAISING/DROPPING等中的一种。 if (tz->temperature >= trip_temp) {
throttle = true;---------------------------------------------------throttle为true表示需要节流,即降温。
trace_thermal_zone_trip(tz, trip, trip_type);
}
mutex_lock(&tz->lock); list_for_each_entry(instance, &tz->thermal_instances, tz_node) {
if (instance->trip != trip)----------------------------------------相同trip不做处理。
continue; old_target = instance->target;
instance->target =get_target_state(instance, trend, throttle);----instance->target是将要设置到Cooling设备的状态。
if (instance->initialized && old_target == instance->target)
continue; /* Activate a passive thermal instance */
if (old_target == THERMAL_NO_TARGET &&
instance->target != THERMAL_NO_TARGET)
update_passive_instance(tz, trip_type, );
/* Deactivate a passive thermal instance */
else if (old_target != THERMAL_NO_TARGET &&
instance->target == THERMAL_NO_TARGET)
update_passive_instance(tz, trip_type, -); instance->initialized = true;
mutex_lock(&instance->cdev->lock);
instance->cdev->updated = false;------------------------------------updated为false表示Cooling设备需要更新状态,在thermal_cdev_update()中会进行判断。
mutex_unlock(&instance->cdev->lock);
} mutex_unlock(&tz->lock);
} static unsigned long get_target_state(struct thermal_instance *instance,
enum thermal_trend trend, bool throttle)
{
struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev = instance->cdev;
unsigned long cur_state;
unsigned long next_target; cdev->ops->get_cur_state(cdev, &cur_state);
next_target = instance->target;
dev_dbg(&cdev->device, "cur_state=%ld\n", cur_state); if (!instance->initialized) {
if (throttle) {
next_target = (cur_state + ) >= instance->upper ?
instance->upper :
((cur_state + ) < instance->lower ?
instance->lower : (cur_state + ));
} else {
next_target = THERMAL_NO_TARGET;
} return next_target;
} switch (trend) {
case THERMAL_TREND_RAISING:------------------------------------升温状态下,next_target为cur_state+1,但是不超过instance->upper。
if (throttle) {
next_target = cur_state < instance->upper ?
(cur_state + ) : instance->upper;
if (next_target < instance->lower)
next_target = instance->lower;
}
break;
case THERMAL_TREND_RAISE_FULL:
if (throttle)
next_target = instance->upper;
break;
case THERMAL_TREND_DROPPING:------------------------------------降温状态下,next_target为cur_state-1,但不低于instance->lower。存在特殊情况为THERMAL_NO_TARGET。
if (cur_state <= instance->lower) {
if (!throttle)
next_target = THERMAL_NO_TARGET;
} else {
next_target = cur_state - ;
if (next_target > instance->upper)
next_target = instance->upper;
}
break;
case THERMAL_TREND_DROP_FULL:
if (cur_state == instance->lower) {
if (!throttle)
next_target = THERMAL_NO_TARGET;
} else
next_target = instance->lower;
break;
default:--------------------------------------------------------stable状态,不改变target值。
break;
} return next_target;
} static void update_passive_instance(struct thermal_zone_device *tz,
enum thermal_trip_type type, int value)
{
if (type == THERMAL_TRIP_PASSIVE || type == THERMAL_TRIPS_NONE)
tz->passive += value;
}
Step Wise在中断触发后根据温度的变化趋势选择Cooling状态。而不是根据trip值选择Cooling状态。
* If the temperature is higher than a trip point,
* a. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_RAISING, use higher cooling
* state for this trip point
* b. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_DROPPING, use lower cooling
* state for this trip point
* c. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_RAISE_FULL, use upper limit
* for this trip point
* d. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_DROP_FULL, use lower limit
* for this trip point
* If the temperature is lower than a trip point,
* a. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_RAISING, do nothing
* b. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_DROPPING, use lower cooling
* state for this trip point, if the cooling state already
* equals lower limit, deactivate the thermal instance
* c. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_RAISE_FULL, do nothing
* d. if the trend is THERMAL_TREND_DROP_FULL, use lower limit,
* if the cooling state already equals lower limit,
* deactivate the thermal instance
如上是step_wise.c中关于Step Wise governor的温控策略。分别对高于或低于trip温度下不同趋势行为做出了解释。
3.2 Fair Share分析
FairShare引入了weight概念。如果一个thermal zone中存在多个Cooling设备,不同的设备降温效果可能不同,用weight表示降温的能力。
weight大的设备得分较高,因此可以选择更深的Cooling状态。
static struct thermal_governor thermal_gov_fair_share = {
.name = "fair_share",
.throttle =fair_share_throttle,
};
int thermal_gov_fair_share_register(void)
{
return thermal_register_governor(&thermal_gov_fair_share);
}
void thermal_gov_fair_share_unregister(void)
{
thermal_unregister_governor(&thermal_gov_fair_share);
}
fair_share_throttle()首先根据温度得出当前trip等级,然后综合不同Cooling的weight等计算出每个Cooling设备的target。
static int fair_share_throttle(struct thermal_zone_device *tz, int trip)
{
struct thermal_instance *instance;
int total_weight = ;
int total_instance = ;
int cur_trip_level =get_trip_level(tz);------------------------------------根据温度获取对应trip等级。 list_for_each_entry(instance, &tz->thermal_instances, tz_node) {
if (instance->trip != trip)
continue; total_weight += instance->weight;
total_instance++;
} list_for_each_entry(instance, &tz->thermal_instances, tz_node) {
int percentage;
struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev = instance->cdev; if (instance->trip != trip)
continue; if (!total_weight)
percentage = / total_instance;----------------------------------在都没有定义weight的情况下,每个Cooling设备同样percentage。
else
percentage = (instance->weight * ) / total_weight;---------------如果存在weight的情况下,根据权重来划分percentage。 instance->target =get_target_state(tz, cdev, percentage,
cur_trip_level);------------------------------------获取当前Cooling设备对应的state。 mutex_lock(&instance->cdev->lock);
instance->cdev->updated = false;
mutex_unlock(&instance->cdev->lock);
thermal_cdev_update(cdev);
}
return ;
} static int get_trip_level(struct thermal_zone_device *tz)
{
int count = ;
int trip_temp;
enum thermal_trip_type trip_type; if (tz->trips == || !tz->ops->get_trip_temp)
return ; for (count = ; count < tz->trips; count++) {
tz->ops->get_trip_temp(tz, count, &trip_temp);
if (tz->temperature < trip_temp)----------------------------------------根据thermal zone的温度值,选择合适的trip等级。
break;
} if (count > ) {
tz->ops->get_trip_type(tz, count - , &trip_type);----------------------仅是更新thermal trace point。
trace_thermal_zone_trip(tz, count - , trip_type);
}
return count;
} static long get_target_state(struct thermal_zone_device *tz,
struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev, int percentage, int level)
{
unsigned long max_state; cdev->ops->get_max_state(cdev, &max_state);
return (long)(percentage * level * max_state) / ( * tz->trips);--------------
}
在weight为0的情况下,不同Cooling设备state均等映射到trip。在只有一个Cooling设备情况下,如果Cooling最大状态和ThermalZone trip最大值相等,怎可以trip和状态一一对应。
* Parameters used for Throttling:
* P1. max_state: Maximum throttle state exposed by the cooling device.
* P2. percentage[i]/:
* How 'effective' the 'i'th device is, in cooling the given zone.
* P3. cur_trip_level/max_no_of_trips:
* This describes the extent to which the devices should be throttled.
* We do not want to throttle too much when we trip a lower temperature,
* whereas the throttling is at full swing if we trip critical levels.
* (Heavily assumes the trip points are in ascending order)
* new_state of cooling device = P3 * P2 * P1
fair_share.c中给出了计算Cooling设备状态的计算公式,new_state=percentage*cur_trip_level*max_state/(100*max_no_of_trips)。
4. Thermal Cooling实例
创建一个Dummy Cooling驱动表示Cooling设备,通过thermal_cooling_device_register()注册Thermal Cooling设备,将其和Thermal Zone绑定。在Thermal Zone中断出发后,通过Governor选择state,然后通过set_cur_state()执行温控操作。
/* bind to generic thermal layer as cooling device*/
static struct thermal_cooling_device_ops dummy_cooling_ops = {
.get_max_state = dummy_cooling_get_max_state,---------------------------Cooling设备最深降温状态。
.get_cur_state = dummy_cooling_get_cur_state,---------------------------当前Cooling状态。
.set_cur_state = dummy_cooling_set_cur_state,---------------------------根据状态,执行温控操作。
}; static int __init dummy_cooling_init(void)
{
int retval; dummy_cooling_dev = thermal_cooling_device_register("dummy_cooling", NULL,
&dummy_cooling_ops);
if (IS_ERR(dummy_cooling_dev)) {
retval = -ENODEV;
} return retval;
}
module_init(dummy_cooling_init); static void __exit dummy_cooling_exit(void)
{
thermal_cooling_device_unregister(dummy_cooling_dev);
}
module_exit(dummy_cooling_exit);
5. Thermal调试以及流程分析
首先使能已有Thermal调试手段,并添加proc节点模拟中断触发;然后基于log分析Thermal流程。
5.1 Thermal调试手段
对Termal的调试可以有两种方式:
- 在thermal_core.c和step_wise.c的include之前#define DEBUG打开调试功能。
- 打开thermal trace point:echo 1 > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/thermal/enable
为了模拟温度变化,添加proc节点,然后使用脚本模拟温度触发流程。
#ifdef DP1000_THERMAL_STUB
static int dp1000_temp_stub = ;
struct thermal_zone_device *thermal_zone_0, *thermal_zone_1;
struct proc_dir_entry *dp1000_temp_proc = NULL;
#endif static int dp1000_thermal_get_temp(struct thermal_zone_device *zone, int *temp)
{
#ifdef DP1000_THERMAL_STUB
*temp = dp1000_temp_stub;--------------------------------------------------------替代从寄存器获取温度流程,使用/proc/dp1000_temp_stub输入的温度值。
#else
...
#endif
return ;
} #ifdef DP1000_THERMAL_STUB
static int dp1000_temp_stub_proc_show(struct seq_file *m, void *v)
{
seq_printf(m, "%d\n", dp1000_temp_stub);
return ;
} static int dp1000_temp_stub_proc_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
return single_open(file, dp1000_temp_stub_proc_show, NULL);
} static ssize_t dp1000_temp_stub_proc_write(struct file *file,
const char __user *buffer, size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
{
int rc; rc = kstrtoint_from_user(buffer, count, , &dp1000_temp_stub);
if (rc)
return rc; thermal_zone_device_update(thermal_zone_0, THERMAL_EVENT_UNSPECIFIED);------------对/proc/dp1000_temp_stub写入温度,触发流程。模拟中断触发流程。
// thermal_zone_device_update(thermal_zone_1, THERMAL_EVENT_UNSPECIFIED); return count;
} static const struct file_operations dp1000_temp_stub_proc_fops = {
.open = dp1000_temp_stub_proc_open,
.read = seq_read,
.llseek = seq_lseek,
.release = single_release,
.write = dp1000_temp_stub_proc_write,
};
#endif static void dp1000_init_thermal(struct dp1000_thermal_priv *priv)
{
...
#ifdef DP1000_THERMAL_STUB
if(!dp1000_temp_proc)
dp1000_temp_proc = proc_create("dp1000_temp_stub", , NULL, &dp1000_temp_stub_proc_fops);------------创建/proc/dp1000_temp_stub节点。
#endif
...
} static int dp1000_thermal_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
...
priv->zone = thermal_zone_device_register("dp1000_thermal", DP1000_THERMAL_TRIPS, ,
priv, &dp1000_thermal_zone_ops, NULL, , );
#ifdef DP1000_THERMAL_STUB
if(priv->zone->id == )
thermal_zone_0 = priv->zone;
else if(priv->zone->id == )
thermal_zone_1 = priv->zone;
#endif
...
}
5.2 Thermal流程分析
使用如下脚本进行Thermal流程调试:
echo > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/enable
echo > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/thermal/enable
echo > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace for i in
do
echo -e "\n"
echo $i > /proc/dp1000_temp_stub
sleep
done cat /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace
得到的结果如下:
[ 35.900013] thermal thermal_zone0: last_temperature=, current_temperature=
[ 35.907277] thermal thermal_zone0: Trip0[type=,temp=]:trend=,throttle=1--------------89度达到trip0的触发温度,而且是升温状态。trip1和trip2都没有throttle。
[ 35.914290] thermal cooling_device0: cur_state=
[ 35.918933] thermal cooling_device0: old_target=-, target=
[ 35.924619] thermal cooling_device0: zone0->target=
[ 35.929608] thermal cooling_device0: zone1->target=
[ 35.935383] thermal cooling_device0: set to state 1--------------------------------------Cooling设备当前状态时0,所以要将状态设置为1。
[ 35.940293] thermal thermal_zone0: Trip1[type=,temp=]:trend=,throttle=
[ 35.947286] thermal thermal_zone0: Trip2[type=,temp=]:trend=,throttle= [ 36.999977] thermal thermal_zone0: last_temperature=, current_temperature=
[ 37.007326] thermal thermal_zone0: Trip0[type=,temp=]:trend=,throttle=
[ 37.014332] thermal cooling_device0: cur_state=
[ 37.018973] thermal cooling_device0: old_target=, target=
[ 37.024570] thermal cooling_device0: zone0->target=
[ 37.029558] thermal cooling_device0: zone1->target=
[ 37.035336] thermal cooling_device0: set to state 2--------------------------------------95度是trip1的触发温度,所以Cooling状态从当前的1设置到2。trip2没有throttle。
[ 37.040248] thermal thermal_zone0: Trip1[type=,temp=]:trend=,throttle=
[ 37.047240] thermal thermal_zone0: Trip2[type=,temp=]:trend=,throttle=
...
从thermal trace可以才看出,首先获取温度,然后选择trip,最后设置Cooling设备。
# TASK-PID CPU# |||| TIMESTAMP FUNCTION
# | | | |||| | |
sh- [] .... 35.899971: thermal_temperature: thermal_zone=dp1000_thermal id= temp_prev= temp=
sh- [] .... 35.907265: thermal_zone_trip: thermal_zone=dp1000_thermal id= trip= trip_type=ACTIVE
sh- [] .n.. 35.935374: cdev_update: type=dummy_cooling target=
sh- [] .... 36.999933: thermal_temperature: thermal_zone=dp1000_thermal id= temp_prev= temp=
sh- [] .n.. 37.007312: thermal_zone_trip: thermal_zone=dp1000_thermal id= trip= trip_type=ACTIVE
sh- [] .n.. 37.035327: cdev_update: type=dummy_cooling target=
sh- [] .n.. 37.040238: thermal_zone_trip: thermal_zone=dp1000_thermal id= trip= trip_type=ACTIVE
sh- [] .... 38.079912: thermal_temperature: thermal_zone=dp1000_thermal id= temp_prev= temp=
sh- [] .n.. 38.087374: thermal_zone_trip: thermal_zone=dp1000_thermal id= trip= trip_type=ACTIVE
sh- [] .n.. 38.115385: cdev_update: type=dummy_cooling target=
...
6. 小结
Thermal Framework一共可以分为四部分,Thermal Core、Thermal Zone、Thermal Governor、Thermal Cooling。
其中Core很稳定,主要是会使用;Governor也比较稳定,已有的Governor能覆盖大部分场景;需要开发的主要有Thermal Zone的Driver和降温设备Cooling。
在开发过程中,可以借助Trace point等措施进行问题定位。
Linux Thermal Framework分析及实施的更多相关文章
- Android/Linux Thermal框架分析及其Governor对比
图表 1 Thermal框架 随着SoC性能的快速提升,功耗也极大提高,带来的负面影响是SoC的温度提高很快,甚至有可能造成物理损坏.同时功耗浪费也降低了电池寿命. 从上图可知,Thermal框架可以 ...
- Linux PWM framework简介和API描述【转】
本文转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/mike8825/article/details/51656400 1. 前言 PWM是Pulse Width Modulation(脉冲宽度调 ...
- Linux Regulator Framework(2)_regulator driver
转自蜗窝科技:http://www.wowotech.net/pm_subsystem/regulator_driver.html 说实话,这篇好难懂啊... 1. 前言 本文从regulator d ...
- 《Unix/Linux网络日志分析与流量监控》获2015年度最受读者喜爱的IT图书奖
<Unix/Linux网络日志分析与流量监控>获2015年度最受读者喜爱的IT图书奖.刊登在<中华读书报>( 2015年01月28日 19 版) 我的2015年新作刊登在< ...
- 使用 Web Tracing Framework 分析富 JS 应用的性能
来自谷歌的 Web Tracing Framework 包含一组工具和脚本,用于 JavaScript 相关代码的性能分析.它是重 JavaScript 应用程序的理想选择,而 JavaScript ...
- Linux Bluetooth内核分析
目录 1. 初始化 2. hci部分 Linux提供了对Bluetooth的支持,核心代码位于net/bluetooth 1. 初始化 主要由subsys_initcall调用函数bt_init()来 ...
- Linux之kernal分析与启动20160610
说一下LINUX内核的分析与启动: 一. 内核启动流程,据此配置内核(机器ID) 1.1 修改Makefile 1.2 选择默认配置 : make s3c2410_defconfig 1.3 make ...
- linux源码分析2
linux源码分析 这里使用的linux版本是4.8,x86体系. 这篇是 http://home.ustc.edu.cn/~boj/courses/linux_kernel/1_boot.html ...
- Linux网络地址转换分析
Linux网络地址转换分析 地址转换用来改变源/目的端口,是netfilter的一部分,也是通过hook点上注册相应的结构来工作. Nat注册的hook点和conntrack相同,只是优先级不同,数据 ...
随机推荐
- 第1章:C++泛型技术基础:模板——《C++泛型:STL原理和应用》读书笔记整理
第1章:C++泛型技术基础:模板 1.2 关于模板参数 1.2.1 模板参数类型 类型参数 typename声明的参数都属于类型参数,它的实参必须为系统内置或者用户自定义的数据类型,包括类模板实体 ...
- Python学习:50 行 Python 代码,带你追到最心爱的人
程序员世纪难题 人们一提到程序员第一反应就是:我知道!他们工资很高啊!但大部分都是单身狗,不懂得幽默风趣,只是每天穿格子 polo 衫的宅男一个.甚至程序员自己也这样形容自己:钱多话少死的早.程序员总 ...
- 【原创】flash中DataGrid数据列显示顺序的解决办法(非数据排序)
今天在用flash做一个简单的地图展示功能,需要把xml绑定到DataGrid,完成后,又仔细看了几遍,发现列的顺序不对,准确的说是不稳定,不固定,于是在网上查了一下,没有相关的内容.于是自己研究了一 ...
- 团队项目之Scrum4
小组:BLACK PANDA 时间:2019.11.24 每天举行站立式会议 提供当天站立式会议照片一张 2 昨天已完成的工作 2 基本实现web富文本编辑功能 后台的编辑接口已经基本完成,还有一些b ...
- mysql从5.6升级到5.7后出现 Expression #1 of ORDER BY clause is not in SELECT list,this is incompatible with DISTINCT
[问题]mysql从5.6升级到5.7后出现:插入数据和修改数据时出错Caused by: com.ibatis.common.jdbc.exception.NestedSQLException: - ...
- PWA 学习笔记(四)
Service Worker 简介: 1.Service Worker 是 PWA 技术基础之一,脱离浏览器主线程的特性,使得 Web App 离线缓存成为可能, 更为后台同步.通知推送等功能提供了思 ...
- 学习之Redis(二)
Redis的对象和数据结构 一.字符串对象(请参考学习之Redis(一):https://www.cnblogs.com/wbq1994/p/12029516.html) 二.列表对象 列表对象的编码 ...
- git上传本地项目到github或者gitlib(两个是一样的)。
第一步:在github上面创建一个repository 点击create就好了.然后会出现下面的页面. 第三步:打开你所在文件夹,或者是新建的文件夹(用来做仓库的)右键会出现下面 选用git B ...
- 升级python2.7至python3.7
最近在centos7下执行命令时,出现以下提示: DEPRECATION: Python 2.7 will reach the end of its life on January 1st, 2020 ...
- (办公)记事本_Linux目录和文件都能操作的命令
参考谷粒学院Linux:http://www.gulixueyuan.com/course/300/task/7082/show .cp 1.1.作用主要是拷贝,可以拷贝文件或者目录. 1.2.语法: ...
