springboot配置文件(一)
一、YAML语法
1、基本语法
k 空格 v 表示一对键值对(必须有空格),以空格的缩进来控制层级关系,只要是左对齐的一列数据,都表示同一个层级。属性和值大小写敏感
server:
port: 8081
servlet-path: /hello
2、值的规则
① 字面量: 普通值
② 字符串默认不用加上单引号和双引号
③ 双引号不会转义字符串里面的特殊字符,也就是说如果字符串中有一个 \n 那么就会换行
④ 单引号会转义特殊字符,特殊字符最终只是一个普通字符串数据
3、对象的写法
比如有一个对象Person和一个Dog对象,如下:
public class Person {
private String username;
private Integer age;
private Boolean boss;
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
//get set toString 方法
}
public class Dog {
private String name;
private Integer age;
//get set toString 方法
}
application.yml配置文件
person:
username: lwb
age: 18
boss: true
birth: 2019/12/8
maps: {name: wt, age: 16}
lists: [lwb, wt]
dog:
name: 小狗
age: 3
上面的代码就是给对象Person 配置注入值的yaml写法
4、多种写法
yaml中,按照缩进来控制层级,但是对象、map、数组、List、set等也可以有另一种写法。
#对象行内写法
person: {username: zhangsan,age: 20}
#数组(List、Set)
pets:
‐ cat
‐ dog
‐ pig
#或者
pets: [cat,dog,pig]
二、application.properties写法回顾实例
person.age=18 person.birth=2019/12/7 person.boss=true person.maps.k1=wt person.maps.k2=19 person.dog.name=小狗 person.dog.age=3 person.lists=a,b,c
三、配置文件注入
要将配置文件中的值注入到javabean对象在,需要确定导入
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
最终的实验环境为:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
要想将配置文件中的值,自动注入到上面的对象Person中,那么就需要将Person交给Spring来管理。因此需要在Person类上加上两个spring的注解:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
@Component
public class Person {
//如上面的属性
}
@ConfigurationProperties:告诉SpringBoot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定,prefix = “person”:配置文件中哪个下面的所有属性进行一一映射。有了上面的配置,那么就可以在我们想获取Person对象的地方自动注入Person对象,并且初始值和配置文件中的配置一致
@Service
public class PersonService {
@Autowired
private Person person;
public void getPerson() {
System.out.println(person);
}
}
四、application.properties写法出现乱码
如二中,使用application.properties的写法所示,其实获取到的汉字可能是乱码,具体解决配置方式如下:

并且在application.properties文件中加上如下的配置:
spring.http.encoding.charset=utf-8 spring.http.encoding.force=true spring.http.encoding.enabled=true
五、使用@Value来设置值
可以使用spring原生注解@Value来注入值
@Component
public class Person {
@Value("${person.username}")
private String username;
@Value("#{11 * 2}")
private Integer age;
@Value("true")
private Boolean boss;
@Value("${person.birth}")
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
//get set toString
}
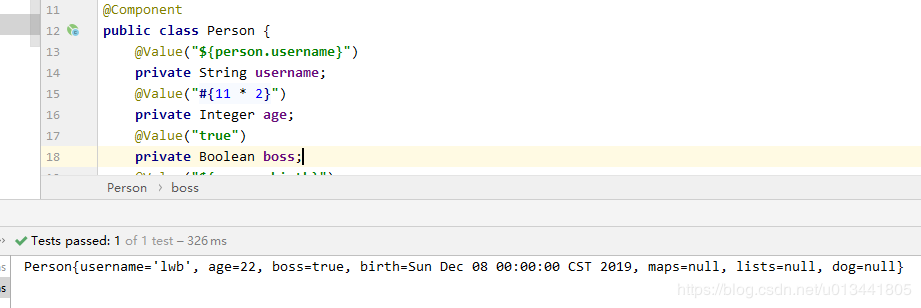
由上例子可以看见,所有的设置值都是简单类型的,如果给maps、lists、dog也加上注入值标签,会出现什么结果呢?
@Component
public class Person {
@Value("${person.username}")
private String username;
@Value("#{11 * 2}")
private Integer age;
@Value("true")
private Boolean boss;
@Value("${person.birth}")
private Date birth;
@Value("${person.maps}")
private Map<String,Object> maps;
@Value("${person.lists}")
private List<Object> lists;
@Value("${person.dog}")
private Dog dog;
// get set toString方法
}
java.lang.IllegalStateException: Failed to load ApplicationContext
at org.springframework.test.context.cache.DefaultCacheAwareContextLoaderDelegate.loadContext(DefaultCacheAwareContextLoaderDelegate.java:132)
at org.springframework.test.context.support.DefaultTestContext.getApplicationContext(DefaultTestContext.java:123)
at org.springframework.test.context.web.ServletTestExecutionListener.setUpRequestContextIfNecessary(ServletTestExecutionListener.java:190)
at org.springframework.test.context.web.ServletTestExecutionListener.prepareTestInstance(ServletTestExecutionListener.java:132)
at org.springframework.test.context.TestContextManager.prepareTestInstance(TestContextManager.java:244)
at org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.createTest(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.java:227)
at org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner$1.runReflectiveCall(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.java:289)
at org.junit.internal.runners.model.ReflectiveCallable.run(ReflectiveCallable.java:12)
at org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.methodBlock(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.java:291)
at org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.java:246)
at org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.java:97)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$3.run(ParentRunner.java:290)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$1.schedule(ParentRunner.java:71)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.runChildren(ParentRunner.java:288)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.access$000(ParentRunner.java:58)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$2.evaluate(ParentRunner.java:268)
at org.springframework.test.context.junit4.statements.RunBeforeTestClassCallbacks.evaluate(RunBeforeTestClassCallbacks.java:61)
at org.springframework.test.context.junit4.statements.RunAfterTestClassCallbacks.evaluate(RunAfterTestClassCallbacks.java:70)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.run(ParentRunner.java:363)
at org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.run(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.java:190)
at org.junit.runner.JUnitCore.run(JUnitCore.java:137)
at com.intellij.junit4.JUnit4IdeaTestRunner.startRunnerWithArgs(JUnit4IdeaTestRunner.java:68)
at com.intellij.rt.execution.junit.IdeaTestRunner$Repeater.startRunnerWithArgs(IdeaTestRunner.java:47)
at com.intellij.rt.execution.junit.JUnitStarter.prepareStreamsAndStart(JUnitStarter.java:242)
at com.intellij.rt.execution.junit.JUnitStarter.main(JUnitStarter.java:70)
Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'person': Injection of autowired dependencies failed; nested exception is java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Could not resolve placeholder 'person.maps' in value "${person.maps}"
可以看见直接报错,其实@ConfigurationProperties和@Value是有区别的,具体如下:
| @ConfigurationProperties | @Value | |
|---|---|---|
| 功能 | 批量注入配置文件中的属性 | 一个个指定 |
| 松散绑定(松散语法)(lastName --> last-name) | 支持 | 不支持 |
| SpEL | 不支持 | 支持 |
| JSR303数据校验 | 支持 | 不支持 |
| 复杂类型封装 | 支持 | 不支持 |
配置文件yml还是properties他们都能获取到值;如果说,我们只是在某个业务逻辑中需要获取一下配置文件中的某项值,使用@Value;如果说,我们专门编写了一个javaBean来和配置文件进行映射,我们就直接使用@ConfigurationProperties;
springboot配置文件(一)的更多相关文章
- 解决spring-boot配置文件使用加密方式保存敏感数据启动报错No decryption for FailsafeTextEncryptor. Did you configure the keystore correctly
spring-boot配置文件使用加密方式保存敏感数据 application.yml spring: datasource: username: dbuser password: '{cipher} ...
- springboot配置文件中使用当前配置的变量
在开发中,有时我们的application.properties某些值需要重复使用,比如配置redis和数据库或者mongodb连接地址,日志,文件上传地址等,且这些地址如果都是相同或者父路径是相同的 ...
- SpringBoot 配置文件存放位置及读取顺序
SpringBoot配置文件可以使用yml格式和properties格式 分别的默认命名为:application.yml.application.properties 存放目录 SpringBoot ...
- [SpringBoot] - 配置文件的多种形式及JSR303数据校验
Springboot配置文件: application.yml application.properties(自带) yml的格式写起来稍微舒服一点 在application.properties ...
- 将springboot配置文件中的值注入到静态变量
SpringBoot配置文件分为.properties和.yml两种格式,根据启动环境的不同获取不同环境的的值. spring中不支持直接注入静态变量值,利用spring的set注入方法注入静态变量 ...
- SpringBoot配置文件 application.properties详解
SpringBoot配置文件 application.properties详解 本文转载:https://www.cnblogs.com/louby/p/8565027.html 阅读过程中若发现 ...
- Spring-Boot配置文件数据源配置项
Spring-Boot配置文件数据源配置项(常用配置项为红色) 参数 介绍 spring.datasource.continue-on-error = false 初始化数据库时发生错误时,请勿停止 ...
- 【日常错误】spring-boot配置文件读取不到
最近在用spring-boot做项目时,遇到自定义的配置文件无法读取到的问题,通过在appcation.java类上定义@PropertySource(value = {"classpath ...
- SpringBoot——配置文件加载位置及外部配置加载顺序
声明 本文部分转自:SpringBoot配置文件加载位置与优先级 正文 1. 项目内部配置文件 spring boot 启动会扫描以下位置的application.properties或者applic ...
- 【SpringBoot】SpringBoot配置文件及YAML简介(三)
SpringBoot配置文件 SpringBoot使用一个全局的配置文件,配置文件名是固定的; application.properties application.yml 配置文件的作用:修改Spr ...
随机推荐
- go proxy athens 部署到k8s
目录 go proxy athens 部署到k8s 一.athens简介 二.部署 1.创建 PersistentVolume 2.创建service 3.创建deployment 4.ci/cd中使 ...
- POJ1743 Musical Theme (后缀数组 & 后缀自动机)最大不重叠相似子串
A musical melody is represented as a sequence of N (1<=N<=20000)notes that are integers in the ...
- tomcat安装与环境变量配置
1.安装tomcat 2.找到tomcat安装路径的bin文件夹 → 打开 startup.bat 3.打开浏览器输入网址 http://localhost:8080 4.配置CATALINA_BAS ...
- ELK-logstash基本用法
一:logstash介绍 Logstash在elk系统中为数据存储,报表查询和日志解析创建了一个功能强大的管道链.Logstash提供了多种多样的 input,filters,codecs和outpu ...
- 【ZooKeeper系列】2.用Java实现ZooKeeper API的调用
温馨提示:在这里我再次提个小要求,希望大家能习惯看官方文档,文档虽然是英文但用词都比较简单,基本都能看懂文档表达的意思.授之以鱼不如授之以渔的道理相信大家都明白,也希望通过猿人谷的这个ZooKeepe ...
- 3年java开发竟然还不知道Lambda的这个坑
背景 有朋友反馈zk连接很慢.整理出zk连接的关键逻辑如下: 上面的代码造成第一次调用ClientZkAgent.getInstance的时候,需耗时10s, 这个时间恰好跟semaphore的超时时 ...
- eclipse设置护眼模式,就是设置为黑色背景,
效果如上图 首先下载jar包,然后放到下面的目录,然后打开eclipse然后选择哪个dark的那个主题就可以了 然而这里只是设置软件部分的, 代码的背景和高亮显示,是在另外一个地方设置, 一般是下载e ...
- Java代码~~汽车租赁系统
租车信息: 输出结果: 代码: 1.先定义抽象类(汽车类:Moto) package cn.aura.demo01; public abstract class Moto { //公共属性 priva ...
- 《MySQL数据库》MySQL数据库安装(linux)
1. 下载安装包: 百度网盘:链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1toGl8O9gMBpDWn0mHWwFyg 提取码: i51g 官网下载:https://dev.mysql ...
- 语句知识总结(js)
函数声明语句和函数定义表达式有什么不同 首先看一下函数声明语句和函数定义表达式的例子,表达式会返回一个值,而语句就是js中的一整句,下面例子中第6行是函数声明语句,第10行是函数定义表达式. f(); ...
