一致性 hash 环
一致性 hash 环
最近做项目 做了一个分发器 ,需要 根据请求携带的参数 把请求分发到 不同的服务器上面,最终我选择使用 一致性hash 环 来实现 ,本篇 就主要讲解一下 一致性hash环 它的基本原理
概述
一致性hash算法 由于 均衡性 持久性的映射特点 被广泛应用于负载均衡领域,比如 nginx 、dubbo 、等等 内部都有一致性hash 的实现 ,比如 dubbo ,当你调用rpc 接口的时候,如果有2个提供者,那么你可以通过配置 让其调用通过 一致性hash 进行计算 然后分发到具体的 某个实例接口上 。
1.hash算法 在负载均衡中的问题
先来看看普通的hash算法的特点,普通的hash算法就是把一系列输入 打散成随机的数据,负载均衡就是利用这一点特性,对于大量请求调用,通过一定的 hash将它们均匀的散列,从而实现压力平均化
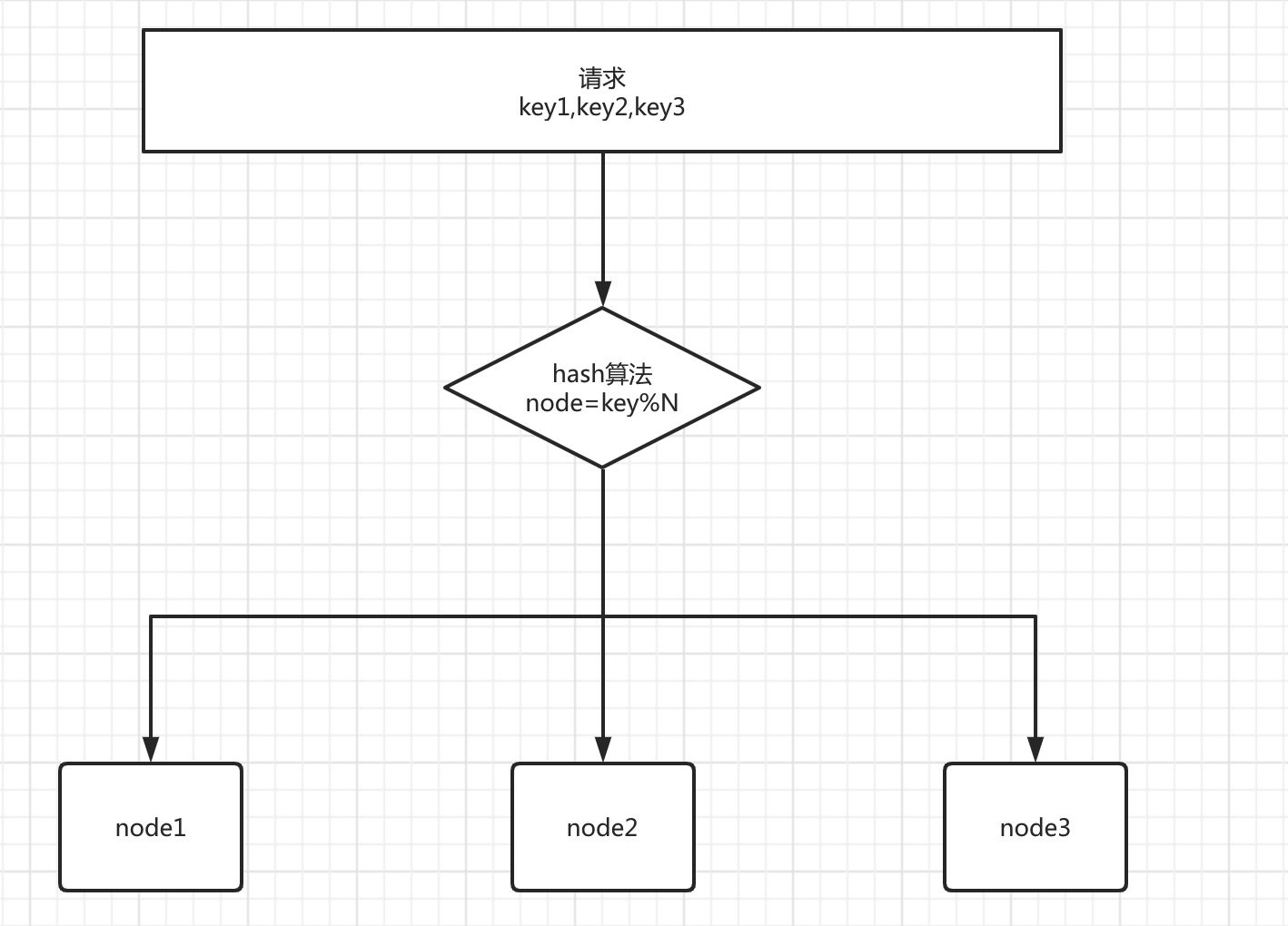
如果上面图中 key作为缓存的key ,node中寸入该key对应的 value,就是一个 简单的分布式缓存系统了。
问题:可以看出 当 N 节点数发生变化的时候 之前所有的 hash映射几乎全部失效,如果集群是无状态的服务 倒是没什么事情,但是如果是 分布式缓存这种,比如 映射的key1 原本是去 node1上查询 缓存的value1, 但是当N节点变化后 hash后的 key1 可能去了 node2 这样 就产生了致命问题。。
2.一致性 hash 算法
一致性hash算法就是来解决 上面的问题
2.1 特点 (重要)
下面说明 一致性hash算法的 2个 重要的特点
平衡性
平衡性是指哈希的结果能够尽可能分布到所有的缓冲中去,这样可以使得所有的缓冲空间都得到利用。很多哈希算法都能够满足这一条件。
单调性
单调性是指如果已经有一些内容通过哈希分派到了相应的缓冲中,又有新的缓冲区加入到系统中,那么哈希的结果应能够保证原有已分配的内容可以被映射到新的缓冲区中去,而不会被映射到旧的缓冲集合中的其他缓冲区。
简单的哈希算法往往不能满足单调性的要求
2.2 原理
一致性哈希将整个哈希值空间组织成一个虚拟的圆环,如假设某哈希函数H的值空间为0-2^32-1(即哈希值是一个32位无符号整形),整个哈希空间环如下:
就是所有的输入值都被映射到 0-2^32-1 之间,组成一个圆环
下一步将各个服务器使用Hash进行一个哈希,具体可以选择服务器的ip或主机名或者其他业务属性作为关键字进行哈希,这样每台机器就能确定其在哈希环上的位置,这里假设将上文中四台服务器使用ip地址哈希后在环空间的位置如下:
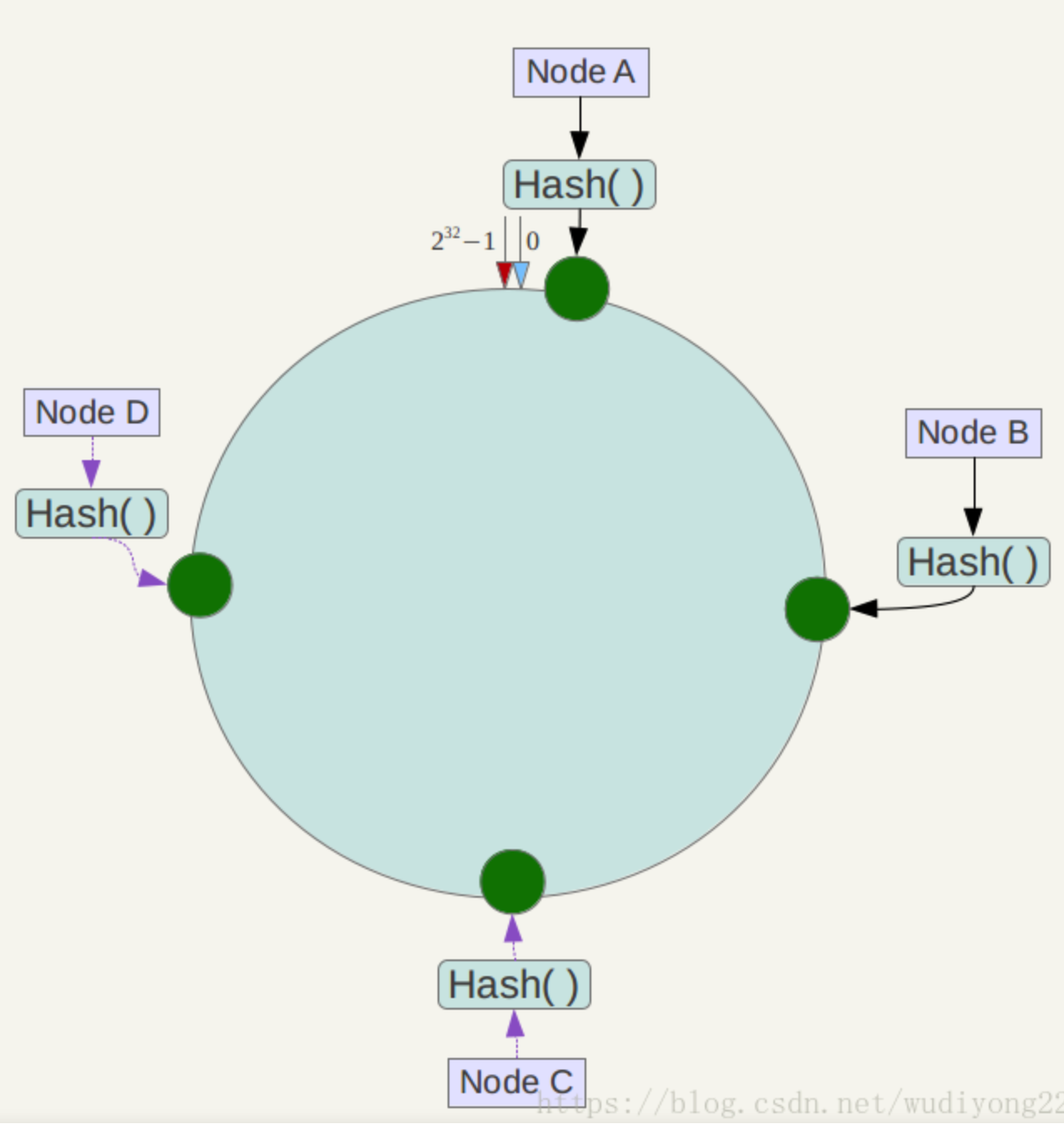
如果服务器数量不多且个数相对稳定,我们也可以手动设置这些服务器的位置,如设A在230-1位置,B在231-1位置,C在3*230-1位置,D在232-1位置,则hash值为02^30-1的数据存储在A中,hash值为2^30-12^31-1的数据存储在B中,以此类推。
**定位数据存储的方法: **将数据key使用相同的函数Hash计算出哈希值,并确定此数据在环上的位置,从此位置沿环顺时针“行走”,第一台遇到的服务器就是其应该定位到的服务器。可以为这些服务器维护一条二分查找树,定位服务器的过程就是在二分查找树中找刚好比其大的节点。
例如我们有Object A、Object B、Object C、Object D四个数据对象,经过哈希计算后,在环空间上的位置如下:
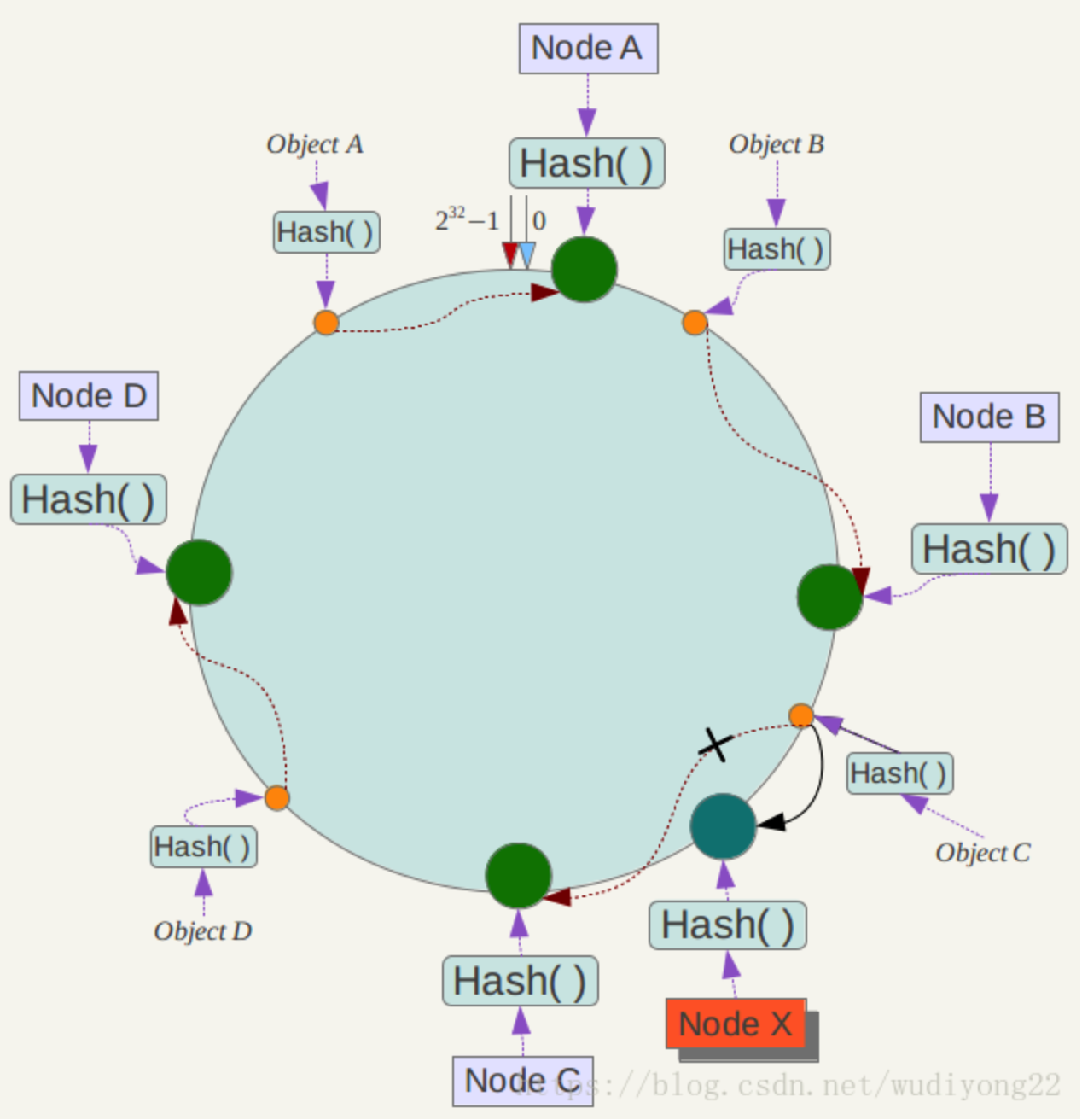
2.3 一致性hash 优点
如上图,假如当节点A宕机了,那么只会影响 objectA 它会被重新映射到 NodeB节点,其他的ObjectB ObjectC ObjectD 都不会受到影响,大大提高了容错性和稳定性
2.4 一致性hash存在的问题
2.3.1 数据分布不均匀
当节点Node很少的时候 比如2台机器,那么 必然造成大量数据集中在NodeA,少量在NodeB
2.3.2 雪崩
当某个节点宕机后,原本属于它的请求 都会被重新hash 映射到 下游节点,会突然造成下游节点压力过大 有可能也会造成 下游节点宕机,从而形成雪崩 这是致命的
为此 引入了 虚拟节点来解决上面两个问题
3.带虚拟节点的一致性hash
就是会在圆环上 根据Node 节点 生成很多的虚拟节点 分布在圆环上,这样当 某个 节点挂了后 原本属于它的请求,会被均衡的分布到 其他节点上 降低了产生雪崩的情况,也解决了 节点数少导致 请求分布不均的请求
即对每一个服务节点计算多个哈希(可以用原节点key+"##xxxk"作为每个虚拟节点的key,然后求hashcode),每个计算结果位置都放置一个此服务节点,称为虚拟节点。具体做法可以在服务器ip或主机名的后面增加编号来实现。
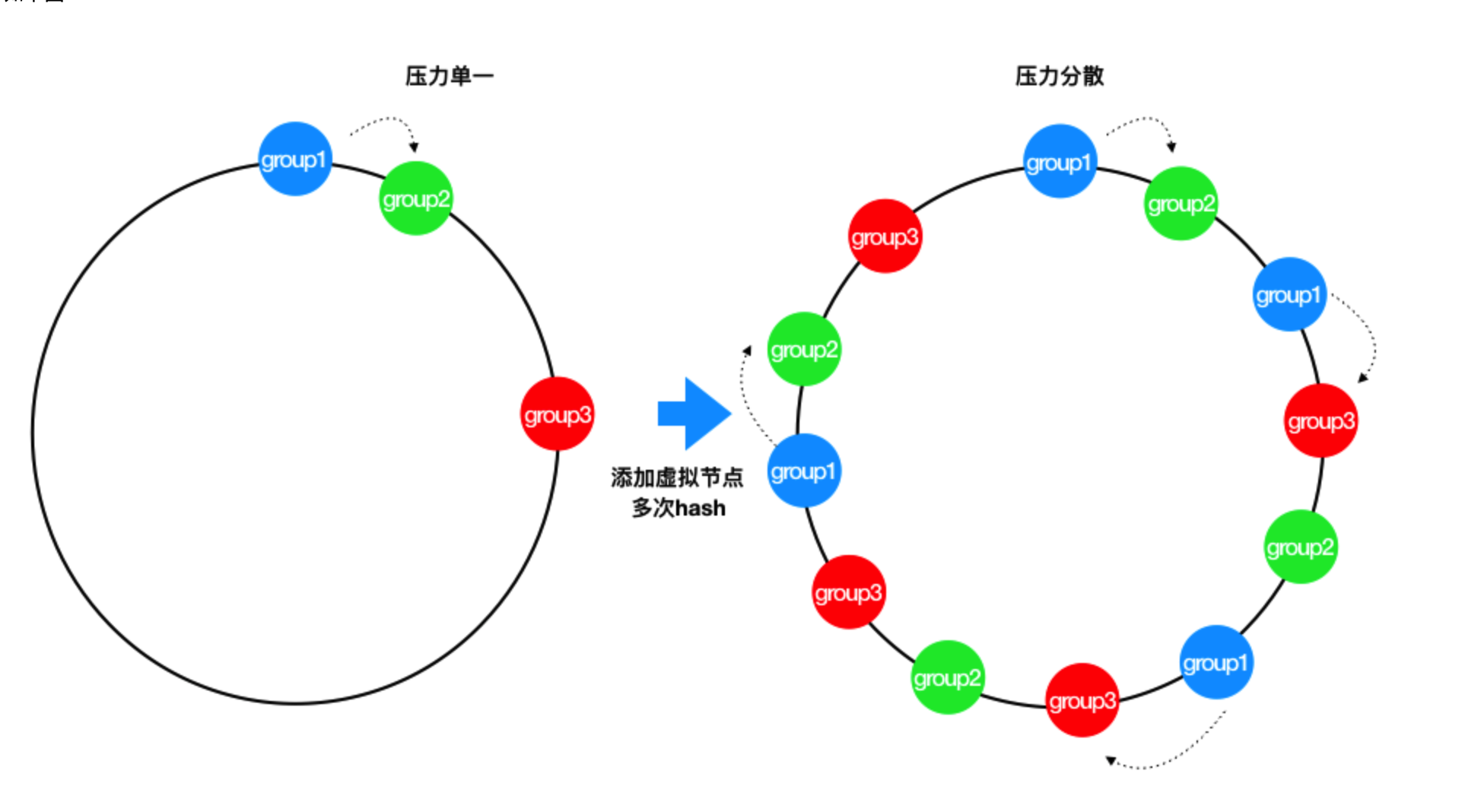
看上图,此时如果 group3节点挂了,那么请求会被均分到 group2 和 group1上面 ,到此 一致性hash的正确生产的使用方式讲解完了 下面来看看一个案例代码。
4. 代码测试
可供选择的有很多,memcached官方使用了基于md5的KETAMA算法,但这里处于计算效率的考虑,使用了FNV1_32_HASH算法,如下:
public class HashUtil {
/**
* 计算Hash值, 使用FNV1_32_HASH算法
* @param str
* @return
*/
public static int getHash(String str) {
final int p = 16777619;
int hash = (int)2166136261L;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
hash =( hash ^ str.charAt(i) ) * p;
}
hash += hash << 13;
hash ^= hash >> 7;
hash += hash << 3;
hash ^= hash >> 17;
hash += hash << 5;
if (hash < 0) {
hash = Math.abs(hash);
}
return hash;
}
}
package com.weareint.dispatchservice.hashloop;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.*;
/**
*
*
* <pre>
* 一致性 hash 虚拟 环
* </pre>
*
* @author johnny
* @date 2021-08-26 9:22 上午
*/
@Component
public class HashVirtualNodeCircle {
/** 真实集群列表 */
private static List<String> instanceNodes;
/** 虚拟节点映射关系 */
private static SortedMap<Integer, String> virtualNodes = new TreeMap<>();
/** 虚拟节点数 */
private static final int VIRTUAL_NODE_NUM = 1000;
/** 刷新 服务实例 */
public void refreshVirtualHashCircle(HashCircleInstanceNodeBuild build) {
// 当集群变动时,刷新hash环,其余的集群在hash环上的位置不会发生变动
virtualNodes.clear();
// 获取 最新节点
instanceNodes = build.instanceNodes();
// 将虚拟节点映射到Hash环上
for (String realInstance : instanceNodes) {
for (int i = 0; i < VIRTUAL_NODE_NUM; i++) {
String virtualNodeName = getVirtualNodeName(realInstance, i);
int hash = HashUtils.getHash(virtualNodeName);
System.out.println("[" + virtualNodeName + "] launched @ " + hash);
virtualNodes.put(hash, virtualNodeName);
}
}
}
private static String getVirtualNodeName(String realName, int num) {
return realName + "&&VN" + num;
}
private static String getRealNodeName(String virtualName) {
return virtualName.split("&&")[0];
}
private static String getServer(String widgetKey) {
int hash = HashUtils.getHash(widgetKey);
// 只取出所有大于该hash值的部分而不必遍历整个Tree
SortedMap<Integer, String> subMap = virtualNodes.tailMap(hash);
String virtualNodeName;
if (subMap.isEmpty()) {
// hash值在最尾部,应该映射到第一个group上
virtualNodeName = virtualNodes.get(virtualNodes.firstKey());
} else {
virtualNodeName = subMap.get(subMap.firstKey());
}
return getRealNodeName(virtualNodeName);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashVirtualNodeCircle hashVirtualNodeCircle = new HashVirtualNodeCircle();
hashVirtualNodeCircle.refreshVirtualHashCircle(
new HashCircleInstanceNodeBuild() {
@Override
public List<String> instanceNodes() {
LinkedList<String> nodes = new LinkedList<>();
nodes.add("192.168.11.23:8090");
nodes.add("192.168.11.23:8093");
nodes.add("192.168.11.23:8094");
return nodes;
}
});
// 生成随机数进行测试
Map<String, Integer> resMap = new HashMap<>();
List<String> plcList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
String plchost = "192.168.0." + i + 1;
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
plcList.add(plchost + ":" + j + 100);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < plcList.size(); i++) {
String plcwideget = plcList.get(i);
String group = getServer(plcwideget);
if (resMap.containsKey(group)) {
resMap.put(group, resMap.get(group) + 1);
} else {
resMap.put(group, 1);
}
}
resMap.forEach(
(k, v) -> {
System.out.println("group " + k + ": " + v + "(" + v / 100.0D + "%)");
});
System.out.println("=========================================");
}
}
可以看到 分布很均衡
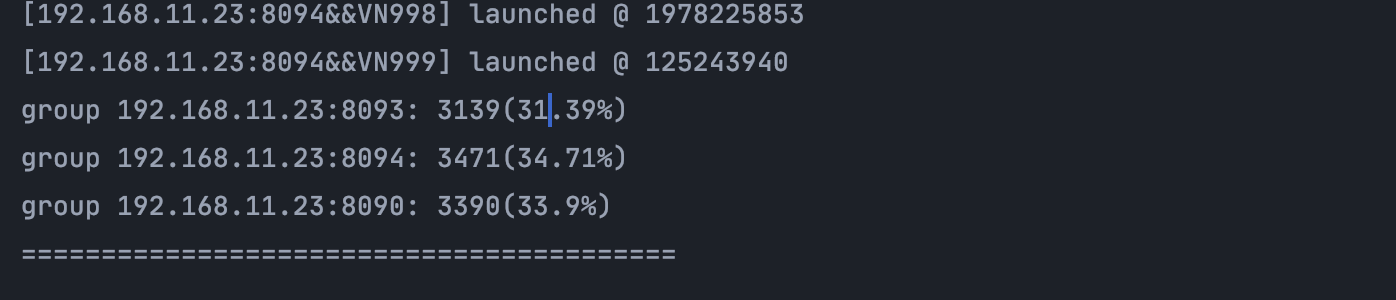
5.Dubbo 一致性Hash 实现
最近给公司做的分发器 使用dubbo 调用远程服务,调研了一下 dubbo 也有自己实现的 一致性hash 不过实际使用起来 发现有些bug ,目前通过SPI机制 自己扩展了一下,来看看 dubbo的 一致性hash实现吧
5.1 版本 dubbo2.7.12
我用的版本是 dubbo2.7.12 已经入了 2.7的坑 不少坑都是自己慢慢调试解决的。
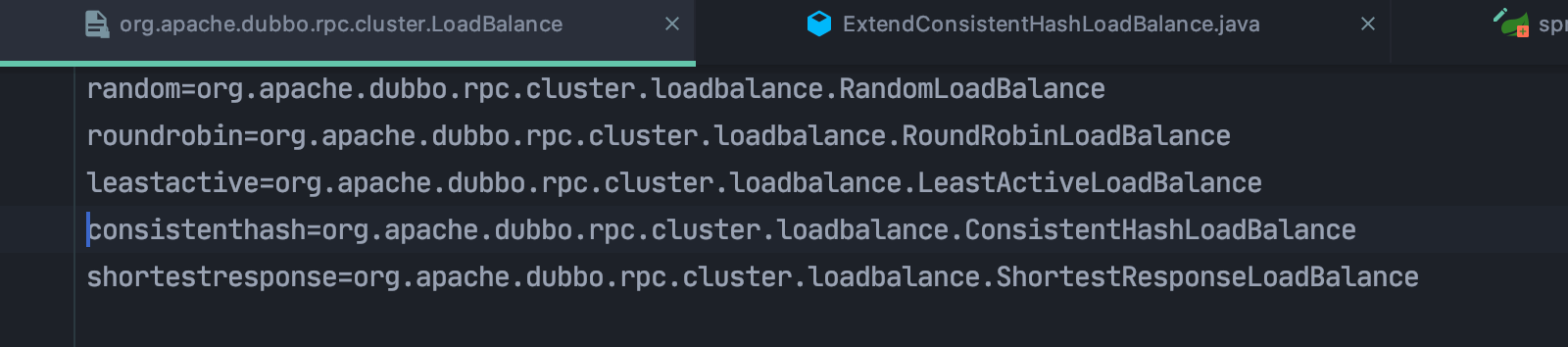
5.2 org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.loadbalance
负载均衡基本就这些 一致性hash,随机 ,轮训,。。 没啥特别的
5.3 dubbo ConsistentHashLoadBalance源码
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.loadbalance;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.URL;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.io.Bytes;
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invocation;
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker;
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.support.RpcUtils;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap;
import static org.apache.dubbo.common.constants.CommonConstants.COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN;
/**
* ConsistentHashLoadBalance
*/
public class ConsistentHashLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
public static final String NAME = "consistenthash";
/**
* Hash nodes name
*/
public static final String HASH_NODES = "hash.nodes";
/**
* Hash arguments name
*/
public static final String HASH_ARGUMENTS = "hash.arguments";
private final ConcurrentMap<String, ConsistentHashSelector<?>> selectors = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, ConsistentHashSelector<?>>();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
String key = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + methodName;
// using the hashcode of list to compute the hash only pay attention to the elements in the list
//有bug 1.invokers 老是变化,导致 不断的 在创建 ConsistentHashSelector
//
int invokersHashCode = invokers.hashCode();
ConsistentHashSelector<T> selector = (ConsistentHashSelector<T>) selectors.get(key);
if (selector == null || selector.identityHashCode != invokersHashCode) {
selectors.put(key, new ConsistentHashSelector<T>(invokers, methodName, invokersHashCode));
selector = (ConsistentHashSelector<T>) selectors.get(key);
}
return selector.select(invocation);
}
private static final class ConsistentHashSelector<T> {
private final TreeMap<Long, Invoker<T>> virtualInvokers;
private final int replicaNumber;
private final int identityHashCode;
private final int[] argumentIndex;
ConsistentHashSelector(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, String methodName, int identityHashCode) {
this.virtualInvokers = new TreeMap<Long, Invoker<T>>();
this.identityHashCode = identityHashCode;
URL url = invokers.get(0).getUrl();
//默认虚拟机节点数 160 ,可以通过
/**
dubbo:
consumer:
parameters:
hash:
nodes: 560 #指定虚拟分片结点数 最终virtualInvokers = nodes * invokerCount
arguments: 0 指定的是 哪个参数作为 key
**/
this.replicaNumber = url.getMethodParameter(methodName, HASH_NODES, 160);
//默认取 第 0 个参数 作为 hash的key
String[] index = COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(url.getMethodParameter(methodName, HASH_ARGUMENTS, "0"));
argumentIndex = new int[index.length];
for (int i = 0; i < index.length; i++) {
argumentIndex[i] = Integer.parseInt(index[i]);
}
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
String address = invoker.getUrl().getAddress();
for (int i = 0; i < replicaNumber / 4; i++) {
byte[] digest = Bytes.getMD5(address + i);
for (int h = 0; h < 4; h++) {
long m = hash(digest, h);
virtualInvokers.put(m, invoker);
}
}
}
}
public Invoker<T> select(Invocation invocation) {
String key = toKey(invocation.getArguments());
byte[] digest = Bytes.getMD5(key);
return selectForKey(hash(digest, 0));
}
private String toKey(Object[] args) {
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder();
for (int i : argumentIndex) {
if (i >= 0 && i < args.length) {
buf.append(args[i]);
}
}
return buf.toString();
}
private Invoker<T> selectForKey(long hash) {
Map.Entry<Long, Invoker<T>> entry = virtualInvokers.ceilingEntry(hash);
if (entry == null) {
entry = virtualInvokers.firstEntry();
}
return entry.getValue();
}
private long hash(byte[] digest, int number) {
return (((long) (digest[3 + number * 4] & 0xFF) << 24)
| ((long) (digest[2 + number * 4] & 0xFF) << 16)
| ((long) (digest[1 + number * 4] & 0xFF) << 8)
| (digest[number * 4] & 0xFF))
& 0xFFFFFFFFL;
}
}
}
6.Dubbo 的 一致性 hash的 bug 和 一些配置参数
6.1 invokers 不断的变化
经过调试 发现 invokers 时不时变化导致 一致在 rehash,其实 很多时候只是 节点的顺序变化而已
解决办法: 我直接把 invokers 节点数 取出来进行排序后拼接 成一个字符串 进行 计算hashcode 就不会总变化了
String invokeKey =
invokers.stream()
.filter(Node::isAvailable)
// 按照ip 和port 排序
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(invoke -> invoke.getUrl().getIp()))
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(invoke -> invoke.getUrl().getPort()))
.map(invoke -> invoke.getUrl().getIp() + ":" + invoke.getUrl().getPort())
.collect(Collectors.joining(","));
6.2 注意 isAvailable
invokers中存在 节点不可用的,如果对于节点不可用的 直接过滤 需要注意 isAvailable
6.3 设置虚拟节点发片数
dubbo:
consumer:
parameters:
hash:
nodes: 560 #指定虚拟分片结点数 最终virtualInvokers = nodes * invokerCount ,默认是160
6.4 设置方法的哪个参数作为 hash的key
dubbo:
consumer:
parameters:
hash:
arguments: 0 #默认就是0
7.SPI 扩展Dubbo 一致性hash 算法 ExtendConsistentHashLoadBalance
7.1 官方文档
官方文档很详细了
https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs/v3.0/references/spis/load-balance/
7.2 ExtendConsistentHashLoadBalance 扩展实现
package com.weareint.dispatchservice.extendconsistenthash;
import com.atw.mdc.entity.protocol.webRequest.PlcReadSimpleRequest;
import com.atw.mdc.entity.protocol.webRequest.PlcWriteSimpleRequest;
import com.weareint.dispatchservice.event.ConnectionRouteEvent;
import com.weareint.dispatchservice.event.NodeChangeEvent;
import com.weareint.dispatchservice.event.NodeChangeService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.Node;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.URL;
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invocation;
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker;
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.loadbalance.AbstractLoadBalance;
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.support.RpcUtils;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisher;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import static org.apache.dubbo.common.constants.CommonConstants.COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN;
/**
*
*
* <pre>
* 扩展 一致性Hash 环 主要是把 hash 的key 只通过 plc 的deviceCode 进行hash , 然后后续添加 Redis 路由表 进行
* </pre>
*
* @author johnny
* @date 2021-08-26 5:32 下午
*/
@Slf4j
public class ExtendConsistentHashLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
public static ApplicationEventPublisher publisher;
public static NodeChangeService nodeChangeService;
public static final String NAME = "consistenthash";
/** Hash nodes name */
public static final String HASH_NODES = "hash.nodes";
/** Hash arguments name */
public static final String HASH_ARGUMENTS = "hash.arguments";
private final ConcurrentMap<String, ExtendConsistentHashLoadBalance.ConsistentHashSelector<?>>
selectors =
new ConcurrentHashMap<
String, ExtendConsistentHashLoadBalance.ConsistentHashSelector<?>>();
public ConcurrentMap<String, ConsistentHashSelector<?>> getSelectors() {
return selectors;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
// String key = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + methodName;
// 只要是 servicekey 就好
String key = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getServiceKey();
// String key = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getParameter("remote.application");
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.info("【remoteApplication:{}】", key);
}
// using the hashcode of list to compute the hash only pay attention to the elements in the
String invokeKey =
invokers.stream()
.filter(Node::isAvailable)
// 按照ip 和port 排序
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(invoke -> invoke.getUrl().getIp()))
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(invoke -> invoke.getUrl().getPort()))
.map(invoke -> invoke.getUrl().getIp() + ":" + invoke.getUrl().getPort())
.collect(Collectors.joining(","));
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.info("【invokeKey : {}】", invokeKey);
}
int invokersHashCode = invokeKey.hashCode();
ExtendConsistentHashLoadBalance.ConsistentHashSelector<T> selector = null;
// 同时submit 可能会有问题 加个锁 可能会有第一次提交生成 虚拟节点
selector = (ExtendConsistentHashLoadBalance.ConsistentHashSelector<T>) selectors.get(key);
// 判断是否invokers 有变化 selector.identityHashCode != invokersHashCode
if (selector == null || selector.identityHashCode != invokersHashCode) {
synchronized (ExtendConsistentHashLoadBalance.class) {
selector =
(ExtendConsistentHashLoadBalance.ConsistentHashSelector<T>)
selectors.get(key);
if (selector == null || selector.identityHashCode != invokersHashCode) {
// 这个 isAvailable 要存在 否则有bug
List<Invoker<T>> availableInvoker =
invokers.stream()
.filter(Node::isAvailable)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
ConsistentHashSelector<T> tConsistentHashSelector =
new ConsistentHashSelector<>(
availableInvoker, methodName, invokersHashCode);
selectors.put(key, tConsistentHashSelector);
selector =
(ExtendConsistentHashLoadBalance.ConsistentHashSelector<T>)
selectors.get(key);
log.info(
"【new selector by invokeKey : {} , availableInvoker:{}】",
invokeKey,
availableInvoker.stream()
.map(
invoke ->
invoke.getUrl().getIp()
+ ":"
+ invoke.getUrl().getPort())
.collect(Collectors.joining(",")));
NodeChangeEvent event = new NodeChangeEvent(this, tConsistentHashSelector);
publisher.publishEvent(event);
}
}
}
String hashKey = selector.toKey(invocation.getArguments());
Invoker<T> select = selector.select(hashKey);
log.info(
"【plcDeviceCode: {} dispatch to ip : {}:{}",
hashKey,
select.getUrl().getIp(),
select.getUrl().getPort());
// deviceCode route table To Redis
ConnectionRouteEvent event = new ConnectionRouteEvent(this, hashKey, select, selector);
publisher.publishEvent(event);
return select;
}
public static final class ConsistentHashSelector<T> {
private final TreeMap<Long, Invoker<T>> virtualInvokers;
public final List<Invoker<T>> invokers;
private final int replicaNumber;
private final int identityHashCode;
private final int[] argumentIndex;
ConsistentHashSelector(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, String methodName, int identityHashCode) {
this.invokers = invokers;
this.virtualInvokers = new TreeMap<Long, Invoker<T>>();
this.identityHashCode = identityHashCode;
URL url = invokers.get(0).getUrl();
this.replicaNumber = url.getMethodParameter(methodName, HASH_NODES, 160);
String[] index =
COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(
url.getMethodParameter(methodName, HASH_ARGUMENTS, "0"));
argumentIndex = new int[index.length];
for (int i = 0; i < index.length; i++) {
argumentIndex[i] = Integer.parseInt(index[i]);
}
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
String address = invoker.getUrl().getAddress();
for (int i = 0; i < replicaNumber / 4; i++) {
byte[] digest = md5(address + i);
for (int h = 0; h < 4; h++) {
long m = hash(digest, h);
virtualInvokers.put(m, invoker);
}
}
}
}
public Invoker<T> select(String key) {
byte[] digest = md5(key);
return selectForKey(hash(digest, 0));
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public String toKey(Object[] args) {
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder();
for (int i : argumentIndex) {
if (i >= 0 && i < args.length) {
// 只取 PlcReadSimpleRequest的 DeviceCode 作为 hash的key
if (args[i] instanceof ArrayList) {
ArrayList<PlcReadSimpleRequest> list =
(ArrayList<PlcReadSimpleRequest>) args[i];
buf.append(list.get(0).getDeviceCode());
// 只取 PlcWriteSimpleRequest DeviceCode 作为 hash的key
} else if (args[i] instanceof PlcWriteSimpleRequest) {
PlcWriteSimpleRequest req = (PlcWriteSimpleRequest) args[i];
buf.append(req.getDeviceCode());
} else if (args[i] instanceof String) {
// PlcConnectionRequest req = (PlcConnectionRequest) args[i];
// 关闭连接
String deviceCode = (String) args[i];
buf.append(deviceCode);
} else {
buf.append(args[i]);
}
}
}
return buf.toString();
}
private Invoker<T> selectForKey(long hash) {
Map.Entry<Long, Invoker<T>> entry = virtualInvokers.ceilingEntry(hash);
if (entry == null) {
entry = virtualInvokers.firstEntry();
}
return entry.getValue();
}
private long hash(byte[] digest, int number) {
return (((long) (digest[3 + number * 4] & 0xFF) << 24)
| ((long) (digest[2 + number * 4] & 0xFF) << 16)
| ((long) (digest[1 + number * 4] & 0xFF) << 8)
| (digest[number * 4] & 0xFF))
& 0xFFFFFFFFL;
}
private byte[] md5(String value) {
MessageDigest md5;
try {
md5 = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
md5.reset();
byte[] bytes = value.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
md5.update(bytes);
return md5.digest();
}
public int getIdentityHashCode() {
return identityHashCode;
}
}
}
7.3 配置spi扩展
extendconsistenthash=com.weareint.dispatchservice.extendconsistenthash.ExtendConsistentHashLoadBalance
7.4 使用自定义的扩展 loadbalance
@DubboReference(loadbalance = "extendconsistenthash")
private IDeviceWriteService deviceWriteService;
7.5 已知扩展
总结
本篇主要讲解了 什么是一致性 hash 它有哪些优点和存在的问题,以及 带虚拟节点的一致性hash,最后介绍了一些 dubbo 的一致性hash 实现,dubbo自带的有bug ,但是提供了 spi 扩展机制 你可以自己去实现 ,目前我就是这样去解决的 。
参考文章 :
https://www.cnblogs.com/fengyun2050/p/12808951.html,
https://blog.csdn.net/wudiyong22/article/details/78687246
欢迎大家访问 个人博客 Johnny小屋
一致性 hash 环的更多相关文章
- 对一致性Hash算法,Java代码实现的深入研究
一致性Hash算法 关于一致性Hash算法,在我之前的博文中已经有多次提到了,MemCache超详细解读一文中"一致性Hash算法"部分,对于为什么要使用一致性Hash算法.一致性 ...
- 分布式算法(一致性Hash算法)
一.分布式算法 在做服务器负载均衡时候可供选择的负载均衡的算法有很多,包括: 轮循算法(Round Robin).哈希算法(HASH).最少连接算法(Least Connection).响应速度算法( ...
- Java实现一致性Hash算法深入研究
一致性Hash算法 关于一致性Hash算法,在我之前的博文中已经有多次提到了,MemCache超详细解读一文中”一致性Hash算法”部分,对于为什么要使用一致性Hash算法和一致性Hash算法的算法原 ...
- 一致性Hash算法与代码实现
一致性Hash算法: 先构造一个长度为232的整数环(这个环被称为一致性Hash环),根据节点名称的Hash值(其分布为[0, 232-1])将服务器节点放置在这个Hash环上,然后根据数据的Key值 ...
- 百度资深架构师带你深入浅出一致性Hash原理
一.前言 在解决分布式系统中负载均衡的问题时候可以使用Hash算法让固定的一部分请求落到同一台服务器上,这样每台服务器固定处理一部分请求(并维护这些请求的信息),起到负载均衡的作用. 但是普通的余数h ...
- 一致性Hash算法介绍(分布式环境算法)
32的整数环(这个环被称作一致性Hash环),根据节点名称的Hash值(其分布范围同样为0~232)将节点放置在这个Hash 环上.然后根据KEY值计算得到其Hash值(其分布范围也同样为0~232 ...
- 一致性Hash(Consistent Hashing)原理剖析
引入 在业务开发中,我们常把数据持久化到数据库中.如果需要读取这些数据,除了直接从数据库中读取外,为了减轻数据库的访问压力以及提高访问速度,我们更多地引入缓存来对数据进行存取.读取数据的过程一般为: ...
- 浅尝一致性Hash原理
写在前面 在解决分布式系统中负载均衡的问题时候可以使用Hash算法让固定的一部分请求落到同一台服务器上,这样每台服务器固定处理一部分请求(并维护这些请求的信息),起到负载均衡的作用.但是普通的余数ha ...
- 对一致性Hash算法及java实现(转)
一致性Hash算法 关于一致性Hash算法,在我之前的博文中已经有多次提到了,MemCache超详细解读一文中"一致性Hash算法"部分,对于为什么要使用一致性Hash算法.一致性 ...
随机推荐
- iOS - TableViewCell分割线 --By吴帮雷
千万别小看UI中得线,否则你的设计师和测试组会无休止地来找你的!!(如果是美女还好,如果是恐龙....) 在开发中运用最多的是什么,对,表格--TableView,之所以称作表格,是因为他天生带有分割 ...
- 【论文考古】Training a 3-Node Neural Network is NP-Complete
今天看到一篇1988年的老文章谈到了训练一个简单网络是NPC问题[1].也就是下面的网络结构,在线性激活函数下,如果要找到参数使得输入数据的标签估计准确,这个问题是一个NPC问题.这个文章的意义在于宣 ...
- pytest(10)-常用执行参数说明
pytest单元测试框架中可以使用命令行及代码pytest.main()两种方式执行测试,且可以加入各种参数来组织执行测试.接下来我们来了解常用的执行参数的含义及其用法. pytest中的执行参数根据 ...
- EMNLP 2017 | Sparse Communication for Distributed Gradient Descent
通过将分布式随机梯度下降(SGD)中的稠密更新替换成稀疏更新可以显著提高训练速度.当大多数更新接近于0时,梯度更新会出现正偏差,因此我们将99%最小更新(绝对值)映射为零,然后使用该稀疏矩阵替换原来的 ...
- RENIX使用模板创建报文——网络测试仪实操
一.简介 RENIX内置多种报文模板,可以直接用来创建一个报文,节省时间 二.操作步骤 1.准备工作:连接机框,占用端口 2.新建或者编辑流 3.切换到 数据包/编辑 界面:点击创建新协议报文 4.在 ...
- 一文带你盘点市场上主流的BI产品主要有哪些
随着时代的发展,商业智能使数据分析和数据可视化的门槛不断降低,使得企业各级人员都能进行数据分析,从而加深业务洞察,推动企业发展.而在数据分析领域,BI产品发挥了十分重要的作用. 市场需求变化日益频繁 ...
- 📚 选择排序和插入排序区别-DS笔记
选择排序法 A[i...n)未排序,A[0...i)已排序 A[i...n]中最小值要放到A[i]的位置 复杂度 \(O(n^2)\) 第一层循环n次 第二层循环:i=0,n次:i=1,n-1次... ...
- 【C# 程序集】在.net中使用GAC 全局程序集缓存
原文地址:https://blog.alswl.com/2011/01/gac/ GAC GAC是什么?是用来干嘛的?GAC的全称叫做全局程序集缓存,通俗的理解就是存放各种.net平台下面需要使用的d ...
- spring 核心容器api
spring api : https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/javadoc-api/ BeanFactory 才是 Spring ...
- Java课程设计---添加学生
1.创建添加窗体 package com.student.view; import java.awt.EventQueue; import javax.swing.ButtonGroup; impor ...
