unix下网络编程之I/O复用(三)
poll函数
在上文unix下网络编程之I/O复用(二)中已经介绍了select函数的相关使用,本文将介绍另一个常用的I/O复用函数poll。poll提供的功能与select类似,不过在处理流设备时,它能够提供额外的信息。
poll函数原型:
|
1
2
3
|
#include<poll.h> int poll (struct pollfd * fdarray , unsigned long nfds , int timeout); //返回:就需描述字的个数,0——超时,-1——出错 |
第一个参数是指向一个结构数组第一个元素的指针,每个数组元素都是一个pollfd结构。如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
struct pollfd { int fd; //descriptor to check short events; //events of interest on fd` short revents; //events tha occurred on fd} |
要测试的条件由events成员指定,函数在相应的revents成语中返回该描述字的状态。(每个描述字都有两个变量,一个为调用值,另一个为返回结果,从而避免使用值-结果参数,这与select函数是不同的)。下图列出了用于指定events标志以及测试revents标志的一些常值。
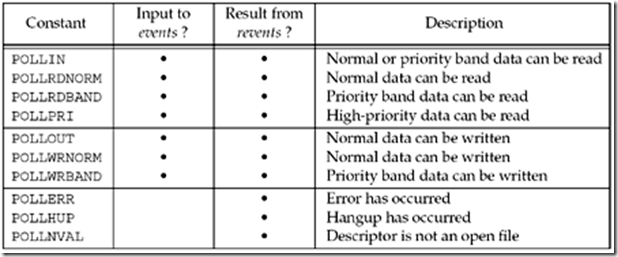
上图需要注意的是,POLLERR,POLLHUP,POLLNVAL是处理错误的描述字,因此它们也就不可以出现在input事件中,即events。poll识别三类数据:普通(normal),优先级带(priority band)和高优先级(high priority)。
对TCP和UPD而言,以下条件引起poll返回特定的revents。
1、 All regular TCP data and all UDP data is considered normal.
2、 TCP's out-of-band data (Chapter 24) is considered priority band.
3、 When the read half of a TCP connection is closed (e.g., a FIN is received), this is also considered normal data and a subsequent read operation will return 0.
4、 The presence of an error for a TCP connection can be considered either normal data or an error (POLLERR). In either case, a subsequent read will return –1 with errno set to the appropriate value. This handles conditions such as the receipt of an RST or a timeout.
5、 The availability of a new connection on a listening socket can be considered either normal data or priority data. Most implementations consider this normal data.
6、 The completion of a nonblocking connect is considered to make a socket writable.
——《unix网络编程》第三版
参数nfds,指示结构数组中元素的个数。
参数timeout:
与select中的timeout不同,poll函数的timeout参数是一int值,表示poll函数返回前等待多长时间,它是毫秒级别的。它有三种情况的取值:1、INFTIM(一个负数值),表示永远等待,即一直阻塞。2、0,表示立即返回,非阻塞。3、>0,表示正待指定数目的毫秒数。
poll函数的返回值:
当poll发生错误时,poll函数的返回值-1,若定时器时间到之前没有任何描述字就绪,则返回0,否则返回就绪描述字的个数,即其revents成员值非0的描述字个数。
如果我们不再关心某个特定描述字,那么可以把与他对应的pollfd结构的fd成员设置成一个负值。poll函数将忽略这样的pollfd结构的events成员,返回时将它的revents成员的值置为0。
poll函数的通信列子:一个简单的TCP回射服务器程序
pollServer.c:使用select机制的服务器程序
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
|
#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>#include <arpa/inet.h>#include <netinet/in.h>#include <sys/socket.h>#include <poll.h>/*环境为ubuntu10.04自带c环境,无法自动引入下列宏,所以自己写在前面了*/#define INFTIM -1#define POLLRDNORM 0x040 /* Normal data may be read. */#define POLLRDBAND 0x080 /* Priority data may be read. */#define POLLWRNORM 0x100 /* Writing now will not block. */#define POLLWRBAND 0x200 /* Priority data may be written. */#define MAXLINE 1024#define OPEN_MAX 16 //一些系统会定义这些宏#define SERV_PORT 10001int main(){ int i , maxi ,listenfd , connfd , sockfd ; int nready; int n; char buf[MAXLINE]; socklen_t clilen; struct pollfd client[OPEN_MAX]; struct sockaddr_in cliaddr , servaddr; listenfd = socket(AF_INET , SOCK_STREAM , 0); memset(&servaddr,0,sizeof(servaddr)); servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET; servaddr.sin_port = htons(SERV_PORT); servaddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY); bind(listenfd , (struct sockaddr *) & servaddr, sizeof(servaddr)); listen(listenfd,10); client[0].fd = listenfd; client[0].events = POLLRDNORM; for(i=1;i<OPEN_MAX;i++) { client[i].fd = -1; } maxi = 0; for(;;) { nready = poll(client,maxi+1,INFTIM); if (client[0].revents & POLLRDNORM) { clilen = sizeof(cliaddr); connfd = accept(listenfd , (struct sockaddr *)&cliaddr, &clilen); for(i=1;i<OPEN_MAX;i++) { if(client[i].fd<0) { client[i].fd = connfd; client[i].events = POLLRDNORM; break; } } if(i==OPEN_MAX) { printf("too many clients! \n"); } if(i>maxi) maxi = i; nready--; if(nready<=0) continue; } for(i=1;i<=maxi;i++) { if(client[i].fd<0) continue; sockfd = client[i].fd; if(client[i].revents & (POLLRDNORM|POLLERR)) { n = read(client[i].fd,buf,MAXLINE); if(n<=0) { close(client[i].fd); client[i].fd = -1; } else { buf[n]='\0'; printf("Socket %d said : %s\n",sockfd,buf); write(sockfd,buf,n); //Write back to client } nready--; if(nready<=0) break; //no more readable descriptors } } } return 0;} |
客户端程序参考上一篇文章。
总结:
本文介绍了poll函数的原型,参数说明,注意事项以及一个简单的代码例子。在unix后续版本中,加入了epoll函数I/O复用机制,它在一定条件下更加高效,在以后的文章中,会对epoll机制再进行详细的描述。之前在学习python的时候,也接触了select和poll,但是当时了解的比较浅显,希望通过最近的学习可以对unix下I/O复用有更深入的认识。
unix下网络编程之I/O复用(三)的更多相关文章
- unix下网络编程之I/O复用(一)
什么是I/O复用? What we need is the capability to tell the kernel that we want to be notified if one or mo ...
- unix下网络编程之I/O复用(五)
前言 本章节是用基本的Linux/Unix基本函数加上select调用编写一个完整的服务器和客户端例子,可在Linux(ubuntu)和Unix(freebsd)上运行,客户端和服务端的功能如下: 客 ...
- unix下网络编程之I/O复用(二)
select函数 该函数允许进程指示内核等待多个事件中的任何一个发生,并仅在有一个或是多个事件发生或经历一段指定的时间后才唤醒它.我们调用select告知内核对哪些描述字(就读.写或异常条件)感兴趣以 ...
- unix下网络编程之I/O复用(四)
首先需要了解的是select函数: select函数 #include<sys/select.h> #include<sys/time.h> int select (int m ...
- TCP/IP网络编程之I/O复用
基于I/O复用的服务端 在前面章节的学习中,我们看到了当有新的客户端请求时,服务端进程会创建一个子进程,用于处理和客户端的连接和处理客户端的请求.这是一种并发处理客户端请求的方案,但并不是一个很好的方 ...
- python3网络编程之socketserver
本节主要是讲解python3网络编程之socketserver,在上一节中我们讲到了socket.由于socket无法支持多用户和多并发,于是就有了socket server. socket serv ...
- GO语言的进阶之路-网络编程之socket
GO语言的进阶之路-网络编程之socket 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.什么是socket; 在说socket之前,我们要对两个概念要有所了解,就是IP和端口 ...
- 网络编程之socket
网络编程之socket socket:在网络编程中的一个基本组件,也称套接字. 一个套接字就是socket模块中的socket类的一个实例. 套接字包括两个: 服务器套接字和客户机套接字 套接字的实例 ...
- java网络编程之TCP通讯
java中的网络编程之TCP协议的详细介绍,以及如何使用,同时我在下面举2例说明如何搭配IO流进行操作, /* *TCP *建立连接,形成传输数据的通道: *在连接中进行大数据量传输: *通过三次握手 ...
随机推荐
- PHP面向对象之对象和引用
在PHP中对象类型和简单变量类型表现可以说是大相径庭,很多数据类型都要可以在写时进行复制,如当写代码$a=$b时,两个变量因为赋予相同的值而告终.所以需要注意的是,这种情况用在对象时就会完全不同了. ...
- 前段时间说了AssetBundle打包,先设置AssetLabels,再执行打包,但是这样有个弊端就是所有设置了AssetLabels的资源都会打包,这次说说不设置AssetLabels,该如何打包AssetBundle
BuildPipeline.BuildAssetBundles() 这个函数,有多个重载,一个不用AssetBundleBuild数组,一个需要,如果设置了AssetLabels,那么这时候是不需要的 ...
- Elasticsearch-->Get Started-->Basic concepts
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/getting-started-concepts.html There ...
- YARN中的失败分析
YARN中的失败分析 对于在YARN中运行的MapReduce程序,需要考虑以下几种实体的失败任务.application master.节点管理器.资源管理器 1. 任务运行失败 任务运行失败类似于 ...
- Python之面向对象总结
一.面向对象 1.面向过程 a.优点:极大的降低了写程序的复杂度,只需要顺着执行的步骤,堆叠代码即可 b.缺点:一套流水线或者流程就是来解决一个问题,代码就是牵一发而东莞全身 2.面向对象 a.优点: ...
- ajax设置Access-Control-Allow-Origin实现跨域访问
ajax跨域访问 1.jsonp方法,jsonp方法是一种非官方方法,这种方法只支持GET方式, 不如POST方式安全.(即使使用jquery的jsonp方法,type设为POST, 也会自动变为GE ...
- EXCEL中,怎样查看一个工作簿中有几个工作表?
EXCEL中,怎样查看一个工作簿中有几个工作表 有几个EXCEL文件,每个文件(工作簿)中都有上百个工作表, 怎样可以一次性查看一个簿包含几个表? 目前好像没有直接可以看到有多少张工作表的按钮,这就需 ...
- python中的list和array的不同之处 2
版权声明:本文为博主非原创文章,未经博主允许可以转载. Python中的list和array的不同之处 python中的list是python的内置数据类型,list中的数据类不必相同的,而a ...
- WPF中的事件及冒泡事件和隧道事件(预览事件)的区别
WPF快速指导10:WPF中的事件及冒泡事件和隧道事件(预览事件)的区别 WPF快速指导10:WPF中的事件及冒泡事件和隧道事件(预览事件)的区别 本文摘要: 1:什么是路由事件: 2:中断事件路 ...
- hdu 1847 Good Luck in CET-4 Everybody!(sg)
Good Luck in CET-4 Everybody! Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K ...
