吴裕雄--天生自然Python Matplotlib库学习笔记:matplotlib绘图(2)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt fig = plt.figure()
fig.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.025, left=0.025, top = 0.975, right=0.975) plt.subplot(2,1,1)
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) plt.subplot(2,3,4)
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) plt.subplot(2,3,5)
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) plt.subplot(2,3,6)
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) # plt.savefig('../figures/multiplot_ex.png',dpi=48)
plt.show()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt n = 20
Z = np.ones(n)
Z[-1] *= 2 plt.axes([0.025, 0.025, 0.95, 0.95]) plt.pie(Z, explode=Z*.05, colors=['%f' % (i/float(n)) for i in range(n)],
wedgeprops={"linewidth": 1, "edgecolor": "black"})
plt.gca().set_aspect('equal')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) # savefig('../figures/pie_ex.png',dpi=48)
plt.show()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt n = 256
X = np.linspace(-np.pi,np.pi,n,endpoint=True)
Y = np.sin(2*X) plt.axes([0.025,0.025,0.95,0.95]) plt.plot (X, Y+1, color='blue', alpha=1.00)
plt.fill_between(X, 1, Y+1, color='blue', alpha=.25) plt.plot (X, Y-1, color='blue', alpha=1.00)
plt.fill_between(X, -1, Y-1, (Y-1) > -1, color='blue', alpha=.25)
plt.fill_between(X, -1, Y-1, (Y-1) < -1, color='red', alpha=.25) plt.xlim(-np.pi,np.pi), plt.xticks([])
plt.ylim(-2.5,2.5), plt.yticks([])
# savefig('../figures/plot_ex.png',dpi=48)
plt.show()

import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D fig = plt.figure()
ax = Axes3D(fig)
X = np.arange(-4, 4, 0.25)
Y = np.arange(-4, 4, 0.25)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
R = np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2)
Z = np.sin(R) ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap=plt.cm.hot)
ax.contourf(X, Y, Z, zdir='z', offset=-2, cmap=plt.cm.hot)
ax.set_zlim(-2,2) # savefig('../figures/plot3d_ex.png',dpi=48)
plt.show()

from pylab import *
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d ax = gca(projection='3d')
X, Y, Z = axes3d.get_test_data(0.05)
cset = ax.contourf(X, Y, Z)
ax.clabel(cset, fontsize=9, inline=1) plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]),
ax.set_zticks([]) ax.text2D(-0.05, 1.05, " 3D plots \n\n",
horizontalalignment='left',
verticalalignment='top',
family='Lint McCree Intl BB',
size='x-large',
bbox=dict(facecolor='white', alpha=1.0, width=350,height=60),
transform = gca().transAxes) ax.text2D(-0.05, .975, " Plot 2D or 3D data",
horizontalalignment='left',
verticalalignment='top',
family='Lint McCree Intl BB',
size='medium',
transform = gca().transAxes) plt.show()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt ax = plt.axes([0.025,0.025,0.95,0.95], polar=True) N = 20
theta = np.arange(0.0, 2*np.pi, 2*np.pi/N)
radii = 10*np.random.rand(N)
width = np.pi/4*np.random.rand(N)
bars = plt.bar(theta, radii, width=width, bottom=0.0) for r,bar in zip(radii, bars):
bar.set_facecolor( plt.cm.jet(r/10.))
bar.set_alpha(0.5) ax.set_xticklabels([])
ax.set_yticklabels([])
# savefig('../figures/polar_ex.png',dpi=48)
plt.show()

import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt n = 8
X,Y = np.mgrid[0:n,0:n]
T = np.arctan2(Y-n/2.0, X-n/2.0)
R = 10+np.sqrt((Y-n/2.0)**2+(X-n/2.0)**2)
U,V = R*np.cos(T), R*np.sin(T) plt.axes([0.025,0.025,0.95,0.95])
plt.quiver(X,Y,U,V,R, alpha=.5)
plt.quiver(X,Y,U,V, edgecolor='k', facecolor='None', linewidth=.5) plt.xlim(-1,n), plt.xticks([])
plt.ylim(-1,n), plt.yticks([]) # savefig('../figures/quiver_ex.png',dpi=48)
plt.show()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation # No toolbar
matplotlib.rcParams['toolbar'] = 'None' # New figure with white background
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6,6), facecolor='white') # New axis over the whole figureand a 1:1 aspect ratio
# ax = fig.add_axes([0,0,1,1], frameon=False, aspect=1)
ax = fig.add_axes([0.005,0.005,0.990,0.990], frameon=True, aspect=1) # Number of ring
n = 50
size_min = 50
size_max = 50*50 # Ring position
P = np.random.uniform(0,1,(n,2)) # Ring colors
C = np.ones((n,4)) * (0,0,0,1) # Alpha color channel goes from 0 (transparent) to 1 (opaque)
C[:,3] = np.linspace(0,1,n) # Ring sizes
S = np.linspace(size_min, size_max, n) # Scatter plot
scat = ax.scatter(P[:,0], P[:,1], s=S, lw = 0.5,
edgecolors = C, facecolors='None') # Ensure limits are [0,1] and remove ticks
ax.set_xlim(0,1), ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_ylim(0,1), ax.set_yticks([]) def update(frame):
global P, C, S # Every ring is made more transparent
C[:,3] = np.maximum(0, C[:,3] - 1.0/n) # Each ring is made larger
S += (size_max - size_min) / n # Reset ring specific ring (relative to frame number)
i = frame % 50
P[i] = np.random.uniform(0,1,2)
S[i] = size_min
C[i,3] = 1 # Update scatter object
scat.set_edgecolors(C)
scat.set_sizes(S)
scat.set_offsets(P)
return scat, animation = FuncAnimation(fig, update, interval=10)
# animation.save('../figures/rain.gif', writer='imagemagick', fps=30, dpi=72)
plt.show()

import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # New figure with white background
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6,6), facecolor='white') # New axis over the whole figureand a 1:1 aspect ratio
ax = fig.add_axes([0.005,0.005,.99,.99], frameon=True, aspect=1) # Number of ring
n = 50
size_min = 50
size_max = 50*50 # Ring position
P = np.random.uniform(0,1,(n,2)) # Ring colors
C = np.ones((n,4)) * (0,0,0,1) # Alpha color channel goes from 0 (transparent) to 1 (opaque)
C[:,3] = np.linspace(0,1,n) # Ring sizes
S = np.linspace(size_min, size_max, n) # Scatter plot
scat = ax.scatter(P[:,0], P[:,1], s=S, lw = 0.5,
edgecolors = C, facecolors='None') # Ensure limits are [0,1] and remove ticks
ax.set_xlim(0,1), ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_ylim(0,1), ax.set_yticks([]) # plt.savefig("../figures/rain-static.png",dpi=72)
plt.show()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt n = 1024
X = np.random.normal(0,1,n)
Y = np.random.normal(0,1,n)
T = np.arctan2(Y,X) plt.axes([0.025,0.025,0.95,0.95])
plt.scatter(X,Y, s=75, c=T, alpha=.5) plt.xlim(-1.5,1.5), plt.xticks([])
plt.ylim(-1.5,1.5), plt.yticks([])
# savefig('../figures/scatter_ex.png',dpi=48)
plt.show()

from pylab import * size = 256,16
dpi = 72.0
figsize= size[0]/float(dpi),size[1]/float(dpi)
fig = figure(figsize=figsize, dpi=dpi)
fig.patch.set_alpha(0)
axes([0,0,1,1], frameon=False) plot(np.arange(4), np.ones(4), color="blue", linewidth=8, solid_capstyle = 'butt') plot(5+np.arange(4), np.ones(4), color="blue", linewidth=8, solid_capstyle = 'round') plot(10+np.arange(4), np.ones(4), color="blue", linewidth=8, solid_capstyle = 'projecting') xlim(0,14)
xticks([]),yticks([])
show()

from pylab import * size = 256,16
dpi = 72.0
figsize= size[0]/float(dpi),size[1]/float(dpi)
fig = figure(figsize=figsize, dpi=dpi)
fig.patch.set_alpha(0)
axes([0,0,1,1], frameon=False) plot(np.arange(3), [0,1,0], color="blue", linewidth=8, solid_joinstyle = 'miter')
plot(4+np.arange(3), [0,1,0], color="blue", linewidth=8, solid_joinstyle = 'bevel')
plot(8+np.arange(3), [0,1,0], color="blue", linewidth=8, solid_joinstyle = 'round') xlim(0,12), ylim(-1,2)
xticks([]),yticks([])
show()

from pylab import * subplot(2,2,1)
xticks([]), yticks([])
text(0.5,0.5, 'subplot(2,2,1)',ha='center',va='center',size=20,alpha=.5) subplot(2,2,2)
xticks([]), yticks([])
text(0.5,0.5, 'subplot(2,2,2)',ha='center',va='center',size=20,alpha=.5) subplot(2,2,3)
xticks([]), yticks([])
text(0.5,0.5, 'subplot(2,2,3)',ha='center',va='center',size=20,alpha=.5) subplot(2,2,4)
xticks([]), yticks([])
text(0.5,0.5, 'subplot(2,2,4)',ha='center',va='center',size=20,alpha=.5) # savefig('../figures/subplot-grid.png', dpi=64)
show()
from pylab import * subplot(2,1,1)
xticks([]), yticks([])
text(0.5,0.5, 'subplot(2,1,1)',ha='center',va='center',size=24,alpha=.5) subplot(2,1,2)
xticks([]), yticks([])
text(0.5,0.5, 'subplot(2,1,2)',ha='center',va='center',size=24,alpha=.5) # plt.savefig('../figures/subplot-horizontal.png', dpi=64)
show()
from pylab import * subplot(1,2,1)
xticks([]), yticks([])
text(0.5,0.5, 'subplot(2,2,1)',ha='center',va='center',size=24,alpha=.5) subplot(1,2,2)
xticks([]), yticks([])
text(0.5,0.5, 'subplot(2,2,2)',ha='center',va='center',size=24,alpha=.5) show()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt eqs = []
eqs.append((r"$W^{3\beta}_{\delta_1 \rho_1 \sigma_2} = U^{3\beta}_{\delta_1 \rho_1} + \frac{1}{8 \pi 2} \int^{\alpha_2}_{\alpha_2} d \alpha^\prime_2 \left[\frac{ U^{2\beta}_{\delta_1 \rho_1} - \alpha^\prime_2U^{1\beta}_{\rho_1 \sigma_2} }{U^{0\beta}_{\rho_1 \sigma_2}}\right]$"))
eqs.append((r"$\frac{d\rho}{d t} + \rho \vec{v}\cdot\nabla\vec{v} = -\nabla p + \mu\nabla^2 \vec{v} + \rho \vec{g}$"))
eqs.append((r"$\int_{-\infty}^\infty e^{-x^2}dx=\sqrt{\pi}$"))
eqs.append((r"$E = mc^2 = \sqrt{{m_0}^2c^4 + p^2c^2}$"))
eqs.append((r"$F_G = G\frac{m_1m_2}{r^2}$")) plt.axes([0.025,0.025,0.95,0.95]) for i in range(24):
index = np.random.randint(0,len(eqs))
eq = eqs[index]
size = np.random.uniform(12,32)
x,y = np.random.uniform(0,1,2)
alpha = np.random.uniform(0.25,.75)
plt.text(x, y, eq, ha='center', va='center', color="#11557c", alpha=alpha,
transform=plt.gca().transAxes, fontsize=size, clip_on=True) plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
# savefig('../figures/text_ex.png',dpi=48)
plt.show()
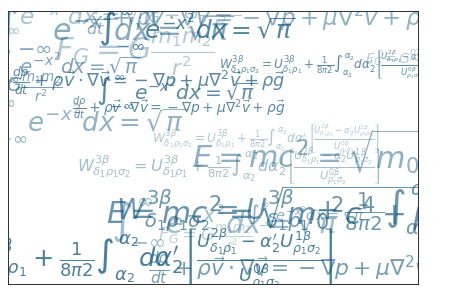
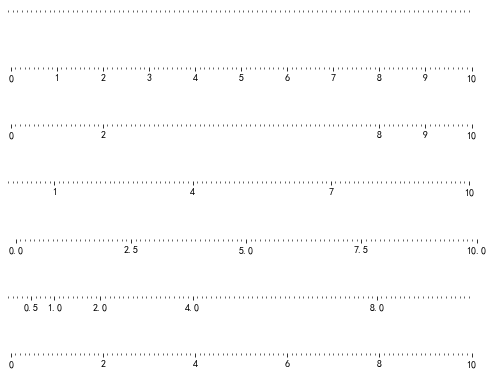
import matplotlib
#matplotlib.use('Agg')
from pylab import * def tickline(): size = 512,32
dpi = 72.0
figsize= size[0]/float(dpi),size[1]/float(dpi)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=figsize, dpi=dpi)
fig.patch.set_alpha(0) ax = axes([0.05, 0, 0.9, 1], frameon=False)
xlim(0,10), ylim(-1,1), yticks([])
ax = gca()
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['left'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data',0))
ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('none')
ax.xaxis.set_minor_locator(MultipleLocator(0.1))
ax.plot(np.arange(11), np.zeros(11), color='none')
return ax ax = tickline()
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(NullLocator()) ax = tickline()
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(MultipleLocator(1.0)) ax = tickline()
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(FixedLocator([0,2,8,9,10])) ax = tickline()
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(IndexLocator(3,1)) ax = tickline()
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(LinearLocator(5)) ax = tickline()
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(LogLocator(2,[1.0])) ax = tickline()
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(AutoLocator())
吴裕雄--天生自然Python Matplotlib库学习笔记:matplotlib绘图(2)的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄--天生自然python Google深度学习框架:Tensorflow实现迁移学习
import glob import os.path import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.python.platfor ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然python Google深度学习框架:经典卷积神经网络模型
import tensorflow as tf INPUT_NODE = 784 OUTPUT_NODE = 10 IMAGE_SIZE = 28 NUM_CHANNELS = 1 NUM_LABEL ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然python Google深度学习框架:图像识别与卷积神经网络
- 吴裕雄--天生自然python Google深度学习框架:MNIST数字识别问题
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data INPUT_NODE = 784 ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然python Google深度学习框架:深度学习与深层神经网络
- 吴裕雄--天生自然python Google深度学习框架:TensorFlow实现神经网络
http://playground.tensorflow.org/
- 吴裕雄--天生自然python Google深度学习框架:Tensorflow基础应用
import tensorflow as tf a = tf.constant([1.0, 2.0], name="a") b = tf.constant([2.0, 3.0], ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然python Google深度学习框架:人工智能、深度学习与机器学习相互关系介绍
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:中级绘图(续二)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------# # R in Action ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:中级绘图(续一)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------# # R in Action ...
随机推荐
- CentOS 7下用firewall-cmd控制端口与端口转发
# 将80端口的流量转发至192.168.0.1的8080端口 1.firewall-cmd --permanent --add-forward-port=port=80:proto=tcp:toad ...
- Zigbee 与 WiFi 的区别
zigbee 在蓝牙技术的使用过程中,人们发现蓝牙技术尽管有许多优点,但仍存在许多缺陷.对工业,家庭自动化控制和遥测遥控领域而言,蓝牙技术显得太复杂,功耗大,距离近,组网规模太小等,……而工业自动化对 ...
- Oracle创表操作记录
Oracle表操作 --主键,复合主键 create table example (id number primary key, name varchar2(20)); create table ex ...
- Java进阶学习(4)之继承与多态(下)
多态变量和向上造型 多态变量 子类和子类型 类定义了类型 子类定义了子类型 子类的对象可以被当作父类的对象来使用 赋值给父类的变量 传递给需要父类对象的函数 放进存放父类对象的容器里 多态变量 Jav ...
- python中给函数传参是传值还是传引用
首先还是应该科普下函数参数传递机制,传值和传引用是什么意思? 函数参数传递机制问题在本质上是调用函数(过程)和被调用函数(过程)在调用发生时进行通信的方法问题.基本的参数传递机制有两种:值传递和引用传 ...
- python中的数学类型及操作
一.概述 整数类型 浮点数类型 复数类型 round()函数 数值运算符 数值运算函数 字符串类型 1.整数类型 整型:用来描述什么:比如身高,体重,年龄等 eg: age=20 height=168 ...
- linux安装nginx以及如何启动,暂停,停止操作
链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/martinl/p/10908607.html 命令kill -9 pid杀死进程,pid是系统的父进程号 Ubuntu下载nginx:https ...
- float和position:absolute脱离文本流的区别
float和position:absolute脱离文本流的区别原创 paediatrician 最后发布于2016-09-19 10:43:05 阅读数 5375 收藏展开 文档流:将窗体自上而下分成 ...
- python+pygame的导弹追踪鼠标游戏设置和说明
1.效果图 2.注意事项,代码里有说明 3.完整的代码 #导出模块 import pygame,sys from math import * #设置RESIZABLE前,必须导出下面的模块,否则报错 ...
- Flutter 中的常见的按钮组件 以及自 定义按钮组件
一.Flutter 中的按钮组件介绍 Flutter 里有很多的 Button 组件很多,常见的按钮组件有:RaisedButton.FlatButton. IconButton.Outlin ...
