Codeforces Round #372 (Div. 2) A B C 水 暴力/模拟 构造
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
ZS the Coder is coding on a crazy computer. If you don't type in a word for a c consecutive seconds, everything you typed disappear!
More formally, if you typed a word at second a and then the next word at second b, then if b - a ≤ c, just the new word is appended to other words on the screen. If b - a > c, then everything on the screen disappears and after that the word you have typed appears on the screen.
For example, if c = 5 and you typed words at seconds 1, 3, 8, 14, 19, 20 then at the second 8 there will be 3 words on the screen. After that, everything disappears at the second 13 because nothing was typed. At the seconds 14 and 19 another two words are typed, and finally, at the second 20, one more word is typed, and a total of 3 words remain on the screen.
You're given the times when ZS the Coder typed the words. Determine how many words remain on the screen after he finished typing everything.
The first line contains two integers n and c (1 ≤ n ≤ 100 000, 1 ≤ c ≤ 109) — the number of words ZS the Coder typed and the crazy computer delay respectively.
The next line contains n integers t1, t2, ..., tn (1 ≤ t1 < t2 < ... < tn ≤ 109), where ti denotes the second when ZS the Coder typed the i-th word.
Print a single positive integer, the number of words that remain on the screen after all n words was typed, in other words, at the second tn.
6 5
1 3 8 14 19 20
3
6 1
1 3 5 7 9 10
2
The first sample is already explained in the problem statement.
For the second sample, after typing the first word at the second 1, it disappears because the next word is typed at the second 3 and 3 - 1 > 1. Similarly, only 1 word will remain at the second 9. Then, a word is typed at the second 10, so there will be two words on the screen, as the old word won't disappear because 10 - 9 ≤ 1.
题意:n个数 从左向右遍历 相邻的数的差值<=c 则计数++ 否则计数清零 输出最后结果
题解:水
/******************************
code by drizzle
blog: www.cnblogs.com/hsd-/
^ ^ ^ ^
O O
******************************/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#define LL __int64
#define pii pair<int,int>
#define MP make_pair
using namespace std;
int n,c;
int a[];
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&c);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
int ans=;
int exm=a[n];
for(int i=n-;i>=;i--)
{
if((exm-a[i])<=c)
{
ans++;
exm=a[i];
}
else
{
break;
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return ;
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
ZS the Coder loves to read the dictionary. He thinks that a word is nice if there exists a substring (contiguous segment of letters) of it of length 26 where each letter of English alphabet appears exactly once. In particular, if the string has length strictly less than 26, no such substring exists and thus it is not nice.
Now, ZS the Coder tells you a word, where some of its letters are missing as he forgot them. He wants to determine if it is possible to fill in the missing letters so that the resulting word is nice. If it is possible, he needs you to find an example of such a word as well. Can you help him?
The first and only line of the input contains a single string s (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 50 000), the word that ZS the Coder remembers. Each character of the string is the uppercase letter of English alphabet ('A'-'Z') or is a question mark ('?'), where the question marks denotes the letters that ZS the Coder can't remember.
If there is no way to replace all the question marks with uppercase letters such that the resulting word is nice, then print - 1 in the only line.
Otherwise, print a string which denotes a possible nice word that ZS the Coder learned. This string should match the string from the input, except for the question marks replaced with uppercase English letters.
If there are multiple solutions, you may print any of them.
ABC??FGHIJK???OPQR?TUVWXY?
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRZTUVWXYS
WELCOMETOCODEFORCESROUNDTHREEHUNDREDANDSEVENTYTWO
-1
??????????????????????????
MNBVCXZLKJHGFDSAQPWOEIRUYT
AABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVW??M
-1
In the first sample case, ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRZTUVWXYS is a valid answer beacuse it contains a substring of length 26 (the whole string in this case) which contains all the letters of the English alphabet exactly once. Note that there are many possible solutions, such as ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ or ABCEDFGHIJKLMNOPQRZTUVWXYS.
In the second sample case, there are no missing letters. In addition, the given string does not have a substring of length 26 that contains all the letters of the alphabet, so the answer is - 1.
In the third sample case, any string of length 26 that contains all letters of the English alphabet fits as an answer
题意:给你一个串 其中只有大写字母和'?' 现在更改问号位置的字符为大写字母 使得存在连续的长度为26的子串含有所有的大写字母
无法实现 输出-1 否则 输出更改之后的字符串
题解:枚举每个长度为 26 的区间,若区间满足条件就记录区间 [l,r] 并生成题目要求的字符串,否则输出 −1 。生成字符串的方法是,统计 [l,r] 区间中缺少哪个字符
map标记 缺少的字母种类的数量必须和当前区间的问号的数量相等
/******************************
code by drizzle
blog: www.cnblogs.com/hsd-/
^ ^ ^ ^
O O
******************************/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#define LL __int64
#define pii pair<int,int>
#define MP make_pair
using namespace std;
char a[];
map<char,int> mp;
int main()
{
cin>>a;
int len=strlen(a);
if(len<)
{
cout<<"-1"<<endl;
return ;
}
int flag=;
for(int i=; i<len; i++)
{
if(i+>=len)
break;
mp.clear();
int exm=;
int gg=;
for(int j=; j<=; j++)
{ if(a[i+j-]=='?')
exm++;
else
{
if(mp[a[i+j-]]==)
{
mp[a[i+j-]]++;
gg++;
}
}
}
if((exm+gg)==)
flag=;
if(flag)
{
flag=i+;
break;
}
}
if(flag==)
{
cout<<"-1"<<endl;
return ;
}
flag--;
for(int i=flag; i<=flag+; i++)
{
if(a[i]=='?')
{
for(char j='A'; j<='Z'; j++)
{
if(mp[j]==)
{
a[i]=j;
mp[j]=;
break;
}
}
}
}
for(int i=; i<len; i++){
if(a[i]=='?'){
a[i]='A';
}}
for(int i=; i<len; i++)
printf("%c",a[i]);
printf("\n");
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
ZS the Coder is playing a game. There is a number displayed on the screen and there are two buttons, ' + ' (plus) and ' ' (square root). Initially, the number 2 is displayed on the screen. There are n + 1 levels in the game and ZS the Coder start at the level 1.
' (square root). Initially, the number 2 is displayed on the screen. There are n + 1 levels in the game and ZS the Coder start at the level 1.
When ZS the Coder is at level k, he can :
- Press the ' + ' button. This increases the number on the screen by exactly k. So, if the number on the screen was x, it becomes x + k.
- Press the '
 ' button. Let the number on the screen be x. After pressing this button, the number becomes
' button. Let the number on the screen be x. After pressing this button, the number becomes 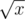 . After that, ZS the Coder levels up, so his current level becomes k + 1. This button can only be pressed when x is a perfect square, i.e. x = m2 for some positive integer m.
. After that, ZS the Coder levels up, so his current level becomes k + 1. This button can only be pressed when x is a perfect square, i.e. x = m2 for some positive integer m.
Additionally, after each move, if ZS the Coder is at level k, and the number on the screen is m, then m must be a multiple of k. Note that this condition is only checked after performing the press. For example, if ZS the Coder is at level 4 and current number is 100, he presses the ' ' button and the number turns into 10. Note that at this moment, 10 is not divisible by 4, but this press is still valid, because after it, ZS the Coder is at level 5, and 10 is divisible by 5.
' button and the number turns into 10. Note that at this moment, 10 is not divisible by 4, but this press is still valid, because after it, ZS the Coder is at level 5, and 10 is divisible by 5.
ZS the Coder needs your help in beating the game — he wants to reach level n + 1. In other words, he needs to press the ' ' button n times. Help him determine the number of times he should press the ' + ' button before pressing the '
' button n times. Help him determine the number of times he should press the ' + ' button before pressing the ' ' button at each level.
' button at each level.
Please note that ZS the Coder wants to find just any sequence of presses allowing him to reach level n + 1, but not necessarily a sequence minimizing the number of presses.
The first and only line of the input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100 000), denoting that ZS the Coder wants to reach level n + 1.
Print n non-negative integers, one per line. i-th of them should be equal to the number of times that ZS the Coder needs to press the ' + ' button before pressing the ' ' button at level i.
' button at level i.
Each number in the output should not exceed 1018. However, the number on the screen can be greater than 1018.
It is guaranteed that at least one solution exists. If there are multiple solutions, print any of them.
3
14
16
46
2
999999999999999998
44500000000
4
2
17
46
97
In the first sample case:
On the first level, ZS the Coder pressed the ' + ' button 14 times (and the number on screen is initially 2), so the number became 2 + 14·1 = 16. Then, ZS the Coder pressed the ' ' button, and the number became
' button, and the number became 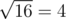 .
.
After that, on the second level, ZS pressed the ' + ' button 16 times, so the number becomes 4 + 16·2 = 36. Then, ZS pressed the ' ' button, levelling up and changing the number into
' button, levelling up and changing the number into 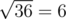 .
.
After that, on the third level, ZS pressed the ' + ' button 46 times, so the number becomes 6 + 46·3 = 144. Then, ZS pressed the ' ' button, levelling up and changing the number into
' button, levelling up and changing the number into 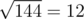 .
.
Note that 12 is indeed divisible by 4, so ZS the Coder can reach level 4.
Also, note that pressing the ' + ' button 10 times on the third level before levelling up does not work, because the number becomes 6 + 10·3 = 36, and when the ' ' button is pressed, the number becomes
' button is pressed, the number becomes 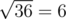 and ZS the Coder is at Level 4. However, 6 is not divisible by 4 now, so this is not a valid solution.
and ZS the Coder is at Level 4. However, 6 is not divisible by 4 now, so this is not a valid solution.
In the second sample case:
On the first level, ZS the Coder pressed the ' + ' button 999999999999999998 times (and the number on screen is initially 2), so the number became 2 + 999999999999999998·1 = 1018. Then, ZS the Coder pressed the ' ' button, and the number became
' button, and the number became 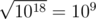 .
.
After that, on the second level, ZS pressed the ' + ' button 44500000000 times, so the number becomes 109 + 44500000000·2 = 9·1010. Then, ZS pressed the ' ' button, levelling up and changing the number into
' button, levelling up and changing the number into 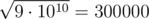 .
.
Note that 300000 is a multiple of 3, so ZS the Coder can reach level 3.

/******************************
code by drizzle
blog: www.cnblogs.com/hsd-/
^ ^ ^ ^
O O
******************************/
//#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstdio>
#define ll long long
#define mod 1000000007
#define PI acos(-1.0)
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
cout<<""<<endl;
for(ll i=; i<=n; i++)
{
printf("%I64d\n",(i+)*(i+)*i-i+);
}
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #372 (Div. 2) A B C 水 暴力/模拟 构造的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #373 (Div. 2) A B C 水 贪心 模拟(四舍五入进位)
A. Vitya in the Countryside time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input s ...
- Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2)A B C 水 暴力 dp
A. Vladik and Courtesy time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input stand ...
- Codeforces Round #407 (Div. 2)A B C 水 暴力 最大子序列和
A. Anastasia and pebbles time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input stan ...
- Codeforces Round #372 (Div. 2)
Codeforces Round #372 (Div. 2) C. Plus and Square Root 题意 一个游戏中,有一个数字\(x\),当前游戏等级为\(k\),有两种操作: '+'按钮 ...
- Codeforces Round #372 (Div. 2) A .Crazy Computer/B. Complete the Word
Codeforces Round #372 (Div. 2) 不知不觉自己怎么变的这么水了,几百年前做A.B的水平,现在依旧停留在A.B水平.甚至B题还不会做.难道是带着一种功利性的态度患得患失?总共 ...
- Codeforces Round #367 (Div. 2) A. Beru-taxi (水题)
Beru-taxi 题目链接: http://codeforces.com/contest/706/problem/A Description Vasiliy lives at point (a, b ...
- Codeforces Round #297 (Div. 2)D. Arthur and Walls 暴力搜索
Codeforces Round #297 (Div. 2)D. Arthur and Walls Time Limit: 2 Sec Memory Limit: 512 MBSubmit: xxx ...
- Codeforces Round #603 (Div. 2) A. Sweet Problem(水.......没做出来)+C题
Codeforces Round #603 (Div. 2) A. Sweet Problem A. Sweet Problem time limit per test 1 second memory ...
- Codeforces Round #334 (Div. 2) A. Uncowed Forces 水题
A. Uncowed Forces Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/604/pro ...
随机推荐
- list集合的遍历3种方法
package com.sort; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; /** ...
- node开发 npm install -g express-generator@4
Node forever : 1,forever start --uid test start app.js 2,forever start --uid test start -a app.js 3, ...
- set常见操作:
(1)sadd 向一个集合中添加一个元素.例如:sadd set1 Hello (2)smembers 查看集合中的所有元素.例如:smembers set1 (3)srem 删除集合中一个指定的元素 ...
- 屏蔽Win10升级通知方法
对于有系统洁癖的我来说,不喜欢还原和自动升级,我更乐意使用全新安装的方式来装系统! 据说微软也知道这种方式有时候的确很讨人嫌,因此就低调的在美国微软社区中给出了屏蔽这项通知的官方"大法&qu ...
- 蓝桥杯 algo——6 安慰奶牛 (最小生成树)
问题描述 Farmer John变得非常懒,他不想再继续维护供奶牛之间供通行的道路.道路被用来连接N个牧场,牧场被连续地编号为1到N.每一个牧场都是一个奶牛的家.FJ计 划除去P条道路中尽可能多的道路 ...
- php可变变量
例子: <?php $a = "b"; $$a = "c"; echo $$a; echo "<br>"; echo $b ...
- python几大排序算法
1.插入排序 原理:有数列[k1,k2,k3...],假设k1是排好序的,插入k2,排序完成,然后再插入k3,以此类推 def insert_sort(arr): for i in range(1,l ...
- scanf
scanf函数: (1)与printf函数一样,都被定义在头文件stdio.h里,因此在使用scanf函数时要加上#include <stdio.h>.它是格式输入函数,即按用户指定的格式 ...
- 2013 imac 安装 win7
昨天晚上安装imac win7系统,其实步骤是很简单的,首先需要一个用boot camp助手做好的win7安装U盘或者有个外接光驱加一张win7光盘,然后用boot camp助理划分一个分区给win7 ...
- HID高级攻击姿势:利用PowerShell脚本进行文件窃取
0×01 引言 又到了期中考试了,我又要去偷答案了,一直发现远程下载运行exe的方式不太好,容易报毒所以这里打算用ps脚本. 0×02 关于HID HID是Human Interface Device ...
