[swarthmore cs75] Compiler 4 – Diamondback
课程回顾
Swarthmore学院16年开的编译系统课,总共10次大作业。本随笔记录了相关的课堂笔记以及第6次大作业。
函数声明
增加函数声明、函数调用的抽象语法;在转换成anf之前还要检查函数声明和调用是否正确。
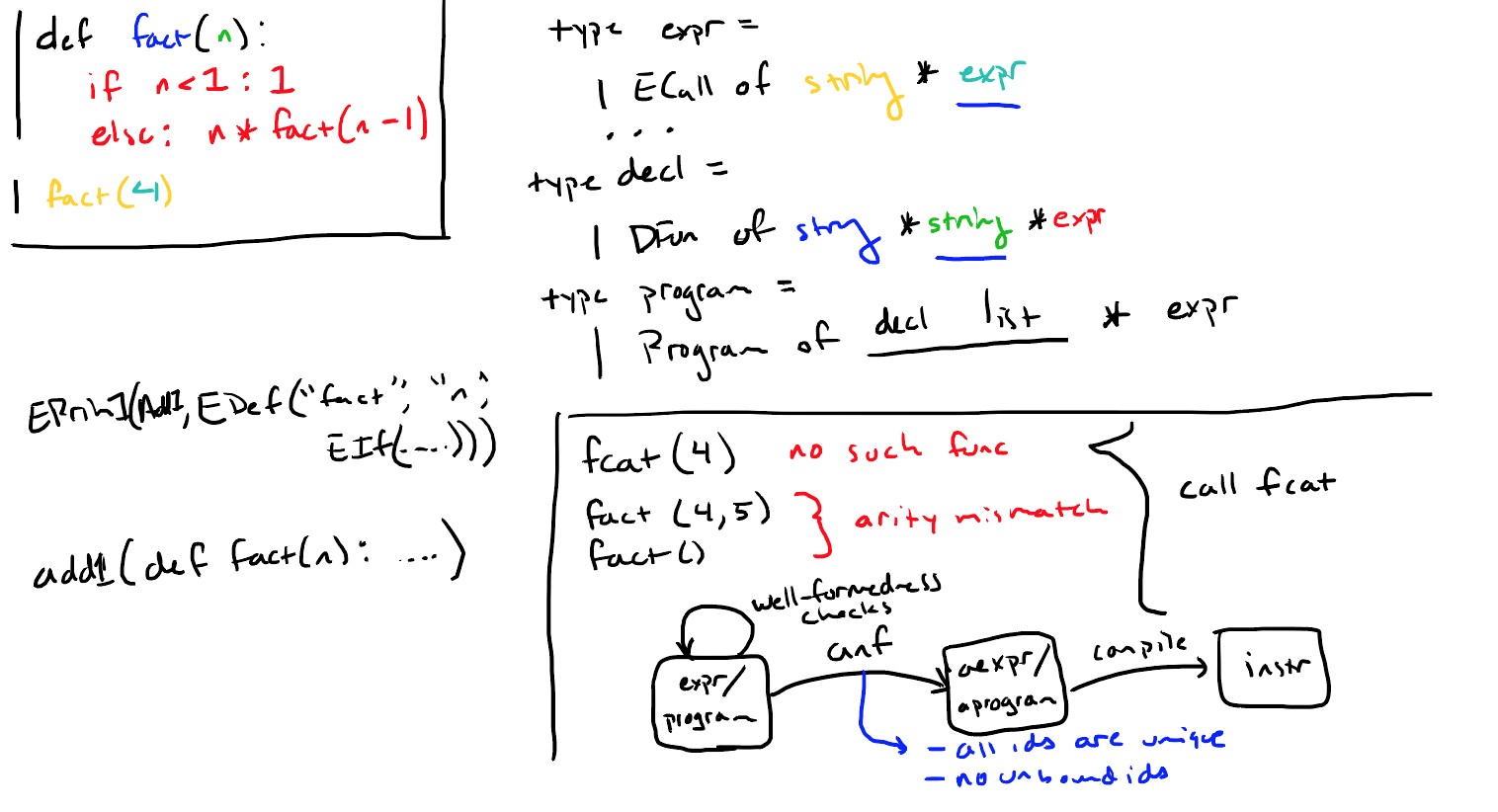
well_formed函数分别检查Program中的的函数声明列表ds和main是否有错误。
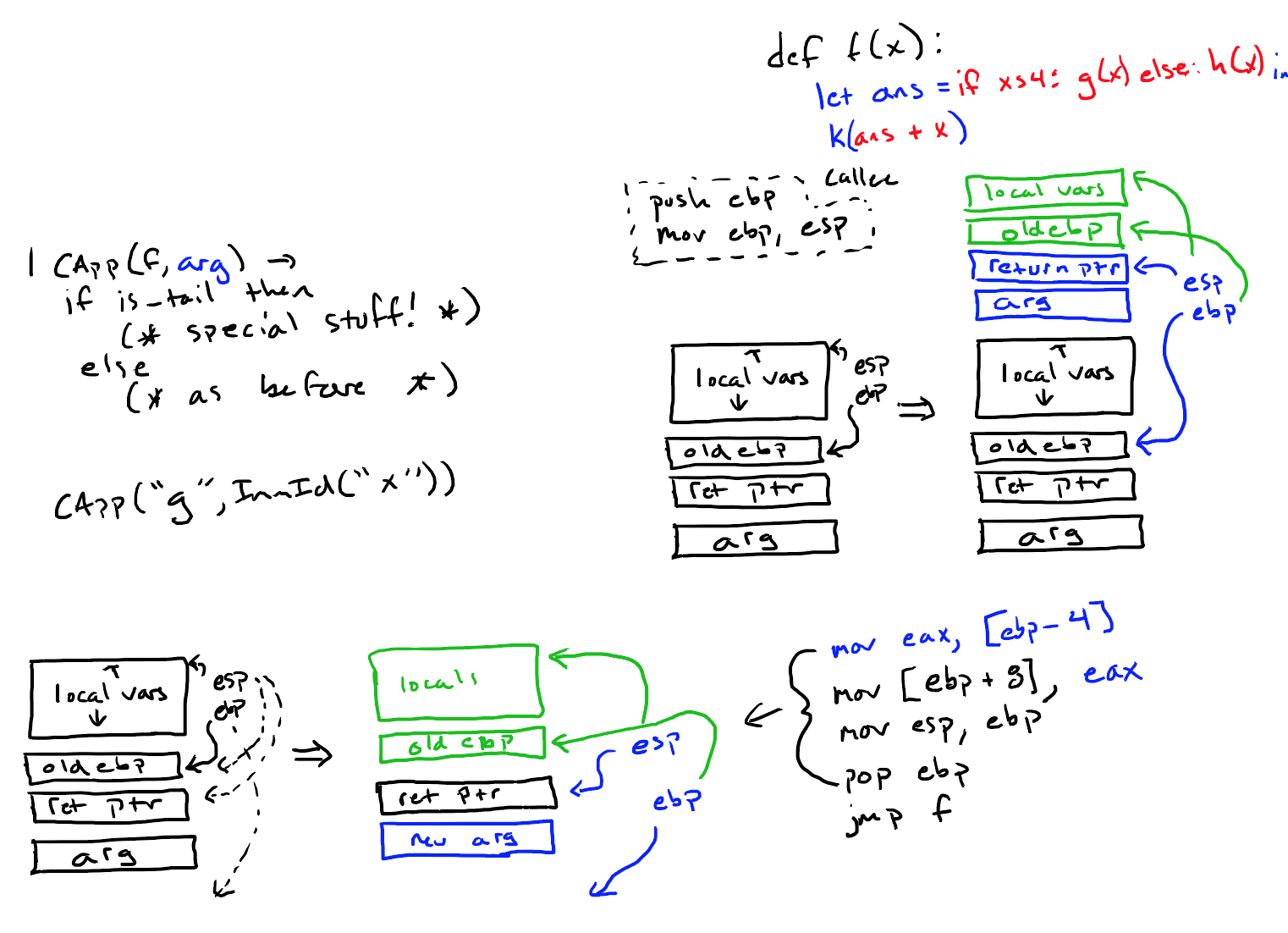
well_formed_decl函数还需要检查函数体是否正确(参考下图右边第一个递归的例子)。
well_formed_expr函数,检查expr中调用的函数是否已经定义,接着递归调用well_formed_expr检查参数(参考下图右边第二例子)。

anf_p将Program转换为anf文法(参考下图fact函数):首先使用anf处理main,接下来用anf_d处理函数声明,anf_d中函数体需要递归处理。

acompile_p为Program生成汇编代码:acompile_decl为函数声明生成汇编代码,acompile_aexpr为main生成汇编代码。
acompile_cexpr为函数调用生成汇编代码。
acompile_decl为函数体生成汇编代码(目前只支持一个参数),包括初始化(如提前分配空间)、递归处理函数体等。

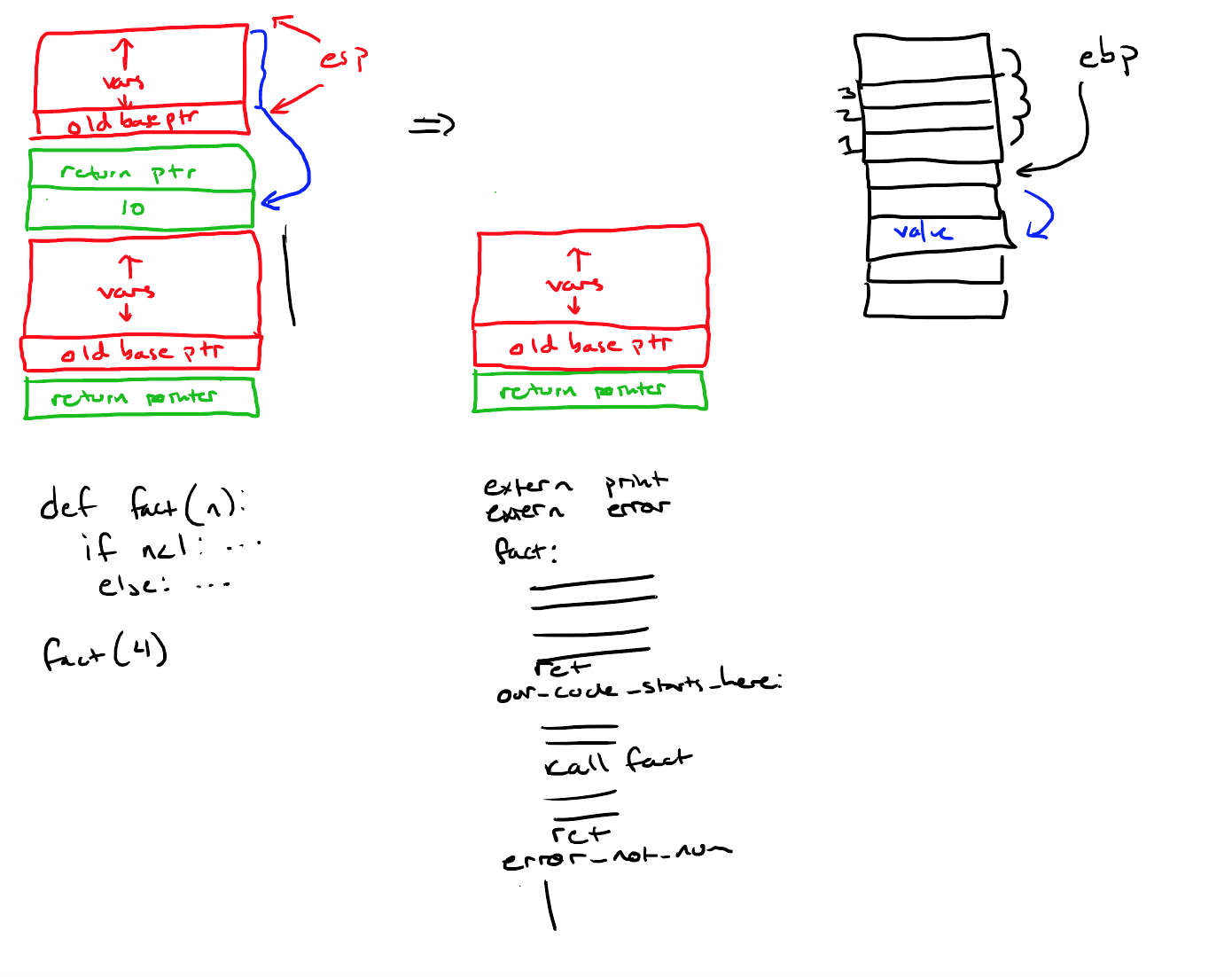
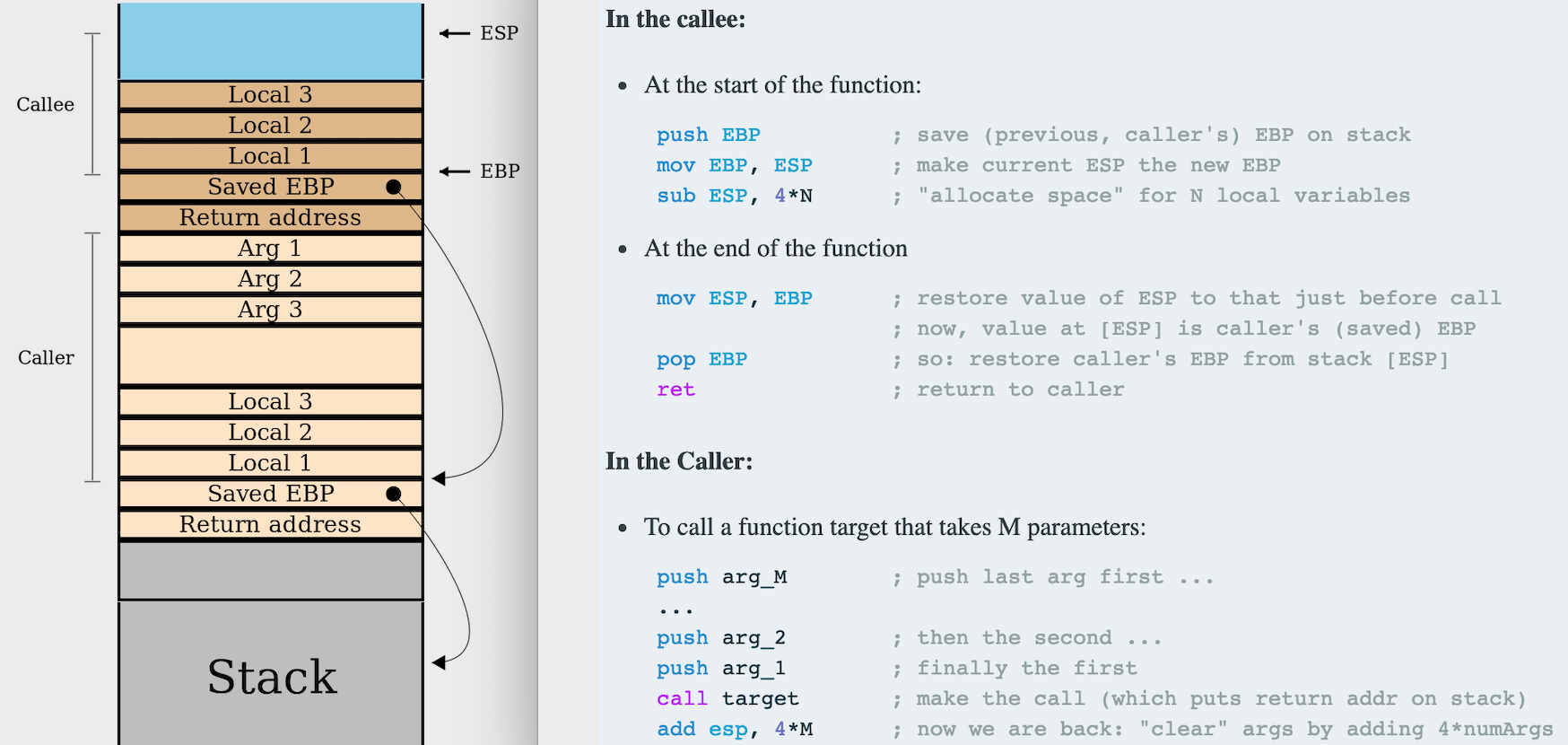
下图为函数调用时栈帧的情况,绿色是Caller的职责,红色是Callee的职责(保存old ebp,申请空间,恢复esp/ebp等)。
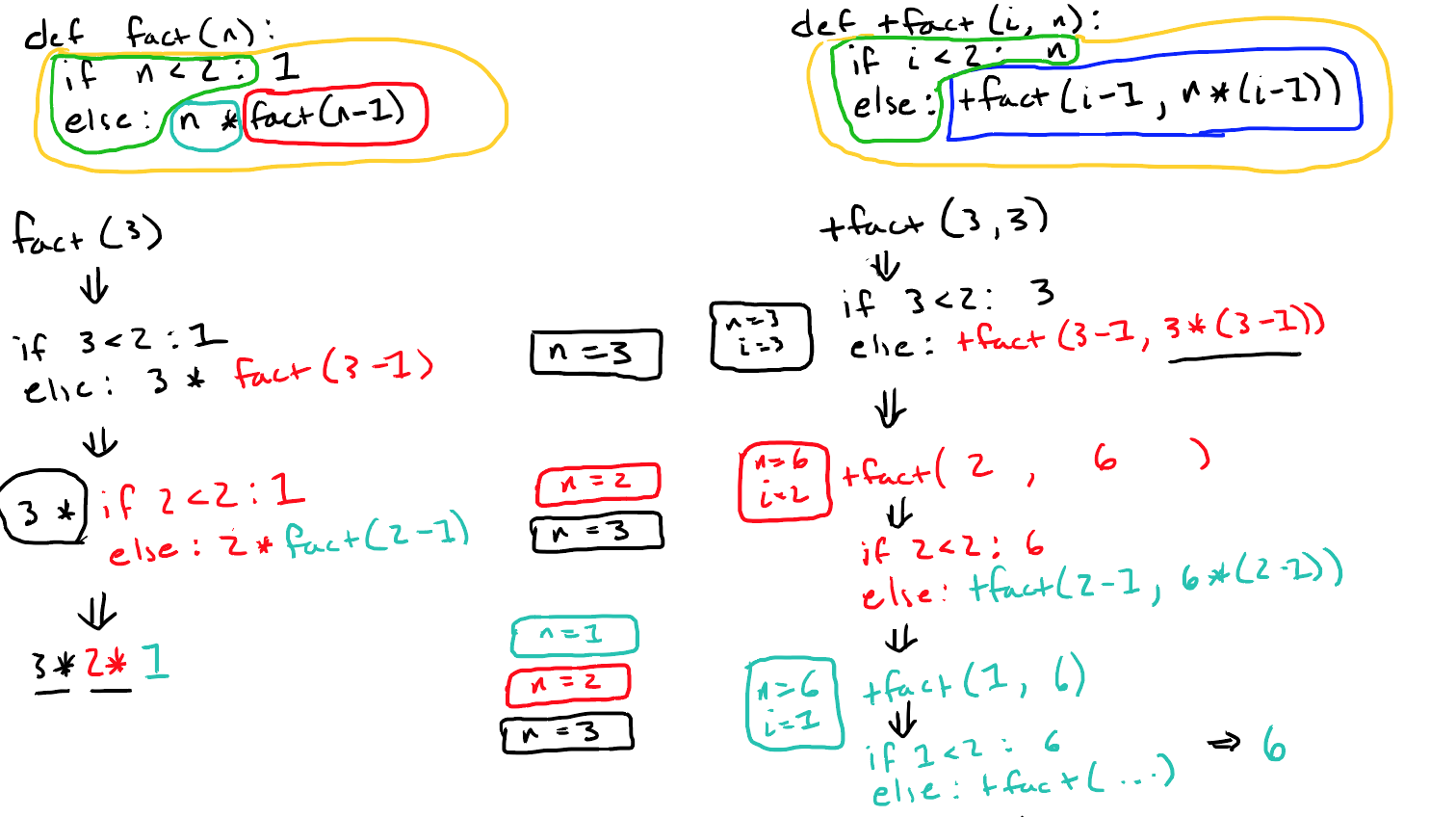
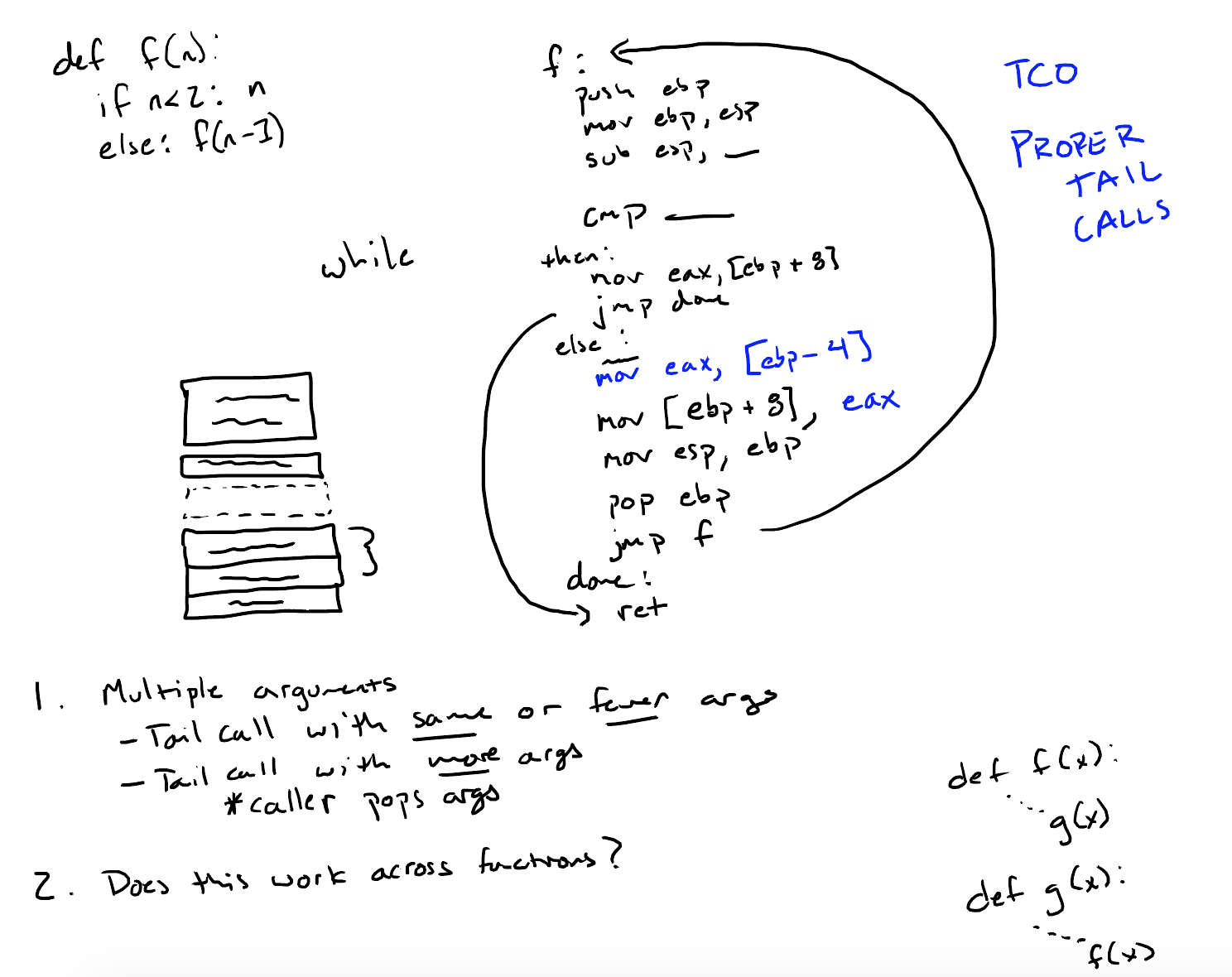
尾递归
普通递归vs.尾递归:普通递归的栈空间使用情况先是达到一个峰值,然后逐渐减小;而尾递归的空间复杂度始终为O(1)。
tail position vs. non tail position:为了能够使用尾递归优化汇编代码,需要确定哪些位置是tail position(一旦该位置表达式求值完成,整个表达式就完成了求值)。
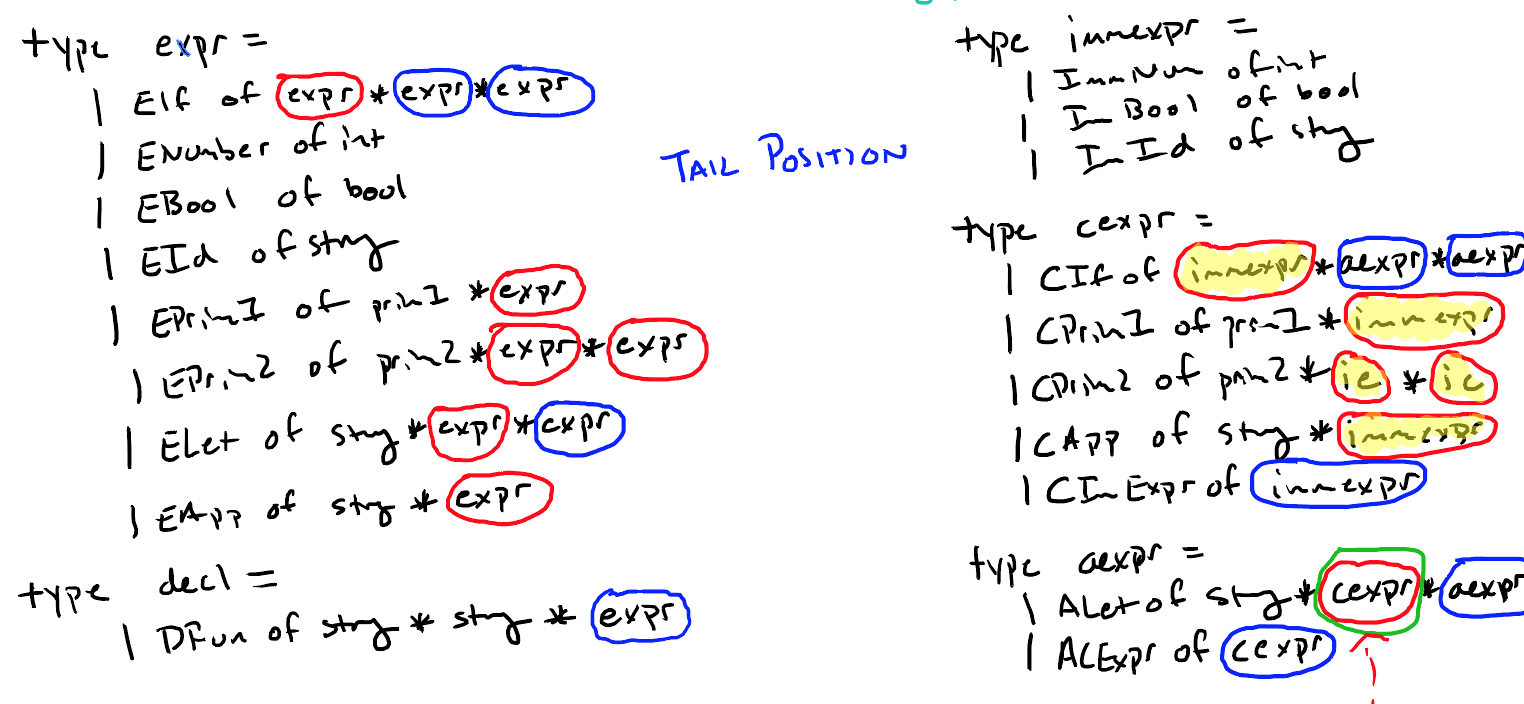
在递归判断tail position的时候,需要注意如果整个表达式是另一个表达式的子表达式,而且这个子表达式的位置不是tail position的时候,这个子表达式的位置则不是tail position。
如:let ans = if ... else ... in k(ans + x),这个整个if表达式的位置就不能算是tail position。
如:let ans = (let x = 10 in x) in ans

Callee的职责:
1. 使用push ebp存储old ebp。
2. 使用mov ebp, esp更新ebp。
3. 为local vars提前分配存储空间。
Caller的职责:
1. 将参数的值[esp-4]移动到eax中。
2. 使用eax覆盖原来的参数[ebp+8]。
3. 将esp指向old ebp。
4. pop ebp,恢复ebp并将esp+4(指向返回地址)。
5. 使用jmp跳转到f函数体(使用call会将返回地址再次压栈)。
tail call optimization & proper tail calls
两个参数的情况:如下图,z存储在[ebp+12],w存储在[ebp+8],如果尾递归调用f(z, y),需要将这两个位置的值进行更新。
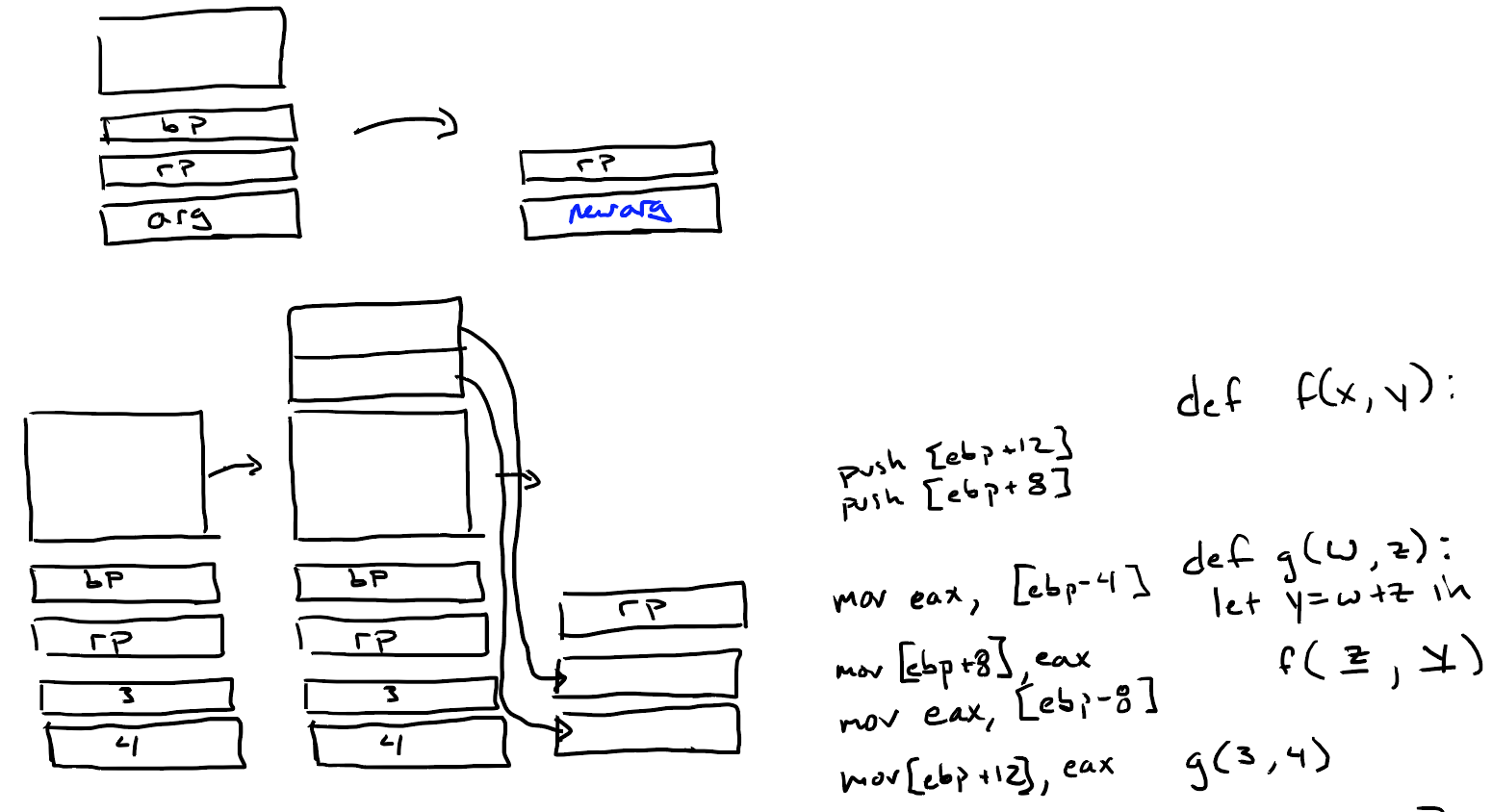
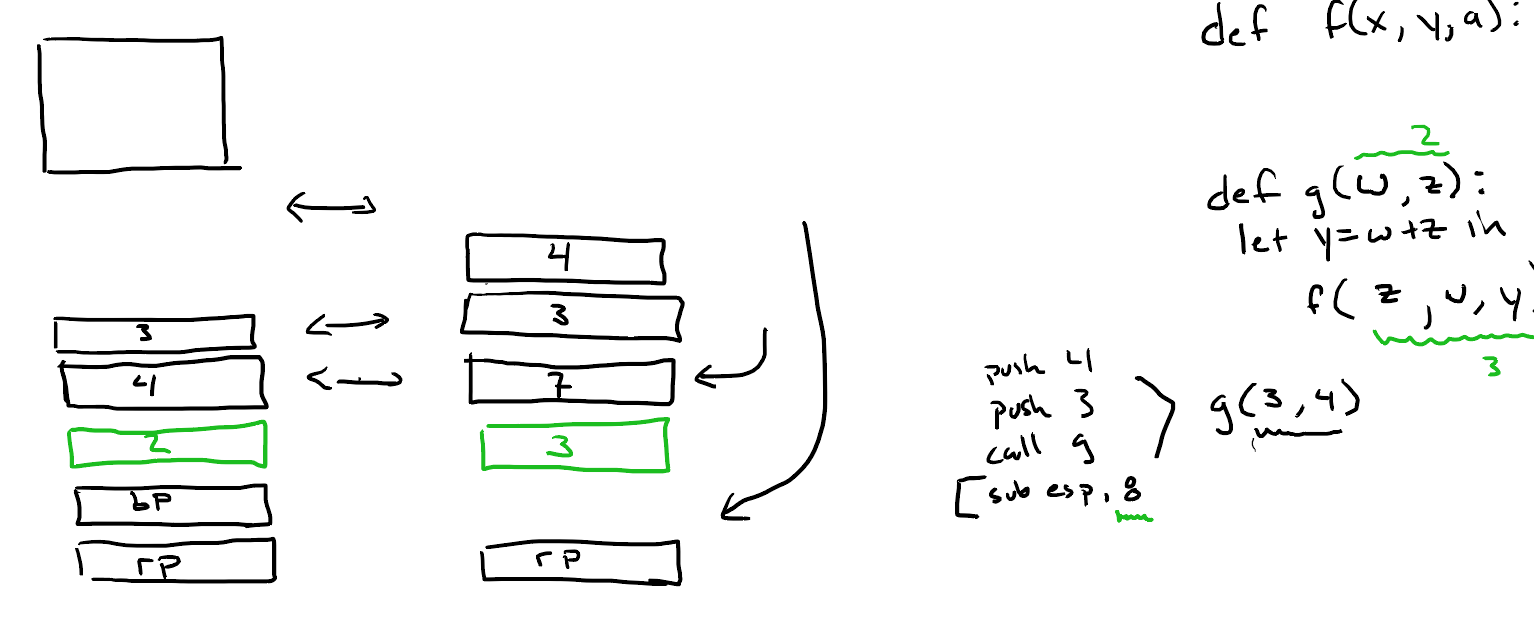
多个参数的情况:
使用c-stack convention:调用者负责将参数格式,参数,返回指针压入栈中。
使用functional language convention:调用者压入返回指针;被调用者负责管理参数。
α-renaming
为了能够使转换成anf的变量名不产生混淆,需要对变量进行重命名。
源代码:let x = 10, y = (let x = 5 in x) + x in y
ANF:
let x = 10 in let x = 5 in y = x + x in y
实现α-renaming:

编程作业
具体语法
<program> :=
| <decls> <expr>
| <expr> <decls> :=
| <decl>
| <decl> <decls> <decl> :=
| def <identifier>(<ids>): <expr>
| def <identifier>(): <expr> <ids> :=
| <identifier>
| <identifier> , <ids> <expr> :=
| let <bindings> in <expr>
| if <expr>: <expr> else: <expr>
| <binop-expr> <binop-expr> :=
| <identifier>
| <number>
| true
| false
| add1(<expr>)
| sub1(<expr>)
| isnum(<expr>)
| isbool(<expr>)
| print(<expr>)
| <identifier>(<exprs>)
| <identifier>()
| <expr> + <expr>
| <expr> - <expr>
| <expr> * <expr>
| <expr> < <expr>
| <expr> > <expr>
| <expr> == <expr>
| ( <expr> ) <exprs> :=
| <expr>
| <expr> , <exprs> <bindings> :=
| <identifier> = <expr>
| <identifier> = <expr>, <bindings>
抽象语法
type prim1 =
| Add1
| Sub1
| Print
| IsNum
| IsBool type prim2 =
| Plus
| Minus
| Times
| Less
| Greater
| Equal type expr =
| ELet of (string * expr) list * expr
| EPrim1 of prim1 * expr
| EPrim2 of prim2 * expr * expr
| EApp of string * expr list
| EIf of expr * expr * expr
| ENumber of int
| EBool of bool
| EId of string type decl =
| DFun of string * string list * expr type program =
| Program of decl list * expr type immexpr =
| ImmNumber of int
| ImmBool of bool
| ImmId of string and cexpr =
| CPrim1 of prim1 * immexpr
| CPrim2 of prim2 * immexpr * immexpr
| CApp of string * immexpr list
| CIf of immexpr * aexpr * aexpr
| CImmExpr of immexpr and aexpr =
| ALet of string * cexpr * aexpr
| ACExpr of cexpr and adecl =
| ADFun of string * string list * aexpr and aprogram =
| AProgram of adecl list * aexpr
代码例子
程序 输出 def sum(n):
if n < 1: 0
else: n + sum(n - 1)
sum(3)6 def min(x, y):
if x < y: x
else: min(y, x)
min(3, 1)1 def f(x, x):
y
f(1)Compile error:
Arity mismatch on call to f (expected 2 arguments, got 1)
Function f has duplicate parameter x
Unbound identifier ydef f(x): x
def f(y): y
f(3)Compile error:
Duplicate function flet x=1, y=2, x=a in x Compile error:
Duplicate binding x
Unbound identifier a
main.c
错误处理:在生成的汇编代码末尾添加了错误类型的label,并将相应的参数压入栈中,main函数中的error函数会接受这些参数。
error_non_number:
push EAX ;; Arg 2: push the badly behaved value
push 1 ;; Arg 1: a constant describing which error-code occurred
call error ;; our error handler
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h> const int ERR_NOT_NUMBER = 1;
const int ERR_NOT_BOOLEAN = 2;
const int ERR_OVERFLOW = 3; extern int our_code_starts_here() asm("our_code_starts_here");
extern int print(int val) asm("print");
extern void error(int errCode, int val) asm("error"); int print(int val) {
if(val & 0x00000001 ^ 0x00000001) {
printf("%d\n", val >> 1);
} else if(val == 0xFFFFFFFF) {
printf("true\n");
} else if(val == 0x7FFFFFFF) {
printf("false\n");
} else {
printf("Unknown value: %#010x\n", val);
}
return val;
} void error(int errCode, int val) {
if (errCode == ERR_NOT_NUMBER) {
fprintf(stderr, "Expected number, but got %010x\n", val);
} else if (errCode == ERR_NOT_BOOLEAN) {
fprintf(stderr, "Expected boolean, but got %010x\n", val);
} else if (errCode == ERR_OVERFLOW) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: arithemetic overflow");
}
exit(errCode);
} int main(int argc, char** argv) {
int result = our_code_starts_here();
print(result);
return 0;
}
compile.ml
静态错误检查:well_formed函数在编译时捕捉了下面的所有错误。
- A function application with the wrong number of arguments should signal an error containing the string "arity"
- A function application of a non-existent function should signal an error containing the string "not defined"
- An identifier without a corresponding binding location should report an error containing the string "unbound"
- A let binding with duplicate names should report an error containg the string "duplicate binding"
- A function declaration with duplicate names in the argument list should report an error containg the string "duplicate parameter"
- If there are multiple function definitions with the same name, report an error containing the string "duplicate function"
- If a numeric constant is too large (as discussed in class), report an error containing the string "too large
let rec well_formed_e (e : expr) (ds : decl list) (env : bool envt) : string list =
(* FILL: you need to implement this *)
match e with
| EApp(fname, args) ->
let found = find_decl ds fname in
let error = match found with
| None -> [sprintf "Function %s is not defined" fname]
| Some(DFun(_, params, _)) ->
let expected = List.length params in
let actual = List.length args in
if expected = actual then []
else [sprintf "Arity mismatch on call to %s (expected %d arguments, got %d)" fname expected actual] in
error @ (List.flatten (List.map (fun arg -> well_formed_e arg ds env) args))
| EPrim2(_, left, right) -> (well_formed_e left ds env) @ (well_formed_e right ds env)
| EPrim1(_, e) -> well_formed_e e ds env
| EIf(cond, thn, els) -> (well_formed_e cond ds env) @ (well_formed_e thn ds env) @ (well_formed_e els ds env)
| ELet([], body) -> well_formed_e body ds env
| ELet((name, value)::rest, body) ->
let found = find rest name in
let error = match found with
| None -> []
| Some(_) -> [sprintf "Duplicate binding %s" name] in
error @ (well_formed_e value ds env) @ (well_formed_e (ELet(rest, body)) ds ((name, true)::env))
| ENumber(n) ->
if n >= -1073741824 && n <= 1073741823 then []
else [sprintf "Number precision too large %d" n]
| EBool(b) -> []
| EId(x) ->
let found = find env x in
let error = match found with
| None -> [sprintf "Unbound identifier %s" x]
| Some(_) -> [] in
error let well_formed_d (d : decl) (ds : decl list) : string list =
(* FILL: you need to implement this *)
match d with
| DFun(fname, args, body) ->
let env = List.map (fun arg -> (arg, true)) args in
let found = find_dup args in
let error = match found with
| None -> []
| Some(x) -> [sprintf "Function %s has duplicate parameter %s" fname x] in
error @ (well_formed_e body ds env) let well_formed_p (p : program) : string list =
match p with
| Program(ds, maine) ->
(* FILL: you may need to add more errors beyond those found from
the declarations and the main expression *)
let found = find_dup (List.map (fun (DFun(fname, _, _)) -> fname) ds) in
let error = match found with
| None -> []
| Some(fname) -> [sprintf "Duplicate function %s" fname] in
(well_formed_e maine ds []) @
(List.flatten (List.map (fun d -> well_formed_d d ds) ds)) @ error
转化为anf语法:
- CApp:一个思路是将函数调用时的参数依次和一个ImmExpr绑定,并保存到一个列表中(可以保持逆序),然后再存入CApp中(具体参考anf_list的实现)
anf e1 (ImmHole(fun imm1 -> anf e2 (ImmHole(fun imm2 -> k [imm1; imm2]))))
(*
This is a slightly modified implementation of ANF. You should read and
understand it (because it's good for you, and because there may be written
questions that reference it). Your interaction with it in this assignment
will be limited, though. The key idea is that there are two kinds of holes in expressions:
immexpr-shaped and cexpr-shaped. For example, a let statement has a
cexpr-shaped hole in the second position, while a prim1 has an immexpr-shaped
hole for its argument. We can fill an immexpr-shaped hole with a cexpr-shaped expression by
introducing a new let binding, and using the temporary id as the immexpr. And
we can fill a cexpr-shaped hole with an immexpr by using CImmExpr. By using the right-shaped holes in the right places, we can avoid creating
intermediate let-bindings except where it's actually necessary. For this assignment, you need to fill in the EApp case.
*)
type hole =
| CHole of (cexpr -> aexpr)
| ImmHole of (immexpr -> aexpr) let fill_imm (h : hole) (v : immexpr) : aexpr =
match h with
| CHole(k) -> (k (CImmExpr(v)))
| ImmHole(k) -> (k v) let fill_c (h : hole) (c : cexpr) : aexpr =
match h with
| CHole(k) -> (k c)
| ImmHole(k) ->
let tmp = gen_temp "" in
ALet(tmp, c, k (ImmId(tmp))) let return_hole = CHole(fun ce -> ACExpr(ce)) let rec anf_list (es : expr list) (k : immexpr list -> aexpr) : aexpr =
(* FILL: you probably want to implement this as a helper for the ECall case *)
let rec helper es immlist =
match es with
| [] -> k immlist
| (e::rest) -> anf e (ImmHole(fun imm -> helper rest (imm::immlist))) in
helper es [] and anf (e : expr) (h : hole) : aexpr =
match e with
| ENumber(n) -> fill_imm h (ImmNumber(n))
| EBool(b) -> fill_imm h (ImmBool(b))
| EId(x) -> fill_imm h (ImmId(x))
| EPrim1(op, e) ->
anf e (ImmHole(fun imm -> (fill_c h (CPrim1(op, imm)))))
| EPrim2(op, left, right) ->
anf left (ImmHole(fun limm ->
anf right (ImmHole(fun rimm ->
(fill_c h (CPrim2(op, limm, rimm)))))))
| EApp(f, args) ->
(* FILL: you need to implement this *)
anf_list args (fun immlist -> fill_c h (CApp(f, immlist)))
| EIf(cond, thn, els) ->
anf cond (ImmHole(fun cimm ->
(fill_c h (CIf(cimm, (anf thn return_hole), (anf els return_hole))))))
| ELet([], body) -> anf body h
| ELet((name, value)::rest, body) ->
anf value (CHole(fun ce ->
ALet(name, ce, anf (ELet(rest, body)) h))) let anf_decl (d : decl) : adecl =
match d with
| DFun(name, args, body) ->
ADFun(name, args, anf body return_hole) let anf_program (p : program) : aprogram =
match p with
| Program(decls, main) ->
AProgram(List.map anf_decl decls, anf main return_hole)
生成汇编代码(格式如下)
;; extern and global stuff
section .text
...
fun_decl1:
;; code for fun_decl1, including stack management
fun_decl2:
;; code for fun_decl2, including stack management
...
our_code_starts_here:
;; main entrypoint, as before, with stack management ;; errors, as before
internal_error_non_number:
...
let compile_to_string prog =
match well_formed_p prog with
| x::rest ->
(* NOTE: This is where errors are reported, by concatenating them all together *)
let errstr = (List.fold_left (fun x y -> x ^ "\n" ^ y) "" (x::rest)) in
failwith errstr
| [] ->
let anfed = (anf_program prog) in
(* FILL: You need to get from ANFed program to full assembly structure
this time, possibly by starting from a previous lab's code *)
let preclude = sprintf "section .text
extern print
extern error
global our_code_starts_here" in
let decls = match anfed with
| AProgram(decls, _) -> decls in
let main = match anfed with
| AProgram(_, main) -> main in
let stack_setup = [
ILabel("our_code_starts_here");
IPush(Reg(EBP));
IMov(Reg(EBP), Reg(ESP));
ISub(Reg(ESP), Const(4 * count_vars main));
] in
let postlude = [
IMov(Reg(ESP), Reg(EBP));
IPop(Reg(EBP));
IRet;
ILabel("error_not_number");
IPush(Reg(EAX));
IPush(Const(1));
ICall("error");
ILabel("error_not_boolean");
IPush(Reg(EAX));
IPush(Const(2));
ICall("error");
ILabel("error_overflow");
IPush(Reg(EAX));
IPush(Const(3));
ICall("error");
] in
let compiled_decls = List.flatten (List.map (fun decl -> acompile_decl decl) decls) in
let compiled_main = acompile_expr main 1 [] in
let as_assembly_string = (to_asm (stack_setup @ compiled_main @ postlude)) in
sprintf "%s%s%s\n" preclude (to_asm compiled_decls) as_assembly_string
下面的代码和之前类似,增加了函数调用的这部分(需遵循C-Stack Convention)
let rec acompile_step (s : cexpr) (si : int) (env : int envt) : instruction list =
let postlude =
[
ITest(Reg(EAX), Const(1));
IJnz("error_not_number")
] in
match s with
| CPrim1(op, e) ->
let eGen = acompile_imm e si env in
let prelude = eGen @ postlude in
begin match op with
| Add1 -> prelude @ [IAdd(Reg(EAX), Const(2));]
| Sub1 -> prelude @ [ISub(Reg(EAX), Const(2));]
| Print -> eGen @ [IPush(Reg(EAX)); ICall("print");]
| IsNum -> eGen @ [IAnd(Reg(EAX), Const(1)); IShl(Reg(EAX), Const(31)); IXor(Reg(EAX), const_true);]
| IsBool -> eGen @ [IAnd(Reg(EAX), Const(1)); IShl(Reg(EAX), Const(31)); IOr(Reg(EAX), const_false);]
end
| CPrim2(op, left, right) ->
let lGen = acompile_imm left si env in
let rGen = acompile_imm right si env in
let imma = acompile_imm_arg right si env in
let preclude = lGen @ postlude @ rGen @ postlude in
begin match op with
| Plus -> preclude @ lGen @ [IAdd(Reg(EAX), imma);] @ [IJo("error_overflow");]
| Minus -> preclude @ lGen @ [ISub(Reg(EAX), imma);] @ [IJo("error_overflow");]
| Times -> preclude @ lGen @ [ISar(Reg(EAX), Const(1)); IMul(Reg(EAX), imma);] @ [IJo("error_overflow");]
| Less -> preclude @ lGen @ [ISub(Reg(EAX), imma); IAnd(Reg(EAX), HexConst(0x80000000)); IOr(Reg(EAX), const_false);]
| Greater -> preclude @ lGen @ [ISub(Reg(EAX), imma); IAnd(Reg(EAX), HexConst(0x80000000)); IAdd(Reg(EAX), const_true);]
| Equal ->
let end_label = gen_temp "end" in
lGen @
[
ICmp(Reg(EAX), imma);
IMov(Reg(EAX), const_false);
IJne(end_label);
IMov(Reg(EAX), const_true);
ILabel(end_label);
]
end
| CIf(cond, thn, els) ->
let else_label = gen_temp "else" in
let endif_label = gen_temp "endif" in
acompile_imm cond si env @
[
ITest(Reg(EAX), Const(1));
IJz("error_not_boolean");
ICmp(Reg(EAX), const_false);
IJe(else_label)
] @
acompile_expr thn si env @
[
IJmp(endif_label);
ILabel(else_label);
] @
acompile_expr els si env @
[
ILabel(endif_label);
]
| CImmExpr(i) -> acompile_imm i si env
| CApp(fname, args) -> (* Caller *)
List.map (fun arg -> IPush(Sized(DWORD_PTR, acompile_imm_arg arg si env))) args @ (* 这里把参数逆序压入栈中 *)
[
ICall(fname);
IAdd(Reg(ESP), Const(4 * List.length args));
] and acompile_expr (e : aexpr) (si : int) (env : int envt) : instruction list =
match e with
| ALet(id, e, body) ->
let preclude = acompile_step e (si + 1) env in
let postlude = acompile_expr body (si + 1) ((id, si)::env) in
preclude @
[
IMov(RegOffset(-4 * si, EBP), Reg(EAX))
] @ postlude
| ACExpr(s) -> acompile_step s si env let acompile_decl (ad : adecl) : instruction list = (* Callee *)
match ad with
| ADFun(fname, args, body) ->
let env = List.mapi (fun i arg -> (arg, -i-2)) args in (* [ebp+8]、[ebp+12]、.... 是压入的参数 *)
[
ILabel(fname);
IPush(Reg(EBP));
IMov(Reg(EBP), Reg(ESP));
ISub(Reg(ESP), Const(4 * count_vars body));
] @
acompile_expr body 1 env @
[
IMov(Reg(ESP), Reg(EBP));
IPop(Reg(EBP));
IRet;
]
遗留问题
- Valgrind不支持最新的osx。
- 未实现Tail Call Optimizaion。
参考资料
[swarthmore cs75] Compiler 4 – Diamondback的更多相关文章
- [swarthmore cs75] Compiler 6 – Garbage Snake
课程回顾 Swarthmore学院16年开的编译系统课,总共10次大作业.本随笔记录了相关的课堂笔记以及第9次大作业. 赋值的副作用:循环元组 下面的代码展示了Python3是如何处理循环列表(pri ...
- [swarthmore cs75] Compiler 6 – Fer-de-lance
课程回顾 Swarthmore学院16年开的编译系统课,总共10次大作业.本随笔记录了相关的课堂笔记以及第8次大作业. First-class function: It treats function ...
- [swarthmore cs75] Compiler 5 – Egg-eater
课程回顾 Swarthmore学院16年开的编译系统课,总共10次大作业.本随笔记录了相关的课堂笔记以及第7次大作业. 抽象语法: 存储方式: 栈中的数据如果最后三位(tag bits)是001表示元 ...
- [swarthmore cs75] Compiler 3 – Cobra
课程回顾 Swarthmore学院16年开的编译系统课,总共10次大作业.本随笔记录了相关的课堂笔记以及第5次大作业. 增加了bool数据表示和比较运算符的支持,具体语法参考下图: 第一种int和bo ...
- [swarthmore cs75] Compiler 2 – Boa
课程回顾 Swarthmore学院16年开的编译系统课,总共10次大作业.本随笔记录了相关的课堂笔记以及第4次大作业. A-Normal Form 在80年代,函数式语言编译器主要使用Continua ...
- [swarthmore cs75] Compiler 1 – Adder
课程回顾 Swarthmore学院16年开的编译系统课,总共10次大作业.本随笔记录了相关的课堂笔记以及第3次大作业. 编译的过程:首先解析(parse)源代码,然后成抽象语法树(AST),再生成汇编 ...
- [swarthmore cs75] inlab1 — Tiny Compiler
课程回顾 Swarthmore学院16年开的编译系统课,总共10次大作业.本随笔记录了inlab1的实践过程. tiny compiler 这个迷你的编译器可以将一个源文件,编译成可执行的二进制代码. ...
- [swarthmore cs75] Lab 1 — OCaml Tree Programming
课程回顾 Swarthmore学院16年开的编译系统课,总共10次大作业.本随笔记录了相关的课堂笔记以及第2大次作业. 比较两个lists的逻辑: let rec cmp l ll = match ( ...
- [swarthmore cs75] Lab 0 Warmup & Basic OCaml
课程回顾 Swarthmore学院16年开的编译系统课,总共10次大作业.本随笔记录了相关的课堂笔记以及第1次大作业. 什么是编译 编译就是执行Program->Program'转换的过程,如下 ...
随机推荐
- ansible批量自动安装LNMP
- Mutex对象
案例一 举一个例子,设计模式中的单例模式,记得当时做机房收费系统的时候就用的单例模式防止一个界面被实例多次,而Mutex对象能达到同样的效果,防止界面被实例化多次,起到控制线程的作用. 案例二 如果大 ...
- css: box-sizing
border-box 宽度包含了边框 content-box 边框不包含在内容区中,会增加到实际的宽度中
- Python设计模式 - UML - 活动图(Activity Diagram)
简介 活动图描述从一个活动到另一个活动的执行顺序.约束条件.引用对象及状态结果等方面的控制流,适用于对业务用例.工作流程或程序实现建模. 活动图建模步骤 - 确定活动图的范围和边界,对哪些工作流.哪些 ...
- Shell 运算相关
一.${str} 二.变量替换 三.3种计算字符串长度的效率比较 四.(())用法 五.expr 六.bc 4种连续整数求和效率 七.条件测试 八.字符串测试
- Hillstone设备管理-恢复出厂设置
1.CLI命令行操作 unset all: 根据提示选择是否保存当前配置y/n: 选择是否重启y/n: 系统重启后即恢复到出厂设置. 2.webUI操作 “系统”—“配置”,点击“清除”按钮,系统会提 ...
- Linux debug
proc文件系统中可以查看一些正在运行的变量如device-tree sh-3.2# cat /proc/device-tree/ #address-cells fixedregulator@9/ # ...
- sqlserver2017 SSAS配置远程访问不成功的问题
sqlserver2017 SSAS通过IIS配置远程访问一直访问不成功的解决办法: 出现这个问题的原因从微软给出的更新包中说的就是: 从 SQL Server 2017 开始,Analysis Se ...
- http标码集合
201 Created告诉客户端,请求成功,资源已经创建.新的资源的网址请看 202 Accepted告诉客户端,请求已经接受,但还没有处理,可以去Location字段查询进展. 200 Ok告诉客户 ...
- 用BlockingQueue实现的简单发布订阅模式
